
Leading Strand:
- A short piece of RNA? called a primer? (produced by an enzyme called primase) comes along and binds to the end of the leading strand. ...
- DNA polymerase? binds to the leading strand and then ‘walks’ along it, adding new complementary? nucleotide? bases (A, C, G and T) to the strand of DNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
- This sort of replication is called continuous.
What is the difference between leading and lagging strand?
What You Need To know About Lagging Strand
- Lagging strand is a replicated strand of DNA which is formed in short segment called Okazaki fragments. ...
- Lagging strand requires DNA ligase to ligate Okazaki fragments together.
- Formation of lagging strand behind a bit later than that of the leading strand.
What are three main steps in DNA replication?
Three steps of DNA replication-Best Info
- Replication Phases info. Replication phases are the phases of DNA reproduction. Replication is the process of doubling DNA. ...
- First Phase. In the first phase, the DNA replication begins with the initiation of the G-phase. ...
- Second Phase. Once a cell has reached the S phase, the DNA elongates. ...
- Third phase. The third phase is elongation. ...
What is a leading strand and a lagging strand?
The leading strand is the strand of nascent DNA which is synthesized in the same direction as the growing replication fork. The synthesis of leading strand is continuous. The lagging strand, on the other hand, is the strand of new DNA whose direction is opposite to the direction of the growing replication fork.
Does the leading strand require DNA ligase?
The requirement of DNA Ligase Besides these, the leading strand does not require DNA ligase while the lagging strand requires DNA ligase to ligate Okazaki fragments together. Conclusion Leading strand is one of the two strands of the double-stranded DNA. Significantly, it opens up in the 3’ to 5’ direction at the replication fork.
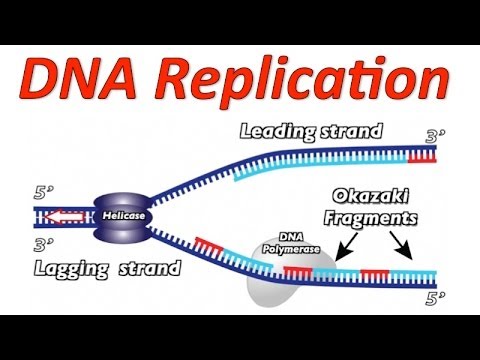
What is the lagging strand in DNA replication?
The lagging strand is a single DNA strand that, during DNA replication, is replicated in the 5′ – 3′ direction (opposite direction to the replication fork). DNA is added to the lagging strand in discontinuous chunks called 'okazaki fragments'.
Is the leading strand from 5 to 3?
Leading and lagging strands One new strand, the leading strand, runs 5' to 3' towards the fork and is made continuously. The other, the lagging strand, runs 5' to 3' away from the fork and is made in small pieces called Okazaki fragments.
Where are the leading and lagging strands in DNA replication?
6:3219:55DNA Replication - Leading Strand vs Lagging Strand & Okazaki FragmentsYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe leading strand moves in the same. Direction as the replication fork. The lagging strand moves inMoreThe leading strand moves in the same. Direction as the replication fork. The lagging strand moves in the opposite. Direction of the replication fork.
How can you identify the leading strand?
The strand that opens in the 3' to 5' direction towards the replication fork is referred to as the lagging strand. The strand that runs in the 5' to 3' direction in the replication fork is referred to as the leading strand. The strand is replicated discontinuously.
Why does DNA synthesis occur 5 '- 3?
DNA replication goes in the 5' to 3' direction because DNA polymerase acts on the 3'-OH of the existing strand for adding free nucleotides.
Why is the 3/5 strand called the lagging strand?
Because DNA polymerase can only synthesize DNA in a 5′ to 3′ direction, the other new strand is put together in short pieces called Okazaki fragments. The Okazaki fragments each require a primer made of RNA to start the synthesis. The strand with the Okazaki fragments is known as the lagging strand.
What is a leading strand and lagging strand?
The main difference between leading and lagging strand is that the leading strand is the DNA strand, which grows continuously during DNA replication whereas lagging strand is the DNA strand, which grows discontinuously by forming short segments known as Okazaki fragments.
What is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in DNA replication quizlet?
What is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in DNA replication? The leading strand is synthesized in the 3' → 5' direction in a discontinuous fashion, while the lagging strand is synthesized in the 5' → 3' direction in a continuous fashion.
Which end of DNA is 5 and 3?
2:094:185' and 3' ends of DNA.mov - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBecause remember DNA is a is a long chain of nucleotides a polymer of nucleotides. So. If we look atMoreBecause remember DNA is a is a long chain of nucleotides a polymer of nucleotides. So. If we look at this you can see that obviously this would be the 5 prime end of that nucleotide.
What does the 3 and 5 stand for in DNA?
Each end of DNA molecule has a number. One end is referred to as 5' (five prime) and the other end is referred to as 3' (three prime). The 5' and 3' designations refer to the number of carbon atom in a deoxyribose sugar molecule to which a phosphate group bonds.
