
What are the determinants of your identity?
Identity encompasses the memories, experiences, relationships, and values that create one’s sense of self. This amalgamation creates a steady sense of who one is over time, even as new facets ...
What is the multiplicative identity?
The multiplicative identity property states that the identity of a number stays the same whenever the number is multiplied by 1. This property is also called the identity property of multiplication. What this means is that any time a number is multiplied by 1, it retains its identity. For example:
What is the multiplicative identity of 0?
Zero (0) is the additive identity and one (0) is the multiplicative identity for all the numbers such as whole numbers, natural numbers, integers, etc. What is Additive Identity? Additive identity of numbers, as the name suggests, is a property of numbers that are applied when carrying out addition operations.
What are the properties of zero?
The Multiplication Property of Zero
- x x 0 = 0
- a ^2 x 0 = 0
- x ^3 y ^5 z ^2 x 0 = 0
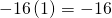
What is the property of 0?
What Is the Zero Property of Multiplication? Zero property of multiplication is defined as “when we multiply any number by zero, the resulting product is always a zero”.
What is identity property and zero property?
The Identity Property of Zero, also called the Additive Identity Property, states that if you add 0 to any number, the result will be that number. Likewise, if you subtract 0 from any number, the result will be that number. Believe it or not, this works for all real numbers.
What is an example of identity property?
The identity property of 1 says that any number multiplied by 1 keeps its identity. In other words, any number multiplied by 1 stays the same. The reason the number stays the same is because multiplying by 1 means we have 1 copy of the number. For example, 32x1=32.
What is zero identity property of addition?
An identity in addition is a number, n, that when added to other numbers, gives the same number n. The additive identity is zero. The identity property of addition simply states that when you add zero to any number, it equals the number itself.
What property is A +(- A )= 0?
the inverse property of additionThe sum of any real number and its additive inverse is zero. This is called the inverse property of addition. If is a real number, then a + ( − a ) = 0 .
What are the 5 properties of zero?
Other properties of zero Any number to the power of 0 is equal to 1. 0 is neither positive nor negative. 0 is neither prime nor composite. If you add two numbers and the sum is zero, we call the two numbers additive inverses or opposites of each other.
Is 0 a a an identity?
For any set of numbers, that is, all integers, rational numbers, and complex numbers, the additive identity is 0. It is because when you add 0 to any number; it doesn't change the number and keeps its identity.
Is 0 the identity for subtraction?
We get that the identity element of subtraction is 0. So, the correct answer is “0”. Note: We need to keep in mind the subtraction is a particular binary operation. The concept of identity element is fixed for all kinds of operations, be it multiplication or addition.
What kind of property is (- 7 )+ 0 =- 7?
Additive Identity Property is expressed as 7+0=7.
What is the additive inverse of 0?
0The number 0 is the only number with its additive inverse being itself.
What are the 4 properties of math?
Math PropertiesCommutative Property.Associative Property.Distributive Property.Identity Property.Inverse Property.
What is the formula of identity property?
Multiplicative Identity Property Formula The multiplicative identity formula is expressed as a × 1 = a, where 'a' is any real number. This shows that when any number is multiplied by 1, the product is the number itself. For example, if we multiply 65 with 1 we get 65 as the product. 65 × 1 = 65.
What is another name for identity property?
The identity property of addition is also known as the additive identity property, according to which when a number is added to zero, it results in the number itself. For example, if 7 is added to 0, the sum is the number itself.
What is identity property of addition example?
The zero property of addition is another name for the identity property of addition. It states that if any number is added to 0, the sum is the number itself. For example, 835 + 0 = 835.
What are the 4 multiplication properties?
Properties of Multiplication. Commutative Property of Multiplication. ... Associative Property of Multiplication. ... Distributive Property of Multiplication. ... Identity Property of Multiplication.
What is an example of identity property of multiplication?
Identity property of multiplication: The product of 1 and any number is that number. For example, 7 × 1 = 7 7 \times 1 = 7 7×1=77, times, 1, equals, 7.
How do you classify identity property?
The identity property states that a number, known as the identity, can be added to, subtracted from, multiplied by, or divided into a number withou...
