
Brain herniation is the shifting of the brain tissue from one space in the brain to another through various folds and openings. Brain herniation occurs when something inside the skull produces pressure that moves brain tissues. This is most often the result of brain swelling or bleeding from a head injury, stroke, or brain tumor.
What is herniation of the brain?
Brain herniation is the displacement of part of the brain through an opening or across a separating structure into a region that it does not normally occupy. 1. Uncal transtentorial herniation
What causes herniation of the skull?
Because the skull is rigid after infancy, intracranial masses or swelling may increase intracranial pressure, sometimes causing protrusion (herniation) of brain tissue through one of the rigid intracranial barriers (tentorial notch, falx cerebri, foramen magnum).
What is the second most common type of brain herniation?
The uncus, part of the temporal lobe, is shifted downward into an area known as the posterior fossa. This is the second most common type of brain herniation. Ascending transtentorial herniation.
What does a brain exam show with a herniated brain?
A brain and nervous system exam shows changes in alertness. Depending on the severity of the herniation and the part of the brain that is being pressed on, there will be problems with one or more brain-related reflexes and nerve functions. Tests may include: X-ray of the skull and neck.
What is the medical term for brain herniation?
A cerebral herniation or brain herniation is a serious medical condition that happens when brain tissues move from one part of the brain to another adjacent part of the brain. It is usually caused when another condition causes swelling or pressure inside the brain.
What are the types of brain herniation?
Brain herniation is classified as follows:Subfalcine herniation.Transalar (transsphenoidal) herniation.Transtentorial uncal herniation.Central (trans-tentorial) herniation (descending and ascending)Cerebellar tonsillar herniation.Transcalvarial herniation.
What is the most common type of brain herniation?
Subfalcine herniation is the most common form of intracranial herniation and occurs when brain tissue is displaced under the falx cerebri. The cingulate gyrus is herniated under the falx, and if progression occurs, other areas of the frontal lobe are involved.
What is a brain stem herniation?
A brain herniation, sometimes described as a cerebral herniation, occurs when brain tissue, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shift from their normal position inside the skull. The condition is usually caused by swelling from a head injury, stroke, bleeding, or brain tumor.
What herniation means?
: to protrude through an abnormal body opening : rupture a herniated intervertebral disk.
Which brain herniation is the most life threatening?
Central herniation Downward herniation can stretch branches of the basilar artery (pontine arteries), causing them to tear and bleed, known as a Duret hemorrhage. The result is usually fatal.
Where is the uncal herniation?
Uncal herniation is the most common cerebral herniation syndrome. The uncus is located in the inferior, medial aspect of the temporal lobe. This structure, and the adjacent parahippocampal gyrus, can herniate through the tentorial notch.
What is brain herniation and how is it related to intracranial pressure?
Brain herniation occurs when increased intracranial pressure causes the abnormal protrusion of brain tissue through openings in rigid intracranial barriers (eg, tentorial notch).
What is central herniation?
Central herniation is the subtype of downward transtentorial herniation of the brain that involves descent of the diencephalon and midbrain. It usually occurs with other types of downward herniation such as uncal herniation.
What herniation means?
Medical Definition of Herniation Herniation: Abnormal protrusion of tissue through an opening.
What is Tentorial herniation?
Brain herniation occurs when increased intracranial pressure causes the abnormal protrusion of brain tissue through openings in rigid intracranial barriers (eg, tentorial notch). When intracranial pressure is increased sufficiently, regardless of the cause, Cushing reflex and other autonomic abnormalities can occur.
Is cerebellar tonsillar ectopia life threatening?
The severity of Chiari malformations can vary dramatically as well. In some cases, affected individuals may not develop any symptoms ( asymptomatic); in others, severe, potentially debilitating or life-threatening symptoms can develop.
What is the most common herniated disc?
Disc herniation can occur in any disc in the spine, but the two most common forms are lumbar disc herniation and cervical disc herniation. The former is the most common, causing low back pain (lumbago) and often leg pain as well, in which case it is commonly referred to as sciatica.
What does the brain stem do?
The brain stem controls the flow of messages between the brain and the rest of the body, and it also controls basic body functions such as breathing, swallowing, heart rate, blood pressure, consciousness, and whether one is awake or sleepy . The brain stem consists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
How do you detect a brain bleed?
Diagnostic tests include: Computerized tomography (CT). A CT scan, a specialized X-ray exam, is usually the first test used to determine if you have bleeding in the brain. Cerebrospinal fluid test. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Cerebral angiogram.
What are the signs of brain death?
