What is signal-to-noise ratio?
Simply, it is the ratio of the light signal to the noise signal. Often expressed in decibels, a ratio when is higher than 1: 1, or greater than 0 dB, indicates that the signal is more compared to noise. Signal to noise ratio is often written as S/N or SNR.
Why is high SNR better?
A higher SNR value means that the signal strength is stronger in relation to the noise levels, which allows higher data rates and fewer retransmissions – all of which offers better throughput.
What affects signal-to-noise ratio?
The SNR, which is proportional to the square root of the NEX, improves as the NEX increases, but scan time also increases linearly with the NEX. Other parameters affecting the SNR are the sequence used, echo time (TE), repetition time (TR), and the flip angle.
What does signal-to-noise ratio mean for amplifiers?
SNR (Signal to Noise Ratio): An amplifier is the same, there is always a very small amount of noise from the electrons whizzing around inside. The goal is to make this background noise imperceptible, this means you hear more of the music and less of the noise. The measure of this is the signal to noise ratio.
Is lower or higher SNR better?
A signal-to-noise ratio over 0 dB indicates that the signal level is greater than the noise level. The higher the ratio, the better the signal quality. For example, a Wi-Fi signal with S/N of 40 dB will deliver better network services than a signal with S/N of 20 dB.
What happens if SNR low?
If the SNR value gets lower than one, the signal becomes unusable. This is called the “noise floor.” Signals close to the noise floor can be subject to data corruption, which will result in retransmissions between the transmitter and receiver.
Is low SNR good or bad?
An SNR greater than 40 dB is considered excellent, whereas a SNR below 15 dB may result in a slow, unreliable connection.
How can we improve signal-to-noise ratio?
What is a Signal-to-Noise Ratio and how can I improve it?using high quality sensors and electronic devices in your camera.using a good electronic architecture when designing your camera.lowering the temperature of the sensor and the other analog devices in your camera.More items...
How can we reduce SNR?
Fixing SNR IssuesRemove Extra WiFi networks. This is especially true if this is a business environment. ... Check for “Noisy” devices. Take a look at the devices around the WiFi router. ... Turn off unneeded signals. Some routers support multiple bands in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz range.
What is a good signal to noise?
25 dB to 40 dB: is deemed to be good. 41 dB or higher: is considered to be excellent.
Do amplifiers improve SNR?
The benefits of adding amplifiers in parallel are improved SNR and lower voltage noise density. For N amplifiers in parallel, the amplifier noise power is reduced by N and the input referred voltage noise density is reduced by √N.
What is a good signal-to-noise ratio image?
As a rule of thumb good quality confocal fluorescence images have a SNR between 20 to 40. Images recorded with a cooled CCD camera on top of a conventional microscope can easily have SNR ratios above 50, even above 100.
Is higher SNR better audio?
A signal-to-noise ratio compares a level of signal power to a level of noise power. It's most often expressed as a measurement of decibels (dB). Higher numbers generally mean a better specification since there's more useful information (the signal) than unwanted data (the noise).
Is 80dB SNR good?
In a studio setting and when selecting equipment, the goal is to: Have a S/N of 60dB or greater. 70dB is even better. 80dB or greater is ideal.
Is high SNR Margin good?
Higher ratios means better cables. Below 10dB is very bad and more than 20dB is good. At higher ratios, more speed can be achieved and lower ratios mean error-prone cable and lower speeds. The SNR margin is the difference between the SNR of the cable and the SNR needed to get an specific speed.
How does SNR affect image quality?
Signal to Noise Ratio is one factor that can have a significant impact on Image quality. In general the higher the signal level the more useful information there is within the image and it is therefore weighted more heavily than the lower level noise.
What is the SNR of a signal?
Signal – Noise = SNR (in dB). Typical examples indicate a signal strength of -67dBm and a noise floor of -92dBm, and punching that into the SNR equation gives a result of 25dB; which is a typical minimum SNR requirement for many wireless LANs.
What is a wireless signal strength indicator?
Signal – this is how strong your wireless client is receiving Wi-Fi signals from access points. It is commonly referred to as Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI), but more accurately called Received Channel Power Indicator (RCPI) in 802.11. I won’t go into the specifics of RSSI vs RCPI here, perhaps a post for another day, however remember that all wireless clients receive signal differently, and some give you a measurement as a percentage and some as dBm (i.e. -65dBm).
