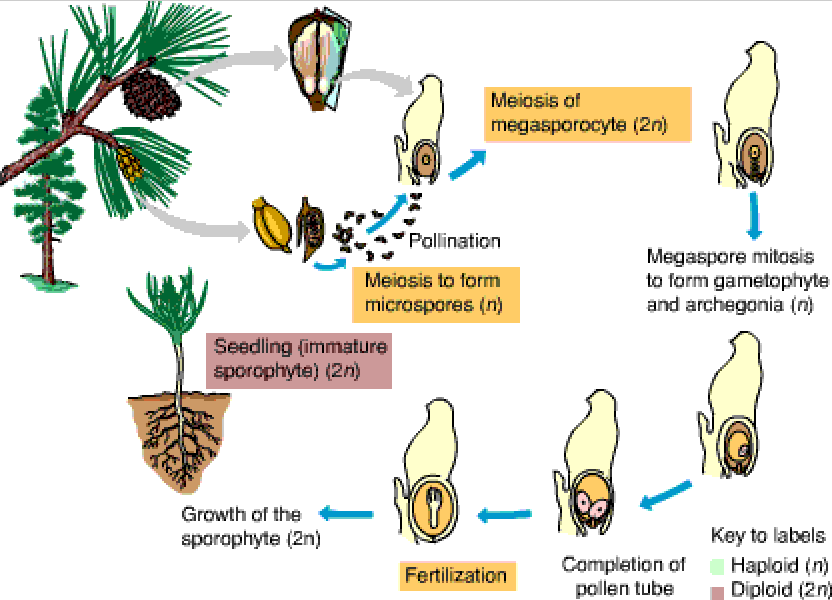
What is the Life Cycle of a Gymnosperm?
- Sporophyte Phase. The sporophyte phase is the spore-bearing phase. ...
- Gametophyte Phase. During the gametophyte phase, the male cones produce sperm, and the female cones produce egg cells. ...
- Pollination Phase. For gymnosperms, much of the pollination is due to wind or other natural means. ...
What is the dominant generation of gymnosperms?
The life cycle of a gymnosperm alternates between a large sporophyte (the dominant generation), which produces two types of spores in cones, and microscopic gametophytes, which produce gametes. Female gametophytes produce eggs, and male gametophytes produce sperm.
What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms Quizlet?
Most gymnosperms have reproductive structures called cones. Male cones produce pollen. Female cones contain at least one ovule. What are 4 types of gymnosperms? What are the four modern-day groups of gymnosperms? The four modern-day groups of gymnosperms are Coniferophyta, Cycadophyta, Gingkophyta, and Gnetophyta.
What plants are gymnosperms?
Key Points on Gymnosperms
- Gymnosperms are non-flowering plants belonging to the sub-kingdom Embophyta.
- The seeds are not enclosed in an ovary or fruit. They are exposed on the surface of the leaf-like structures of the gymnosperms.
- They can be classified as Coniferophyta, Cycadophyta, Ginkgophyta and Gnetophyta.
- Gymnosperms are found in boreal and temperate forests.
What are examples of gymnosperms?
Gymnosperms are quite essential, and their uses include:
- Most, especially the conifers, act as a source of wood. ...
- They act as a source of medicine. ...
- Some, such as pines, act as a turpentine source used in paints and polishes. ...
- They act as a source of food. ...
- They are used in making plastics and linoleum. ...
- Some are used as ornamentals, such as monkey puzzle plants.
- They act as a source of rosin, a type of resin. ...

What stage of a gymnosperms life cycle takes place inside the seed?
The zygote develops into an embryo within a seed, which forms from the ovule inside the female cone. If the seed germinates, it may grow into a mature sporophyte tree, which repeats the cycle.
Where does the cycle of a gymnosperm develop?
In gymnosperms, the gametophyte generation takes place in a cone, which forms on the mature sporophyte plant. Each male gametophyte is just a few cells inside a grain of pollen. Each female gametophyte produces an egg inside an ovule. Pollination must occur for fertilization to take place.
