
How to relieve vasoconstriction?
Treatment of vasoconstriction
- Medications: There is a wide variety of medications which can be used to combat vasoconstriction. ...
- Exercise: Exercise enhances blood flow and nutrient delivery to the body. ...
- Avoidance of cold: Exposure to cold temperatures causes the blood vessels by constricting. ...
- Stay away from stress: It has been found that stress also leads to vasoconstriction. ...
What are the symptoms of vasodilation?
Symptoms of vasodilation. A 42-year-old member asked: What are the symptoms of vasodilation? Dr. Atique Mirza answered. Internal Medicine - Cardiology 31 years experience. Flushing : Vasodilator ion can cause lowe BP , flushing, dizziness, lightheaded ness ect. 4.8k views Answered >2 years ago.
Why does sympathetic nervous system cause vasoconstriction?
· 3 yr. ago The effect of sympathetic nervous system activation on most blood vessels is vasoconstriction, so there is reduced blood to the abdominal viscera and the skin. This means there is more blood directed to skeletal muscle, the heart, and the brain — the parts of the body that need it most in fight or flight situations.
Does vasoconstriction increase blood pressure?
Vasoconstriction reduces the volume or space inside affected blood vessels. When blood vessel volume is lowered, blood flow is also reduced. At the same time, the resistance or force of blood flow is raised. This causes higher blood pressure. Untreated high blood pressure ( hypertension) can lead
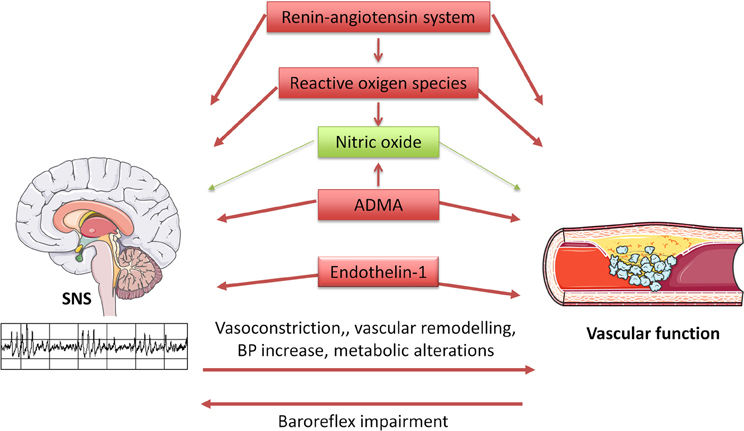
What is vasodilation and why is it important?
Vasodilation is a mechanism to enhance blood flow to areas of the body that are lacking oxygen and/or nutrients. The vasodilation causes a decrease in systemic vascular resistance (SVR) and an increase in blood flow, resulting in a reduction of blood pressure.
What is the purpose of vasoconstriction?
Vasoconstriction in your life. Vasoconstriction of the blood vessels is a natural part of your body balancing its systems. Vasoconstriction is needed to help maintain healthy blood flow and keep your body temperature from getting too cold. It can also raise blood pressure when it's necessary.
What is the importance of vasodilation during exercise?
Exercise: Vasodilation enables the delivery of extra oxygen and nutrients to the muscles during exercise.
How does vasodilation and vasoconstriction help maintain homeostasis?
Blood vessels supplying blood to the skin can swell or dilate - vasodilation. This causes more heat to be carried by the blood to the skin, where it can be lost to the air. Blood vessels can shrink down again - vasoconstriction. This reduces heat loss through the skin once the body's temperature has returned to normal.
What does vasoconstriction do to blood flow?
Normally, the vessels that supply blood to the skin constrict or narrow in response to cold temperatures. This reaction, called "vasoconstriction," decreases blood flow to the skin, which helps to minimize heat loss from the warm blood and therefore preserve a normal internal or "core" temperature.
How does vasoconstriction affect blood pressure?