What is SNR in a device?
SNR is also a metric used by some client devices to determine roaming behaviour. RSSI/RCPI, noise, and data rate can also be used as metrics; so you can understand how this relates back to ensuring your design your environment properly for high SNR.
What is SNR in wireless?
SNR is a big influence on the data rates a wireless client can experience , as it impacts the modulation and coding efficiency that can be achieved given some other key factors (number of spatial streams, guard interval length, channel width).
What happens when you double the channel width?
Every time you double you channel width, you double the strength of your noise floor!
What is noise floor?
Noise – this is actually a measurement of the noise floor, which consists of all other energy and signals on the spectrum that you aren’t trying to receive.
Is SNR important for 802.11ax?
With 802.11ax around the corner, SNR is going to be even more critical when you’re attempting to achieve 1024QAM modulation and understand different characteristics of how the 802.11ax PHY operates (OFDMA/resource units/subcarriers & tones). It is best to be prepared now with the understanding of how SNR influences these elements, and how SNR is impacted in today’s Wi-Fi environments.
How to measure noise level?
Because the difference in these levels can be quite large, we state the ratio of the signal level to the noise level using the decibel (dB) scale. The decibel scale is logarithmic. As such, a difference of 6 dB represents a doubling of the amplitude ratio, 20 dB is ten times the amplitude, 40 dB is 100 times, 60 dB is 1000 times and 80 dB is 10,000 times and so on.
Why is the Lack of Noise Important?
Blacker is better. When you think about your audio system, a ‘more negative’ S/N ratio means that the noise is quieter than the audio signal. We don’t want to listen to noise. -90 dB is better than -80 dB. Got it? Clear?
Where does noise occur?
Noise happens in source units, signal processors and amplifiers. Once you add noise to the signal chain, it’s essentially impossible to remove it.
What are the sources of shot noise?
Devices like transistors and diodes, which have different layers of materials inside, are common sources of Shot Noise. There are many more types of noise. As you can imagine, the amount of noise generated by any one of these devices is minuscule.
What is signal to noise ratio?
Signal-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the power of a signal (meaningful input) to the power of background noise (meaningless or unwanted input):
When do you square the signal and noise?
However, when the signal and noise are measured in volts (V) or amperes (A), which are measures of amplitude, they must first be squared to obtain a quantity proportional to power, as shown below:
What is quantization noise?
This is because the minimum possible noise level is the error caused by the quantization of the signal, sometimes called quantization noise. This noise level is non-linear and signal-dependent; different calculations exist for different signal models. Quantization noise is modeled as an analog error signal summed with the signal before quantization ("additive noise").
What is the difference between optical and modulation frequency?
Optical signals have a carrier frequency (about 200 THz and more) that is much higher than the modulation frequency. This way the noise covers a bandwidth that is much wider than the signal itself. The resulting signal influence relies mainly on the filtering of the noise. To describe the signal quality without taking the receiver into account, the optical SNR (OSNR) is used. The OSNR is the ratio between the signal power and the noise power in a given bandwidth. Most commonly a reference bandwidth of 0.1 nm is used. This bandwidth is independent of the modulation format, the frequency and the receiver. For instance an OSNR of 20 dB/0.1 nm could be given, even the signal of 40 GBit DPSK would not fit in this bandwidth. OSNR is measured with an optical spectrum analyzer .
What does SNR mean in audio?
SNR is usually taken to indicate an average signal-to-noise ratio, as it is possible that instantaneous signal-to-noise ratios will be considerably different. The concept can be understood as normalizing the noise level to 1 (0 dB) and measuring how far the signal 'stands out'.
What is SNR in engineering?
Signal-to-noise ratio ( SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise.
What is SNR in math?
An alternative definition of SNR is as the reciprocal of the coefficient of variation, i.e., the ratio of mean to standard deviation of a signal or measurement:
How to reduce signal to noise ratio?
Persistent broadband sounds like talking, HVAC blowers, wind and moving water sources will increase the noise floor of the recording, and can effectively decrease your signal to noise ratio below usable levels. In this instance, it is best to shut off any equipment making the sound, or to move away from the source of the sound altogether.
What is signal to noise?
