
What does isotopic mean?
n. One of two or more atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers. [ iso- + Greek topos, place (so called because the isotopes of a chemical element occupy the same position in the periodic table of elements) .] American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition.
How to write in isotope form?
Using the field equations to create correctly formatted isotopes in Word.Press Ctrl+F9 - Word will insert a pair of curly braces { }Inside the { } type eq ...
How do you write isotopic symbols?
Isotopes are written in two different ways. They can be written using their symbol with the mass number (to the upper left) and atomic number (to the lower left) or the isotope name is written with a dash and the mass number. For example: Two naturally occurring isotopes of chlorine are chlorine-35 & chlorine-37.
What does isotopic signature mean?
An isotopic signature (also isotopic fingerprint) is a ratio of non-radiogenic 'stable isotopes', stable radiogenic isotopes, or unstable radioactive isotopes of particular elements in an investigated material. The ratios of isotopes in a sample material are measured by isotope-ratio mass spectrometry against an isotopic reference material.This process is called isotope analysis
What is an isotope?
An isotope is one of two or more species of atoms of a chemical element with the same atomic number and position in the periodic table and nearly i...
Why do isotopes have different properties?
Differences in the properties of isotopes can be attributed to either of two causes: differences in mass or differences in nuclear structure. Scien...
When are isotopes stable?
Isotopes are said to be stable if, when left alone, they show no perceptible tendency to change spontaneously. A uniform scale of nuclear stability...
How were isotopes discovered?
The existence of isotopes emerged from two independent lines of research, the first being the study of radioactivity. The unambiguous confirmation...
What is the term used to describe isotopes?
The term nuclide is used to describe particular isotopes, notably in cases where the nuclear rather than the chemical properties of an atom are to be emphasized. The lexicon of isotopes includes three other frequently used terms: isotones for isotopes of different elements with the same number of neutrons, isobars for isotopes of different elements with the same mass number, and isomers for isotopes identical in all respects except for the total energy content of the nuclei.
What is an isotope?
An isotope is one of two or more species of atoms of a chemical element with the same atomic number and position in the periodic table and nearly identical chemical behavior but with different atomic masses and physical properties. Every chemical element has one or more isotopes.
How were isotopes discovered?
The existence of isotopes emerged from two independent lines of research, the first being the study of radioactivity. The unambiguous confirmation of isotopes in stable elements not associated directly with either uranium or thorium came with the development of the mass spectrograph.
What are the properties of an isotope?
Many important properties of an isotope depend on its mass. The total number of neutrons and protons ( symbol A ), or mass number, of the nucleus gives approximately the mass measured on the so-called atomic-mass-unit (amu) scale. The numerical difference between the actual measured mass of an isotope and A is called either the mass excess or ...
What are isotones and isobars?
The lexicon of isotopes includes three other frequently used terms: isotones for isotopes of different elements with the same number of neutrons, isobars for isotopes of different elements with the same mass number , and isomers for isotopes identical in all respects except for the total energy content of the nuclei.
What is the atomic number of a bar of uranium?
A bar of pure uranium, for instance, would consist entirely of atoms with atomic number 92 . The periodic table of the elements assigns one place to every atomic number, and each of these places is labeled with the common name of the element, as, for example, calcium, radon, or uranium. YouTube. IAEAvideo.
Do all elements have the same number of neutrons?
Not all the atoms of an element need have the same number of neutrons in their nuclei. In fact, it is precisely the variation in the number of neutrons in the nuclei of atoms that gives rise to isotopes. Hydrogen is a case in point. It has the atomic number 1.
What does the name "isotope" mean?
The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos ( ἴσος "equal") and topos ( τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table.
How are isotopes separated?
Lighter elements such as lithium, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen are commonly separated by gas diffusion of their compounds such as CO and NO. The separation of hydrogen and deuterium is unusual because it is based on chemical rather than physical properties, for example in the Girdler sulfide process. Uranium isotopes have been separated in bulk by gas diffusion, gas centrifugation, laser ionization separation, and (in the Manhattan Project) by a type of production mass spectrometry .
What is the difference between isotopes and nuclides?
