Key Takeaways
- A 401 (k) plan is a company-sponsored retirement account to which employees can contribute income, while employers may match contributions.
- There are two basic types of 401 (k)s—traditional and Roth—which differ primarily in how they're taxed.
- With a traditional 401 (k), employee contributions are pre-tax, meaning they reduce taxable income, but withdrawals are taxed. 1
What is a 401(k) account?
It’s a special account that you can sign up for at work, if your employer offers one, and it’s designed specifically to help you save for retirement. Here’s the 101 on 401 (k)s.
How does a 401(k) work?
If your employer offers a 401 (k) and you meet the eligibility requirements, you can enroll in the plan and begin making contributions via payroll. Before you start making contributions, though, you’ll need to decide: 401 (k)s come in two distinct flavors: Traditional and Roth.
What is 401(k) for retirement?
A 401 (k) can help you start saving for retirement. Whether you want to retire to a quiet life on the beach or spend your golden years globetrotting to exotic locations, one thing is for sure: Retirement is likely to be the most expensive thing you ever pay for. And unlike other major life purchases (cars, homes, ...
What are the flavors of 401(k)?
How much you want to save. What you want to do with the money you save. 401 (k)s come in two distinct flavors: Traditional and Roth. Although at their heart they aim to achieve the same purpose — to encourage Americans to save more for retirement by offering tax incentives — they do this in drastically different ways.
When did 401(k) start?
It started when Congress passed the Revenue Act of 1978, which included a provision that was added to the Internal Revenue Code — Section 401 (k) — that allowed employees to avoid being taxed on deferred compensation. In 1980, benefits consultant Ted Benna referred to Section 401 (k) while researching ways to design more tax-friendly retirement ...
What factors play into your retirement contribution decision?
Apart from knowing the limits, other factors that’ll play into your contribution decision will include how much you think you’ll need to save for retirement, whether you’re saving for retirement through other types of accounts and how much you can actually afford to contribute each month.
Who came up with the idea of Section 401(k)?
In 1980, benefits consultant Ted Benna referred to Section 401 (k) while researching ways to design more tax-friendly retirement programs for a client. He came up with the idea to allow employees to save pre-tax money into a retirement plan while receiving an employer match.
What is a 401 (k) plan and how does it work?
A 401 (k) plan is a tax-deferred retirement savings vehicle offered by employers as a way to help employees save for their retirement. It allows employees to direct a portion of their earnings into the account and defer paying income tax on it until they withdraw it in retirement.
Requirements for a 401 (k) Plan
The requirements for joining a workplace 401 (k) plan depend on the employer and/or plan sponsor. Employers may require a worker to be with the company for a minimum amount of time before they can contribute to a company 401 (k) savings plan.
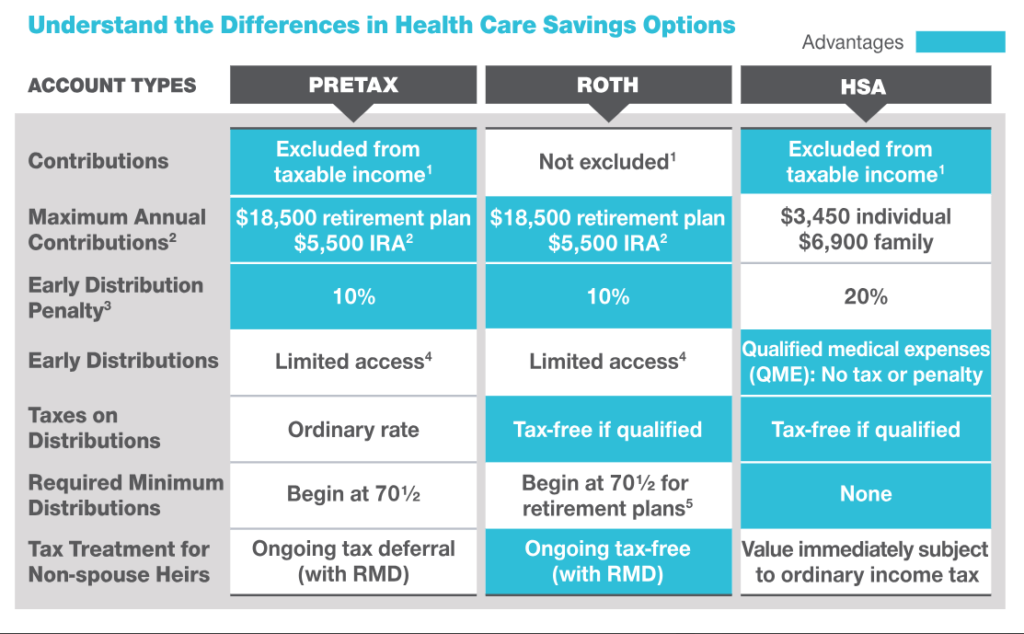
Traditional 401 (k) vs. Roth 401 (k)
There are some important differences between traditional 401 (k)s and Roth 401 (k)s to note.
Employer 401 (k) matching contribution
Some employers offer to match employees’ contributions into a sponsored 401 (k) plan. This means that for every dollar the employee saves, the employer deposits a matching contribution. This can be dollar-for-dollar or a specific percentage (such as $0.50 for every dollar).
