
When Does Independent Assortment Occur?
What did Gregor Mendel do?
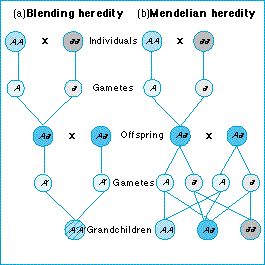
What is the law of independent assemblage?
Why do plants have yellow and round alleles?
How many alleles does each gamete have?
What are the two traits of independent assortment in meiosis?
What does it mean when two rabbits are mixed?
See 4 more
About this website
How does law of Independent Assortment relate to meiosis?
During meiosis, the pairs of homologous chromosome are divided in half to form haploid cells, and this separation, or assortment, of homologous chromosomes is random. This means that all of the maternal chromosomes will not be separated into one cell, while the all paternal chromosomes are separated into another.
What is a law of Independent Assortment?
What is the law of independent assortment? Mendel's law of independent assortment states that the alleles of two (or more) different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another. In other words, the allele a gamete receives for one gene does not influence the allele received for another gene.
What does independent assortment mean in meiosis?
Definition of independent assortment : formation of random combinations of chromosomes in meiosis and of genes on different pairs of homologous chromosomes by the passage according to the laws of probability of one of each diploid pair of homologous chromosomes into each gamete independently of each other pair.
How does the law of Independent Assortment play a role in meiosis what effect does this have on the resulting cells?
It is the specific process of meiosis, resulting in four unique haploid cells, that results in these many combinations. This independent assortment, in which the chromosome inherited from either the father or mother can sort into any gamete, produces the potential for tremendous genetic variation.
What is Independent Assortment quizlet?
independent assortment is the random sorrting of chromosomes, during the making of gametes. it ends up being individual gametes. crossing over. crossing over is chromosomes come together and can become twisted, and they pull apart which causes them to break, rearange then reattach. You just studied 3 terms!
Does Independent Assortment only occur in meiosis?
The physical basis for the law of independent assortment lies in meiosis I of gamete formation, when homologous pairs line up in random orientations at the middle of the cell as they prepare to separate.
How does meiosis lead to segregation and independent assortment quizlet?
During Meiosis, chromosomes line up or assort independently of one another. Therefore , genes located on separate chromosome pairs will also segregate independent of one another.
What is independent and dependent assortment?
1:512:59Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment Explained - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe alleles are often placed in the same gamete. During meiosis the percentage of time they travelMoreThe alleles are often placed in the same gamete. During meiosis the percentage of time they travel to the same gamete. Together is dependent on how close together they are on the chromosome.
What is Independent Assortment vs segregation?
The law of segregation states that every individual possesses two alleles and only one allele is passed on to the offspring. The law of independent assortment states that the inheritance of one pair of genes is independent of inheritance of another pair.
What is an example of independent assortment?
A good example of independent assortment is Mendelian dihybrid cross. The presence of new combinations - round green and wrinkled yellow, suggests that the genes for the shape of the seed and color of the seed are assorted independently.
What is Independent Assortment and when does this process occur?
The Law of Independent Assortment states that during a dihybrid cross (crossing of two pairs of traits), an assortment of each pair of traits is independent of the other. In other words, during gamete formation, one pair of trait segregates from another pair of traits independently.
1. What are the reasons for Independent Assortment?
The reason behind the independent assortment is based on meiosis which is a type of cell division in which one cell divides twice to produce four c...
2. What was the experiment done by Mendel to develop the Law of Independent Assortment?
Mendel established the two fundamental principles from his experiment of performing a di-hybrid cross of two varieties of breeding pea plants of ro...
3. Does an Independent Assortment always occur?
Independent assortment usually occurs spontaneously in cases of reproduction when alleles of two or more genes assort independently into gametes. I...
4. What are the key takeaway points from this topic?
The key points of the law of independent assortment can be listed as follows:Genes usually never influence each other when alleles are sorted into...
5. Explain the Law of Independent Assortment with an example.
It is quite easy to understand the Law of Independent Assortment with an example. Let us consider an example of birds with two visible traits as fo...
