
The identity property states that when a fraction is added to the inverse of itself the result is 0. This is written as: a/b+ (-a/b)=0. For Example: 7/8+(-7/8)=0. 3/5+(−3/5)=0. Identity Property of Multiplication. This property states that when a fraction is multiplied with the inverse of itself the result is 1. It is written as: a/b*b/a=1. For Example. 3/5*5/3=1. 1/5*5=1. Distributive Property. According to the distributive property of fractions:
How do you find the identity property of fractions?
Identity Property - 1 (1) Using the Multiplicative Identity of 1 , multiply each fraction by 1 . ... 2 (3) Complete the Multiplication of the two groups of fractions. Note that after the multiplication is complete, the denominators of both of the remaining fractions are the same : Note: ... 3 (4) Add the Fractions . ... 4 (5) The Final Answer :
What is the identity property in math?
The identity property is one of the most fundamental properties that exist for numbers and arithmetic operations. The identity property focuses on the situations when a given number remains the same after being added, multiplied, subtracted, and divided by a particular constant.
What are the properties of fractions?
Fractions are real numbers and they therefore have the same properties of commutatitivity, associativity and distributivity as the real numbers. The above properties and other rules of fractions are be used to simplify and factor expressions including fractions.
What is the multiplicative identity for the set of all numbers?
The multiplicative identity for the set of all real numbers is 1 (one). Any real number can be multiplied by the number 1 without changing its value. (1) Using the Multiplicative Identity of 1 , multiply each fraction by 1 .
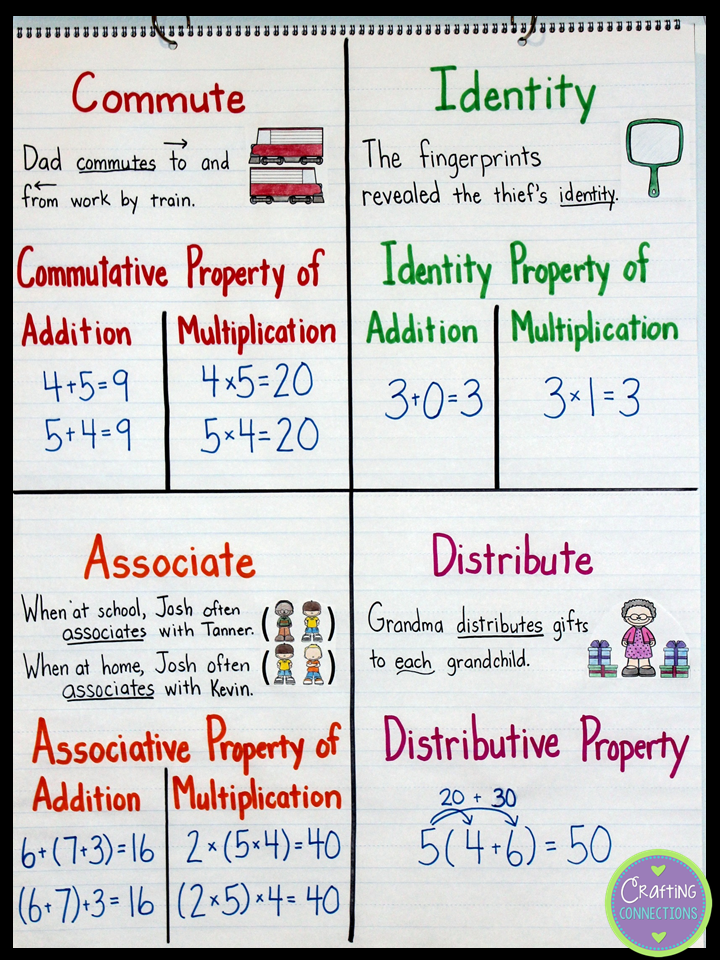
What is the identity property?
Identity property states that when any number is combined with an identity either 0 or 1, the end result will be the number itself. The property is applicable while using the four main arithmetic operations - addition, multiplication, subtraction, and division.
What is the example of identity property?
The identity property of 1 says that any number multiplied by 1 keeps its identity. In other words, any number multiplied by 1 stays the same. The reason the number stays the same is because multiplying by 1 means we have 1 copy of the number. For example, 32x1=32.
What is an example of identity property of multiplication?
Identity property of multiplication: The product of 1 and any number is that number. For example, 7 × 1 = 7 7 \times 1 = 7 7×1=77, times, 1, equals, 7.
