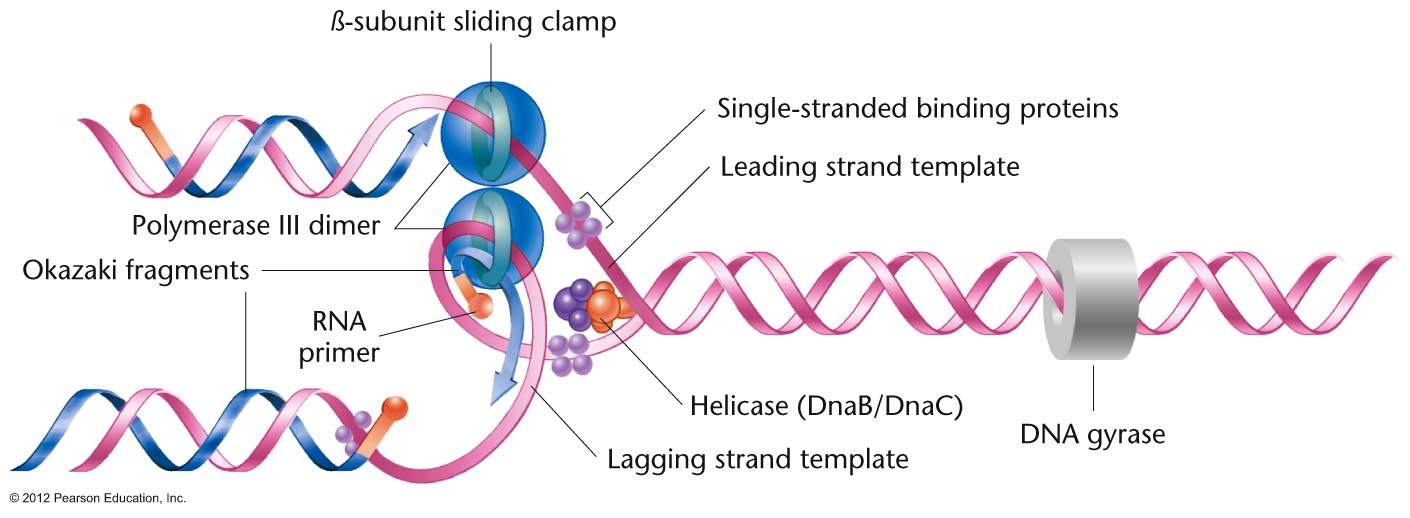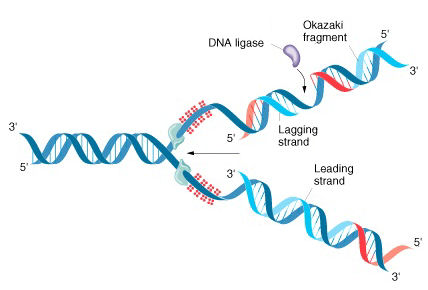
What is the difference between leading and lagging strand?
What You Need To know About Lagging Strand
- Lagging strand is a replicated strand of DNA which is formed in short segment called Okazaki fragments. ...
- Lagging strand requires DNA ligase to ligate Okazaki fragments together.
- Formation of lagging strand behind a bit later than that of the leading strand.
What is a leading strand and a lagging strand?
The leading strand is the strand of nascent DNA which is synthesized in the same direction as the growing replication fork. The synthesis of leading strand is continuous. The lagging strand, on the other hand, is the strand of new DNA whose direction is opposite to the direction of the growing replication fork.
Why does DNA have both leading and lagging strands?
Leading and lagging strand are the two types of DNA strands found in the double-stranded DNA molecule. They are classified based on the pattern of replication. However, the leading and the lagging strand are complementary to each other. Furthermore, both strands are made up of DNA nucleotides, which link to each other through phosphodiester bonds.
Does the leading strand require DNA ligase?
The requirement of DNA Ligase Besides these, the leading strand does not require DNA ligase while the lagging strand requires DNA ligase to ligate Okazaki fragments together. Conclusion Leading strand is one of the two strands of the double-stranded DNA. Significantly, it opens up in the 3’ to 5’ direction at the replication fork.

