
Causes
The frontal lobe dementia life expectancy can be as long as seventeen years, but some patients only live two years as they soon succumb to complications of the disease. Frontal lobe dementia is distinguished from other types of dementia by the presence of abnormalities in the nerve cells of the brain — known as Pick bodies.
Symptoms
What is the prognosis for frontotemporal dementia (FTD)? The outcome for people with frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is poor. The disease progresses steadily and often rapidly, becoming full blown in less than 2 years in some individuals and taking more than 10 years in others.
Complications
What is the life expectancy of people with Pfeiffer disease? Those with Pfeifer syndrome type 1 usually live a normal life and life span. Unfortunately, those with Pfeiffer syndrome type II and III have the high chance of developing complications, which could shorten their life expectancy.
How long does a person live with frontal lobe dementia?
Life expectancy for many diseases is often expressed as a 5-year survival rate (the percent of patients who will be alive 5 years after diagnosis). The 5-year life expectancy for people with COPD ranges from 40% to 70%, depending on disease severity. This means that 5 years after diagnosis 40 to 70 out of 100 people will be alive.
What is the prognosis of frontotemporal dementia (FTD)?
What is the life expectancy of someone with Pfeiffer syndrome?
What is the life expectancy of COPD after diagnosis?

What are the final stages of FTD?
In later stages, patients develop movement disorders such as unsteadiness, rigidity, slowness, twitches, muscle weakness or difficulty swallowing. Some patients develop Lou Gherig's disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). People in the final stages of FTD cannot care for themselves.
How quickly does frontotemporal dementia progress?
Most cases are diagnosed in people aged 45-65, although it can also affect younger or older people. Like other types of dementia, frontotemporal dementia tends to develop slowly and get gradually worse over several years.
Is frontotemporal dementia a terminal?
FTD is not life-threatening ─ people may live with it for years. But it can lead to an increased risk for other illnesses that can be more serious. Pneumonia is the most common cause of death, with FTD. People are also at increased risk for infections and fall-related injuries.
What is the life expectancy for FTD?
The length of progression varies from 2 to over 20 years. Over time, FTD predisposes an individual to physical complications such as pneumonia, infection, or injury from a fall. The most common cause of death is pneumonia. Average life expectancy is 7 to 13 years after the start of symptoms.
What are 5 extreme behavior changes found with FTD?
Lack of interest (apathy), which can be mistaken for depression. Repetitive compulsive behavior, such as tapping, clapping or smacking lips. A decline in personal hygiene. Changes in eating habits, usually overeating or developing a preference for sweets and carbohydrates.
How do you slow down frontotemporal dementia?
Medications. Antidepressants. Some types of antidepressants, such as trazodone, may reduce the behavioral problems associated with frontotemporal dementia. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) — such as citalopram (Celexa), paroxetine (Paxil) or sertraline (Zoloft) — also have been effective in some people.
What is the most common cause of death in dementia patients?
One of the most common causes of death for people with dementia is pneumonia caused by an infection. A person in the later stages of dementia may have symptoms that suggest that they are close to death, but can sometimes live with these symptoms for many months.
Does frontotemporal dementia run in families?
Familial genes In some families, there is a single faulty gene that will definitely cause FTD if it is passed down from a parent to a child. This is known as 'familial FTD'. About 10 to 15 in every 100 people with FTD have this type. Any child of a person with familial FTD has a 1 in 2 chance of getting the same gene.
What is frontotemporal dementia caused by?
Frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism can be an inherited disease caused by a genetic tau mutation. Symptoms include movement problems similar to those of Parkinson's disease, such as slowed movement, stiffness, and balance problems, and changes in behavior or language.
What are some of the first symptoms noticed in frontal lobe dementia?
What are the early signs of frontal lobe dementia?Loss of inhibitions. This means a person has trouble controlling themselves. ... Apathy. This usually causes a lack of interest or motivation. ... Loss of empathy. ... Compulsive behaviors. ... Changes in diet or mouth-centered behaviors. ... Loss of executive function.
What causes dementia to progress rapidly?
other long-term health problems – dementia tends to progress more quickly if the person is living with other conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes or high blood pressure, particularly if these are not well-managed.
