
What are the bones used to move the knee?
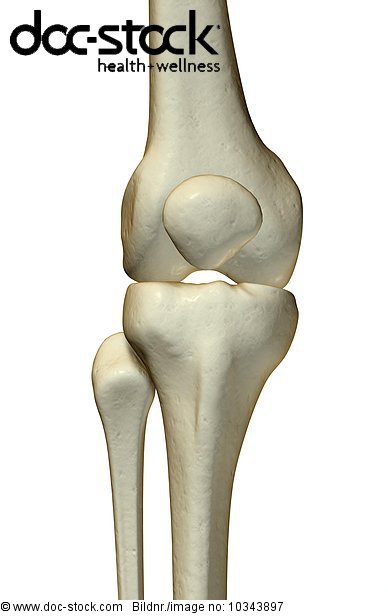
- Femur (thigh bone) – the longest bone in the body; The round knobs at the end of the bone (near the knee) are called condyles. ...
- Tibia (shin bone) – runs from the knee to the ankle. ...
- Patella (kneecap) – a semi-flat, triangular bone that is able to move as the knee bends. ...
Which bone is also known as the knee cap?
What are the names of the 4 bones in the leg including the knee cap?
- Femur – the bone in the thigh.
- Patella – the knee cap.
- Tibia – the shin bone, the larger of the two leg bones located below the knee cap.
- Fibula – the smaller of the two leg bones located below the knee cap.
How many bones are in the knee?
Various nerves and blood vessels supply the muscles and bones of the knee. There are four bones around the knee: the thigh bone (femur), the shin bone (tibia), knee cap (patella), and the fibula (see image to the left): Femur (thigh bone) – the longest bone in the body; The round knobs at the end of the bone (near the knee) are called condyles.
What bones form the knee joint?
The knee consists of three bones:
- femur – the upper leg bone, or thigh bone
- tibia – the bone at the front of the lower leg, or shin bone
- patella – the thick, triangular bone that sits over the other bones at the front of the knee, or kneecap.

What is the bone at the center of the knee called?
Commonly referred to as the kneecap, this nearly heart-shaped bone at the center of the knee helps extend the knee and protect the joint from impact. A tendon at the top of the patella and a ligament at the bottom hold the bone in place. As the knee bends, the patella slides along a groove in the femur.
What bone connects the tibia and femur?
This long, straight bone connects with the knee and the ankle. Fractures to this bone require less force than those that cause fractures to the femur. Falls from great heights, sporting injuries, or car accidents can cause them. The knee joint is where the tibia and femur meet.
What are the two ligaments that hold bones together?
Two of the ligaments between the femur and tibia, the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), create a cross and provide stability to the joint.
What is the second largest bone in the leg?
The second largest bone in the leg — and the human body — is the tibia , also called the shinbone. This long, straight bone connects with the knee and the ankle.
What happens when the knee bends?
As the knee bends, the patella slides along a groove in the femur. Sometimes, due to numerous complications, the kneecap comes out of its groove and becomes dislocated, an injury known as patellar subluxation. Fibrous bands called ligaments hold these bones together.
What is the longest bone in the human body?
The femur, or th ighbone, is the longest and largest bone in the human body. It is the only bone in the upper leg. The head of the femur creates the ball-and-socket joint of the hip, and the lower portion creates the upper portion of the knee. The bone’s shape resembles a walking stick.
What are the elements that protect the bones and keep the knee joint moving fluidly?
Surrounding the connection of the bones, various elements such as bursa (fluid-filled sacs), fat pads, and cartilage pads (strong, flexible tissue called menisci), protect the bones and keep the knee joint moving fluidly .
What is the function of the knee?
The knee is designed to fulfill a number of functions: support the body in an upright position without the need for muscles to work. helps to lower and raise the body. provides stability. acts as a shock absorber. allows twisting of the leg. makes walking more efficient. helps propel the body forward.
What are the menisci of the knee?
The knee has two menisci: 1 medial – on the inner side of the knee, this is largest of the two 2 lateral – on the outer side of the knee
Why do you need knee guards?
Use knee guards in sports where knees could get injured. Maintaining strong, flexible leg muscles and seeking prompt medical attention for all knee injuries is essential to assure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of the injury.
What ligament prevents the femur from sliding backwards?
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) – prevents the femur from sliding backward on the tibia, and the tibia from sliding forward on the femur.
How long does it take to heal a knee injury?
It is also important to begin strengthening and stretching exercises 24-48 hours after minor injuries, or as advised by a doctor. There should be a gradual return to normal activities.
What is the most commonly injured joint in adolescents?
Injury prevention. The knee is a complex structure and one of the most stressed joints in the body. It is the largest joint, vital for movement, and vulnerable to injury. The knee is the most commonly injured joint by adolescent athletes with an estimated 2.5 million. Trusted Source.
