
What is ionic strength?
The concept of ionic strength was first introduced by Lewis and Randall in 1921 while describing the activity coefficients of strong electrolytes. The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution.
What is molar ionic strength of a solution?
The molar ionic strength, I, of a solution is a function of the concentration of all ions present in that solution. where one half is because we are including both cations and anions, c i is the molar concentration of ion i (M, mol/L), z i is the charge number of that ion, and the sum is taken over all ions in the solution.
How do you calculate ionic strength from concentration?
You can use an ionic strength calculator to find ionic strength of a solution, which minimizes math errors. Select "ion" and input concentration of solution. For example if the concentration is 1.0 M, type 1 for concentration. Press "Calculate" or "Ionic Strength" to complete the calculation.
What is the ionic strength of a 3m salt?
Furthermore, each ion’s concentration is the same as the concentration of the salt, 3 mol/L. Hence, the ionic strength is 3 M.
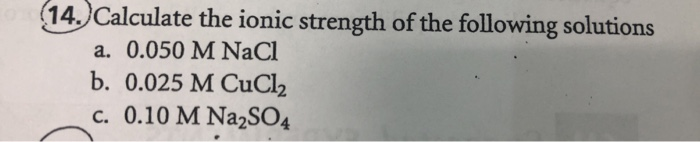
How do you find the ionic strength of a solution?
How to calculate the ionic strength of a solution?Calculate the power of the charge numbers.Multiply the squared charge numbers by the ionic concentration.Add up all the products of the ionic concentration and charge numbers.Divide the sum value by 2.More items...•
Is ionic strength the same as molarity?
For a 1:1 electrolyte such as 0.1 M NaClO4 the ionic strength is equal to the molarity of the electrolyte.
What is ionic strength solubility?
Ionic strength and tonicity modifiers. Ionic strength can impact the behavior of proteins resulting in salting in (increased solubility) or salting out (decreased solubility). The decrease in solubility with an increase in ionic strength is usually attributed to the colloidal stability of a protein.
What is the purpose of ionic strength?
The ion interaction with water and other ions in the solution is marked. The ionic strength formula is used to calculate half of each ionic species' total concentration.
What is the ionic strength of water?
Based on this equation, a 0.5 molar CaCl2 solution has an ionic strength of I = 3 × 0.5 M = 1.5 M....Activity & Ionic Strength.surface waterI = 0.001 – 0.005 Mpotable water, groundwaterI = 0.001 – 0.02 MseawaterI = 0.7 MJan 15, 2021
How do you determine the strength of a solution?
Strength of solution = Mass of solute ( g ) Volume of solution ( L )...Strength or concentration:The strength of the solution is defined as the amount of solute in gram dissolved per liter of the solution.It represents the strength or concentration of the solution.It expresses in grams per liter.More items...
Does ionic strength increase solubility?
The basic principle illustrated is that in the absence of a com- mon ion, the solubility of an electrolyte increases as ionic strength increases.
What is low ionic strength solution?
Acronym for “Low Ionic Strength Saline.” LISS is used in blood bank testing to potentiate reactions between antibodies and red blood cells. Under normal testing conditions, red blood cells have a negative surface charge, and sodium ions (Na+) in saline solutions aggregate around the red cell surface.
How does ionic strength affect the rate of reaction?
The reaction rate increases continuously as the ionic strength increases with alpha-chymotrypsin. With trypsin, the rate increases at low ionic strengths but as the ionic strength further increases a gradual inhibitory effect is observed.
How does ionic strength affect pH?
On increasing the ionic strength it is observed that the pH optimum moves towards lower pH values when z = - 1 or z = 0, remains the same if z = + 1 and shifts to a higher pH for z = +2.
What factors contribute to greater ionic strength?
The strength of the ionic bond is directly dependent upon the quantity of the charges and inversely dependent on the distance between the charged particles. A cation with a 2+ charge will make a stronger ionic bond than a cation with a 1+ charge.
Does salt increase ionic strength?
Adding salt increases the ionic strength, lowering the chemical activity of the binding partners so that it's like there's less of them, so there's less binding. We can also tie chemical activity into solubility and the salting-in/salting-out curve.