Some of the signs of brain death include: The pupils don't respond to light. The person shows no reaction to pain. The eyes don't blink when the eye surface is touched (corneal reflex). The eyes don't move when the head is moved (oculocephalic reflex).
Where does a brain herniation occur?
Brain herniation can occur: From side to side or down, under, or across rigid membrane like the tentorium or falx. Through a natural bony opening at the base of the skull called the foramen magnum. Through openings created during brain surgery.
Why does my brain herniate?
Causes. Brain herniation occurs when something inside the skull produces pressure that moves brain tissues. This is most often the result of brain swelling or bleeding from a head injury, stroke, or brain tumor. Brain herniation can be a side effect of tumors in the brain, including: Metastatic brain tumor. Primary brain tumor.
What is the term for the shifting of the brain tissue from one space in the brain to another?
Brain herniation is the shifting of the brain tissue from one space in the brain to another through various folds and openings. The major areas of the brain have one or more specific functions. Brain hernia is a condition in which a portion of the brain is displaced because of increased pressure inside the skull.
What is the outlook of a herniated brain?
Outlook (Prognosis) People who have a brain herniation have a serious brain injury. They may already have a low chance of recovery due to the injury that caused the herniation. When herniation occurs, it further lowers the chance of recovery. The outlook varies, depending on where in the brain the herniation occurs.
What is the brain and nervous system exam?
A brain and nervous system exam shows changes in alertness. Depending on the severity of the herniation and the part of the brain that is being pressed on, there will be problems with one or more brain-related reflexes and nerve functions. Tests may include: X-ray of the skull and neck. CT scan of the head.
What is the best way to reduce brain swelling?
Medicines that decrease brain swelling, such as mannitol, saline, or other diuretics. Placing a tube in the airway ( endotracheal intubation) and increasing the breathing rate to reduce the levels of carbon dioxide (CO 2) in the blood.
How to reverse a herniated brain?
To help reverse or prevent a brain herniation, the medical team will treat increased swelling and pressure in the brain. Treatment may involve: Placing a drain into the brain to help remove cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Medicines to reduce swelling , especially if there is a brain tumor.
Which structure is herniated in the brain?
Brain herniation is classified based on the structure through which tissue is herniated: Transtentorial (uncal) herniation: The medial temporal lobe is squeezed by a unilateral mass across and under the tentlike tentorium that supports the temporal lobe.
Why do temporal lobes herniate?
Central herniation: Both temporal lobes herniate through the tentorial notch because of bilateral mass effects or diffuse brain edema.
What is an upward transtentorial herniation?
Upward transtentorial herniation can occur when an infratentorial mass (eg, tumor in the posterior fossa, cerebellar hemorrhage) compresses the brain stem, kinking it and causing patchy brain stem ischemia. The posterior 3rd ventricle becomes compressed.
Why does the skull have a cushing reflex?
Because the skull is rigid after infancy, intracranial masses or swelling may increase intracranial pressure, sometimes causing protrusion (herniation) of brain tissue through one of the rigid intracranial barriers (tentorial notch, falx cerebri, foramen magnum). When intracranial pressure is increased sufficiently, regardless of the cause, Cushing reflex and other autonomic abnormalities can occur. Cushing reflex includes systolic hypertension with increased pulse pressure, irregular respirations, and bradycardia.
What is the cingulate gyrus pushed under?
The cingulate gyrus is pushed under the falx cerebri by an expanding mass high in a cerebral hemisphere. In this process, one or both anterior cerebral arteries become trapped, causing infarction of the paramedian cortex. As the infarcted area expands, patients are at risk of transtentorial herniation, central herniation, or both.
What nerves are involved in herniation?
As herniation progresses, the ipsilateral cerebral peduncle. In about 5% of patients, the contralateral 3rd cranial nerve and cerebral peduncle. Eventually, the upper brain stem and the area in or around the thalamus.
What are the symptoms of a compressed hernia?
Specific symptoms vary based on which structures are compressed; patients also have impaired consciousness and other neurologic deficits caused by the disorder causing herniation.
What are the symptoms of a brain herniation?
One or both pupils may be dilated and fail to constrict in response to light. Vomiting can also occur due to compression of the vomiting center in the medulla oblongata. Severe headaches and seizures as a result of increased intracranial pressure are not uncommon . Cardiovascular and pulmonary symptoms may also be present as the brain loses function, but might also be associated with bleeding. They can include: hypertension, respiratory depression, arrhythmia and in severe cases cardiac arrest.
What is the term for the pressure in the skull that causes the brain to shift?
Brain herniation. Brain herniation is a potentially deadly side effect of very high pressure within the skull that occurs when a part of the brain is squeezed across structures within the skull. The brain can shift across such structures as the falx cerebri, the tentorium cerebelli, and even through the foramen magnum ...