Signal-to-noise, then, is simply the ratio of desired signal (S) in relationship to unwanted noise (N). When we think about signal-to-noise in our audio equipment, we’re simply asking if our equipment is quiet enough to carry the audio signal without being distracting.
What happens when noise level and signal are too close together?
If the noise level and the signal are too close together, the noise becomes like a crowded bar, and our signal, like a conversation becomes more difficult and more distracting to hear.
What is noise in audio?
Noise is any constant sound that is not your signal. It is typically a sound source that you’re trying to filter out, or rise above, in order to communicate some other audio information. Noise can range from an inaudible drone, to a clearly perceptible hiss, to a cacophony of loud machinery. In sound, we typically deal with self-noise (the hiss ...
What is noise in recording?
Where signal-to-noise can get confusing is in defining ”what is noise”. In a recording, noise refers to anything that is not the information we are recording. In our pub scenario, noise is anything that is not our conversation. However, if we are recording the crowd in the bar, noise refers to any constant sound that is not your crowd.
Is voltage a measurement of sound?
However, voltage isn’t often a meaningful measurement in audio, as we tend to think in terms of how things sound, rather than how they conduct electricity. Therefore, in audio, we express signal to noise in dB. This value is already calculated and converted from the signal and noise voltage. It's more meaningful in audio terms of measurement.
What is signal to noise ratio?
Signal to noise ratio is a measurement of the audio signal level compared to the noise level present in the signal. SNR specifications are used in components such as amplifiers, CD/DVD players etc.,
How to improve signal to noise ratio?
A further way to improve signal to noise ratio is by filtering. One can use filters to exclude noise at frequencies which are not of interest for the particular purpose. Instrumentation amplifiers which have a lot of headroom can help here, by allowing you to put the filters after the first stage of amplification, where it won’t affect the high input impedance.
What is SNR in a signal?
It is the ratio of signal power to noise power at the region of interest (Basically SNR is important in receiving and).
How does noise affect communication?
For communication to be effective the signal’s power content should be very very large as compared to noise. If noise power will be not very less than signal power then there will be more ineffective output, so here SNR will be comparatively lesser, as a result the quality of signal at the receiver end will be more degraded. If noise power is comparatively much less than the signal power ,the quality of signal received at receiver end will be good comparatively.
What does SNR mean in a receiver?
It indicates how strong your signal is when compared to the channel noise. When the signal power is equal to the noise power, the SNR is 0 dB. The receiver can’t distinguish between the signal and the noise. As a side note, the noise model that we generally take into consideration is AWGN and hence noise is always added to the original signal and the receiver receives a signal that is added with noise.
What is the difference between noise and signal?
In this case, we can be talking about either/or/both acoustic and electromagnetic phenomena (and maybe some other things). Signal implies some coherent signal that we can interpret as information. Noise implies a random pattern of waves that can’t be interpreted. When signal is heavily buried in noise, it can take special coding and redundancy processing to extract the signal from the noise.
Why is noise ratio important?
So signal/noise ratio means that optimization of deliverance of a message (voice, music, speech, etc.) moves along a clear noiseless channel, so that the intended message can be decoded clearly by the receiver.
Why is it important to calculate the signal to noise ratio?
The importance of accurately calculating the signal to noise ratio is imperative to the ultimate goal of efficient and accurate designs. Furthermore, computing the SNR will also provide insight into design functionality and design performance. The time to realize that a design is not feasible is before the manufacturing phase. Therefore, it is essential to assess design parameters through calculations as well as simulation.
Why is Signal to Noise Ratio Important?
Also, in a scenario such as this, we would consider this to be a signal to noise issue or the equivalent of a signal to noise ratio that is below acceptable parameters.
How to calculate SNR?
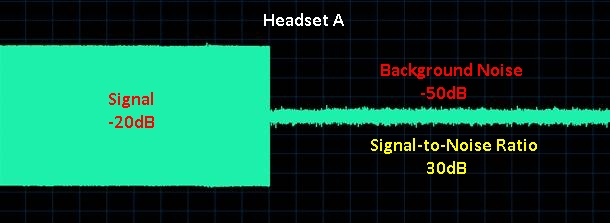
So, if your SNR measurements are already in decibel form, then you can subtract the noise quantity from the desired signal: SNR = S - N. This is because when you subtract logarithms, it is the equivalent of dividing normal numbers. Also, the difference in the numbers equals the SNR. For example, you measure a radio signal with a strength of -10 dB and a noise signal of -50 dB. -10 - (-50) = 40 dB.
