
What is the critical temperature set-point in the hypothalamus?
The critical temperature set-point in the hypothalamus above which sweating begins and below which shivering begins is determined mainly by the degree of activity of the heat temperature receptors in the anterior hypothalamic-preoptic area.
What are the zones of the hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus is composed of three longitudinally oriented cell columns, or zones, that run the entire rostrocaudal length of the hypothalamus (Figure 1.2). These zones can be further subdivided into four nuclear groups, or regions, based on rostrocaudal position.
What is the anatomy of the hypothalamus?
1.1 Anatomy of the Hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is composed of three longitudinally oriented cell columns, or zones, that run the entire rostrocaudal length of the hypothalamus (Figure 1.2). These zones can be further subdivided into four nuclear groups, or regions, based on rostrocaudal position.
How are set points represented in the brain?
These set points are represented in the brain by specific discharge rates in neurons dedicated to the monitoring and control of specific physiological processes. Thus, separate groups of neurons are dedicated to the control of heart rate, temperature, etc., by their set point discharge rate.
What is the setpoint for body temperature?
98.6°FFor example, the set point for normal human body temperature is approximately 37°C (98.6°F). Physiological parameters, such as body temperature and blood pressure, tend to fluctuate within a normal range a few degrees above and below that point.
What is the hypothalamic thermoregulatory center?
Similar to a thermostat, this brain area detects deep brain temperature, integrates temperature information from peripheral body sensors, and-based on these inputs--controls body temperature homeostasis.
What resets the hypothalamic thermostat?
Fever is our body's reaction to injury, inflammation, certain hormonal storms, and infections—all of which release certain chemicals called toxins and cytokines, which reset the hypothalamus thermostat upwards.
When the set point is increased as in fever the hypothalamus initiates?
The hypothalamus stimulates vasodilatation to increase insensible loss (for every 1 °C elevation of body temperature, there is a 10% insensible loss) and activates the sweat glands to increase perspiration production.
What is the thermoregulatory Centre?
The human body maintains the temperature that enzymes work best, which is around 37°C. This process is controlled by the thermoregulatory centre, which is contained in the hypothalamus in the brain, and it contains receptors sensitive to the temperature of the blood.
How does the hypothalamic thermostat work?
When your hypothalamus senses that you're too hot, it sends signals to your sweat glands to make you sweat and cool you off. When the hypothalamus senses that you're too cold, it sends signals to your muscles that make your shiver and create warmth.
Can the hypothalamus be reset?
Chance HRT is a simple technique to reset the Hypothalamus. The Hypothalamus is called the “Brain of the Brain.” This technique allows the Hypothalamus to regain control over so many of the body's functions.
What is set point theory?
Set point theory states that our bodies have a preset weight baseline hardwired into our DNA. According to this theory, our weight and how much it changes from that set point might be limited. The theory says some of us have higher weight set points than others and our bodies fight to stay within these ranges.
Why is the set point theory important?
Scientists believe understanding individual factors is crucial. Genetics, hormones, and environment all play a role. The set point theory is just one concept researchers are studying to understand body weight. There are many reasons some of us struggle to lose weight.
How does the body fight to maintain the higher set point weight?
When we try to lose weight, our body fights to maintain the higher set point weight by slowing down metabolism. This can limit weight loss. There’s a second theory for weight called the “settling point” model. This concept suggests our weight is influenced by more than just one factor.
Can you reset your set point?
According to set point theory, yes. In order to reset our set point to a lower level, set point theory proponents recommend going slowly with weight loss goals. A gradual 10 percent step-down weight loss approach with persistent maintenance at each stage can help prepare the body to accept the new lower set point.
Where does the efferent projection of the hypothalamus end?
Descending efferent projections of the hypothalamus through these pathways terminate on parasympathetic nuclei of the brainstem such as the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus. Unidirectional afferent input to the hypothalamus is derived from the spinohypothalamic tract and the retino-hypothalamic tract.
How many nuclei are there in the hypothalamus?
There are eleven major nuclei in the hypothalamus (Figure 1.5). The functions of many of these will be covered in further detail in later sections. However, a brief note on the organization of these can be useful. The nuclei can be grouped based on their locations in the hypothalamic zones and regions.
What is the rostral continuation of the sulcus limitans?
Also visible on the medial surface of the brain is the hypothalamic sulcus, which is the rostral continuation of the sulcus limitans that defines the superior boundary of the hypothalamus. Finally, the internal capsule that is only visible on coronal or horizontal sections of the brain forms the lateral boundary.
What is the role of the SCN in the physiology of the brain?
The SCN has projections into multiple hypothalamic nuclei that control the specific functions that show daily or annual rhythms. Thus, the SCN is considered as a master pacemaker that regulates the functions of multiple intra- and extra-hypothalamic slave oscillators.
Where is the supraoptic nucleus located?
Both of these nuclei, along with the supraoptic nucleus, located just above the optic chiasm in the anterior region of the medial zone extending laterally into the lateral zone , have key roles in neuroendocrine regulation.
Which part of the brain has the most complex circuitry?
The hypothalamus has the most complex circuitry of any brain region. Like other brain areas there are neural interconnections. But unlike other brain areas, there are also extensive non-neural communication pathways between the hypothalamus and other brain regions and the periphery. Neural Connections.
What is the process of maintaining a steady state of equilibrium?
Homeostasis is the process by which a steady state of equilibrium, or constancy, in the body with respect to physiological functions and chemical compositions of fluids and tissues is maintained. Physiological set points refer to the baseline level at which functions such as heart rate, and at which chemical compositions such as plasma sodium ...
How does the hypothalamus maintain the set point?
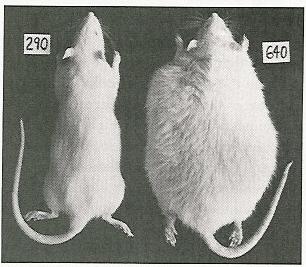
If you eat less and begin losing weight, the hypothalamus attempts to maintain the set-point by increasing your hunger and appetite so you’ll eat more, and by decreasing your metabolism so you’ll burn fewer calories. Of course that makes it pretty frustrating, and often very difficult, when we’re trying to lose weight!
What is the body's set point?
The body likes things to remain the same – that’s called homeostasis. This also applies to your weight. Whatever your weight has been for a period of time (months) is what the body considers to be normal. This is what we refer to as the set point. A part of the brain called the hypothalamus, helps maintain the set-point.
What is set point theory?
The set point theory states that a person’s body has a set point weight at which it is programmed to be comfortable. This theory proposes that the body will sabotage itself during weight loss by slowing down metabolism (the body’s rate of burning calories).
What part of the brain controls appetite?
This is what we refer to as the set point. A part of the brain called the hypothalamus, helps maintain the set-point. It does this by controlling hunger and appetite (your desire to eat) and metabolism (the rate at which you burn calories).
What causes the hypothalamic thermostat to raise?
Numerous proteins and their breakdown products, and certain substances, particularly lipopolysaccharide toxins liberated from bacterial cell layers, can raise the set-point of the hypothalamic thermostat. Substances that cause this impact are called pyrogens.
What is the normal temperature of the human body?
The normal temperature of the human body is considered to be 37 degrees C ...