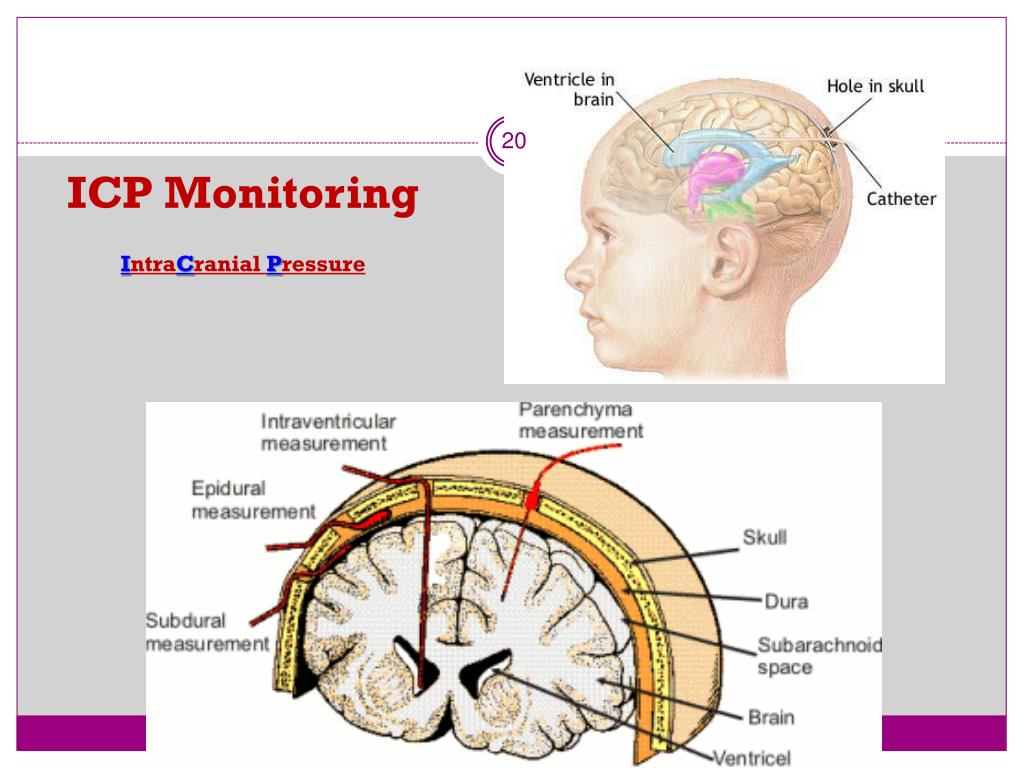
What is the term for the extension of the dura mater that separates the cerebellum from the cereb?
The tentorium is an extension of the dura mater that separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum. There are two major classes of herniation: supratentorial and infratentorial. Supratentorial refers to herniation of structures normally found above the tentorial notch, and infratentorial refers to structures normally found below it.
Why is herniation fatal?
Because herniation puts extreme pressure on parts of the brain and thereby cuts off the blood supply to various parts of the brain, it is often fatal. Therefore, extreme measures are taken in hospital settings to prevent the condition by reducing intracranial pressure, or decompressing (draining) an hematoma which is putting local pressure on ...
What is Kernohan's notch?
Another important finding is a false localizing sign, the so-called Kernohan's notch, which results from compression of the contralateral cerebral crus containing descending corticospinal and some corticobulbar tract fibers. This leads to Ipsilateral hemiparesis in reference to the herniation and contralateral hemiparesis with reference to the cerebral crus.
Which part of the temporal lobe is squeezed so much that it moves towards the tentorium?
In uncal herniation, a common subtype of transtentorial herniation, the innermost part of the temporal lobe, the uncus, can be squeezed so much that it moves towards the tentorium and puts pressure on the brainstem, most notably the midbrain.
What happens if the brain stem is disrupted?
The disrupted brainstem can lead to decorticate posture, respiratory center depression and death. Other possibilities resulting from brain stem distortion include lethargy, slow heart rate, and pupil dilation.
Where does the temporal lobe herniate?
The uncinate process of the temporal lobe herniates into the anterior part of the opening of the tentorium cerebelli
What is the term for the displacement of part of the brain through an opening or across a separating structure into?
OVERVIEW. Brain herniation is the displacement of part of the brain through an opening or across a separating structure into a region that it does not normally occupy.
What is brain displacement?
Displacement of brain through a defect in the skull, such as a fracture site or following craniectomy.