What is SNR in a signal?
In other words, SNR is the ratio of signal power to the noise power, and its unit of expression is typically decibels (dB). Also, a ratio greater than 0 dB or higher than 1:1, signifies more signal than noise. Aside from the technical definition of SNR, the way I define it in other terms is by using a comparative.
What is SNR in radio?
In basic terms, SNR is the difference between the desired signal and the noise floor. Also, in terms of definition, the noise floor is the specious background transmissions that are produced by other devices or by devices that are unintentionally generating interference on a similar frequency.
What is SNR in engineering?
Also, SNR is a measurement parameter in use in the fields of science and engineering that compares the level of the desired signal to the level of background noise.
How many dB is good?
25 dB to 40 dB: is deemed to be good.
I. What is the Contrast to Noise Ratio in Radiology?
Radiology as a field has many terms individuals often find confusing and contrast to noise ratio has been one of the common confusing terms. So, what then is a contrast to noise ratio (CNR)?
II. How is Contrast to Noise Ratio Calculated?
Firstly, we must consider the signal-to-noise ratio when calculating contrast to noise ratio as it enables us to acquire the necessary averages which will help calculate the contrast to noise values. And the signal to noise ratio is given as the average signal divided by the noise.
III. What is the Importance of Contrast to Noise Ratio?
Since the contrast to noise ratio shows the relationship between two regions of signal intensity differences, it also translates to the fact that it Improves and increases insight on the definite differences between two regions of interest.
Conclusion
So, in a nutshell, we have seen what contrast to noise ratio is and we have also examined signal to noise ratio and as discussed, a contrast to noise ratio is the parameter or metric employed to determine the quality of an image during an inspection.
All The Noise, All The Time!
The Sound of Noise
How We Measure Noise
Clarifying The Mysterious Signal-To-Noise Ratio
Why Is The Lack of Noise Important?
Overview
- An easy way to hear what noise sounds like is to connect a set of headphones to your laptop computer and turn the volume up fairly high. You’ll hear a hiss through the headphones. That’s noise. (Note: Please be careful, we want you as an audio enthusiast for life. Take those headphones off before your computer plays a sound and you risk damaging your hearing.)
Definition
- There are a few ways to quantify the noise an electronic component creates. One method is to simply state the noise on the output of the device in absolute terms. The measurement could be in volts or watts, and quantifies the amplitude of the noise signal. You won’t see this used to describe audio components, however. The most common method of quantifying the noise that …
Alternate definition
- If you look at an amp spec from more than about 10 years ago, or you see a number that is abnormally high, they may be rating the noise level using the maximum output capability of the amplifier as the comparing factor. If we measure an amplifier’s noise output level at 1 watt to be 85 dB, then you increase the amplifier’s output to 10 watts, assum...
Modulation system measurements
- How can we quantify the desire not to add noise to our signal? Here is a simple analogy. If you purchased a TV in recent years, you may have heard the expression ‘blacker blacks.’ ‘Blacker blacks’ refers to how dark the screen gets when there is no signal. Blacker is better. When you think about your audio system, a ‘more negative’ S/N ratio means that the noise is quieter than th…
Noise reduction
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise.
SNR, bandwidth, and channel capacity of a communication channel are connected by the Shannon…
Digital signals
Signal-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the power of a signal (meaningful input) to the power of background noise (meaningless or unwanted input):
where P is average power. Both signal and noise power must be measured at the same or equivalent points in a system, and within the same system bandwidth.
Depending on whether the signal is a constant (s) or a random variable (S), the signal-to-noise ra…
Optical signals
An alternative definition of SNR is as the reciprocal of the coefficient of variation, i.e., the ratio of mean to standard deviation of a signal or measurement:
where is the signal mean or expected value and is the standard deviation of the noise, or an estimate thereof. Notice that such an alternative definition is only useful for variables that are always non-negative (such as photon counts and luminance), and it is only an approximation since . …
Types and abbreviations
Channel signal-to-noise ratio is given by
where W is the bandwidth and is modulation index
Output signal-to-noise ratio (of AM receiver) is given by
Channel signal-to-noise ratio is given by
Output signal-to-noise ratio is given by