FAQs about 401 (k) plans
If an individual changes jobs or otherwise leaves their workplace, they have a few options for their 401 (k) savings.
The bottom line
A 401 (k) is a retirement savings vehicle offered by many employers. It offers tax advantages and investment opportunities and has higher contribution limits than other retirement accounts such as IRAs. Both types of accounts allow account owners to access the savings as early as age 59½ without penalty.
What Is a 401 (k) Plan?
A 401 (k) plan is an employer-sponsored qualified retirement plan that is intended to help employees grow their retirement savings.
What is a comparison chart for 401(k)?
The Internal Revenue Service provides a comparison chart that shows the differences in plan contributions, income limits and distributions . Employers generally offer two main categories of 401 (k) plans for their employees: traditional and Roth.
How long do you have to hold a Roth 401(k)?
To be considered qualified, the account must be held for at least five years, and the participant must be at least 59 ½ years old. Distributions resulting from disability or death also meet the criteria. Roth 401 (k) plans are also subject to the same required distribution rules as traditional 401 (k) plans.
What is the penalty for withdrawing money from a 401(k)?
If you need to withdraw money from your plan before reaching the age of 59 ½, you will pay a 10 percent penalty. The IRS assesses a 6 percent penalty for excessive contributions above the annual limit, as well. These penalties are easily avoidable, and they do not occur unless you break the established rules of 401 (k) plans.
When is 401(k) withdrawal taxable?
Unless the participant is still working, the IRS requires that distributions begin no later than age 72, or 70 ½ if the participant turned 70 1/2 before January 1, 2020.
What is the maximum 401(k) contribution for 2021?
The 401 (k) plan contribution limit for 2021 is $19,500 with an additional $6,500 for employees aged 50 and over. The higher your contributions, the lower your federal income tax for the tax year.
What is the Employee Retirement Income Security Act?
The Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 is a federal law that protects retirement plan money through standards set for employers. According to the U.S. Department of Labor, “The law also establishes detailed funding rules that require plan sponsors to provide adequate funding for your plan.”
What should 401(k)s do?
A large majority of plan sponsors (85 percent) think the core purpose of a 401 (k) plan is to provide income sources during retirement, rather than savings. It’s a major shift.
What does a DC plan sponsor want?
When looking at DC plan design, plan sponsors want simplicity. Nine in ten plan sponsors believe that it is in the best interests of plan participants to keep plan design changes simple, since complexity, such as too many choices and features, often leads to participant inertia. Connected to this goal of simplicity , 58 percent of plan sponsors do not believe that withdrawal solutions with minimum guarantees are easy to understand for the average DC plan participant.
Do 401(k) accounts have to be communicated as lifetime income?
The poll found nearly all plan sponsors agreed that it would be helpful if 401 (k) account balances were required to be communicated as lifetime income–in addition to the total account balance–on benefit statements, similar to Social Security statements currently. A nearly equal number of plan sponsors agree that it is important for ...
Do DC 401(k) plans include annuities?
A nearly equal number of plan sponsors agree that it is important for the DOL to make it easier for plan sponsors to include income annuities in DC plans. “Today, only six percent of plan sponsors say that their 401 (k) plan includes a guaranteed lifetime income option,” Rafaloff added.
What is 401(k) history?
History of the 401 (k) The term "401 (k)" refers to Section 401 (k) of the Internal Revenue Code. The provision allows employees to avoid taxation on parts of their income if they elect to receive it as deferred compensation rather than as direct pay. 2 . Benna designed the 401 (k) plan for a bank client seeking to give employees additional ...
Who created the 401(k) plan?
As the most widely used and well-known retirement savings plans in the United States, 401 (k) plans were the brainchild of benefits consultant Ted Benna. In 1979, Benna noticed that the rules established in the Revenue Act of 1978 made it possible for employers to establish simple, tax-advantaged savings accounts for their employees. 1 .
Why did Ronald Reagan kill the 401(k)?
Indeed, the U.S. Treasury Department under Ronald Reagan proposed killing the 401 (k) in 1984. 7 The concern was that tax receipts would fall too fast as more workers funded their retirement plans.
How many people are in 401(k) in 2019?
In 1983, 7.1 million employees participated in a 401 (k) plan, a number that grew to 38.9 million by 1993. 4 As of 2019, 401 (k) plans covered an estimated 80 million people ...
When did the 401(k) tax relief act come into effect?
In 2001, Congress passed the Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act, which enabled catch-up contributions for participants age 50 and older. The act also allowed companies to offer Roth 401 (k) accounts, which require post-tax contributions but provide the benefit of tax-free growth and distribution. 6 .
Who offered the first 401(k) plan?
However, the bank rejected the idea because it had never been done before, so Benna offered the first 401 (k) plan to his own employees at The Johnson Companies. 1 By 1981, the IRS had proposed formal rules for 401 (k) plans. 3 . By the next year, several large companies began to offer new 401 (k) plans to employees.
Do 401(k) plans have tax benefits?
Employees receive two significant benefits from 401 (k) plans and other tax-exempt retirement accounts: first, there is the obvious tax benefit. 8 Second, employees have a way to protect their retirement savings from losing real purchasing power through inflation.