What are the leading strands and lagging strands during DNA replication?
The leading strand is the strand of nascent DNA which is synthesized in the same direction as the growing replication fork. The synthesis of leading strand is continuous. The lagging strand, on the other hand, is the strand of new DNA whose direction is opposite to the direction of the growing replication fork.
What is the leading strand in DNA replication?
The leading strand is a single DNA strand that, during DNA replication, is replicated in the 3' – 5' direction (same direction as the replication fork). DNA is added to the leading strand continuously, one complementary base at a time.
What is the lagging strand in DNA replication?
The lagging strand is a single DNA strand that, during DNA replication, is replicated in the 5′ – 3′ direction (opposite direction to the replication fork). DNA is added to the lagging strand in discontinuous chunks called 'okazaki fragments'.
What's the difference between leading and lagging strand?
The separated DNA strands form a replication fork, where both the DNA strands get replicated forming a lagging and leading strand. The major difference between a lagging and leading strand is that the lagging strand replicates discontinuously forming short fragments, whereas the leading strand replicates continuously.
Is 5 to 3 leading or lagging?
The other strand is called the lagging strand. This is the parent strand that runs in the 5' to 3' direction toward the fork, and it's replicated discontinuously.
What is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in DNA replication quizlet?
What is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in DNA replication? The leading strand is synthesized in the 3' → 5' direction in a discontinuous fashion, while the lagging strand is synthesized in the 5' → 3' direction in a continuous fashion.
Which strand is the lagging strand?
The lagging strand is the second strand of the DNA double helix. The strand opens up in the 5' to 3' direction. Therefore, the new strand growth has to occur away from the replication fork as the direction of DNA replication occurs only in the 5' to 3' direction.
What is Okazaki fragments in DNA replication?
Okazaki fragments are short sections of DNA formed at the time of discontinuous synthesis of the lagging strand during replication of DNA. It is essential as it allows for the synthesis of both the daughter strands required for cell division.
What is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in DNA replication quizlet?
What is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in DNA replication? The leading strand is synthesized in the 3' → 5' direction in a discontinuous fashion, while the lagging strand is synthesized in the 5' → 3' direction in a continuous fashion.
Which strand is the lagging strand?
The lagging strand is the second strand of the DNA double helix. The strand opens up in the 5' to 3' direction. Therefore, the new strand growth has to occur away from the replication fork as the direction of DNA replication occurs only in the 5' to 3' direction.
What is the order of DNA replication?
How is DNA replicated? Replication occurs in three major steps: the opening of the double helix and separation of the DNA strands, the priming of the template strand, and the assembly of the new DNA segment. During separation, the two strands of the DNA double helix uncoil at a specific location called the origin.
Why is the lagging strand discontinuous in replication?
On the upper lagging strand, synthesis is discontinuous, since new RNA primers must be added as opening of the replication fork continues to expose new template. This produces a series of disconnected Okazaki fragments.
What is the lagging strand of DNA?from onlyzoology.com
Lagging Strand. Both the leading strand and the lagging strand of DNA are the newly synthesized DNA strands formed during the process of DNA replication. The leading strand as the name suggests is a complete continuous strand that is synthesized rapidly during DNA replication on the 3’→5′ polarity template of DNA.
What are the two strands of DNA called?from onlyzoology.com
The two separate strands of the DNA are called template strands because the template strand in 5’→3′ direction will synthesize the lagging strand. Whereas, the template strand in 3’→5′ direction will synthesize the leading strand. That’s how the Leading Strand and Lagging Strand are formed.
What is the replication fork?from onlyzoology.com
The replication fork looks like a fork in the DNA that is composed of the two separate strands of the DNA called template strands.
Why does the leading strand of DNA run continuously without fragmentation?from onlyzoology.com
So, what happens is that the leading strand runs 5′ to 3′ continuously without any fragmentation because the DNA polymerase is also moving in the same direction as the replication fork.
