How long does a viral infection last?
How many stages of infection are there?
What is the term for an organism that invades the body?
What is stage 2 HIV?
What is the incubation stage?
How long does the prodromal stage last?
What is the decline stage of a disease?
See 4 more
About this website

What are the stages of viral infection?
The viral life cycle can be divided into several major stages: attachment, entry, uncoating, replication, maturation, and release.
How long does a viral infection usually last?
A viral infection usually lasts only a week or two. But when you're feeling rotten, this can seem like a long time! Here are some tips to help ease symptoms and get better faster: Rest.
What are the 4 stages of infection?
Key Points. The first phase is characterized by complete lack or very few symptoms. ... Key Terms. ... Stages of Disease. ... STAGE 1: INCUBATION PERIOD. ... STAGE 2: PRODROMAL PERIOD. ... STAGE 3: ACUTE PERIOD. ... STAGE 4: CONVALESCENCE PERIOD.
What is a serious viral infection?
Viral Infections Viruses cause familiar infectious diseases such as the common cold, flu and warts. They also cause severe illnesses such as HIV/AIDS, Ebola, and COVID-19. Viruses are like hijackers. They invade living, normal cells and use those cells to multiply and produce other viruses like themselves.
How do you beat a viral infection?
How can you care for yourself at home?Get plenty of rest if you feel tired.Take an over-the-counter pain medicine if needed, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), or naproxen (Aleve). ... Be careful when taking over-the-counter cold or influenza (flu) medicines and Tylenol at the same time.More items...
What is the best treatment for viral infection?
Antiviral medications help the body fight off harmful viruses. The drugs can ease symptoms and shorten the length of a viral infection. Antivirals also lower the risk of getting or spreading viruses that cause herpes and HIV.
What is the final stage of the infectious process?
Convalescence. The final stage of infection is known as convalescence. During this stage, symptoms resolve, and a person can return to their normal functions. Depending on the severity of the infection, some people may have permanent damage even after the infection resolves.
What are the 5 stages of infection?
The five stages of infection include the incubation, prodromal, illness, decline, and convalescence periods.
What are the five signs of an infection?
Know the Signs and Symptoms of InfectionFever (this is sometimes the only sign of an infection).Chills and sweats.Change in cough or a new cough.Sore throat or new mouth sore.Shortness of breath.Nasal congestion.Stiff neck.Burning or pain with urination.More items...
Can you spread a viral infection?
Like bacterial infections, many viral infections are also contagious. They can be transmitted from person to person in many of the same ways, including: coming into close contact with a person who has a viral infection. contact with the body fluids of a person with a viral infection.
What are 3 types of viral infections?
Viral infections include: the common cold, which mainly occurs due to rhinovirus, coronavirus, and adenovirus. encephalitis and meningitis, resulting from enteroviruses and the herpes simplex virus (HSV), as well as West Nile Virus. warts and skin infections, for which HPV and HSV are responsible.
What happens if you take antibiotics for a viral infection?
If you take an antibiotic when you have a viral infection, the antibiotic attacks bacteria in your body. These are bacteria that are helpful or are not causing disease. This incorrect treatment can then promote antibiotic-resistant properties in harmless bacteria that can be shared with other bacteria.
How do you tell if an infection is viral or bacterial?
Bacterial infections are caused by bacteria, while viral infections are caused by viruses....Bacterial InfectionsSymptoms persist longer than the expected 10-14 days a virus tends to last.Fever is higher than one might typically expect from a virus.Fever gets worse a few days into the illness rather than improving.
When should I go to the doctor for a viral infection?
“If you are reaching the 10-day mark of a cold and are not feeling any better, you should see your doctor,” says Christine Kirlew, M.D., an internal medicine physician at Piedmont. “Most cold viruses last seven to 10 days, so if it lasts longer than that, it could be a bacterial infection and require antibiotics.”
Can you spread a viral infection?
Like bacterial infections, many viral infections are also contagious. They can be transmitted from person to person in many of the same ways, including: coming into close contact with a person who has a viral infection. contact with the body fluids of a person with a viral infection.
What are examples of viral infection?