Vasoconstriction results in increased peripheral vascular resistance. This results in the increase of force with which blood flows and leads to high blood pressure. This condition is referred to as hypertension and causes damage to the heart.
Does exercise cause vasodilation or vasoconstriction?
The results from the present study show that acute blockade of α-adrenergic receptors in the vasculature of exercising skeletal muscles produces vasodilation. These data demonstrate that there is sympathetic vasoconstriction in active skeletal muscles even at high exercise intensities.
Why does vasodilation lower blood pressure?
Vasodilators are medications that open (dilate) blood vessels. They affect the muscles in the walls of the arteries and veins, preventing the muscles from tightening and the walls from narrowing. As a result, blood flows more easily through the vessels. The heart doesn't have to pump as hard, reducing blood pressure.
How does vasodilation cool you down?
Vasodilation is a response to being too hot. The process includes the widening of blood vessels at the skin surface to increase heat loss through the surface of the skin.
How do vasoconstriction and vasodilation contribute to the homeostasis of body temperature?
For example, vasodilation brings more blood and heat to the body surface, facilitating radiation and evaporative heat loss, which helps to cool the body. However, vasoconstriction reduces blood flow in peripheral blood vessels, forcing blood toward the core and the vital organs found there, conserving heat.
How does vasoconstriction maintain body temperature?
In endotherms, warm blood from the body's core typically loses heat to the environment as it passes near the skin. Shrinking the diameter of blood vessels that supply the skin, a process known as vasoconstriction, reduces blood flow and helps retain heat.
Does vasoconstriction increase heart rate?
This decrease in afferent signaling from the baroreceptor causes an increase in efferent sympathetic activity and a reduction in parasympathetic activity, which leads to vasoconstriction, increase heart rate, increase contractility, and an increase in BP.
How does vasoconstriction keep you warm?
Vasoconstriction and vasodilation In endotherms, warm blood from the body's core typically loses heat to the environment as it passes near the skin. Shrinking the diameter of blood vessels that supply the skin, a process known as vasoconstriction, reduces blood flow and helps retain heat.
Does vasoconstriction decrease heart rate?
This decrease in afferent signaling from the baroreceptor causes an increase in efferent sympathetic activity and a reduction in parasympathetic activity, which leads to vasoconstriction, increase heart rate, increase contractility, and an increase in BP.
Do Vasoconstrictors raise blood pressure?
Vasoconstricting and vasodilating medications work in different ways. While vasoconstricting medications tighten your blood vessels to raise blood pressure, vasodilating medications dilate or widen them to improve blood flow and lower blood pressure.
Why does vasoconstriction occur in sympathetic?
Sympathetic innervation of the peripheral vasculature causes vasoconstriction primarily through the action of norepinephrine at postsynaptic α-adrenergic receptors. Cotransmitters such as neuropeptide Y also have a role in this vasoconstriction.
What is the process of vasodilation?
The process involves the narrowing of blood vessels at the skin surface to reduce heat loss through the surface of the skin . Vasodilation is a response to being too hot.
How does sweat work?
Sweat is produced by the sweat glands and travels up the sweat duct and out of the sweat pore onto the skin surface. Here it will evaporate, taking excess body heat with it. Your body uses this mechanism to cool down. previous.
What are the conditions that need to be maintained in a steady state?
Conditions inside our body need to be maintained in a steady state. Blood sugar level and temperature are regulated carefully. Lifestyle choices such as drugs and alcohol can affect this homeostasis.
Why is vasodilation important?
Vasodilation is an important process which keeps the body functioning in normal conditions. The endogenous substances and drugs are able to cause vasodilation are known as vasodilators. Dilation of arteries and arterioles has a significant therapeutic value in decreasing arterial blood pressure and heart rate.
What is the difference between vasodilation and vasoconstriction?
The key difference between vasoconstriction and vasodilation is that vasoconstriction increases the resistance and decreases the blood flow while vasodilation decreases the resistance and increases the blood flow.