How many types of cartilage are there in the knee?
There are two types of cartilage in the knee:
What is the knee?
The knee is a complex joint that flexes, extends, and twists slightly from side to side.
What are the two connective tissues that connect the major muscles of the knee?
Another common sporting injury is pulling or straining the hamstring tendons , two groups of string-like connective tissues at the back of the knee and thigh that connect some of the major muscles of the knee.
Why does my knee hurt so bad?
Knee problems and knee pain are common as the knee is a frequent point of contact during traumatic accidents and is as prone to wear and tear due to its weight-bearing nature . It is also a common site for arthritis pain. Other knee problems include: Fractured kneecap. Torn meniscus.
Where is the kneecap held in place?
The kneecap slides along a groove in the femur as the knee bends. It is held in place by a ligament at the bottom and a tendon on top. Those connect to the femur and tibia. Sometimes, due to numerous complications, the kneecap comes out of its groove and becomes dislocated.
Which bone is not directly affected by hinge joint action?
The fibula (calf bone), the other bone in the lower leg, is connected to the joint but is not directly affected by the hinge joint action. Another bone, the patella (kneecap), is at the center of the knee. Two concave pads of cartilage (strong, flexible tissue) called menisci minimize the friction created at the meeting of the ends ...
What are the two concave pads of cartilage called?
Two concave pads of cartilage (strong, flexible tissue) called menisci minimize the friction created at the meeting of the ends of the tibia and femur. There are also several key ligaments, a type of fibrous connective tissue, that connect these bones. The four key ligaments of the knee are: Damage to the ACL, such as a tear, is a common knee ...
Which bone is located next to the tibia?
The femur (thigh bone) The patella (kneecap) A fourth bone, the fibula, is located just next to the tibia and knee joint, and can play an important role in some knee conditions. The tibia, femur, and patella, all are covered with a smooth layer of cartilage where they contact each other at the knee joint.
Which ligament is on the inner side of the knee?
One ligament is on each side of the knee joint—the medial collateral ligament on the inner side, and the lateral collateral ligament on the outer side. Ligament injuries typically result in complaints of the instability of the knee joint. Guide to Understanding Your Knee Ligaments.
What are the four major ligaments that surround the knee joint?
Two of these ligaments are in the center of the joint, and they cross each other. These are called the cruciate ligaments and consist of the anterior cruciate ligament and the posterior cruciate ligament.
How many types of cartilage are there in the knee?
There are two types of the cartilage of the knee joint:
What is the bursa in front of the kneecap?
The bursa in front of the kneecap is prone to swelling, especially when people injure their knee or perform activities that involve kneeling on hard surfaces. Inflammation of the bursa, called prepatellar bursitis, is common in people who do flooring work or cleaning work and have to spend a lot of time kneeling. 4 .
What is the bursa in the knee?
Joint Bursa. A bursa is a structure in your body that is placed between two moving parts. In your knee, there is a prominent bursa just in front of your knee and underneath the skin. The bursa functions as a means to allow for smooth movement between these two structures (skin and the bone).
What is the synovium?
Joint Capsule and Lining. The synovium is the lining of the joint space. The synovium is a layer of tissue that defines the joint space. The synovial cells produce a slippery, viscous fluid called synovial fluid within the joint.
What are the bones of the foot called?
These make up the ankle and upper portion of the foot. The seven tarsal bones are: Calcaneus: The largest bone of the foot, it is commonly referred to as the heel of the foot. Talus: This bone creates the lower portion of the ankle joint.
Which bone is the second largest?
The second largest bone in body is the tibia, also called the shinbone. This long bone connects with the knee at one end and the ankle at the other. Next to the tibia is the fibula, the thinner, weaker bone of the lower leg.
What are the 3 bones of the big toe?
The three toe bones include the distal phalanges at the tip, middle phalanges, and proximal phalanges closest to the metatarsals . The big toes don’t have middle phalanges. Last medically reviewed on March 30, 2015.
What is the calf bone?
It is also known as the calf bone, as it sits slightly behind the tibia on the outside of the leg. The fibula is connected via ligaments to the two ends of the tibia. The patella, commonly known as the kneecap, is at the center of the knee. It aids in knee extension and protects the joint.
What is the second largest bone in the human body?
Bones. The femur, or thighbone, is the longest and largest bone in the human body. At its top, it helps create the ball-and-socket joint of the hip; its lower end helps create the knee joint. The second largest bone in body is the tibia, also called the shinbone.
Where is the cuboid bone located?
Cuboid: This multisurface bone sits on the outside of the foot near the fifth phalange (little toe). Cuneiforms: These three small bones are closest to the five metatarsal bones. They sit in a row beginning at the inside of the foot and end at the cuboid.