Why does DNA replication start with a small opening?from onlyzoology.com
As the two strands cannot unwind in the entire length of the DNA molecule due to high energy requirement , therefore, the replication starts with a small opening of DNA helix. This results in the formation of the Y-shaped structure called the replication fork.
What is the direction of the lagging strand?from onlyzoology.com
Its direction is 3’→5′.
How are leading strands formed?from onlyzoology.com
During the process of DNA replication, the main enzymes are the DNA helicases that separate the double-stranded DNA into single strands allowing each strand to be copied (synthesized) into a new strand. We know that the DNA double helix is very stable.
What is the lagging strand of DNA?
Lagging Strand. Both the leading strand and the lagging strand of DNA are the newly synthesized DNA strands formed during the process of DNA replication. The leading strand as the name suggests is a complete continuous strand that is synthesized rapidly during DNA replication on the 3’→5′ polarity template of DNA.
Why is DNA added to the lagging strand discontinuously?
DNA is added to the lagging strand discontinuously with the formation of various fragments because the DNA primase enzyme cannot work in the 3’→5′ direction. And so, for maintaining the antiparallel nature of DNA the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously.
How are leading strands formed?
During the process of DNA replication, the main enzymes are the DNA helicases that separate the double-stranded DNA into single strands allowing each strand to be copied (synthesized) into a new strand. We know that the DNA double helix is very stable.
What is the direction of the lagging strand?
Its direction is 3’→5′.
Why is it important to have two different DNA strands in two different directions?
The importance of these two different strands in two different directions is very much necessary for DNA replication to occur smoothly.
What are the fragments of a lagging strand called?
Various fragments are seen during the synthesis of a lagging strand. These fragments are called Okazaki fragments.
Why does DNA need ATP?
We know that the DNA double helix is very stable. So, energy needs to be provided in the form of ATP in order to separate the two strands together.
Where is the lagging strand of DNA located?
A lagging strand is one of two strands of DNA found at the replication fork, or junction, in the double helix; the other strand is called the leading strand. A lagging strand requires a slight delay before undergoing replication, and it must undergo replication discontinuously in small fragments.
What is a lagging strand?
A lagging strand is the name for one of the two DNA strands in a double helix that is undergoing replication. This lesson will explain which strand is lagging and how it is replicated. Create an account.
What happens to the bottom strand of DNA?
But, what about the bottom strand on the left and the upper strand on the right? These strands are lagging strands. Obviously, this DNA needs to undergo replication, but it's not that simple. Remember, our polymerase can only move towards the left on the top strand and towards the right on the bottom strand. So, the original polymerase will be unable to reverse direction and replicate these bits.
What is the name of the bubble in DNA replication?
DNA Replication. DNA replication begins when the DNA double helix unwinds. The open region containing the separated DNA strands is called the replication bubble. Imagine a replication bubble where the top strand has its 5' end on the left and its 3' end on its right.
How does DNA replicate?
When DNA replicates, it must unwind at a replication fork , found on either side of a replication bubble. One strand can replicate continuously, the leading strand, but the lagging strand must be replicated in chunks of DNA called Okazaki fragments. Replication requires the use of different methods because DNA polymerase, an enzyme that builds new DNA strands, can only build DNA by adding bases to the 3' side. The lagging strand needs to wait for the DNA to unwind a bit before a polymerase can jump in and replicate another chunk.
How many bases can a DNA polymerase add to a DNA chain?
DNA polymerase can only add bases to the 3' end of a DNA chain. This means the new strand can only be built by adding bases to the 3' side of the growing chain. In order to build the new strand in the 5'-to-3' direction, the polymerase must read the original strand in the 3'-to-5' direction.
Why does DNA not zip along?
Of course, it will not have much DNA to zip along because it will soon reach the portion that was already replicated by the original polymerase that is continuously chugging along towards the right. As the polymerase on the leading strand causes the DNA to further unwind, more lagging strand is exposed.
How does DNA polymerase replicate lagging DNA?