What are some of the first symptoms noticed in frontal lobe dementia?
What are the early signs of frontal lobe dementia?Loss of inhibitions. This means a person has trouble controlling themselves. ... Apathy. This usually causes a lack of interest or motivation. ... Loss of empathy. ... Compulsive behaviors. ... Changes in diet or mouth-centered behaviors. ... Loss of executive function.
What does frontotemporal dementia feel like?
Frontotemporal dementia usually causes changes in behaviour or language problems at first. These come on gradually and get worse slowly over time. Eventually, most people will experience problems in both of these areas. Some people also develop physical problems and difficulties with their mental abilities.
What stage of dementia does Sundowning start?
Sundowners can occur at any stage of Alzheimer's disease, but it typically peaks during the middle stages. Symptoms may be mild and inconsistent during the early stages of Alzheimer's but worsen over time before tapering toward the end of the patient's life.
What are the symptoms of frontotemporal dementia?
Symptoms of FTD start gradually and progress steadily, and in some cases, rapidly. They vary from person to person, depending on the areas of the brain involved. These are common symptoms:
How is frontotemporal dementia treated?
Currently, no treatments are available to cure or slow the progression of FTD, but healthcare providers may prescribe medicine to treat symptoms. Antidepressants may help treat anxiety and control obsessive-compulsive behaviors and other symptoms. Prescription sleeping aids can help ease insomnia and other sleep disturbances. Antipsychotic medicine may reduce irrational and compulsive behaviors.
What is the cause of dementia?
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), a common cause of dementia, is a group of disorders that occur when nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are lost. This causes the lobes to shrink. FTD can affect behavior, personality, language, and movement.
When does FTD start?
Symptoms typically first occur between the ages of 40 and 65 and can include changes in personality and behavior, progressive loss of speech and language skills, and sometimes physical symptoms such as tremors or spasms. FTD tends to progress over time.
When does dementia start?
These disorders are among the most common dementias that strike at younger ages. Symptoms typically start between the ages of 40 and 65, but FTD can strike young adults and those who are older. FTD affects men and women equally.
Is FTD life threatening?
FTD is not life-threatening ─ people may live with it for years. But it can lead to an increased risk for other illnesses that can be more serious. Pneumonia is the most common cause of death, with FTD. People are also at increased risk for infections and fall-related injuries.
Is FTD inherited?
Although experts believe that some cases of FTD are inherited, most people with FTD have no family history of it or other types of dementia.
How long does frontotemporal dementia last?
Even so, when it comes to how long can a person live with frontotemporal dementia, it is typically between 6 and 8 years once the symptoms start.
How old is the average person with frontotemporal dementia?
This area of the brain becomes damaged and can even shrink. Frontotemporal dementia age of onset can be as early as the age of 40, with 54 being the average age of onset, and is often misdiagnosed in younger adults as a psychiatric issue and in older adults as Alzheimer’s. Older adults can start to see symptoms all the way into their 80s.
What are the symptoms of frontotemporal dementia?
Some of the signs of frontotemporal dementia include the following: 1 Lack of inhibition 2 Loss of empathy 3 Speech difficulties 4 Issues with balance 5 Inappropriate behavior 6 Poor judgment 7 Mood changes 8 Compulsive behavior
How does frontotemporal dementia differ from Alzheimer's?
Frontotemporal dementia differs from Alzheimer’s, as it affects a different area of the brain. Because of that, you may not see the early confusion in patients that you normally see in other types of dementia.
What is the purpose of blood tests for dementia?
Blood tests are used to determine if there is another source causing the symptoms. Neuropsychological testing can be done to determine the type of dementia someone is suffering from, and brain scans can help discover tumors or blood clots that might be causing the symptoms.
How long does it take for a behavioral variant to get worse?
Moderate Behavioral Variant – The symptoms of this disease will remain the same for the first few years, but they will get worse over that period . You may also notice your loved one starts compulsively cleaning areas of your home and collecting objects.
Is there a risk factor for frontotemporal dementia?
As for frontotemporal dementia risk factors, there is only one, and that’s having a family history of dementia.
How long does frontotemporal dementia last?
Some people may need 24-hour care at home or at living facilities or nursing homes. The speed of decline varies from person to person, but the disease course typically ranges from two to 10 years.