A nuclide is a species of an atom with a specific number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, for example carbon-13 with 6 protons and 7 neutrons. The nuclide concept (referring to individual nuclear species) emphasizes nuclear properties over chemical properties, whereas the isotope concept (grouping all atoms of each element) emphasizes chemical over nuclear. The neutron number has large effects on nuclear properties, but its effect on chemical properties is negligible for most elements. Even for the lightest elements, whose ratio of neutron number to atomic number varies the most between isotopes, it usually has only a small effect although it matters in some circumstances (for hydrogen, the lightest element, the isotope effect is large enough to affect biology strongly). The term isotopes (originally also isotopic elements, now sometimes isotopic nuclides) is intended to imply comparison (like synonyms or isomers ). For example, the nuclides 12#N#6C#N#, 13#N#6C#N#, 14#N#6C#N#are isotopes (nuclides with the same atomic number but different mass numbers ), but 40#N#18Ar#N#, 40#N#19K#N#, 40#N#20Ca#N#are isobars (nuclides with the same mass number ). However, isotope is the older term and so is better known than nuclide and is still sometimes used in contexts in which nuclide might be more appropriate, such as nuclear technology and nuclear medicine .
How are isotopes used to determine the concentration of a substance?
Isotopes are commonly used to determine the concentration of various elements or substances using the isotope dilution method , whereby known amounts of isotopically-substituted compounds are mixed with the samples and the isotopic signatures of the resulting mixtures are determined with mass spectrometry.
What is the name of the element that indicates the atomic number?
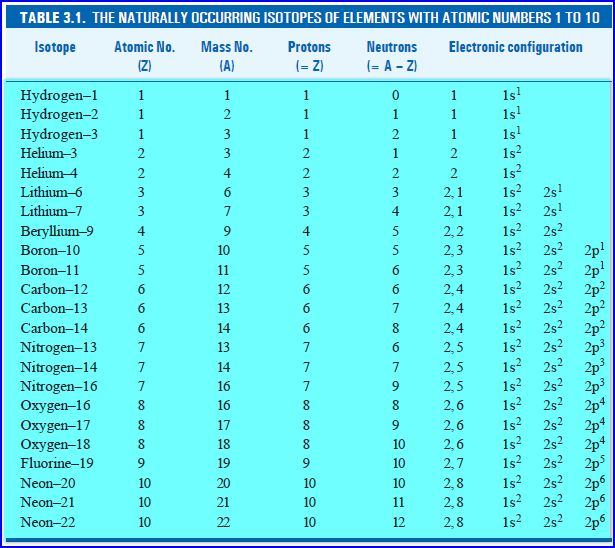
An isotope and/or nuclide is specified by the name of the particular element (this indicates the atomic number) followed by a hyphen and the mass number (e.g. helium-3, helium-4, carbon-12, carbon-14, uranium-235 and uranium-239 ).
What is the atomic number of carbon?
The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means ...
Which isotope has zero neutrons?
From left to right, the isotopes are protium ( 1 H) with zero neutrons, deuterium ( 2 H) with one neutron, and tritium ( 3 H) with two neutrons. Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element ), ...
How to write isotopes?
Isotopes are primarily represented in two different ways: 1 By writing the name of the element followed by a hyphen and the mass number of the isotope. For example, uranium-235 and uranium-239 are two different isotopes of the element uranium. 2 By following the AZE notation (also known as the standard notation). This involves writing the symbol of an element and prefixing the atomic number in subscript and the mass number in superscript. For example, the uranium-235 isotope can be represented as 23592 U and the uranium-239 isotope can be represented as 23992 U.
What is the term for a stable isotope?
Some isotopes are known to have extremely long half-lives (in the order of hundreds of millions of years). Such isotopes are commonly referred to as stable nuclides or stable isotopes. Common examples of stable nuclides include carbon-12, carbon-13, oxygen-16, oxygen-17, and oxygen-18.
What are isotopes of carbon?
In other words, isotopes are variants of elements that differ in their nucleon numbers due to a difference in the total number of neutrons in their respective nuclei. For example, carbon-14, carbon-13, and carbon-12 are all isotopes of carbon.
How are isotopes used in chemistry?
An important application of isotopes is in the determination of the isotopic signature of element samples via isotope analysis. This is generally done via the process of isotope ratio mass spectrometry.
What are some examples of radioactive isotopes?
Examples of radioactive isotopes include carbon-14, tritium (hydrogen-3), chlorine-36, uranium-235, and uranium-238.
How many neutrons are in carbon-14?
Carbon-14 contains a total of 8 neutrons, carbon-13 contains a total of 7 neutrons, and carbon-12 contains a total of 6 neutrons. Isotopes are primarily represented in two different ways: By writing the name of the element followed by a hyphen and the mass number of the isotope. For example, uranium-235 and uranium-239 are two different isotopes ...
How many isotopes are in the primordial nuclide?
Primordial nuclides are the nuclides that have existed since the formation of the solar system. Of the 339 naturally occurring isotopes on Earth, a total of 286 isotopes are known to be primordial isotopes.