In this fashion, DNA polymerase would be able to replicate the lagging strand of the DNA molecule, simply by making short lengths at a time. Okazaki and his colleagues worked with the bacteria E. coli to find out whether this hypothesis was correct. Eventually, they proved their theory of discontinuous replication, and the short lengths of DNA came to be known as Okazaki fragments. So, the Okazaki fragments are the short pieces of daughter DNA that are made on the lagging strand by DNA polymerase.
Which direction does the lagging strand run?
The other strand is called the lagging strand. This is the parent strand that runs in the 5' to 3' direction toward the fork, and it's replicated discontinuously. Now let's talk about the difference between continuous and discontinuous replication.
What are the short pieces of daughter DNA that are made on the lagging strand by DNA polymerase?
Eventually, they proved their theory of discontinuous replication, and the short lengths of DNA came to be known as Okazaki fragments. So, the Okazaki fragments are the short pieces of daughter DNA that are made on the lagging strand by DNA polymerase. DNA Ligase.
What happens when DNA helicase opens up the replication fork?
When DNA helicase opens up the replication fork, the result is two parent strands that are exposed and waiting for new pairing strands to be built. The leading strand's free end is a 3' end, and the end that's nearest to the replication fork is the 5' end.
How does DNA helicase work?
So, the two enzymes work in sync with each other. The more DNA helicase splits open the fork , the more DNA polymerase keeps adding daughter nucleotides to the new strand. This is what it means for DNA replication to work in a continuous fashion. But this only occurs on the leading strand.
What is the end of DNA called?
Scientists name the ends of the DNA strands according to the carbons in the sugar ring. One end is called the 3' end, and the other is called the 5' end. So, on any complete molecule of DNA, one strand will run from 3' to 5', and the other will run from 5' to 3'. DNA strands run antiparallel to one another.
How does Okazaki know the backbone of DNA?
Okazaki understood the DNA molecule, and he knew that DNA backbones run in opposite directions. Remember that the strands in a DNA molecule are oriented antiparallel to one another. You can think of the two strands like arrows, with the arrowhead of one strand matching up with the tail of the other strand. Scientists name the ends of the DNA strands according to the carbons in the sugar ring. One end is called the 3' end, and the other is called the 5' end. So, on any complete molecule of DNA, one strand will run from 3' to 5', and the other will run from 5' to 3'.
Why are there multiple origins of replication in eukaryotic cells?
In eukaryotic cells there are multiple origins of replication because there are many chromosomes that are much larger. In prokaryotic cells there is only one origin of replication because there is one circular chromosome in the cell. Explain the process of DNA replication. - Helicase breaks down hydrogen bonds between bases and unzips ...
Which enzyme synthesizes in the 5' to the 3' end of a nucleotide?
However, the enzyme DNA polymerase III can only synthesize in the 5' to the 3' end after attaching to a 3' part of a nucleotide. This creates either a lagging strand or leading strand from the origin of replication. Contrast the number of origins of replication in prokaryotic cells with the number in eukaryotic cells.
What enzyme bonds DNA nucleotides to RNA?
short segments of RNA (Approx 10 nucleotides long) that allow DNA polymerase III to bond and synthesize the complementary strand. DNA polymerase III. an enzyme that adds DNA nucleoside triphosphates to RNA primer in the 5' to 3' end.
What is the significance of complementary base pairing in the conservation of the base sequence of DNA?
Since DNA has a complementary base pairing, when the DNA is unzipped, the new strand that is created is the same as the other strand that was removed from the original DNA.
Why is DNA polymerase discontinuous?
On the lagging strand, since DNA moves from the 3' to 5' end, the synthesis is discontinuous because DNA polymerase III can only move from the 5' to the 3' and multiple primers are needed to synthesize the other strand from the origin of replication to the replication fork.
Why is DNA the same as the old one?
This is the reason that when DNA is replicated, every new DNA helix that is created is the same as the old one.
What is DNA helix?
Tap card to see definition 👆. DNA is a double stranded helix. This is what allows the DNA to be unzipped. Additionally, since DNA is antiparallel, from the origin of replication, a leading and lagging strand is formed, creating 2 different manners in which the complementary strand is synthesized.