How many people have frontotemporal dementia?
Approximately 60% of people with frontotemporal dementia (FTD) are between the ages of 45 and 64. It is estimated that about 10% of dementia cases are the result of FTD. Men and women are affected about equally.
What is frontotemporal dementia?
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is a group of disorders that result from damage to the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. Depending on the location of the damage, the disorder causes changes in social behavior, personality, and/or loss of language skills. In addition, some people (between 10% and 20%) with FTD also develop neuromuscular ...
What are the different types of FTD?
FTD consists of three subtypes: 1 Behavioral variant FTD (bvFTDO). This is also called frontal variant FTD). This subtype accounts for about 50% of all cases of FTD. Persons with bvFTD experience progressive changes in personality, behavior, emotions, and planning and problem-solving skills. 2 Nonfluent primary progressive aphasia (PPA). This is also called agrammatic PPA). People with this subtype have difficulty forming and speaking words because the brain has trouble planning and performing the facial muscle movements needed to produce speech. They often seem to have problems with grammar, such as leaving out words or mixing up words, effortful speech, and communicate with shorter, simpler, sometimes incomplete phrases. 3 Semantic variant PPA. This is also called temporal variant FTD or semantic dementia. People with this subtype slowly lose their ability to understand the meanings of words, recognize everyday objects and familiar faces, and/or use common items.
What is the most common cause of dementia?
In addition, some people (between 10% and 20%) with FTD also develop neuromuscular and movement disorders, such as parkinsonism or motor neuron disease (also known as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or Lou Gehrig’s disease). FTD is a common cause of early dementia. Symptoms worsen over time as more parts of the brain are affected.
What is the term for the loss of brain cells?
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) occurs when abnormal proteins (there are many kinds) build up in the brain. This leads to death of brain cells and deterioration and shrinkage (atrophy) of the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. Sometimes the disease is genetic, and passed down through families, but in most cases no specific cause can be found.
How to diagnose behavioral variant FTD?
Diagnosis is typically based on the clinical judgment of the doctor. Often, people with behavioral variant FTD don't believe they need to see a doctor. And when they do, they may ace the standard memory tests for dementia. Therefore, interviewing loved ones about the patients’ symptoms is often key to making the diagnosis, as patients typically cannot recognize changes in their behavior. Lab tests and brain scans will also be done to exclude other causes of impairment. Brain scans may be normal early in the course of disease. As the disease worsens, up to 65% of patients will show signs of brain damage in the frontal and temporal lobes.
How long does a person live with frontotemporal dementia?
The average life expectancy for someone living with frontotemporal dementia is between seven and 13 years from the time of diagnosis. The most common cause of death for people living with FTD is pneumonia.
What is frontotemporal dementia?
Frontotemporal dementia is the most common type of frontotemporal degeneration, an umbrella term for a handful of unusual disorders that typically erode the frontal and temporal parts of the brain.
How long does FTD last?
A progression of symptoms in individuals can persist for two to about 20 years. People with FTD have a higher risk of falling or suffering from a urinary tract infection or pneumonia, Ghoshal says. FTD is not by itself typically fatal, but it is associated with a shorter life span.
How many people are affected by FTD?
FTD is not nearly as common as Alzheimer's disease, which affects an estimated 5.8 million people in the U.S., according to the Alzheimer's Association. Overall, an estimated 50,000 to 60,000 people nationwide live with FTD, says Susan L-J Dickinson, chief executive officer of the Association for Frontotemporal Degeneration. That figure may be low. "We believe that this estimate is likely an undercount, because misdiagnosis is common," Dickinson says. "Getting an accurate diagnosis of FTD depends on having access to health professionals who have experience diagnosing it. Because getting an accurate diagnosis takes 3.6 years on average, a significant number of Americans are likely never accurately diagnosed with FTD." The disorder if often misdiagnosed as a psychiatric condition, Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease, she says. Consequently, some people with FTD are prescribed treatments for other illnesses.
Why is FTD so difficult to diagnose?
Why FTD Is Difficult to Diagnose. One of the key reasons FTD is difficult to diagnose is that there are currently no biomarkers for the disease. That means medical professionals must wait for an autopsy to make a confirmed diagnosis.
