Where is the incisive foramen located?
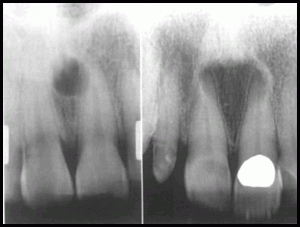
Feb 11, 2022 · The incisive foramen (also known as nasopalatine foramen or anterior palatine foramen) is the oral opening of the nasopalatine canal. It is located in the maxilla in the incisive fossa, midline in the palate posterior to the central incisors, at the junction of the medial palatine and incisive sutures. It can be single or multiple.
What is the difference between the incisive and interventricular foramen?
Medical Definition of incisive foramen : any of the openings of the incisive canal into the incisive fossa Learn More About incisive foramen Dictionary Entries Near incisive foramen incisive canal incisive foramen incisive fossa See More Nearby Entries Cite this Entry “Incisive foramen.”
What is the incisive foramen in a cat?
The incisive foramen (also known as nasopalatine foramen or anterior palatine foramen) is the oral opening of the nasopalatine canal. It is located in the maxilla in the incisive fossa, midline in the palate posterior to the central incisors, at the junction of …
Where is the incisive fossa located in the mouth?
The incisive foramen, noted briefly in dorsal view of the skull, is a single opening between the premaxillae (Figure 8.18b). The much larger maxillae follow the premaxillae posteriorly. Both of these bones bear conical teeth, set in a single marginal series in deep sockets in the bone, a condition termed thecodont.

What is the function of incisive foramen?
Function. The incisive foramen allows for blood vessels and nerves to pass. These include: the pterygoopalatine nerves to the hard palate.
What runs in the incisive canal?
The maxillary incisive canal runs through the maxilla in the midline. It connects the inferior nasal cavity with the superior oral cavity, opening at the incisive foramen posterior to the central maxillary incisor teeth. It contains the descending palatine artery and the nasopalatine nerve.Oct 5, 2021
What structure passes through incisive foramen?
The foramen leads to a short canal that connects the nasal and oral cavities. The terminal branches of the greater palatine arteries pass through the canal into the nose, and branches of the sphenopalatine nerves pass down through the canals to the anterior surface of the hard palate.
What travels through incisive foramen?
It transmits the greater palatine artery and vein from the oral to the nasal cavity and the nasopalatine nerve in the opposite direction.Mar 17, 2014
How many births are there with cleft lip?
Cleft lip and cleft palate are common malformations, with an incidence of approximately 1 in 1000 births (cleft lip) and 1 in 2500 births (cleft palate). Numerous combinations and degrees of severity exist, ranging from a unilateral cleft lip to a bilateral cleft lip associated with a fully cleft palate.
How to tell if you have a cleft palate?
Clinical Signs. Clinical signs of a cleft palate vary depending on what embryologic process failed to complete. Those involving the oronasal cavity can be primary (anterior to the incisive foramen) or secondary (caudal to the incisive foramen) with the latter potentially involving the hard and/or soft palates.
What are the two major groups of cleft lip and palate?
There are two major groups of cleft lip and palate, anterior and posterior deformities, with the incisive foramen as the dividing landmark. The anterior deformities include cleft lip, with or without cleft upper jaw, and cleft between the primary and secondary palates (Fig. 11.10A, B).
Which nerve carries parasympathetic nerves?
The sphenopalatine foramen has been mentioned earlier. The sphenopalatine nerve (a branch of the maxillary nerve V2) carries post ganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the sphenopalatine ganglion via the foramen into the nasal cavity. It passes down the lateral wall of the septum to reach the upper opening of the incisive foramen.
What connects the nasal cavity and the foramen?
The foramen leads to a short canal that connects the nasal and oral cavities. The terminal branches of the greater palatine arteries pass through the canal into the nose, and branches of the sphenopalatine nerves pass down through the canals to the anterior surface of the hard palate. The canal also connects the oral cavity with ...
What is the vagus foramen?