How do you know which end is 3 and 5?
3' end/5' end: A nucleic acid strand is inherently directional, and the "5 prime end" has a free hydroxyl (or phosphate) on a 5' carbon and the "3 prime end" has a free hydroxyl (or phosphate) on a 3' carbon (carbon atoms in the sugar ring are numbered from 1' to 5').
Why does a DNA strand grow only in the 5 to 3 direction quizlet?
Why does DNA synthesis only proceed in the 5' to 3' direction? Because DNA polymerases can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of a polynucleotide strand.
Which direction is the leading strand?
One of the strands is oriented in the 3’ to 5’ direction (towards the replication fork), this is the leading strand. The other strand is oriented in the 5’ to 3’ direction (away from the replication fork), this is the lagging strand. As a result of their different orientations, the two strands are replicated differently:
What is the name of the DNA fragments that are added to the lagging strand?
Chunks of DNA, called Okazaki fragments, are then added to the lagging strand also in the 5’ to 3’ direction. This type of replication is called discontinuous as the Okazaki fragments will need to be joined up later.
How does DNA replication work?
What is DNA replication? 1 The first step in DNA replication is to ‘unzip’ the double helix structure of the DNA? molecule. 2 This is carried out by an enzyme? called helicase which breaks the hydrogen bonds? holding the complementary? bases? of DNA together (A with T, C with G). 3 The separation of the two single strands of DNA creates a ‘Y’ shape called a replication ‘fork’. The two separated strands will act as templates for making the new strands of DNA. 4 One of the strands is oriented in the 3’ to 5’ direction (towards the replication fork), this is the leading strand?. The other strand is oriented in the 5’ to 3’ direction (away from the replication fork), this is the lagging strand?. As a result of their different orientations, the two strands are replicated differently:
What is the shape of DNA that is formed when two strands of DNA are separated?
The separation of the two single strands of DNA creates a ‘Y’ shape called a replication ‘fork’. The two separated strands will act as templates for making the new strands of DNA.
What is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself during cell division?
DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself during cell division.
Why is the new strand proofread?
The new strand is proofread to make sure there are no mistakes in the new DNA sequence.
What happens to DNA after replication?
Following replication the new DNA automatically winds up into a double helix.
How is DNA replicated?
When DNA begins to replicate, a replication bubble is formed that can be detected visually by electron microscopy. A specific sequence of bases- known as the origin of replication – determines where this replication bubble begins. Inside of the bubble, two Y-shaped replication forks result where DNA is actively replicated on either side of the region. The replication forks are formed as the double strands of DNA are separated by helicase in both directions away from the origin of replication. It is at the replication fork that DNA replication proteins attach to fulfill their functions.
Which enzyme relieves tension by making cuts in the DNA and rejoining them before the replication fork arrives?
Topoisomerase: Because unwinding of the DNA by helicase creates tension further down the strand, this enzyme relieves tension by making cuts in the DNA and rejoining them before the replication fork arrives.
Why is DNA polymerase 3 important?
Because eukaryotic DNA is linear, they have ends that create a challenge. For the leading strand, DNA polymerase III can continue down the entire length of DNA. However, in the lagging strand, a primer must be added in front of the Okazaki fragment being synthesized before DNA polymerase III can attach and synthesize the new DNA strand opposite of the replication fork. Once the last Okazaki fragment is synthesized, a small DNA segment is leftover at the tip of the strand. This segment cannot be left unattended. If this DNA isn’t replicated, then genetic material will be lost each time replication occurs. After several replication cycles, this can result in lost information that could be critical for the individual to survive.
What is the process of DNA replication?
Definition. DNA replication is a process that occurs during cellular division where two identical molecules of DNA are created from a single molecule of DNA. As a semiconservative process, a single molecule containing two strands of DNA in double helix formation is separated, where each strand serves as a template for the new DNA molecules.
Why is the double helix anti-parallel?
Because the double helix is anti-parallel and DNA polymerase only synthesizes new DNA from 5′-3′, the template strand reading 3′-5′ results in a continuous, leading strand, while the template strand reading 5′-3′ results in a discontinuous, lagging strand. Being a highly regulated process, multiple proteins are required both during ...
How many hydrogen bonds are there in DNA?
Hydrogen bonds connect the complimentary base pairs, where an adenine- thymine pair has two hydrogen bonds and a guanine-cytosine pair has three hydrogen bonds. A single DNA molecule results in double helix formation when two DNA strands are matched and bonded.
What direction does DNA run?
DNA has directionality that can run either 3′-5′ or 5′-3′ based off of the carbons in the sugar group. The two strands of DNA in the double helix must run opposite to each other in an anti-parallel fashion. Therefore, if the first strand starts at the 3′ end and finishes at the 5′ end, then the second strand must run opposite, starting at the 5′ end and finishing at the 3′ end.
Which strand of DNA is the newly synthesized strand of DNA?
