
What is meant by "peer review" in science?
A peer review generally addresses three common areas: Quality: How well did the researchers conduct their study, and how reliable are its conclusions? These points test the credibility and accuracy of the science under evaluation. Relevance: Is the paper of interest to readers of this journal and appropriate to this field of work? Importance: What clinical impact could the research have? ...
Why is peer review an important part of scientific research?
Peer review has an important function, as it ensures that only high quality research is disseminated and available as a body of scientific evidence. Such evidence frequently becomes part of mainstream thinking and practice, so it is vital that conclusions that these are based on are the subject of valid methods and accurate presentation.
What is the purpose of peer reviews?
What is peer review?. Peer review is designed to assess the validity, quality and often the originality of articles for publication. Its ultimate purpose is to maintain the integrity of science by filtering out invalid or poor quality articles.
How reliable is peer review?
Peer review sometimes picks up fraud by chance, but generally it is not a reliable method for detecting fraud because it works on trust. A major question, which I will return to, is whether peer review and journals should cease to work on trust. THE DEFECTS OF PEER REVIEW.

Validate Work and Research
A lot of hard work goes into scientific research. Scientists work through years of research, experiments, mistakes, and successes to build enough data for a strong manuscript. While seeking help and collaboration from others in your field is a good idea throughout your scientific process, it’s necessary to present your completed work to others.
Expert Quality Control
In addition to validating the idea behind the work, part of the importance of peer review in a scientific publication revolves around quality control for the manuscript itself.
Preserve Publication Reputation
Scientific publications—especially large, well-known publications—have a reputation to uphold. If they publish a manuscript that is incomplete or inaccurate, readers will hold them responsible. The peer-review process helps publications ensure that every piece they accept is a worthwhile read for their audience.
What is the importance of peer review?
Part 1: The Importance of Peer Review: An Introduction. Part 2: Researcher Responsibility in the Peer Review Process. Part 3: Ethics and Integrity in Peer Reviewed Research. Within my career, service has been one of the most rewarding aspects of scholarship. Service to an academic community can occur in various forms.
What is peer review in academic journals?
For example, submissions for publication in academic journals often undergo the peer review process. In this case, an editor of a journal will often solicit a group of people with discipline-specific academic qualifications and expertise related to various topics within the scope of the journal. Potential reviewers usually submit a curriculum vita to demonstrate their area of expertise and, if accepted, they remain “on call” for a period of time. During this time, a reviewer’s role is that of a judge or referee for determining the quality and appropriateness of submissions for future publication within the journal. This is why you also may hear someone refer to these journals as “refereed” journals.
What are the Types of Peer Review?
Good question! There are several types of peer-review processes. The most common is the double-blind peer review process. This occurs when all identifying information is removed from a scholarly submission and it is given to a reviewer who has been selected often because of their expertise in the same or a similar discipline (Darling, 2015). The reviewer will evaluate the paper, using the selected criteria provided by the organization, and likely provide both quantitative and qualitative feedback for both the author and the organization. The more positive the rating (feedback), the more likely the submission will be accepted. This process is named double-blind, as both the submitter and evaluator remain anonymous throughout the entire evaluation process and is often the preferred mode of evaluation, as it allows for a more unbiased review of a submission, as the author’s name and affiliated institution are removed (Rittman & Classen, 2016).
How Do I Become a Peer Reviewer?
There are various opportunities to become a peer reviewer. There are some opportunities with a short-term commitment, such as a reviewer of proposals for conference presentations. Assignments, such as serving on an editorial board for a book or reviewing for a journal, often require a lengthier, more time-consuming commitment.
Where Should I Look to Become a Reviewer?