A few notable examples that have garnered the attention of the public health community and the population at large include: COVID 19, Ebola, SARS, Influenza, Zika, Yellow fever, Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV / AIDS), Human papillomavirus (HPV), Viral gastroenteritis, Varicella, and Viral hepatitis.
What are the five stages of infectious disease? - Answers
The incubation stage.This is the silent stage because often it is not known when the pathogen gains entry into the host and starts replicating. The length of the incubation period depends on the ...
How Long Does Influenza Viral Infection Last?
There are four subtypes of influenza virus known as Influenza viruses A, B, C and D. The flue is active viral infection observed every winter season in the United States. Infection rapidly spreads in groups, school and during travelling in groups.
How long does a virus last?
Most viral infection last for 3 to 7 days. Viral infection rarely lasts over 7 days. The number of days the viral infection stays in human body depends on following factors-. Rapid Multiplication of Viruses- Viruses triggers formation of duplicate nucleic acid in number of several thousands. Viruses triggers conversion of host protein molecules ...
How Long Does Measles Infection Last?
Infection spreads with contact, cough droplets, sharing towels and toys. Virus can live on dry or wet surface for several hours. Measles can cause death if ignored.
What is the cause of viral infection?
Viral infection is caused by viruses . Viruses are active microscopic protein molecules. Protein molecules are known as nucleic acid. There are several thousand viruses identified in lab that causes infection in human and animals. Long term viral infections are observed in immunocompromised individual. Viral infection can cause serious systemic effects or death if ignored.
How long does interferon stay in the blood?
Presence of higher concentration of interferon helps to restrict viral infection for 3 to 5 days. Antibodies- Most human blood contains antibodies. Antibodies are microscopic protein molecules.
How many types of viruses are there?
There are over 100 varieties of viruses identified. The virus growth is observed over the skin, genitals, mouth and throat mucosal membrane. Symptoms- Genital warts, cluster bumps over skin of groin, penis, scrotum, vulva and vagina. Papillomavirus kind of viral infection lasts for one to two years or several years.
How are viruses formed?
These additional nucleic acid or viruses are formed by using the host protein. Such multiplication creates several thousands of viruses. The spread of infection within the body depends on number of active viruses. The infection prolongs if multiplication of virus continues for several days.
How do viruses leave the body?
Many animal viruses, such as HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), leave the infected cells of the immune system by a process known as budding, where virions leave the cell individually. During the budding process, the cell does not undergo lysis and is not immediately killed. However, the damage to the cells that the virus infects may make it impossible for the cells to function normally, even though the cells remain alive for a period of time. Most productive viral infections follow similar steps in the virus replication cycle: attachment, penetration, uncoating, replication, assembly, and release (Figure 1).
What are the steps of the virus replication cycle?
Most productive viral infections follow similar steps in the virus replication cycle: attachment, penetration, uncoating, replication, assembly, and release (Figure 1). Figure 1.
What are the learning outcomes of viral replication?
Learning Outcomes. List the steps of replication and explain what occurs at each step. A virus must use its host-cell processes to replicate. The viral replication cycle can produce dramatic biochemical and structural changes in the host cell, which may cause cell damage. These changes, called cytopathic effects, ...
What is the reproductive cycle of influenza?
Figure 1. The influenza reproductive cycle. In influenza virus infection, glycoproteins on the capsid attach to a host epithelial cell. Following this, the virus is engulfed. RNA and proteins are then made and assembled into new virions.
How do viruses enter the cell?
Some enveloped viruses enter the cell when the viral envelope fuses directly with the cell membrane. Once inside the cell, the viral capsid degrades, and then the viral nucleic acid is released and becomes available for replication and transcription.
What is the role of mRNA in a viral cell?
The viral mRNA directs the host cell to synthesize viral enzymes and capsid proteins, and assemble new virions. Of course, there are exceptions to this pattern. If a host cell does not provide the enzymes necessary for viral replication, viral genes supply the information to direct synthesis of the missing proteins.
How does a virus attach to a cell?
A virus attaches to a specific receptor site on the host cell membrane through attachment proteins in the capsid or via glycoproteins embedded in the viral envelope. The specificity of this interaction determines the host—and the cells within the host—that can be infected by a particular virus. This can be illustrated by thinking of several keys and several locks, where each key will fit only one specific lock.