How long do gymnosperms live?
These are the only leaves the plant will ever grow, and they may live a hundred years or more and reach several meters, usually torn into strips. Male or female strobili grow from the margins of the upper stem. The conifers are the largest and most successful group of living gymnosperms.
What is the life cycle of angiosperm?
The angiosperm life cycle consists of a sporophyte phase and a gametophyte phase. The cells of a sporophyte body have a full complement of chromosomes (i.e., the cells are diploid, or 2n); the sporophyte is the typical plant body that we see when we look at an angiosperm.
How long does it take for gymnosperms to reproduce?
approximately one yearReproductive Process It takes approximately one year for the pollen tube to grow and migrate towards the female gametophyte. The male gametophyte containing the generative cell splits into two sperm nuclei, one of which fuses with the egg, while the other degenerates.
How do gymnosperms grow?
gymnosperm, any vascular plant that reproduces by means of an exposed seed, or ovule—unlike angiosperms, or flowering plants, whose seeds are enclosed by mature ovaries, or fruits. The seeds of many gymnosperms (literally, “naked seeds”) are borne in cones and are not visible until maturity.
What is the main plant of gymnosperms?
The main types of plants in the gymnosperm group are conifers. Gymnosperms are plants that produce cones as their reproductive structures instead of producing flowers, as angiosperms do. The vast majority of gymnosperms are conifers such as pine trees.
What are living gymnosperms?
The gymnosperms ( pronunciation (help·info) lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae, the living members of which are also known as Acrogymnospermae.
Why are gymnosperms so successful?
Gymnosperms possess several key evolutionary innovations compared to earlier groups such as the clubmosses and ferns. They produce sperm-containing pollen, which is carried through the air by the wind to the female. This innovation has freed these plants from the need for water for sexual reproduction.
How are the life cycles of angiosperms and gymnosperms different?
Though they both have sporophyte-dominated life cycles, angiosperms and gymnosperms differ in that angiosperms have flowers, fruit-covered seeds, and double fertilization, while gymnosperms do not have flowers, have “naked” seeds, and do not have double fertilization (more on this later).
What are the steps in gymnosperm reproduction?
Life Cycle of GymnospermsOn a mature Sporophyte plant, cones develop. ... Female spores mature into female gametophytes inside female cones. ... Pollen is transported from a male cone to a female cone during pollination. ... The zygote matures into an Embryo within a seed, which emerges from the ovule within the female cone.
What are the 5 stages of plant life cycle?
They follow a cyclic process of starting a new life, growing, and then coming back to the starting stage (reproducing). There are the 5 stages of plant life cycle. The seed, germination, growth, reproduction, pollination, and seed spreading stages.
Where are the seeds of a gymnosperm located?
conesGymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form cones, or solitary as in yew, Torreya, Ginkgo.
Which part of the pine life cycle is the male gametophyte?
Which part of the pine life cycle is the male gametophyte? - Mature pollen grain.
How are the life cycles of angiosperms and gymnosperms similar?
Though they both have sporophyte-dominated life cycles, angiosperms and gymnosperms differ in that angiosperms have flowers, fruit-covered seeds, and double fertilization, while gymnosperms do not have flowers, have “naked” seeds, and do not have double fertilization (more on this later).
Which part of the pine life cycle is the sporophyte?
Stage 1: Male cones (pollen cones) and female cones (ovuliferous cones) are formed on the adult tree or the spore-bearing plant (sporophyte). Stage 2: Several male cones are formed in a cluster beneath a new shoot.
What is the life cycle of a gymnosperm?
Life Cycle of Gymnosperms. In the life cycle of gymnosperms, the dominant sporophyte phase alternates with the short gametophyte phase. The sporophyte plant produces spores, while the gametophyte bears gametes. Leaf through this article to get an insight about gymnosperm life cycle in detail.
How many gymnosperms are there?