For instance, I often receive unsolicited emails containing requests for my service as a reviewer. Yet, in conducting research on each journal and the publisher, I have found that some are “predatory” in nature. This is where you often see the “pay to publish” model or the “vanity presses” model where there is not a rigorous peer review process for submissions. There are also other tale-tell signs to look for, such as a poorly crafted website, an ambiguous review process, a small or “upcoming” editorial board, and/or the publish er is responsible for numerous journals (Beall, 2017). Not all solicitations will fall under this category, but it is important, as due diligence, to conduct your own research before volunteering for service as a peer reviewer. Publishing resources, such as Cabell’s Directory ( www.cabells.com) and Ulrich’s Periodicals Directory ( www.ulrichsweb.serialssolutions.com ), are helpful resources for identifying valid publications for both service and submission. These are also located within the UOP Library site, as well. Like it or not, in academia, we are often judged by our affiliations!
What is service in academics?
Whether holding an official position on an organizational board or volunteering for a committee assignment within an institution, service is a recompensing way to contribute constructively to one’s discipline, institution, or the academy as a whole.
Is peer review open or single blind?
Peer review may also occur in other formats within the review process. In the single-blind peer review process, authors are not informed of the identity of the reviewer, yet reviewers have access to the identity of the author (Darling, 2015). The open peer review process makes the identities of both the author and reviewer available ...
What Is Peer Review in Science?
Peer review in science is a process where the work conducted is validated for authenticity and quality. The work must be original and be conducted by following the scientific process.
Why Is Peer Review Important in Science?
Conducting peer review is important in any discipline, since it is a validation process. However, in the field of science and medicine, the outcome of peer review is to determine if the research is valid and should continue or be repeated.
Peer Review Examples
When an academic seeks to be published in science, they generally want to be featured in an academic journal or to apply for grants to increase funding. Publishing in academic journals is prestigious and in some cases is a requirement for many professions in the research and education.
Types of Peer Reviews
Most of the articles professionals write are with the intention of being published in a journal. Each journal may have their own process for peer review. There are 4 common types: single-blind, double-blind, triple-blind, and open reviews. Most of the processes occur under single-blind, where the author does not know the peer reviewer.
Why is peer review important?
The increased use of the peer review process is due to two main factors.1 The first is the proliferation of manuscripts. In the past, editors of journals often had to struggle to collect enough papers to fill ...
How is peer review done?
Once an author submits a manuscript, it is initially reviewed by an editor of the journal to determine its suitability according to the guidelines set by the editorial policy. The manuscript could be rejected without additional review if the content does not fall within the scope of the journal, if it does not follow editorial policy and procedural guidelines, or it has already been accepted in another journal (in press). If the manuscript is not rejected when first received, it is then sent out for review to a minimum of two additional reviewers in the journal’s list of reviewers who are considered experts in the content of the paper. This process is usually a closed review adopted by most journals and can be a single-blinded review where the reviewers’ identities are withheld from the authors but the reviewers are aware who wrote the paper they are evaluating, or a double-blinded review where the identity of the authors is also concealed during the review process.5 When the chosen reviewers have accepted their assignment, they are given a time period to review the paper, usually with the help of a checklist similar to the sample given above. The reviewers return their recommendations and report to the editor who assesses them collectively and then makes a decision whether to reject the manuscript outright, to withhold judgment pending major or minor revisions, to accept it pending satisfactorily completed revisions, or to accept it as written (which is rare).1 For a manuscript requiring revisions, the authors have to submit the revised manuscript incorporating the recommendations of the reviewers. Once the manuscript has been revised satisfactorily, it is accepted and prepared for publication that may take several months.
What is a checklist for a reviewer?
Many journals use some form of a checklist for the reviewer to critically appraise the article submitted. Below are some sample review guidelines on how reviewers appraise an original article and which authors should be cognizant of to help them in the preparation of their manuscripts.
What is peer review in medical journals?
The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) defines peer review as “the critical assessment of manuscripts submitted to journals by experts who are usually not ...
Why are scientific journals more selective?
When the need for evidence-based practice evolved, submissions to scientific journals increased such that editors have to be more selective in what get published in their journals. The second reason is the explosion of new information and technology. Areas of expertise have expanded to become more specialized and sophisticated.
Why are reviewers chosen?
Reviewers are chosen for the expertise they have in a particular field, obtained by training or research works in the same field or related disciplines.
What is the purpose of a research article?