6. What is the Basic Rule for the Laws of Inheritance?
According to Mendel, the 3 rules of inheritance include the principles of the law of dominance, the law of segregation, and the law of independent...
7. When Does an Independent Assortment Usually Occur?
Independent assortment is common to sexual reproduction, where 2 gametes fuse to form a diploid embryo (zygote) that comes with the DNA material fr...
8. What will be the Result of an Independent Assortment?
The independent assortment resulting from the meiosis of a homologous pair will have an independent and unique set of characteristic combinations.
9. What is the Ratio for an Independent Assortment?
The phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 will be the classic number for any independent assortment that happens between any di-hybrid genetic pairs.
10. What is Required for an Assortment to Occur Independently?
More than 2 alleles, either different or genetically similar are needed for getting unique chromosomes from the result of an independent assortment...
Explain the law of independent assortment with a suitable example.
A good example of independent assortment is Mendelian dihybrid cross. The presence of new combinations - round green and wrinkled yellow, suggests that the genes for the shape of the seed and color of the seed are assorted independently.
What is the Law of Independent Assortment? - Study.com
What is Independent Assortment? This lesson will discuss this principle, where and when it occurs, and how it influences genetic diversity. It will also show an example using a Punnett square.
What is the phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1?
The phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 will be the classic number for any independent assortment that happens between any di-hybrid genetic pairs.
What is the law of independent assortment?
The law of independent assortment also called Mendel's laws of inheritance, is the foundation for the massive history of human genetics. Developed by Gregor Johann Mendel (1822-1884), he proposed this context based on 2 fundamental principles: Law of dominance. Law of segregation. Law of independent assortment.
How many alleles are needed to get unique chromosomes?
More than 2 alleles, either different or genetically similar are needed for getting unique chromosomes from the result of an independent assortment in the progeny.
What is the process of Mendel's law of independent assortment?
To understand the reason behind Mendel's law of independent assortment, it is essential to learn about the process of ‘Meiosis’ in brief. Meiosis is a biological process, where 1 cell divides 2 times to produce 4 cells called haploids. The 4 resultant cells will possess half its amount of genetic data. These cells are nothing but our sex cells ...
What are the characteristics of pea plants?
The characteristics were noted upon the pea plants’ colour (yellow and green) and shape (round and wrinkled). Following which he had the question of how different genes inherited independently to one another, hence resulting in the formation of the 3 postulates which is the principle of independent assortment.
What is the ratio of F2?
The F2 progeny was labelled in the ratio of 9:3:3:1; the phenotypic ratio of 3:1 was inherited and scattered individually.
What seeds did the F1 runner get?
In the F1 progeny (first generation crossing) he obtained round-yellow seeds ONLY.
What happens if a female and a male become parents?
If the male and the female decide to become parents themselves, the law of independent assortment dictates that their sex cells will carry a random assortment of their genotype for long eyelashes.
What is the genotype of a parent with a recessive allele?
If a parent has a recessive allele, the genotype, or scientific notation of the allele, is dd . If a parent has a dominant allele, the genotype is Dd or DD. Parents with dominant alleles may make more than one Punnett square. Parents then arrange their genotype variants vertically and horizontally, below a graph.
How do Punnett squares work?
Punnett squares combine a knowledge of family genetic history with parent pheno types to produce a matrix of possible offspring phenotypes. To create a Punnett square, parents determine whether they have the dominant allele ( D) or the recessive allele ( d) of a visible trait. If a parent has a recessive allele, the genotype, or scientific notation of the allele, is dd. If a parent has a dominant allele, the genotype is Dd or DD. Parents with dominant alleles may make more than one Punnett square.
How many phenotypes are there in Punnett squares?
While Punnett squares for single- gene traits (like those pictured below) tend to produce only four possible phenotypes, there are traits whose genetic structures are so complex, they produce hundreds of possibilities. Nonetheless, Punnett squares make independent assortment more predictable.
What is the term for the expression of a gene, either dominant or recessive?