Laterally is the large vagus foramen, for the vagus nerve. The lateral carotid foramen, nearly as large, is ventral to the vagus foramen and serves for passage of the internal carotid artery. Farther laterally, ventral to a prominent crest on the paraoccipital process, is the cranioquadrate passage.
What is the area of anesthesia?
iii. Area of anesthesia: nose, cheek, lip, and eyelid of the ipsilateral face. This regional nerve block allows for anesthesia of the upper lip and may be used bilaterally to completely block the upper lip, which can help in anesthesia without relying on local infiltration that can obscure the vermilion border. b.
What is the nasopalatine foramen?
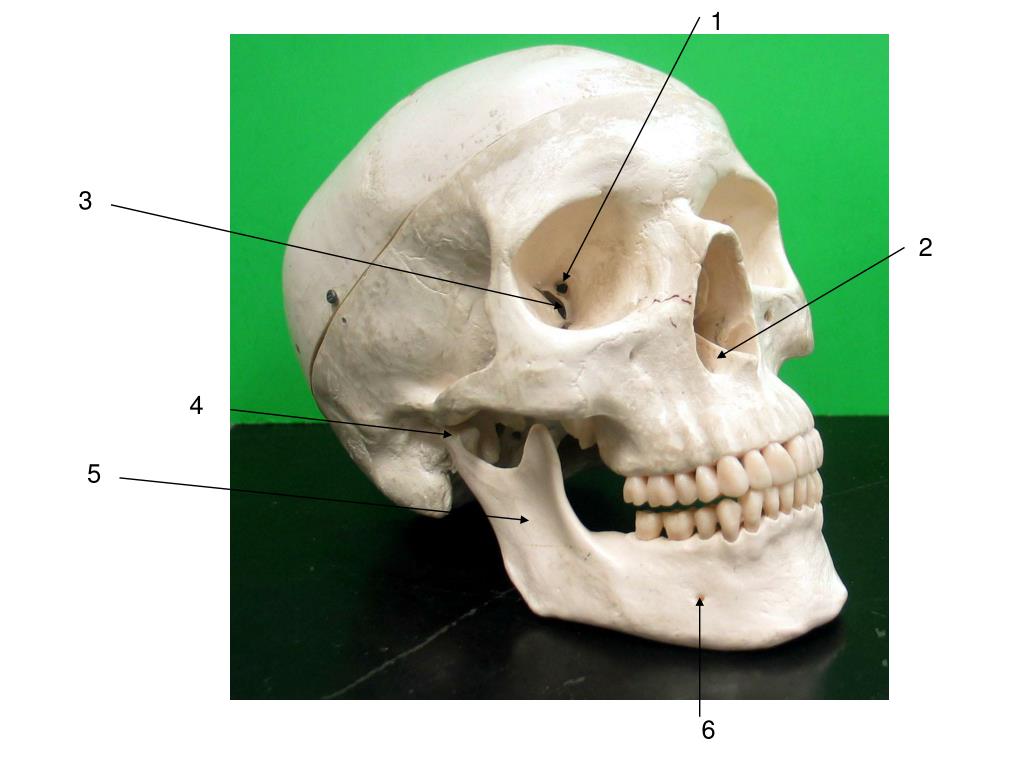
Anatomical terms of bone. In the human mouth, the incisive foramen, also called anterior palatine foramen, or nasopalatine foramen is a funnel-shaped opening in the bone of the oral hard palate immediately behind the incisor teeth where blood vessels and nerves pass.
What is the incisive foramen?
Incisive foramen. The bony palate and alveolar arch. In the human mouth, the incisive foramen, also called anterior palatine foramen, or nasopalatine foramen is a funnel-shaped opening in the bone of the oral hard palate immediately behind the incisor teeth where blood vessels and nerves pass. The incisive foramen is continuous with ...
Which nerves are sent to the incisive foramen?
The incisive foramen receives the nasopalatine nerves from the floor of the nasal cavity along with the sphenopalatine artery supplying the mucous membrane covering the hard palate of the mouth. In many other species, the incisive foramina allow for passage of ducts to the vomeronasal organ .