How are cosmogenic isotopes formed?
Cosmogenic isotopes are formed when the atmosphere reacts with the rays emitted from stars or when geological materials on the Earth's surface are irradiated by cosmic rays directly. Carbon-14, chlorine-36 and hydrogen-3, also known as tritium, are all cosmogenic isotopes.
What are anthropogenic isotopes?
Anthropogenic isotopes are man-made or result from human activities, such as testing weapons and processing nuclear fuels. These isotopes are useful in the fields of oceanography and hydrology since they can be used to study flow, currents and sedimentation rates. Anthropogenic isotopes include some cosmogenic isotopes, such as carbon-14, chlorine-36 and hydrogen-3, as well as krypton-85.
How to determine the number of neutrons in an element?
The number of neutrons can be determined by taking the difference between the atomic mass and the atomic number. The atomic masses of the elements that are reflected in the periodic table are calculated from averages of the different isotopes and their abundance.
What is the difference between isotopes and neutrons?
Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but that have a different number of neutro ns. Since the atomic number is equal to the number of protons and the atomic mass is the sum of protons and neutrons, we can also say that isotopes are elements with the same atomic number but different mass numbers. Let us take a look at an example.
How to find neutrons in hydrogen?
The number of neutrons can be calculated by calculating the difference between the atomic mass and atomic number.
Why are radioactive isotopes useful?
They are typically useful when performing experiments in the environment and in the field of geochemistry. These isotopes can help determine the chemical composition and age of minerals and other geologic objects.
What are elements made of?
Atoms and elements are made of protons, neutrons and electrons. The nucleus is made of protons and neutrons, and the electrons surround the nucleus, as shown in the illustration below. The sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons is equal to the atomic mass.
Where did the word "isotope" come from?
Isotope Word Origin and History. The term "isotope" was introduced by the British chemist Frederick Soddy in 1913, as recommended by Margaret Todd. The word means "having the same place" from the Greek words isos "equal" (iso-) + topos "place.".
What is the initial isotope of a radioactive reaction?
When radioisotopes undergo radioactive decay, the initial isotope may be different from the resulting isotope. The initial isotope is called the parent isotope, while the atoms produced by the reaction are called daughter isotopes. More than one type of daughter isotope may result.
What is the mass number of an isotope with 6 protons and 6 neutrons?
For example, an isotope with 6 protons and 6 neutrons is carbon-12 or C-12. An isotope with 6 protons and 7 neutrons is carbon-13 or C-16. Note the mass number of two isotopes may be the same, even though they are different elements. For example, you could have carbon-14 and nitrogen-14. The mass number may be given in the upper left side ...
How many isotopes are there in the periodic table?
There are 250 isotopes of the 90 naturally occurring elements and there are over 3,200 radioactive isotopes, some of which are natural and some synthetic. 1 Every element on the periodic table has multiple isotope forms.
What is 131 isotope?
An Introduction to Isotopes. Iodine 131 (I-131) is a radioactive isotope used for hyperthyroidism treatment and is stored in a lead box. Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels.
Which isotope has the most protons?
With the exception of hydrogen, the most abundant isotopes of the natural elements have the same number of protons and neutrons. The most abundant isotope of hydrogen is protium, which has one proton and no neutrons.
Why are isotopes different from each other?
The physical properties of isotopes are different from each other because these properties often depend on mass. This difference may be used to separate isotopes of an element from each other by using fractional distillation and diffusion.
Why is isotope notation important?
Isotope notation, also known as nuclear notation, is important because it allows us to use a visual symbol to easily determine an isotope's mass number, atomic number, and to determine the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus without having to use a lot of words. Additionally, N = A −Z. Example 1: What is the isotopic notation for ...
What is the difference between isotopes and neutrons?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons in their atomic nuclei. All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons, which is the atomic number of that element. However, because different isotopes have different numbers of neutrons, they can differ in mass number, which is the sum ...
What are atoms that have the same protons?
OR... Isotopes are atoms that have the same proton no. but different nucleon no. The chemical properties of an element is determined by its electronic configuration, which is then determined by the no. of protons it has. Since isotopes have the same no of protons at its nucleus, they have the same chemical properties.
How many neutrons are in carbon-14?
The chemical symbol for carbon is C. Now write the isotopic notation for carbon-14. We can determine the number of neutrons as 14 −6 = 8 neutrons. Example 2.
Do isotopes have the same number of protons?
Since isotopes have the same no of protons at its nucleus, they have the same chemical properties. However the fact that they have different no. of neutrons means that the isotopes will have different physical properties (e.g. density, mass).