Allele – A possible expression of a gene, either dominant or recessive. Recombination – The process that combines the independently-assorted genes from parent sex cells to create the genotype, and inform the eventual phenotype, of offspring. Phenotype – The physical manifestation of a genotype.
What is independent assortment?
Independent assortment is a genetic term that refers to the variation of chromosomes, or genetic information, during sex cell division. This variation allows for genetic differentiation in offspring.
What is the first part of the principle of independent assortment?
The first part of the principle of independent assortment is basically the definition of independent assortment.
What happens to the gametes in meiosis?
The segregation of gametes and the independent assortment of traits occurs in meiosis. As a result, each offspring ends up with the full number of chromosomes containing randomly assorted alleles from each parent.
What is the law of segregation?
The law of segregation states that the parental genes must separate randomly and equally into gametes during meiosis so there is an equal chance of the offspring inheriting either allele. No allele is favored or has an advantage over another.
What is the process of creating sperm and egg gametes?
Meiosis is the process of creating sperm and egg gametes. Each gamete contains half ( haploid) the number of chromosomes an individual needs, so fertilization results in the offspring receiving one allele for a trait from each parent. The law of segregation states that the parental genes must separate randomly and equally into gametes during meiosis so there is an equal chance of the offspring inheriting either allele. No allele is favored or has an advantage over another.
Why are dominant alleles always expressed in the phenotype?
The law of dominance says dominant alleles (a variation of a gene) are always expressed in the phenotype (appearance) of an organism because they mask the effects of recessive alleles. Recessive traits are seen only when the offspring inherit the recessive allele for the trait from both parents.
Which scientist observed segregation in his experiments?
Mendel observed segregation in his experiments when parental pea plants with two traits produced offspring that all expressed the dominant traits, but their offspring expressed dominant and recessive traits in a 3:1 ratio.
When does independent assortment occur?
Like segregation, independent assortment occurs during meiosis, specifically in prophase I when the chromosomes line up in random orientation along the metaphase plate. Crossing over, the exchange and recombination of genetic information between chromosomes also occurs in prophase I and adds to the genetic diversity of the offspring.
Can you inherit an allele?
This law says inheriting an allele has nothing to do with inheriting an allele for any other trait. The alleles from parents are passed on independently to the offspring. After fertilization, the resulting zygote (s) can end up with any combination of chromosomes from the parents and all the possible combinations occur with equal frequency.
When Does Independent Assortment Occur?
Independent assortment occurs during the process of meiosis. Meiosis is similar to mitosis, only the final product is gamete cells. Gamete cells have half the DNA of regular, diploid cells and are considered haploid. This is a necessary part of sexual reproduction which allows two gamete cells to then fuse together to create a diploid zygote, containing all the DNA necessary to create a new organism.
What did Gregor Mendel do?
Gregor Mendel performed many experiments involving breeding pea plants. In doing so, he gleaned information about how “units of heredity ” work, which would later on become known as genes after DNA was discovered and determined to be the material that encodes genetic information.
What is the law of independent assemblage?
The Law of Independent Assortment states that different genes and their alleles are inherited independently within sexually reproducing organisms. During meiosis, chromosomes are separated into multiple gametes. Genes linked on a chromosome can rearrange themselves through the process of crossing-over.
Why do plants have yellow and round alleles?
This occurred because each of the parent plants only gave their offspring one allele and because yellow and round were dominant traits and masked the green and/or wrinkled traits in certain individual plants. The diagram below depicts Mendel’s dihybrid cross.
How many alleles does each gamete have?
C. This law ensures that each gamete only gets 1 allele for each gene
What are the two traits of independent assortment in meiosis?
As a basic example, let us consider a hypothetical population of bunny rabbits that only have two visible traits: fur color (black or white), and eye color (green or red). The black fur allele (B) is dominant over the white (b), while the green eye allele (G) is dominant over red (g).
What does it mean when two rabbits are mixed?
What this means is that both rabbits look black with green eyes, but are really they have a heterozygous genotype. Both rabbits have the genotype BbGg. In this population of 2 rabbits, all the individuals have the same mixture of characteristics.
