
What is Kolb's model of learning?
Kolb's Learning Styles and Experiential Learning Cycle By Saul McLeod, updated 2017 David Kolb published his learning styles model in 1984 from which he developed his learning style inventory. Kolb's experiential learning theory works on two levels: a four-stage cycle of learning and four separate learning styles.
What is Kolb learning style inventory (KLSI)?
The Kolb Learning Style Inventory version 4.0 (KLSI 4.0) revised in 2011, is the latest revision of the original Learning Style Inventory developed by David A. Kolb. Like its predecessors, the KLSI 4.0 is based on experiential learning theory (Kolb 1984) and is designed to help individuals identify the way they learn from experience.
What is the learning style inventory and learning cycle?
Kolb’s Learning Style Inventory and Kolb’s Learning Cycle are the two key models in current use relating to adult learning and development. Knowing your own and your team’s learning style allows you to grow and develop more effectively, building skills and experience, allowing you to meet your life goals.
What is experiential learning theory by David Kolb?
Kolb’s experiential learning theory builds on the work of Rogers, Jung and Piaget, and was first published in 1984. Kolb’s experiential theory also links with Myers-Briggs Type Indicator and Honey and Mumford Learning Style.
What is the learning style inventory?
Learning style inventories are designed to help respondents determine which learning style they have. These inventories typically take the form of a questionnaire that focuses on how people prefer to learn. Respondents choose the answers that most closely resemble their own preferences.
What does Kolb's learning cycle mean?
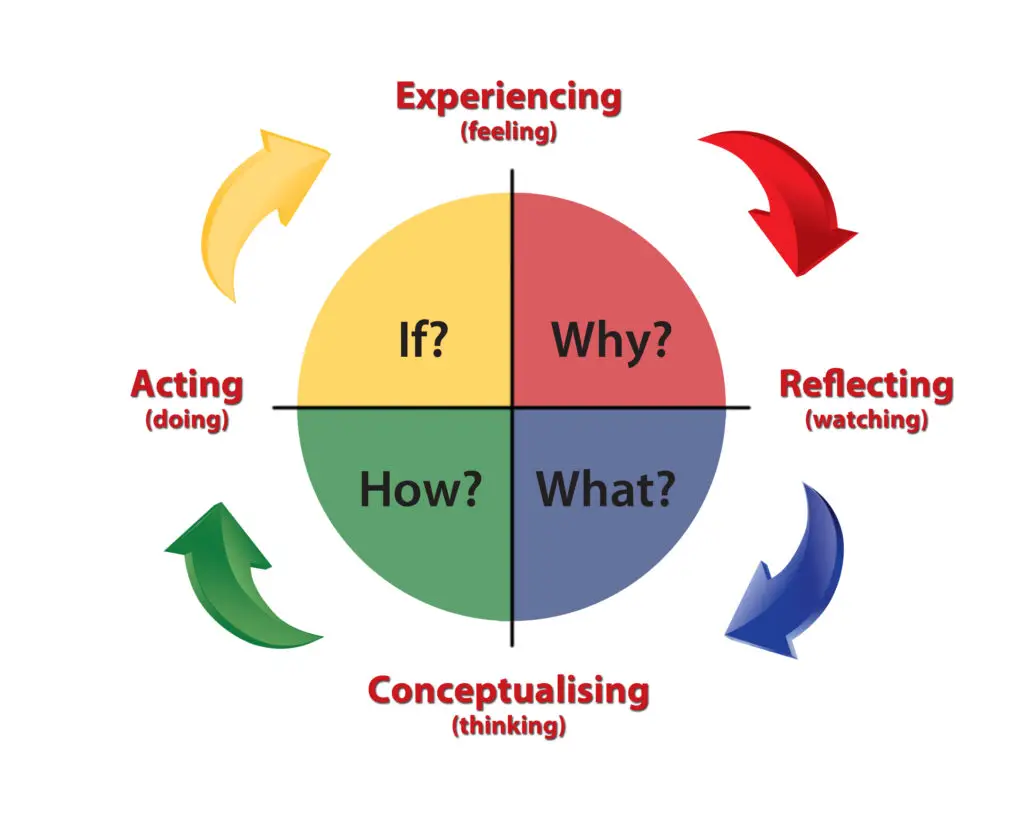
The experiential learning cycle According to Kolb, effective learning can only take place when an individual completes a cycle of the four stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization and active experimentation.