Both the leading strand and the lagging strand of DNA are the newly synthesized DNA strands formed during the process of DNA replication.
How are leading strands formed?
During the process of DNA replication, the main enzymes are the DNA helicases that separate the double-stranded DNA into single strands allowing each strand to be copied (synthesized) into a new strand. We know that the DNA double helix is very stable.
What is the direction of the lagging strand?
Its direction is 3’→5′.
Why is DNA added to the lagging strand discontinuously?
DNA is added to the lagging strand discontinuously with the formation of various fragments because the DNA primase enzyme cannot work in the 3’→5′ direction. And so, for maintaining the antiparallel nature of DNA the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously.
What is the lagging strand of DNA?
Lagging Strand. Both the leading strand and the lagging strand of DNA are the newly synthesized DNA strands formed during the process of DNA replication. The leading strand as the name suggests is a complete continuous strand that is synthesized rapidly during DNA replication on the 3’→5′ polarity template of DNA.
Why is it important to have two different DNA strands in two different directions?
The importance of these two different strands in two different directions is very much necessary for DNA replication to occur smoothly.
What are the fragments of a lagging strand called?
Various fragments are seen during the synthesis of a lagging strand. These fragments are called Okazaki fragments.
Which strand of DNA can be replicated continuously?
The strands that can replicate continuously are called the leading strands .
How does DNA replicate?
When DNA replicates, it must unwind at a replication fork , found on either side of a replication bubble. One strand can replicate continuously, the leading strand, but the lagging strand must be replicated in chunks of DNA called Okazaki fragments. Replication requires the use of different methods because DNA polymerase, an enzyme that builds new DNA strands, can only build DNA by adding bases to the 3' side. The lagging strand needs to wait for the DNA to unwind a bit before a polymerase can jump in and replicate another chunk.
What happens to the bottom strand of DNA?
But, what about the bottom strand on the left and the upper strand on the right? These strands are lagging strands. Obviously, this DNA needs to undergo replication, but it's not that simple. Remember, our polymerase can only move towards the left on the top strand and towards the right on the bottom strand. So, the original polymerase will be unable to reverse direction and replicate these bits.
What is the name of the bubble in DNA replication?
DNA Replication. DNA replication begins when the DNA double helix unwinds. The open region containing the separated DNA strands is called the replication bubble. Imagine a replication bubble where the top strand has its 5' end on the left and its 3' end on its right.
How many bases can a DNA polymerase add to a DNA chain?
DNA polymerase can only add bases to the 3' end of a DNA chain. This means the new strand can only be built by adding bases to the 3' side of the growing chain. In order to build the new strand in the 5'-to-3' direction, the polymerase must read the original strand in the 3'-to-5' direction.
What is a lagging strand?
A lagging strand is the name for one of the two DNA strands in a double helix that is undergoing replication. This lesson will explain which strand is lagging and how it is replicated. Create an account.
Why does DNA not zip along?
Of course, it will not have much DNA to zip along because it will soon reach the portion that was already replicated by the original polymerase that is continuously chugging along towards the right. As the polymerase on the leading strand causes the DNA to further unwind, more lagging strand is exposed.
How is the leading strand synthesized?
the leading strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the lagging strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 5' end. the lagging strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the leading strand is synthesized in short fragments that are ultimately stitched together.
What is the name of the enzyme that synthesizes leading and lagging strands during replication?
DNA polymerase is a directional enzyme that synthesizes leading and lagging strands during replication. DNA is a polymer consisting of four monomers: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. DNA is the genetic material. Bacterial replication is fundamentally different from eukaryotic replication.
What is the lagging strand?
The lagging strand is characterized by a series of short segments of DNA (Okazaki fragments) that will be joined together to form a finished lagging strand. The experiments that led to the discovery of Okazaki fragments gave evidence for which of the following ideas?
What is a single strand of DNA?
a single strand of DNA. a series of nucleosomes wrapped around two DNA molecules. a chromosome with different numbers of genes in different cell types of an organism. a single linear molecule of double-stranded DNA plus proteins. Selected Answer: a single linear molecule of double-stranded DNA plus proteins.
Which is slower, prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
The rate of elongation during DNA replication is slower in prokaryotes than in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes produce Okazaki fragments during DNA replication, but eukaryotes do not. Selected Answer: Prokaryotic chromosomes have a single origin of replication, whereas eukaryotic chromosomes have many.
Which type of chromosome has a single origin of replication?
Prokaryotic chromosomes have a single origin of replication, while eukaryotic chromosomes have multiple origins of replication. . DNA replication in prokaryotic cells is conservative. DNA replication in eukaryotic cells is semi-conservative.
Which direction do prokaryotes add nucleotides?
DNA polymerases of prokaryotes can add nucleotides to both 3' and 5' ends of DNA strands, while those of eukaryotes function only in the 5' → 3' direction. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. Selected Answer: Prokaryotic chromosomes have a single origin of replication, while eukaryotic chromosomes have multiple origins ...