What is the formula of identity property?
Multiplicative Identity Property Formula The multiplicative identity formula is expressed as a × 1 = a, where 'a' is any real number. This shows that when any number is multiplied by 1, the product is the number itself. For example, if we multiply 65 with 1 we get 65 as the product. 65 × 1 = 65.
What is an identity in math example?
An algebraic identity is an equality that holds for any values of its variables. For example, the identity ( x + y ) 2 = x 2 + 2 x y + y 2 (x+y)^2 = x^2 + 2xy + y^2 (x+y)2=x2+2xy+y2 holds for all values of x and y.
What are the 4 types of properties?
Let A , B , C are three integers.. Commutative property :2 . Associative property :3 . Distributive property :4 . Identity property :
Why is it called identity property?
An identity property is a property that applies to a group of numbers in the form of a set. It cannot be applied to any individual number only. It is named identity property because when applied to a number, the number keeps its 'identity. ' The identity property is true for all arithmetic operations.
How do you identify properties in math?
0:004:27Identify the Commutative, Associate, and Distributive Properties of Real ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFor example two plus three equals three plus two we can easily verify this is true two plus threeMoreFor example two plus three equals three plus two we can easily verify this is true two plus three equals five. And so does three plus two next we have the commutative property of multiplication.
What's the identity property of addition?
Additive Identity Property of 0 An additive identity is a number, which when added to any number, gives the sum as the number itself. It means that additive identity is “0” as adding 0 to any number, gives the sum as the number itself. Example: 2 + 0 = 2. 0 + 5 = 5.
What is identity property for kids?
Another important addition rule that kids must learn in mathematics is the identity property of addition. This means that when a zero is added to an addition equation, it does not change the number.
What is identity property Grade 2?
In math, an identity is a number, n, that when added to other numbers, gives the same number, n. The additive identity is always zero. This brings us to the identity property of addition, which simply states that when you add zero to any number, it equals the number itself.
What is identity rule?
In logic, the law of identity states that each thing is identical with itself. It is the first of the historical three laws of thought, along with the law of noncontradiction, and the law of excluded middle.
Which of the following is an example of identity property of addition?
An example of the identity property of addition is 5 + 0 = 5. This is true because adding zero to any number will not change its value.
What is an example of inverse property?
Applying the Inverse Property of Addition. In mathematics, inverse operations are operations that reverse one another. Addition and subtraction are inverse operations. For example, if you take any number and add 5 to it and then subtract 5 from the total, you will be back to the original number.
What is the associative property example?
The associative property of addition states that the grouping of numbers does not change their sum. For example, (75 + 81) + 34 = 156 + 34 = 190; and 75 + (81 + 34) = 75 + 115 = 190. The sum of both the sides is 190.
What are the 4 properties of addition?
The 4 main properties of addition are commutative, associative, distributive, and additive identity.
What are fractions in Maths?
Fractions are the numerical values that are a part of the whole. A whole can be an object or a group of objects. If a number or a thing is divided...
How to solve fractions?
To add or subtract fractions, we have to check if the denominators are the same or different. For the same denominators, we can directly add or sub...
What are the 3 types of fractions in Maths?
The 3 types of fractions in Maths are Proper fractions, Improper fractions, and Mixed fractions.
Give real-life examples of fractions.
If a watermelon is divided into four equal parts, then each part is a fraction of ¼. Similarly, if a pizza is divided into three equal parts, then...
What is a unit fraction?
A fraction with numerator 1 is called a unit fraction. Examples are ½, ⅓, ¼, ⅕, 1/7, 1/10, etc.
What property is applied to fractions?
Similar to Numbers and Integers, associative property gets applied in fractions too, over Addition and Multiplication.
Which property of addition does fractions follow?
In this example, the answer will be on both the LHS and RHS side. Hence we can say that fractions follow the associative property of addition.
What is a fraction? Give examples?
A fraction tells us how many parts of a whole we have a numerator, and a denominator. For example, 1/2 is a fraction.
How to add fractions to wholes?
Step 2: If the fractions to be added are Unlike fractions, add them by finding the LCM of the denominators or by using the cross multiplication method, as shown in Case 2.
What is it called when fractions have the same denominators?
And these fractions with the same denominators are called “Like Fractions .”
What is a fraction that is less than one?
Fractions that are less than one are known as proper fractions, and the numerator (is less than the denominator. A fraction with a numerator that is greater than or equal to the denominator is known as an improper fraction. It represents a number greater than or equal to one.