1. To help select quality articles for publication and filter out studies that were poorly conceived, designed, or executed, with the selection based upon the following: a. The scientific merit and validity of the article and its methodology; b.
Why is peer review important?
The Importance and Limitations of Peer-Review. Peer-review is a critical part of the functioning of the scientific community, of quality control, and the self corrective nature of science. But it is no panacea. It is helpful to understand what it is, and what it isn’t, its uses and abuses.
What does it mean when a research is peer reviewed?
When the statement is made that research is “peer-reviewed” this is usually meant to refer to the fact that it has been published in a peer-reviewed journal. Different scientific disciplines have different mechanisms for determining which journals are legitimately peer-reviewed.
What is post publication peer review?
The term peer-review is sometimes used to refer to the fact that papers are read and reviewed by the broader scientific community once they are published. However, this post-production review should not be confused with “peer-reviewed” and that term should not be used to refer to post-publication review, ...
What is the basic criterion for peer review?
The basic criterion is that there is a formalized process of peer-review prior to publication – so this presents a barrier to publication that acts as a quality control filter. Typically, the journal editor will give a submitted paper to a small number of qualified peers – recognized experts in the relevant field.
What does an editor do when reviewing a paper?
The editor also reviews the paper, and may break a tie among the reviewers or add their own comments. The process, although at times painful, is quite useful in not only checking the quality of submitted work, but improving the quality. A reviewer, for example, may point out prior research the authors did not comment on, or may point our errors in the paper which can be fixed.
What is a scientific paper?
Scientific papers are not written for non-scientists to understand. They are written for specialist scientists in the relevant field to understand. If you don’t understand a paper, you need to read its references, and then the sub-references and then the sub-sub-references.
What happens if an author thinks they were unfairly treated by one journal?
If an author thinks they were treated unfairly by one journal, they can always go to another or they can talk directly to the editor to appeal a decision and try to make their case. Perhaps the biggest weakness of peer-review, however, is when an entire discipline of peers is lacking in some fundamental way.
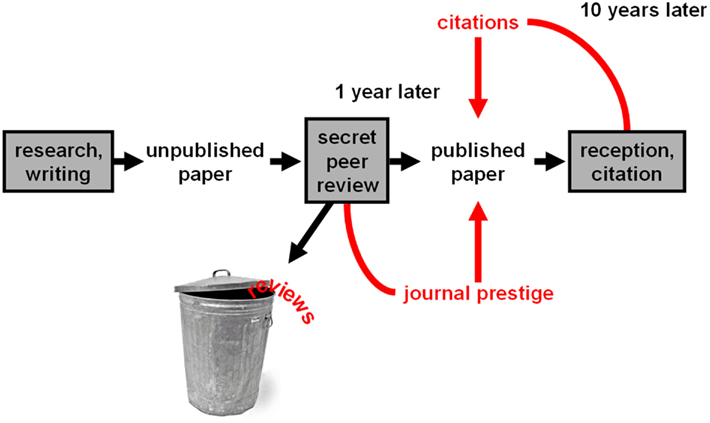
What Is Peer Review?
What Are The Types of Peer Review?
- Good question! There are several types of peer-review processes. The most common is the double-blind peer review process. This occurs when all identifying information is removed from a scholarly submission and it is given to a reviewer who has been selected often because of their expertise in the same or a similar discipline (Darling, 2015). The reviewer will evaluate the paper…
How Do I Become A Peer Reviewer?
- There are various opportunities to become a peer reviewer. There are some opportunities with a short-term commitment, such as a reviewer of proposals for conference presentations. Assignments, such as serving on an editorial board for a book or reviewing for a journal, often require a lengthier, more time-consuming commitment. For example, submissions for publicatio…
Where Should I Look to Become A Reviewer?
- I have to note the importance of being selective in affiliation. You will want to align your service with academic journals and conferences that are scholarly in nature. For instance, I often receive unsolicited emails containing requests for my service as a reviewer. Yet, in conducting research on each journal and the publisher, I have found that some are “predatory” in nature. This is wher…