What are the 4 stages of David Kolb's learning cycle?
Toolbox - Kolb's Four Stages of Learning Concrete Experience (CE): feeling. Reflective Observation (RO): watching. Abstract Conceptualization (AC): thinking. Active Experimentation (AE): doing.
Why is Kolb learning cycle important?
The benefits of Kolb's learning cycle include: Each stage of the model is associated with a different preferred learning style. This ensures that all preferred learning styles are used as you step through the model. The model provides a blend of traditional teaching plus hands-on learning.
How do you use Kolb's learning cycle with example?
1:5910:58Kolb's Learning Cycle Explained with Example - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo this step aims to create a concrete. Experience through doing the second step is reflectiveMoreSo this step aims to create a concrete. Experience through doing the second step is reflective observation. And this means taking a step back from the act of doing to look at the bigger picture and
How do you use Kolb's reflective model?
Kolb's Cycle of Reflective Practice1) Concrete Experience. This stage required you to experience something. ... 2) Reflective Observation. This stage required you to think about the experience. ... 3) Abstract Conseptualsim. This stage is all about learning from your experience. ... 4) Active Experiementation.
What is Kolb's reflection model?
Kolb's reflective model is referred to as “experiential learning”. The basis for this model is our own experience, which is then reviewed, analysed and evaluated systematically in three stages. Once this process has been undergone completely, the new experiences will form the starting point for another cycle.
What is Kolb's experiential learning style?
Kolb's experiential learning style theory is typically represented by a four-stage learning cycle in which the learner 'touches all the bases': 1. Concrete Experience - a new experience or situation is encountered, or a reinterpretation of existing experience. 2.
What is Kolb's view of learning?
Kolb (1984) views learning as an integrated process with each stage being mutually supportive of and feeding into the next. It is possible to enter the cycle at any stage and follow it through its logical sequence.
What is Kolb's learning theory?
Kolb's learning theory (1984) sets out four distinct learning styles, which are based on a four-stage learning cycle (see above). Kolb explains that different people naturally prefer a certain single different learning style.
What did Kolb believe?
Kolb believed that we cannot perform both variables on a single axis at the same time (e.g., think and feel). Our learning style is a product of these two choice decisions.
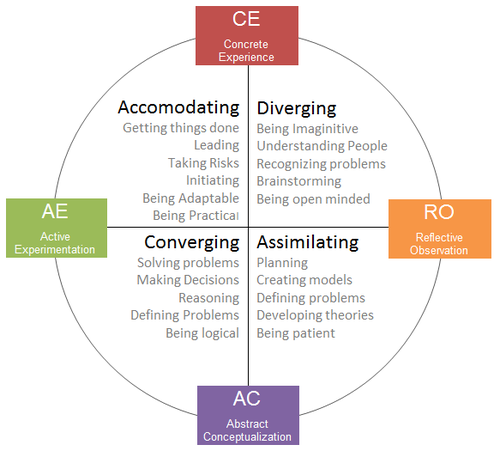
Why is assimilating learning important?
This learning style is important for effectiveness in information and science careers.
Why is Kolb's style called diverging?
Kolb called this style 'diverging' because these people perform better in situations that require ideas-generation, for example, brainstorming. People with a diverging learning style have broad cultural interests and like to gather information.
Why is knowing a person's learning style important?
Knowing a person's (and your own) learning style enables learning to be orientated according to the preferred method.
What is Kolb Learning Style Inventory 3.1?
The KOLB Learning Style Inventory 3.1 is the original version of the leading measure for learning style (available in online and paper format). It helps individuals and teams understand their respective learning styles and to work more effectively as a result. Use the Search function (upper right) to find our other learning tests including optional “The Kolb Team Learning Experience” companion product.
Who developed the learning style inventory?
Based on experiential learning theory, the learning style inventory was developed by David Kolb Ph.D. with research that began in 1971. It identifies four phases in the learning process. Experiencing: learning from experiences, being sensitive to feelings and people.
What is the learning style assessment?
The Learning Style Inventory is a statistically reliable and valid, 12-item assessment tool, developed by David A. Kolb , Ph.D. Based on Experiential Learning Theory, it identifies preferred learning styles, and explores the opportunities different styles present for:
What is a kobl 3.1?