Where does a brain herniation occur?
Brain herniation can occur: From side to side or down, under, or across rigid membrane like the tentorium or falx. Through a natural bony opening at the base of the skull called the foramen magnum. Through openings created during brain surgery.
What causes a herniated brain?
Herniation of the brain can also be caused by other factors that lead to increased pressure inside the skull, including: 1 Collection of pus and other material in the brain, usually from a bacterial or fungal infection ( abscess) 2 Bleeding in the brain (hemorrhage) 3 Buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to brain swelling ( hydrocephalus) 4 Strokes that cause brain swelling 5 Swelling after radiation therapy 6 Defect in brain structure, such as a condition called Arnold-Chiari malformation
Why does my brain bleed?
This is most often the result of brain swelling or bleeding from a head injury, stroke, or brain tumor. Brain herniation can be a side effect of tumors in the brain, including: Metastatic brain tumor. Primary brain tumor. Herniation of the brain can also be caused by other factors that lead to increased pressure inside the skull, including:
What causes swelling in the brain after radiation?
Bleeding in the brain (hemorrhage) Buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to brain swelling ( hydrocephalus) Strokes that cause brain swelling. Swelling after radiation therapy. Defect in brain structure, such as a condition called Arnold-Chiari malformation.
What is the best way to reduce brain swelling?
Medicines that decrease brain swelling, such as mannitol, saline, or other diuretics. Placing a tube in the airway ( endotracheal intubation) and increasing the breathing rate to reduce the levels of carbon dioxide (CO 2) in the blood.
What is the loss of all brainstem reflexes?
Loss of all brainstem reflexes (blinking, gagging, and pupils reacting to light) Respiratory arrest (no breathing) Wide (dilated) pupils and no movement in one or both eyes. Exams and Tests. Expand Section. A brain and nervous system exam shows changes in alertness.
How to reverse a herniated brain?
To help reverse or prevent a brain herniation, the medical team will treat increased swelling and pressure in the brain. Treatment may involve: Placing a drain into the brain to help remove cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Medicines to reduce swelling , especially if there is a brain tumor.
What is the term for a herniated brain?
A cerebral herniation or brain herniation is a serious medical condition that happens when brain tissues move from one part of the brain to another adjacent part of the brain. It is usually caused when another condition causes swelling or pressure inside the brain. Cerebral herniations are severe and need immediate treatment.
What causes cerebral herniation?
Strokes. Both ischemic strokes (caused by blocked arteries) and hemorrhagic strokes (caused by excess bleeding) can lead to cerebral herniations. Strokes cause stress and damage to brain cells, leading to cerebral herniations.
Where do subfalcine herniations occur?
Subfalcine herniations. These take place in a part of the brain called the cingulate gyrus. The cingulate gyrus is a part of the brain just behind the frontal lobe. During these herniations, the cingulate gyrus is pushed into another part of the brain that is much deeper and farther back into the skull.
Why does my brain swell?
Brain swelling. Brain swelling is often caused by infections like measles, mumps, polio, or rabies. However, with the advent of vaccines and modern medical care, brain swelling is not very common.
Where is the temporal lobe located?
Central herniations. These occur in the temporal lobe. The temporal lobe is located in the middle of the brain, above the beginning of your spinal cord. During a central herniation, the temporal lobe gets pushed down to the tentorial notch, which is the closest part of the brain to the spine.
Does radiation make your brain swell?
Radiation therapy. Radiation treatments often make the brain swell. This is usually a short-term swelling, but you should pay attention if you begin to experience severe headaches, sickness, or seizures after your radiation treatment.
Overview
Diagnosis
The tentorium is an extension of the dura mater that separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum. There are two major classes of herniation: supratentorial and infratentorial. Supratentorial refers to herniation of structures normally found above the tentorial notch, and infratentorial refers to structures normally found below it.
Signs and symptoms
Brain herniation frequently presents with abnormal posturing, a characteristic positioning of the limbs indicative of severe brain damage. These patients have a lowered level of consciousness, with Glasgow Coma Scores of three to five. One or both pupils may be dilated and fail to constrict in response to light. Vomiting can also occur due to compression of the vomiting center in the medu…
Causes
Causes of brain herniation include:
• Brain edema
• Hematoma
• Stroke
• Tumour
Treatment
Treatment involves removal of the etiologic mass and decompressive craniectomy. Brain herniation can cause severe disability or death. In fact, when herniation is visible on a CT scan, the prognosis for a meaningful recovery of neurological function is poor. The patient may become paralyzed on the same side as the lesion causing the pressure, or damage to parts of the brain cause…
See also
• Second-impact syndrome