How many stages of the viral lifecycle are there?
In order to reproduce and cause infection, the virus goes through seven stages of the viral lifecycle:
What happens to a virus after it enters a cell?
The stages of a virus infection follows the viral lifecycle. After the virus enters a host cell and replicates its genetic material to form a new virus, viral shedding occurs in which the virus is released to infect new host. As the virus continues to replicate, it produces symptoms of an infection in the host.
How do viruses replicate?
Once released from the host cell, the virus is able to find new cells to infect in order to repeat the process of viral replication. As discussed above, some viruses immediately move on to repeat this process in a new host cell, while other viruses remain dormant until the conditions are right for replication. These two distinctions represent the primary difference between productive and nonproductive infection. During productive infection, as with chronic hepatitis, the virus actively replicates itself in the host to produce a variety of symptoms associated with a specific infection. A productive infection, once established in the host, can result in chronic infections. In a chronic infection like hepatitis, the virus goes through periods of activity and dormancy in which the host repeatedly experiences the symptoms associated with the infection, followed by periods of remission.
How do viruses attach to their host cells?
During attachment, the first step in viral replication, the virus binds to the host cell by interacting with the cell membrane of the host . The host cell membrane consists of a phospholipid bilayer from which protein receptors extend. They typically act as receptors for proteins made by the body. Viruses likewise possess capsids or protective envelopes embedded with receptors. In the first stage of viral infection, the virus uses one of these proteins, known as an attachment protein, to initiate the virus infection cycle. Upon binding to the host cell, the viral capsid or envelope meshes with the membrane of the host cell.
What happens after the virion is replicated?
After the genetic material has been replicated, assembly of the new virion occurs. The term virion refers to a fully packaged virus that is capable of causing infection. The genetic material is gathered and a new capsid forms. The process of assembly happens at the same time as maturation, in which the virion is transformed into an infectious particle.
What is nonproductive infection?
By contrast, nonproductive infection represents a process where the virus is present in the host cell, but not actively replicating or causing infection. This constitutes a latent infection that only produces symptoms once the conditions are right for the virus to resume replication. With HIV infection, for example, there is often a significant period of latency before an individual starts to show symptoms of infection. The shingles virus associated with chicken pox also produces a similar period of latency between infection and the actual display of symptoms.
How many types of viruses are there?
There are two broad types of viruses, DNA and RNA viruses. The methods of replication used by a virus differ not only by the viral type, but also according to the host species which it infects. However, there are seven common steps of viral infection that are recognized by scientists:
What are viral infections?
Viral infection is defined as the pathological state in which the human body is attacked by one or more viral agents thatpropagate rapidly within the body.
Where are viral infections common?
Overview of viral infections. Viruses thrive in a wide range of environments and even in extreme climatic conditions. Hence the incidences of viral infections are common in different parts of the world. The inhabitants of the tropics and the subtropics are the potential victims of these infections. In such climatic zones, viral infections often ...
What is the flu associated with?
Flu is typically associated with influenza. It is a viral infection that attacks and damages the respiratory tract, affecting the lungs, throat, and nose. It is usually mediated by the influenza virus (Type A, B or C). Flu is accompanied by fever with intermittent chills, lung congestion, headaches, body-aches and few other obvious symptoms. Flu, like common cold is also seasonal.
Why are viral infections widespread in the tropics?
In the low and middle-income countries, viral infections are widespread due to the presence of a large immunocompromised population. Dietary habits and general lifestyle trends ...
How long does it take for chicken pox to show up?
One should have knowledge of the following signs of chicken pox so that he/she can take precautions in time-. Skin rashes (within 3-4 days), low-grade fever, body pains, headaches, fatigue, loss of appetite and runny nose.
How to boost immunity to a viral infection?
Taking vitamin and probiotic supplements to boost your immunity is also beneficial while treating a viral infection. These natural remedies can help you build a stronger defense against any viral attack.
What is the term for a disease that attacks the immune system?
Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a form of a sexually transmitted disease that attacks and destroys the immune system of the body, destroying the White Blood Cells (WBC) completely.
How long does a viral infection last?
Symptoms can last up to a week for many viral respiratory infections, such as the flu.
How many stages of infection are there?