The KOLB Learning Style Inventory 3.1 is one of four versions of the KOLB assessments and is the premiere product for assessing learning style for individuals and teams. Use it for things like teamwork, handling conflict, communication and career choice and to find out why teams do or don’t work well. See the other KOLB tools including the KOLB Team Learning Experience too.
What is the LSI?
The LSI recognizes individual learning preferences, while encouraging individuals to expand and apply their learning strengths. Understanding your own style – and that of other people – can help you tune into the needs of others so that you and your team work more effectively.
What is Kolb's learning style?
Kolb’s Learning Style Inventory and Kolb’s Learning Cycle are the two key models in current use relating to adult learning and development. Knowing your own and your team’s learning style allows you to grow and develop more effectively, building skills and experience, allowing you to meet your life goals.
Why do people have a preferred learning style?
People tend to have a preferred learning style, so will learn more effectively if they have access to learning resources that utilize their preferred learning style. People will tend to be frustrated, affecting their ability to learn, if the only learning opportunities available to them do not allow them to use their preferred learning style. For example, an “Accommodating” learning style need to get their hands on experience quickly, so will rebel against instructions and rules.
Who developed the experiential learning theory?
Kolb’s experiential learning theory builds on the work of Rogers, Jung and Piaget, and was first published in 1984. Kolb’s experiential theory also links with Myers-Briggs Type Indicator and Honey and Mumford Learning Style.
Information
The purpose of our website is only to help students to assist them in finding the best suitable instrument for their research especially in Pakistan where students waste a lot of time in search of the instruments. It is totally free of cost and only for creating awareness and assisting students and researchers for good researches.
Help Us Improve This Article
Did you find an inaccuracy? We work hard to provide accurate and scientifically reliable information. If you have found an error of any kind, please let us know.
Why are learning style inventories useful?
3 At best, learning style inventories might be a way for students to develop study habits that keep them interested and engaged in the learning process. Students may find it useful to discover their preferences ...
When did learning styles become popular?
This notion that people possess different learning styles first became a popular concept during the 1970s. 1 Since then, learning style theories have had a tremendous impact on the field of education. Teachers often utilize learning style inventories at the outset of a class to discover more about students and to help students better understand ...
What is the learning style of Fleming?
In Fleming's VARK learning style model, learners are identified as one of four different types: visual, auditory, reading/writing and kinesthetic. In 1992, he published a questionnaire based on his model that was designed to help people learn more about their individual style. 5 The model and questionnaire quickly became very popular among students and educators, and both remain widely used today.
What is the Lsi assessment?
4 The assessment allows students to discover their learning style and also provides information on how educators can use this information to best serve students as well as possible strategies for accommodating different learning styles.
Who is the model for an intelligent and adaptive tutor used on web by Jackson's Learning Styles Profiler and Expert?
Ghadirli HM, Rastgarpour M. Model for an intelligent and adaptive tutor used on web by Jackson's Learning Styles Profiler and Expert Systems. Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists. 2012;1.
Can people be classified based on their learning style?
Many theories exist suggesting that people can be classified based on their predominant learning 'style.'. Most of these ideas propose that all people learn differently and that designing instruction based on these learning styles can enhance the educational process. This notion that people possess different learning styles first became ...
Is learning style inventory good?
Learning style inventories remain a popular classroom tool despite the fact that research has found little evidence that matching a student's learning preferences to instructional methods produces better educational outcomes. A number of studies have found that students taught according to their identified learning style do no better than students who are not matched to their style. 2
What is the Kolb Learning Style Inventory?
The Kolb Learning Style Inventory version 4.0 (KLSI 4.0) revised in 2011, is the latest revision of the original Learning Style Inventory developed by David A. Kolb. Like its predecessors, the KLSI 4.0 is based on experiential learning theory (Kolb 1984) and is designed to help individuals identify the way they learn from experience. The Kolb Learning Style Inventory 4.0 is the first major revision of the KLSI since 1999 and the third since the original LSI was published in 1971. Based on many years of research involving scholars around the world and data from many thousands of respondents, the KLSI 4.0 includes four major additions-- A new nine learning style typology, assessment of learning flexibility, an expanded personal report focused on improving learning effectiveness, and improved psychometrics. The technical specifications are designed to adhere to the standards for educational and psychological testing developed by the American Educational Research Association, the American Psychological Association, and the National Council on Measurement in Education (1999).