What is the difference between a larger numerator and a smaller denominator?
The larger the numerator the larger the fraction, and the larger the denominator the smaller the fraction. If the denominators are the same, the fraction with a larger numerator is larger and if the numerators are the same, the fraction with the larger denominator is smaller.
What are the properties of fractions?
Similar to real numbers and whole numbers, a fractional number also holds some of the important properties. They are: 1 Commutative and associative properties hold true for fractional addition and multiplication 2 The identity element of fractional addition is 0, and fractional multiplication is 1 3 The multiplicative inverse of a/b is b/a, where a and b should be non zero elements 4 Fractional numbers obey the distributive property of multiplication over addition
What are Fractions?
Definition 1: A fraction represents a numerical value, which defines the parts of a whole.
How to simplify two fractions?
If the denominators of the two fractions are different, we have to simplify them by finding the LCM of denominators and then making it common for both fractions.
How to add and subtract fractions?
To add or subtract fractions, we have to check if the denominators are same or different. For same denominators, we can directly add or subtract the numerators, keeping the denominator common. But if the denominators are different, then we need to simplify them by finding the LCM.
When multiplying two fractions, what is the rule?
Rule #2: When we multiply two fractions, then the numerators are multiplied as well as the denominators are multiplied. Later simplify the fraction.
What are equivalent fractions?
Two fractions are equivalent to each other if after simplification either of two fractions is equal to the other one. For example, ⅔ and 4/6 are equivalent fractions. Since, 4/6 = (2×2)/ (2×3) = 2/3.
What is the lowest part of a fraction?
Denominator: It is the lower or bottom part that represents the total parts in which the fraction is divided.
What is multiplicative identity?
A multiplicative identity is a number that can be multiplied by any number without changing the value of that other number. The multiplicative identity for the set of all real numbers is 1 (one). Any real number can be multiplied by the number 1 without changing its value.
What analogy is used to illustrate the identity property?
The identity property can be illustrated using the "clock" analogy as follows:
What is additive identity?
An additive identity is a number that can be added to any number without changing the value of that other number.
How can identity be applied to different fields of study?
People working in different fields of study have developed their own specialized systems to identify and catalog what is important to them. Examples of these differences can be seen in how individual identity is used in biological identification (DNA), music, psychology, archaeology, architecture, etc.
What is the closing property of a number?
Third , when real numbers are added or multiplied, the result is always another real number (this is called the "closure" property). [This is not the case with all arithmetic operations. For example, the square root of a -1 yields an imaginary number.]
What is real number?
First , Real numbers are an ordered set of numbers. This means real numbers are sequential. The numerical value of every real number fits between the numerical values two other real numbers.
Do we run out of real numbers?
Second , we never run out of real numbers. The quantity of real numbers available is not fixed. There are an infinite number of values available. The availability of numbers expands without end. Real numbers are not simply a finite "row of separate points" on a number line. There is always another real number whose value falls between any two real numbers (this is called the "density" property).
What is the identity property of multiplication?
Here are a few examples of identity property of multiplication, This property holds true for division as well because dividing any number by 1 equals the number itself.
What is Identity Property?
An identity property is a property that applies to a group of numbers in the form of a set. It cannot be applied to any individual number only.
What is zero identity?
Zero is called an additive identity and it can be added to any real number without changing its value . Here are the few examples of identity property of addition, This property holds true for subtraction as well because subtracting 0 from any number equals the number itself.
Why is 1 called divisive identity?
This property holds true for division as well because dividing any number by 1 equals the number itself. Therefore, 1 is also called divisive identity.
Is 0 a subtractive identity?
This property holds true for subtraction as well because subtracting 0 from any number equals the number itself. Therefore, 0 is also called a subtractive identity.
What is the identity property of multiplication?
The identity property of multiplication simply states that a number equals itself when multiplied by 1. If you multiply 8 and 2, the product is 16, so the factors 8 and 2 have changed their identity to the product 16. But if you multiply 8 by 1, the product is 8, so the factor 8 has been able to keep its identity.
What is 5*1 in math?
1) 5*1 = 5. This can be thought of as the number 5 added to itself 1 time, resulting in 5.
What is the meaning of multiplication?
Multiplication is basically the process of adding an integer to itself a certain number of times. So, if we just have an integer multiplied with the number 1, then it is not being added to itself any number of times. It is just itself.