What are the four types of properties?
The four types of identity properties are: identity property of addition ( a + 0 = a ) identity property of subtraction ( b - 0 = b ) identi...
Is there a division identity property?
There is a division identity property. The division identity property states that any number can be divided by 1 without changing the identity of t...
What is an example of multiplicative identity property?
An example of the multiplicative identity property, which states that any number can be multiplied by 1 without changing the identity of the number...
Why is the additive identity of a number 0?
For any set of numbers, that is, all integers, rational numbers, complex numbers, the additive identity is 0. It is because when you add 0 to any number ; it doesn’t change the number and keeps its identity.
What is additive identity?
Additive identity is a number, which when added to any number, gives the sum as the number itself. It means that additive identity is “0” as adding 0 to any number, gives the sum as the number itself. For any set of numbers, that is, all integers, rational numbers, complex numbers, the additive identity is 0. ...
How many mathematical properties are there in addition?
There are four mathematical properties of addition. These are:
What does it mean when no one joins the game?
As no one joined the game, this means there was no change in the number of kids.
Is 0 a natural number?
However, additive identity cannot be associated to natural numbers, since 0 is not considered as a natural number. Natural numbers start from 1.
What is the identity property?
Identity property. An identity element is a number that, when used in an operation with another number, results in the same number. The additive and multiplicative identities are two of the earliest identity elements people typically come across; the additive identity is 0 and the multiplicative identity is 1.
How to visualize the identity property of addition?
One way to visualize the identity property of addition is to use objects to represent addition. Adding 0 objects to any number of objects just leaves the same number of objects. The figure below represents the addition problem 3 + 0.
What is the identity property of multiplication?
The identity property of multiplication states that the product of 1 and any number equals that number. It can be written as follows, where a is any number.
Can a value be substituted for a number?
Any value can be substituted for a. It doesn't matter how large or small the number. Adding 0 (or subtracting 0 for that matter) will result in the same number.
What Is Identity Property?
A definition of identity property is that the identity property states that a number, known as the identity, can be added to, subtracted from, multiplied by, or divided into a number without changing the number. The four basic properties used with numbers are commutative, associative, distributive, and identity. These properties apply to sets of numbers rather than individual numbers.
What is the identity property of subtraction?
What is the identity property of subtraction? The identity property of subtraction says that the identity element, 0, can be subtracted from any number without changing the original number. The original number can be positive, negative, a whole number, a fraction, a decimal, or even an unknown variable. Its identity will not be changed when 0 is subtracted from it. Here are a few examples of the identity property of subtraction:
Why is the identity element one used in two operations?
The identity element is one because any other number can be multiplied or divided by one without changing the original number. No other number can be multiplied by or divided into another number without changing the identity of the primary number.
What is the only number that can be multiplied by without changing the identity of the number?
In this example, n = 1 , the only number that a number can be multiplied by without changing the identity of the number. This is an example of the identity property of multiplication.
How many identity elements are there?
There are two identity elements, 0 and 1. Each identity element is used in different operations.
Does the identity of the number change when subtracted from 0?
In each example, 0 is subtracted from the number, but the identity of the number does not change.

Using The Identity Property of 0
- Step 1:Identify all the terms in the mathematical expression that are not zero. Step 2:Perform all addition and/or subtraction operations while disregarding the zero term.
Using The Identity Property of 0: Adding 0 Example
- Find the sum for the expression {eq}12 + 0 + 5{/eq}. Step 1:Identify all the terms in the mathematical expression that are not zero. From the given mathematical expression, the non-zero terms are 12 and 5. Step 2:Perform all addition and/or subtraction operations while disregarding the zero term. To simplify the given mathematical expression, we will disregard the zero term an…
Using The Identity Property of 0: Subtracting 0 Example
- Find the resulting difference from the expression {eq}18 - 6 - 0{/eq}. Step 1:Identify all the terms in the mathematical expression that are not zero. From the given expression, we have a minuend of {eq}18{/eq} and a subtrahend of {eq}6{/eq}. Step 2:Perform all addition and/or subtraction operations while disregarding the zero term. According to the identity property of 0 subtracting z…