How many metatarsal bones are there in the foot?
The five metatarsal bones in each foot create the body of the foot. Numbered one through five, the bone that sits behind the big toe is No. 1 and the one behind the little toe is No. 5.
What is the cartilage on the knee called?
Your knee contains a c-shaped pad of cartilage called the meniscus which cushions your femur (thigh bone) and your tibia (shin bone). Any wear or tear damage on that area makes that cushion degenerate and become less effective.
Why does my knee hurt?
Your knee contains a c-shaped pad of cartilage called the meniscus which cushions your femur (thigh bone) and your tibia (shin bone). Any wear or tear damage on that area makes that cushion degenerate and become less effective. For many patients with bone on bone knee pain, the cause is from overuse or overworked muscles that become shortened and imbalanced over time. This results in the compression of the thigh bone and shin bone which will eventually wear down the meniscus. The overly compressed knee joint will cause chronic pain and also prevent patients from moving their knees in a normal range of motion (bending and extending).
What does bone on bone pain feel like?
Patients who suffer from bone on bone pain tend to feel aching, stiffness, soreness, or pain in the knee which prevents them from moving or bending the knee comfortably. After an extended period of time living with this pain, patients will seek out any kind of solution that will help get their lives back on track.
What happens if you compress your knee?
This results in the compression of the thigh bone and shin bone which will eventually wear down the meniscus. The overly compressed knee joint will cause chronic pain and also prevent patients from moving their knees in a normal range of motion (bending and extending).
Can stem cell therapy help knee pain?
Rather than undergoing dangerous and invasive surgeries with long recovery times and copious amounts of prescription pain pills, patients have started choosing stem cell therapy as a non-surgical solution to stop their knee pain once and for all.
What is the purpose of the meniscus in the knee?
The job of the meniscus is to cushion the knee joint and transfer forces between the tibia and femur, the thigh and shin bones.
Why is the knee joint thick?
The reason that the knee needs this extra thick layer is to protect it from the huge forces that go through the joint as we move.
How Can I Look After My Knees?
The best way to do this is by doing knee strengthening exercises.
How to tell if a knee is torn?
One of the most common signs of a knee meniscal tear is locking - where the knee gets stuck. This happens which a flap of torn knee meniscus gets stuck in the joint block movement. By wiggling your leg around, you can usually move the torn flap of meniscus out of the way, but the problem will keep occurring. If this is the case, arthroscopic surgery will be advised to trim the damaged flap of knee meniscus.
How to tell if meniscus is broken?
One of the most common signs of a meniscal tear is locking - where the knee gets stuck.
How does a femur help the tibia?
1) Helps the tibia and femur to fit better to each other (increases surface area contact by 40-60%), making the joint more stable. 2) Provides a smooth surface between the femur and tibia, preventing bone rubbing on bone. 3) Helps ensure correct weight distribution between the tibia and femur. 4) Act as shock absorbers/cushions reducing ...
Why do menisci tear?
when playing sports or during a fall. This tends to tear part of the cartilage and can cause bleeding in the joint resulting in swelling. As we age, our cartilage becomes more brittle and can start to wear away. This also makes them more prone to injury.
Mechanism
Types
- There are two types of cartilage of the knee joint. Articular cartilage is the smooth lining that covers the end of the bone. When the smooth articular cartilage is worn away, knee arthritis is the result. Cartilage is a resilient structure that resists damage, but when injured it has a difficult time healing.
Clinical significance
- The other type of cartilage in the knee joint is called the meniscus. When people talk about 'cartilage tears,' they are usually referring to a meniscus tear. The meniscus is a shock absorber that sits between the end of the thigh bone and the top of the shin bone. One ligament is on each side of the knee joint; the medial collateral ligament on the inner side, and the lateral collateral li…
Function
- Muscles propel the knee joint back and forth. A tendon connects the muscle to the bone. When the muscle contracts, the tendons are pulled, and the bone is moved. The knee joint is most significantly affected by two major muscle groups. The quadriceps muscles provide strength and power with knee extension (straightening) and the hamstrings muscles allow for strength and p…
Pathophysiology
- The synovium is the lining of the joint space. The synovium is a layer of tissue that defines the joint space. The synovial cells produce a slippery, viscous fluid called synovial fluid within the joint. In conditions that cause inflammation of the joint, there can be an abundance of synovial fluid produced, that leads to swelling of the knee joint.
Overview
- A bursa is a structure in your body it is placed between Two moving parts. In your knee, there is a prominent bursa just in front of your knee, and underneath the skin. The bursa functions as a means to allow for smooth movement between these two structures (skin in the bone). There are actually hundreds of bursa spread throughout your body, but if you in particular seemed becaus…