The evolution of gymnosperms can be traced back to the Paleozoic era, during which they were found abundantly. At present, there are approximately 700-900 living gymnosperm species. They are basically woody, large-sized and bear evergreen foliage. The leaves are reduced, of which many gymnosperms have needle-shaped leaves.
How do gymnosperms get pollinated?
The production of sperm cells and egg cells is followed by pollination process. Pollination of gymnosperms takes place by means of winds and natural agents. Over here, the pollen grains containing the sperm cells are carried to the female gametophyte of the ovulate cones by wind or insects.
What is the sporophyte phase?
Sporophyte: Spore-bearing Phase. The sporophyte phase represents the adult, photosynthetic, diploid gymnosperm plant that produces the male cones (or pollen cones) and the female cones (ovulate cones). The former is usually smaller than the latter one. They develop in the same plant (monoecious) or different plants (dioecious).
What are the different types of gymnosperms?
Of these, the Coniferophyta represents the largest group. Similar to other evolved plants, alternation of generations are present in the life cycle of gymnosperms. Two different forms that alternate each other are the spore bearing plant (sporophyte) and gamete bearing structure (gametophyte). The former is the dominant one and lasts for a longer period than the gametophyte phase in the gymnosperm life cycle. For simple understanding, you can study the life cycle of spruce or pine.
How long does it take for a gymnosperm to fertilize?
Thus, the time period between pollination and fertilization in gymnosperms is quite long, about a year. This newly formed sporophyte is enclosed in a seed in the form of an embryo.
How long does it take for pollen to go to the female gametophyte?
In the mean time, pollen grains germinate to form pollen tubes, which take about a year and make their way to the female gametophyte for fertilization.
What is the life cycle of a gymnosperm?
Gymnosperm Life Cycle. Gymnosperms reproduce with an alteration of generations, meaning their reproductive cycle has both haploid and diploid phases. As in all other vascular plants, gymnosperms have a sporophyte dominant life cycle (the sporophyte is the diploid multicellular stage, which comprises the body of the plant, i.e., a leafy tree).
What is a gymnosperm?
Gymnosperms are a group of plants which produce seeds that are not contained within an ovary or fruit. The seeds are open to the air and are directly fertilized by pollination. “Gymnosperm”, from the Greek, gymnos, “naked” and sperma, “seed”, develop their seeds on the surface of scales and leaves, which often grow to form cone or stalk shapes, ...
Why are gnetophyta distinguishable?
The gnetophyta are distinguishable within the gymnosperms because they have vessel elements, a system of channels mostly found in the angiosperms, which transport water within the plant.
What is the name of the tree with a single, stout, cylindrical, woody trunk?
The appearance of the cycads (division Cycadophyta) typically constitutes a single, stout, cylindrical, woody trunk and a crown of large, hard and stiff, evergreen compound leaves, which grow directly from the trunk in a rosette formation. The cycads are dioecious, meaning that each individual plant is either all male or all female.
What is the phase of a gametophyte?
The gametophyte phase is relatively short, and sees gametes produced on the reproductive organs , which are usually cones. The female ovulate cone, or megasporophyll, bear the megasporangium, diploid cells, which undergo meiosis to produce four haploid spores. Of these haploid spores, only one survives as the megaspore.
Where did Gingko biloba originate?
Native only to China, Ginkgo biloba is cultivated globally for use in various traditional medicines and as a food source.
How many families are there in the Cycadaceae?
The cycads were much more numerous in the past than today, peaking in ‘the age of the cycads’ – the Jurassic period. There are only three extant families within the cycads today: the Cycadaceae, Stangeriaceae and Zamiaceae.
What is the Life Cycle of a Gymnosperm?
For this unit study, we will focus on the life cycle of a conifer.
How many Gymnosperms are there?
Gymnosperms date back to the Paleozoic era where they were an abundant plant. Today, there are about 700 to 900 living species. They are thought to be the first vascular plants on lade, and they first appeared about 245 million years ago.
Why is Gymnosperm called Gymnosperm?
The name gymnosperm comes from a Greek word that means naked seeds. They are so named because the seeds are not enclosed in an ovary and instead are on the surface.