What is learning style?
Reprinted with permission of the author (Zull 2002) Learning style describes the unique ways individuals spiral through the learning cycle based on their preference for the four different learning modes—CE, RO, AC, & AE. Because of one’s genetic makeup, particular life experiences, and the demands of the present environment, a preferred way of choosing among these four learning modes is developed. The conflict between being concrete or abstract and between being active or reflective is resolved in patterned, characteristic ways. Much of the research on ELT has focused on the concept of learning style using the Kolb Learning Style Inventory (KLSI) to assess individual learning styles (Kolb & Kolb 2005b). In the KLSI a person’s learning style is defined by their unique combination of preferences for the four learning modes defining a “kite” shape profile of their relative preference for the four phases of the learning cycle. Because each person's learning style is unique, everyone's kite shape is a little different.
What is ELT learning?
ELT is a dynamic view of learning based on a learning cycle driven by the resolution of the dual dialectics of action/reflection and experience/abstraction. Learning is defined as “the process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience. Knowledge results from the combination of grasping and transforming experience.” (Kolb, 1984, p. 41). Grasping experience refers to the process of taking in information, and transforming experience is how individuals interpret and act on that information. The ELT model portrays two dialectically related modes of grasping experience—Concrete Experience (CE) and Abstract Conceptualization (AC)—and two dialectically related modes of transforming experience—Reflective Observation (RO) and Active Experimentation (AE).
How many learning styles are there in KLSI 4.0?
The nine learning styles of the KLSI 4.0
What is the process of creating knowledge?
6. Learning is the process of creating knowledge. In ELT, knowledge is viewed as the transaction between two forms of knowledge: social knowledge, which is co- constructed in a socio-historical context, and personal knowledge, the subjective experience of the learner. This conceptualization of knowledge stands in contrast to that of the “transmission” model of education in which pre-existing, fixed ideas are transmitted to the learner. ELT proposes a constructivist theory of learning whereby social knowledge is created and recreated in the personal knowledge of the learner.
What is the relationship between learning and the environment?
5. Learning results from synergetic transactions between the person and the environment. In Piaget’s terms, learning occurs through equilibration of the dialectic processes of assimilating new experiences into existing concepts and accommodating existing concepts to new experience. Following Lewin’s famous formula that behavior is a function of the person and the environment, ELT holds that learning is influenced by characteristics of the learner and the learning space.
What is convergent learning?
An individual with a converging style has AC and AE as dominant learning abilities. People with this learning style are best at finding practical uses for ideas and theories. They have the ability to solve problems and make decisions based on finding solutions to questions or problems. Individuals with a Converging learning style prefer to deal with technical tasks and problems rather than with social issues and interpersonal issues. These learning skills are important for effectiveness in specialist and technology careers. In formal learning situations, people with this style prefer to experiment with new ideas, simulations, laboratory assignments, and practical applications.
The Experiential Learning Cycle
Learning Styles
- Learning Styles
Kolb's learning theory (1984) sets out four distinct learning styles, which are based on a four-stage learning cycle (see above). Kolb explains that different people naturally prefer a certain single different learning style. Various factors influence a person's preferred style. For example, social …
Learning Styles Descriptions
- Learning Styles Descriptions
Knowing a person's (and your own) learning style enables learning to be orientated according to the preferred method. That said, everyone responds to and needs the stimulus of all types of learning styles to one extent or another - it's a matter of using emphasis that fits best with the gi…
Educational Implications
- Educational Implications
Both Kolb's (1984) learning stages and cycle could be used by teachers to critically evaluate the learning provision typically available to students, and to develop more appropriate learning opportunities. Educators should ensure that activities are designed and carried out in ways that … - APA Style References
Kolb, D. A. (1976). The Learning Style Inventory: Technical Manual. Boston, MA: McBer. Kolb, D.A. (1981). Learning styles and disciplinary differences, in: A.W. Chickering(Ed.) The Modern American College(pp. 232–255). San Francisco, LA: Jossey-Bass. Kolb, D. A. (1984). Experientia…