There are five stages of infection: incubation. prodromal. illness. decline. convalescence. This article will explain each of the five stages of infection in detail, describing how long they can last and giving examples of infections. It will also highlight what the stages of infection are, specifically in people with HIV. 1.
What is the term for an organism that invades the body?
Illness. Decline. Convalescence. In HIV. Summary. Infection occurs when an organism, such as a virus or bacterium, invades the body. The infectious agent rapidly multiplies in the body’s tissues. Although not all infections result in disease, some can trigger the immune system, causing symptoms of illness.
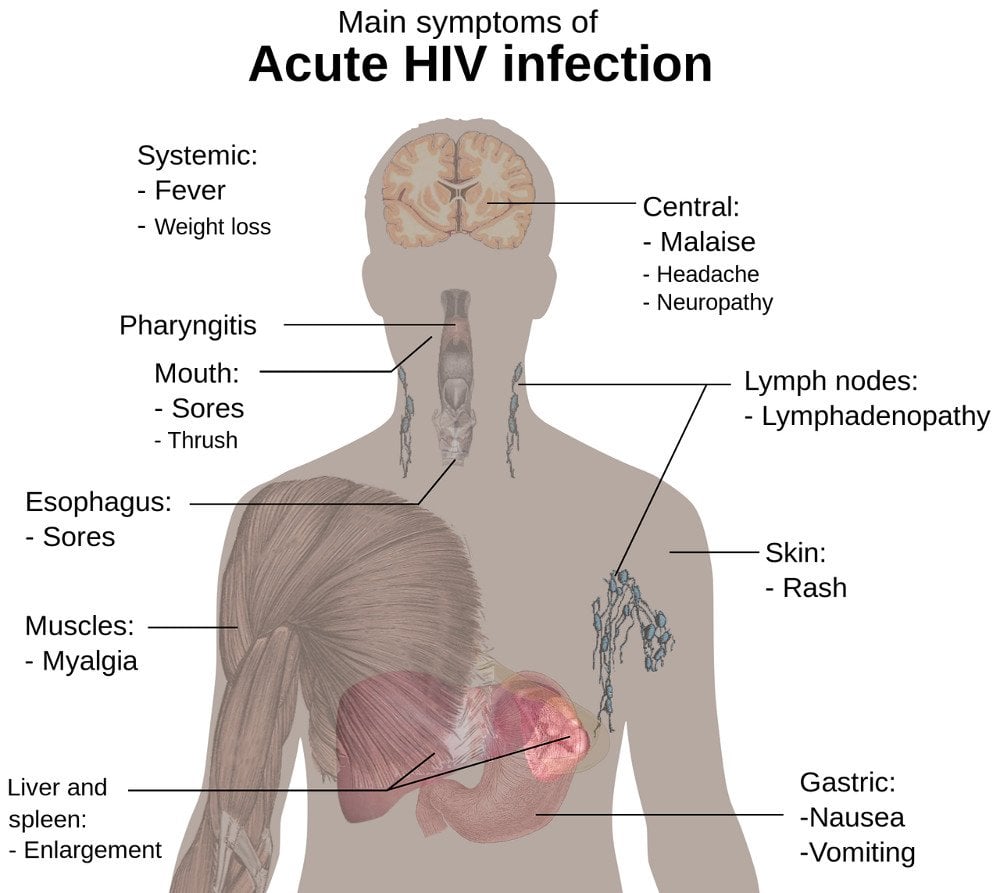
What is stage 2 HIV?
Stage 2: Chronic HIV infection. If left untreated, acute HIV infection progresses to chronic HIV, which can last for decades. In chronic HIV, the virus continues to replicate and destroy CD4 cells. People may not experience symptoms at this stage.
What is the incubation stage?
The incubation stage includes the time from exposure to an infectious agent until the onset of symptoms. Viral or bacterial particles replicate during the incubation stage.
How long does the prodromal stage last?
The duration of the prodromal stage varies depending on the type of infection. For example, the flu has a short incubation period of about 2 days. Trusted Source. . As a result, the prodromal stage may overlap with the incubation stage and the onset of illness. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
What is the decline stage of a disease?
The decline stage occurs when the number of infectious microbes declines and symptoms resolve.
