
The hierarchy of research evidence - from well conducted meta-analysis down to small case series
- Ranking of trial designs. The hierarchy indicates the relative weight that can be attributed to a particular study design. ...
- Concerns and caveats. ...
- Insert diagram re the GRADE system here: The Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine have also developed individual levels of evidence depending on the type of clinical question which needs to ...
What are the different levels of evidence in research?
Evidence Levels: Level I: Experimental, randomized controlled trial (RCT), systematic review RTCs with or without meta-analysis. Level II: Quasi-experimental studies, systematic review of a combination of RCTs and quasi-experimental studies, or quasi-experimental studies only, with or without meta-analysis.
What is the highest level of evidence in research?
This study "challenges the concept of population-level herd immunity through natural infection alone ... occur as a result of more transmissible variants," Croda said in a statement. "Further research on the need for vaccination for those with a previous ...
What are the three levels of evidence?
Level III: Evidence obtained from well-designed controlled trials without randomization, quasi-experimental. Level IV: Evidence from well-designed case-control and cohort studies. Level V: Evidence from systematic reviews of descriptive and qualitative studies. Level VI: Evidence from a single descriptive or qualitative study
What is the hierarchy of scientific evidence?
A hierarchy of evidence (or levels of evidence) is a heuristic used to rank the relative strength of results obtained from scientific research. There is broad agreement on the relative strength of large-scale, epidemiological studies. More than 80 different hierarchies have been proposed for assessing medical evidence.
.png)
What are the 5 levels of evidence?
Johns Hopkins Nursing EBP: Levels of EvidenceLevel I. Experimental study, randomized controlled trial (RCT) ... Level II. Quasi-experimental Study. ... Level III. Non-experimental study. ... Level IV. Opinion of respected authorities and/or nationally recognized expert committees/consensus panels based on scientific evidence. ... Level V.
What is the best hierarchy of evidence?
Both systems place randomized controlled trials (RCT) at the highest level and case series or expert opinions at the lowest level. The hierarchies rank studies according to the probability of bias. RCTs are given the highest level because they are designed to be unbiased and have less risk of systematic errors.
What does the pyramid of hierarchy of evidence tell us?
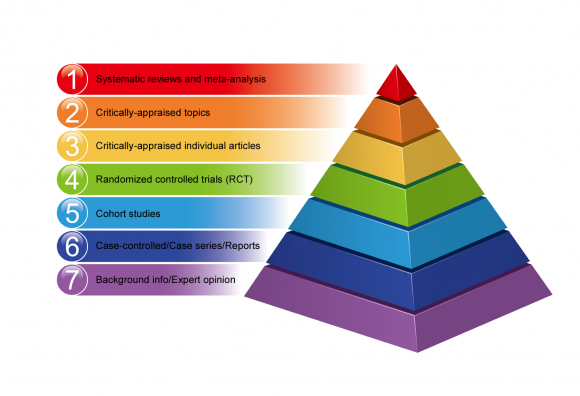
The evidence pyramid is an easy way to visualize this hierarchy of evidence. At the top of the pyramid is filtered evidence including systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and critical appraisals. These studies evaluate and synthesize the literature. The top of the pyramid represents the strongest evidence.
What is Level 4 evidence in research?
Filtered evidence: Level IV: Evidence from guidelines developed from systematic reviews. Level V: Evidence from meta-syntheses of a group of descriptive or qualitative studies. Level VI: Evidence from evidence summaries of individual studies. Level VII: Evidence from one properly designed randomized controlled trial.
Where is qualitative research in the hierarchy of evidence?
At the apex of the hierarchy are the ideal, well-developed qualitative studies. These studies often build on earlier studies, commencing with a comprehensive literature review, which provides the conceptual framework for initial data collection.
Where is quantitative research in the hierarchy of evidence?
Evidence Pyramid Studies with the highest internal validity, characterized by a high degree of quantitative analysis, review, analysis, and stringent scientific methodoloy, are at the top of the pyramid. Observational research and expert opinion reside at the bottom of the pyramid.
Why is it important to consider the levels of evidence?
It is therefore important to be able to determine which evidence is the most authoritative. So-called 'levels of evidence' are used for this purpose and specify a hierarchical order for various research designs based on their internal validity (see table below).