How does a gymnosperm pollinate?
For gymnosperms, much of the pollination is due to wind or other natural means. The pollen that contains the sperm cells is carried to the female cones either by wind or by insects that fly from cone to cone.
What is the difference between angiosperms and gymnosperms?
One key difference between the two types of plants is that angiosperms are seasonal, and they die or are dormant in the winter. Gymnosperms, however, are evergreen and do not lose their leaves or die in the winter.
What is a gymnosperm?
Gymnosperms are in a group of plants called seed plants, also called spermatophytes. Before seeds, plants could not grow in a dry world. When plants evolved to have seeds, vascular plants could then drop seeds on land, which allowed them to spread across the Earth.
What is the vascular system of a plant?
A plant’s vascular system allows water to move from the root to the rest of the plant. Without it, plants can not survive on land. However, the gymnosperm is thought to be the first vascular plant, and thus the first plant that could survive on land.
What are Gymnosperms?
Gymnosperms, which translates to "naked seeds," are a diverse group of seed plants. The angiosperms are a sister group to one group of gymnosperms (the Gnetales), making the gymnosperms a paraphyletic group, according to the "anthophyte" hypothesis. The term "paraphyletic group" refers to a group that does not include all descendants of a single common ancestor. The "netifer" theory, on the other hand, indicates that Gnetophytes are sister to conifers, making gymnosperms monophyletic and sister to angiosperms. Further, molecular and anatomical research may shed light on these connections.
What are the characteristics of a gymnosperm?
Naked seeds, separate female and male gametophytes, pollen cones and ovulate cones, pollination by wind and insects, and tracheid are all characteristics of gymnosperms (which transport water and solutes in the vascular system).
What is the sprophyll in Gymnosperm?
Gymnosperm seeds are not enclosed in an ovary; instead, modified leaves called sporophylls protect them only partially. The word strobilus (plural = strobili) refers to a dense cluster of sporophylls around a central stalk, as seen in pine cones. When seeds mature, they are encased in sporophyte tissues. The integument is a layer of sporophyte tissue that covers the megasporangium and, later, the embryo.
How many ovules are there in a female cone?
Two ovules per scale are found in female cones, also known as ovulate cones. Each ovule has a small passage that opens near the sporophyll's base. The micropyle is the passage through which a pollen tube can expand later. In each ovule, one megaspore mother cell, or megasporocyte, goes through meiosis. Three of the four cells die, leaving only one to grow into a female multicellular gametophyte that encircles archegonia (an archegonium is a reproductive organ that contains a single large egg). A sticky pollination drop traps windblown pollen grains near the micropyle opening as the female gametophyte develops.
How many phyla are there in a gymnosperm?
Gymnosperms are divided into four phyla today. Coniferophyta, Cycadophyta, and Ginkgophyta have similar seed development patterns as well as secondary cambium production (cells that generate the vascular system of the trunk or stem and are partially specialized for water transportation). The three phyla, on the other hand, are not phylogenetically related. Since they develop true xylem tissue with vessels as well as the tracheid found in the rest of the gymnosperms, Gnetophyta is considered the closest group to angiosperms. Likely, the vessel components in the two classes evolved independently.
Where do Gymnosperms live?
In the Mesozoic period, Gymnosperms were the most common phylum. They've evolved to live in areas where freshwater is scarce for most of the year, or in bogs with nitrogen-deficient soil. As a result, they remain the dominant phylum in the coniferous biome, or taiga, where evergreen conifers benefit from the cold and dry climate. During the winter, evergreen conifers maintain low levels of photosynthesis and can take advantage of the first sunny days of spring. Conifers are more vulnerable to leaf infestations than deciduous trees because most conifers do not lose their leaves all at once.
Do gymnosperms shed in winter?
These are the most well-known gymnosperm species. They are evergreen trees that look like cones. As a result, they don't shed in the winter. Their leaves resemble needles or scales. These plants have winged seeds that are produced in female cones.