What is Vasodilation?
Vasodiation is the widening of blood vessels. Vasodilation is the opposite process of vasoconstriction. As a result of vasodilation, smooth muscles of the blood vessel walls become relaxed. The internal diameter of blood vessels increases during the vasodilation. When blood vessel walls are dilated, the surface area of the lumen increases. Hence, the vascular resistance decreases. When resistance decreases, it enhances blood flow through the vessels. The blood pressure also decreases due to dilation of the blood vessels.
How does vasodilation affect blood pressure?
During vasoconstriction, smooth muscles of the blood vessel walls constrict by reducing the internal diameter of the vessel. In oppose to that, vasodilation relaxes the smooth muscles of the blood vessel walls by increasing the internal diameter of the vessel.
Why does the radius of the artery decrease?
The radius of the artery or arteriole is decreased due to vasoconstriction. This happens due to the constriction of the smooth muscles in the walls of arteries or arterioles. The lumen becomes narrower when the smooth muscles constrict. When lumen becomes narrow, the surface area, which contacts blood, decreases.
How does venoconstriction affect blood flow?
In veins, venoconstriction enhances the blood flow. When vasoconstriction increases the blood pressure in veins, it enhances the blood movement through veins. Thus, venoconstriction increases the return of blood to the heart. Figure 01: Vasoconstriction.
Does vascular resistance decrease blood pressure?
Hence, the vascular resistance decreases. When resistance decreases, it enhances blood flow through the vessels. The blood pressure also decreases due to dilation of the blood vessels. Vasodilation is an important process which keeps the body functioning in normal conditions.
What is the effect of vasodilation on the body?
All organ systems in the body are affected by vasodilation. Vasodilation increases blood flow to tissues throughout the body.
What is the mechanism of vasodilation?
Vasodilation is a mechanism to enhance blood flow to areas of the body that are lacking oxygen and/or nutrients. The vasodilation causes a decrease in systemic vascular resistance (SVR) and an increase in blood flow, resulting in a reduction of blood pressure. Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels as a result of the relaxation ...
What are the mediators involved in vasodilation?
Other mediators involved in vasodilation are generated during enhanced muscle activity. These stimuli include pCO, lactate, K, and adenosine. Venous pCO levels increase during exercise due to the high turnover of the Krebs cycle to meet the oxygen demands of skeletal muscle. There is a net gain in lactic acid produced by exercising muscle due to increased glycolysis activity. Skeletal muscle cells release K ions into the interstitium during an action potential. During exercise, there is also an increase in the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), yielding adenosine. The above mediators produced can diffuse to adjacent arterioles and have powerful vasodilatory effects to increase the oxygen and nutrient supply to exercising muscle when demand is enhanced. [7]
What is the first line of treatment for anaphylactic shock?
This situation leads to the activation of the inflammatory cascade, and immediate epinephrine is the first-line treatment. [1]
What is the process of new blood vessel formation?
Angiogenesis is the process of new blood vessel formation. It occurs as a response to signaling from endothelial cells in an existing blood vessel. The most notable signals are vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and fibroblast growth factor family (FGF). [4] .
What are the stimuli that cause relaxation?
Numerous stimuli, including acetylcholine, ATP, adenosine, bradykinin, histamine, and shear stress, can activate eNOS and COX pathways that form nitric oxide (NO) and prostacyclin, respectively.
When does vasodilation occur?
Mechanism. Vasodilation occurs when the smooth muscle located in the blood vessel walls relax.
How long does vasoconstriction last?
This vasoconstriction lasts five to ten minutes ...
What causes edema in the blood vessels?
The main factor involved in causing vasodilation is histamine. Histamine also causes blood vessels to become porous, allowing the tissue to become edematous because proteins from the bloodstream leak into the extravascular space, which increases its osmolar load and draws water into the area.