What is the most superior class of evidence?
Primary evidence is considered to be the superior class of evidence. Such evidence is an original document that needs to be submitted before the court for inspection. It is admissible without any prior notice. Such evidence must be presented before the court before the secondary evidence.
What are the 7 levels of evidence?
Levels of Evidence TableLevel of evidence (LOE)DescriptionLevel VEvidence from systematic reviews of descriptive and qualitative studies (meta-synthesis).Level VIEvidence from a single descriptive or qualitative study.Level VIIEvidence from the opinion of authorities and/or reports of expert committees.4 more rows•Feb 4, 2022
What is a level 1 research study?
Level I: High quality randomized trial or prospective study; testing of previously developed diagnostic criteria on consecutive patients; sensible costs and alternatives; values obtained from many studies with multiway sensitivity analyses; systematic review of Level I RCTs and Level I studies.
What are the classes of evidence?
There are four types evidence by which facts can be proven or disproven at trial which include:Real evidence;Demonstrative evidence;Documentary evidence; and.Testimonial evidence.
Which type of research provides the strongest evidence?
Well done systematic reviews, with or without an included meta-analysis, are generally considered to provide the best evidence for all question types as they are based on the findings of multiple studies that were identified in comprehensive, systematic literature searches.
Is the most superior class of evidence?
Primary evidence is considered to be the superior class of evidence. Such evidence is an original document that needs to be submitted before the court for inspection. It is admissible without any prior notice.
Why is systematic review the highest level of evidence?
In the Pyramid of Evidence Based Medicine, a Systematic Review of Randomized Control Trials is located at the top; because so many studies are used, it greatly reduces bias. One of the first steps researchers take is to conduct an organized search to find and collect all of the relevant studies. This part is key.
What is the strongest type of study?
A well-designed randomized controlled trial, where feasible, is generally the strongest study design for evaluating an intervention's effectiveness.
What is the hierarchy of a study?
The hierarchy indicates the relative weight that can be attributed to a particular study design. Generally, the higher up a methodology is ranked, the more robust it is assumed to be. At the top end lies the meta-analysis – synthesising the results of a number of similar trials to produce a result of higher statistical power. At the other end of the spectrum lie individual case reports, thought to provide the weakest level of evidence.
What is the best level of evidence?
The Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine have also developed individual levels of evidence depending on the type of clinical question which needs to be answered. For example, to answer questions on how common a problem is, they define the best level of evidence to be a local and current random sample survey, with a systematic review being the second best level of evidence. The complete table of clinical question types considered, and the levels of evidence for each, can be found here. 5
What is evidence based medicine?
Evidence-based medicine has been described as ‘the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients.’ 1 This involves evaluating the quality of the best available clinical research, by critically assessing techniques reported by researchers in their publications, and integrating this with clinical expertise. Although it has provoked controversy, the hierarchy of evidence lies at the heart of the appraisal process.
What are the inequalities in health?
Inequalities in health (e.g. by region, ethnicity, soci-economic position or gender) and in access to health care, including their causes. The impact of political, economic, socio-cultural, environmental and other external influences. Introduction to study designs - intervention studies and randomised controlled trials.
Is the hierarchy accepted in medical literature?
The hierarchy is widely accepted in the medical literature, but concerns have been raised about the ranking of evidence, versus that which is most relevant to practice. Particular concerns are highlighted below.
Advantages of The Hierarchy of Evidence
- The hierarchy provides an easy visualization of study designs that gives researchers and knowledge consumers a crude method to identify how much confidence should be invested in a study based upon the design of the trial in relation to other types of studies in the pyramid.
Caveats of The Hierarchy of Evidence
- The hierarchy can be overly simplistic and should not be used to definitively judge the value of a study simply by its design. While systematic reviews and meta-analyses (SR/MAs) are at the top of the hierarchy and represent the highest level of evidence, this does not mean that these studies are always free from methodological issues and bias. The same concept is applicable to any tria…
What to Watch For in The Hierarchy of Evidence
- The following is a guide that briefly outlines the construction and rational for the hierarchy levels, proceeding from the highest level of evidence to the lowest: 1. SR/MAs are the highest level of evidence. These trials assess the consistency of results and risk of bias between all studies investigating a topic and demonstrate the overall effect of an intervention or exposure amongst …