What is the unit of ionic strength?
mol kg 1Accord- ing to this definition, ionic strength has units of mol kg 1. Many textbooks (e.g. 2–4) use this definition. where ci is the ionic concentration in units of molarity (mol L 1 or mol dm 3).
How do you calculate the molarity of an ion?
As mass / volume = molarity * molar mass , then mass / (volume * molar mass) = molarity . Substitute the known values to calculate the molarity: molarity = 5 / (1.2 * 36.46) = 0.114 mol/l = 0.114 M . You can also use this molarity calculator to find the mass concentration or molar mass.
How do you find the ionic strength of 0.2 M na2hpo4?
This is Expert Verified Answer Ionic strength of the solution is known as the function of all Ion present in solution. Hence Ionic strength = 0.6 M.
What is the ionic strength of a solution containing 0.15 M NaCl and 0.25 m CaCl2?
Question: What is the ionic strength of a solution containing 0.15 M NaCl and 0.25 M CaCl2? The answer is 0.775 M BUT what are the steps to obtain that answer?
What is the ionic strength of a solution?
The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution. Ionic compounds, when dissolved in water, dissociate into ions. The total electrolyte concentration in solution will affect important properties such as the dissociation constant or the solubility of different salts. One of the main characteristics of a solution with dissolved ions is the ionic strength. Ionic strength can be molar (mol/L solution) or molal (mol/kg solvent) and to avoid confusion the units should be stated explicitly. The concept of ionic strength was first introduced by Lewis and Randall in 1921 while describing the activity coefficients of strong electrolytes.
What is ionic strength?
Ionic strength can be molar (mol/L solution) or molal (mol/kg solvent) and to avoid confusion the units should be stated explicitly. The concept of ionic strength was first introduced by Lewis and Randall in 1921 while describing the activity coefficients of strong electrolytes.
What is the molar ionic strength of an ion?
The molar ionic strength, I, of a solution is a function of the concentration of all ions present in that solution. where one half is because we are including both cations and anions, ci is the molar concentration of ion i (M, mol/L), zi is the charge number of that ion, and the sum is taken over all ions in the solution.
What is the role of ionic strength in Debye-Hückel theory?
The ionic strength plays a central role in the Debye–Hückel theory that describes the strong deviations from ideality typically encountered in ionic solutions. It is also important for the theory of double layer and related electrokinetic phenomena and electroacoustic phenomena in colloids and other heterogeneous systems.
Why is ionic strength used in stability constant determination?
Media of high ionic strength are used in stability constant determination in order to minimize changes, during a titration, in the activity quotient of solutes at lower concentrations.
Which ions contribute to the ionic strength?
Generally multivalent ions contribute strongly to the ionic strength.
Is sodium chloride ionic or ionic?
For a 1:1 electrolyte such as sodium chloride, where each ion is singly-charged, the ionic strength is equal to the concentration. For the electrolyte MgSO 4, however, each ion is doubly-charged, leading to an ionic strength that is four times higher than an equivalent concentration of sodium chloride: Generally multivalent ions contribute strongly ...
How to find ionic strength?
Use this formula to calculate ionic strength: I= 1/2 n∑i (CiZi )squared, where "I" represents ionic strength, "n" represents the number of ions in solution, "i" represents the specific ion in solution, "Ci" represents the concentration to the /th species, such as moles per liter, "Zi" represents the valence or oxidation number of the /th species and "∑" represents the summation of concentrations and valences of all ions. Remember positive and negative ions cannot separate, which needs to be considered as a factor in the equation.
Why is ionic strength important?
Knowing ionic strength is important to chemists because ions have an electrical charge that attract or repel each other. This attraction and repulsion causes ions to behave in certain ways. Basically ionic strength represents interactions between the ions in water and the ions of a solution.
What equations use input concentrations and valences?
Input concentrations and valences into the Debye and Huckel equation.
What is ionic strength?
Ionic strength is a function of concentration and charge of all ions in a given solution (see Equation 1). Direct measurement of ionic strength is seldom used in ecological studies. Causal assessors are more likely to have access to measures which generally correlate with ionic strength.