Overview
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have almost the same chemical properties, they have differ…
Isotope vs. nuclide
A nuclide is a species of an atom with a specific number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, for example carbon-13 with 6 protons and 7 neutrons. The nuclide concept (referring to individual nuclear species) emphasizes nuclear properties over chemical properties, whereas the isotope concept (grouping all atoms of each element) emphasizes chemical over nuclear. The neutron number has large effects on nuclear properties, but its effect on chemical properties is negligibl…
Notation
An isotope and/or nuclide is specified by the name of the particular element (this indicates the atomic number) followed by a hyphen and the mass number (e.g. helium-3, helium-4, carbon-12, carbon-14, uranium-235 and uranium-239). When a chemical symbol is used, e.g. "C" for carbon, standard notation (now known as "AZE notation" because A is the mass number, Z the atomic number, and E for element) is to indicate the mass number (number of nucleons) with a superscript at …
Radioactive, primordial, and stable isotopes
Some isotopes/nuclides are radioactive, and are therefore referred to as radioisotopes or radionuclides, whereas others have never been observed to decay radioactively and are referred to as stable isotopes or stable nuclides. For example, C is a radioactive form of carbon, whereas C and C are stable isotopes. There are about 339 naturally occurring nuclides on Earth, of which 286 are primordial nuclides, meaning that they have existed since the Solar System's formation.
History
The existence of isotopes was first suggested in 1913 by the radiochemist Frederick Soddy, based on studies of radioactive decay chains that indicated about 40 different species referred to as radioelements (i.e. radioactive elements) between uranium and lead, although the periodic table only allowed for 11 elements between lead and uranium inclusive.
Several attempts to separate these new radioelements chemically had failed. For example, Sod…
Variation in properties between isotopes
A neutral atom has the same number of electrons as protons. Thus different isotopes of a given element all have the same number of electrons and share a similar electronic structure. Because the chemical behavior of an atom is largely determined by its electronic structure, different isotopes exhibit nearly identical chemical behavior.
Occurrence in nature
Elements are composed either of one nuclide (mononuclidic elements), or of more than one naturally occurring isotopes. The unstable (radioactive) isotopes are either primordial or postprimordial. Primordial isotopes were a product of stellar nucleosynthesis or another type of nucleosynthesis such as cosmic ray spallation, and have persisted down to the present because their rate of decay is so slow (e.g. uranium-238 and potassium-40). Post-primordial isotopes wer…
Atomic mass of isotopes
The atomic mass (mr) of an isotope (nuclide) is determined mainly by its mass number (i.e. number of nucleons in its nucleus). Small corrections are due to the binding energy of the nucleus (see mass defect), the slight difference in mass between proton and neutron, and the mass of the electrons associated with the atom, the latter because the electron:nucleon ratio differs among isotopes.
The mass number is a dimensionless quantity. The atomic mass, on the other hand, is measure…
What Are isotopes?
- Isotopes can be defined as the variants of chemical elements that possess the same number of protons and electrons, but a different number of neutrons. In other words, isotopes are variants of elements that differ in their nucleon ( The total number of protons and neutrons) numbers due to a difference in the total number of neutronsin their respect...
Table of Contents
Stable Isotopes, Primordial Isotopes, and Radioactive Isotopes
- Some isotopes have unstable atomic nuclei that undergo radioactive decay. These isotopes are radioactive in nature and are, therefore, known as radioisotopes (or radionuclides). Examples of radioac...
- Some isotopes are known to have extremely long half-lives (in the order of hundreds of millions of years). Such isotopes are commonly referred to as stable nuclides or stable isotopes. Com…
- Some isotopes have unstable atomic nuclei that undergo radioactive decay. These isotopes are radioactive in nature and are, therefore, known as radioisotopes (or radionuclides). Examples of radioac...
- Some isotopes are known to have extremely long half-lives (in the order of hundreds of millions of years). Such isotopes are commonly referred to as stable nuclides or stable isotopes. Common examp...
- Primordial nuclides are the nuclides that have existed since the formation of the solar system. Of the 339 naturally occurring isotopes on Earth, a total of 286 isotopes are known to be primordial...
Comparison Between Isotopes and Isobars
- An isotope is a variation of an element that possesses the same atomic number but a different mass number. A group of isotopes of any element will always have the same number of protons and electrons. They will differ in the number of neutrons held by their respective nuclei. An example of a group of isotopes is hydrogen-1 (protium), hydrogen-2 (deuterium), and hydrogen-…