How does ionic strength affect surface water?
The ionic strength of surface waters is influenced by numerous human activities, in both waterbodies and their associated watersheds. The more extensive the relevant sources and activities , the more likely increased ionic strength will impair surface waters.
What are the measurements of electrical conductivity, salinity, and total dissolved solids?
Measurements of electrical conductivity, salinity and total dissolved solids (TDS) are often used to represent the ionic strength of water (see Ways to Measure tab). These measurements generally increase with increasing ion content. This module provides advice for deciding whether or not to include increased ionic strength as a candidate cause of biological impairment.
What are some examples of ionic stressors?
For example, bioavailability of toxic metals can vary with ionic strength, and decreases in pH affect total ionic strength and ionic composition.
How do human activities affect ionic strength?
Geologic and natural sources of ions, in combination with human activities (e.g., agricultural, resource extraction and industrial practices), can contribute to changes in the ion content of streams and rivers. Human activities can increase ionic strength either directly (i.e., introducing new ions) or indirectly (i.e., decreasing ion uptake in watershed, increasing ion delivery to freshwater systems).
How does ionic strength affect freshwater biota?
There is debate among scientists as to the exact mechanisms responsible for toxicity associated with ionic strength, but evidence appears to indicate that elevated ionic strength, or large fluctuations in ionic strength over relatively short time periods, may affect freshwater biota via several modes of action including osmotic stress, increased competition for gill binding sites, and increased ion exchange.
When should ionic strength be a candidate cause?
Ionic strength should be a candidate cause when human sources and activities, site observations or biological effects support portions of the source-to-impairment pathways (Figure 2). This diagram and some of the other information also may be useful in Step 3: Evaluate Data from the Case.
What is the ionic strength of a solution?
The ionic strength of a solution is a calculated using the concentration of dissolved substances in a solution along with the valence of the species in question. Ionic strength represents the relative interactions of ions with water molecules and other ions in a solution.
Why is ionic strength important?
Since ionic strength relates to the activity of ions, In order for the results of experiments to be comparable, solutions of comparable ionic strength are used.
What is ionic strength?
What is Meant by the Ionic Strength? The ionic strength of a solution is defined as the measure of ion concentration in the solution. When ionic compounds are dissolved in water, it dissociates into ions. The main characteristic of the solution with the dissolved ions is an ionic strength.
How to Use the Ionic Strength Calculator?
Step 1: Enter the concentration and valency separated by a comma in the respective input field

Overview
The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution. Ionic compounds, when dissolved in water, dissociate into ions. The total electrolyte concentration in solution will affect important properties such as the dissociation constant or the solubility of different salts. One of the main characteristics of a solution with dissolved ions is the ionic strength. Ionic strength can be molar (mol/L solution) or molal (mol/kg solvent) and to avoid confusion the units s…
Quantifying ionic strength
The molar ionic strength, I, of a solution is a function of the concentration of all ions present in that solution.
where one half is because we are including both cations and anions, ci is the molar concentration of ion i (M, mol/L), zi is the charge number of that ion, and the sum is taken over all ions in the solution. For a 1:1 electrolyte such as sodium chloride, where each ion is singly-charged, the ioni…
Non-ideal solutions
Because in non-ideal solutions volumes are no longer strictly additive it is often preferable to work with molality b (mol/kg of H2O) rather than molarity c (mol/L). In that case, molal ionic strength is defined as:
in which
i = ion identification number z = charge of ion
Importance
The ionic strength plays a central role in the Debye–Hückel theory that describes the strong deviations from ideality typically encountered in ionic solutions. It is also important for the theory of double layer and related electrokinetic phenomena and electroacoustic phenomena in colloids and other heterogeneous systems. That is, the Debye length, which is the inverse of the Debye parameter (κ), is inversely proportional to the square root of the ionic strength. Both molar and m…
See also
• Activity (chemistry)
• Activity coefficient
• Bromley equation
• Davies equation
• Debye–Hückel equation
External links
• Ionic strength
• Ionic strength introduction at the EPA web site