How to diagnose FTD?
There's no one clinical diagnostic test that physicians can use to diagnose FTD, says Dr. James Leverenz, a behavioral neurologist at the Cleveland Clinic. In investigating symptoms that could cause FTD, doctors typically start by ruling out other possible causes, such as stroke or a tumor, Leverenz says. An MRI can help doctors determine if there's a disproportionate amount of shrinkage in the frontal part of the brain, which could suggest FTD. Doctors can also use a PET scan to look for a pattern of reduced metabolism in the frontal or temporal parts of the brain, which could suggest FTD, he says. Other tests, like cerebrospinal fluid testing, can be useful to exclude Alzheimer's as a cause of the symptoms, Leverenz says.
How long does it take to get FTD diagnosed?
Because getting an accurate diagnosis takes 3.6 years on average, a significant number of Americans are likely never accurately diagnosed with FTD.". The disorder if often misdiagnosed as a psychiatric condition, Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease, she says.
Why is life expectancy increasing with dementia?
Life expectancy with dementia is increasing year on year as scientists and doctors find better ways to manage the disease. However, because of the nature of its progression dementia is known as a ‘life limiting’ illness.
How long does someone live with Alzheimer's?
However, dementia progresses differently in everyone, meaning people can live anywhere from 2 years to 26 years after diagnosis. The main way in which health care professionals estimate dementia life expectancy is by using ...
What factors can influence dementia life expectancy?
Below you can find a bit more information about how each factor can alter how long someone living with dementia might live.
How long does Lewy body dementia last?
Lewy body Dementia - While the average was found to be between 5-7 years, the range can be between 2 and 20 years. Frontotemporal Dementia (Pick's Disease) - 8 years. Young Onset Dementia - Although a diagnosis at a young age should imply a longer life expectancy, with Young Onset dementia this is sadly not the case.
What are the behavioural changes associated with dementia?
These include distress, agitation, aggression, restlessness, hallucinations, sundowning, and disrupted sleep . Live-in Care. As dementia progresses it may become harder for someone to live safely at home.
What is dementia in the brain?
Dementia is an illness of progressive cell damage. It starts in the parts of the brain that deal with memory and slowly moves to parts of the brain that control other functions. Sadly, this will eventually cause major organs to stop working. Below you can find a summary of some of the things you can expect when caring for someone in the later stages of dementia.
Why do people with dementia eat less?
This can be for a variety of reasons including difficulty chewing and swallowing. It's important to encourage them to continue to eat. Read our tips on helping someone with dementia to eat more.
How long does dementia last?
1.5 to 2.5 years. 2.5 years or less. People with early onset or young-onset dementia live for about the same number of years after diagnosis as those with more common forms of dementia. About 5% of cases of Alzheimer’s disease are young-onset, meaning symptoms develop between the ages of 30 and 60.
How long do people with young onset dementia live?
People with young-onset dementia live an average of 10 years with the disease.
How long do you live with dementia?
By far the most common form of dementia is Alzheimer’s disease, and the average life expectancy after diagnosis is 10 years. Other dementias have different life expectancies. Someone with vascular dementia lives for about five years after diagnosis. Someone who has dementia with Lewy bodies will typically live for six to twelve more years.
How long does a person with vascular dementia live?
Someone with vascular dementia lives for about five years after diagnosis. Someone who has dementia with Lewy bodies will typically live for six to twelve more years. Average life expectancies for the most common types of dementia are as follows: Dementia type. Average life expectancy following diagnosis. Alzheimer’s. 8 – 12 years.
What is the scale used to measure dementia?
The scale most commonly used by health professionals for the stages of dementia is the Global Deterioration Scale (GDS), also called the Reisberg Scale. The table below shows a patient’s average life expectancy by the stage of dementia. These are averages based on studies of large numbers of Alzheimer’s patients.
How long does it take to live with Alzheimer's?
The average number of years a person lives with Alzheimer’s disease is about 10. Keep in mind, however, that there’s a gap between when symptoms begin and when a diagnosis is actually sought.
How does knowing how quickly a disease is expected to progress affect care decisions?
Knowing how quickly the disease is expected to progress symptomatically can impact care decisions. If the disease is predicted to come on very quickly, for example, then skipping traditional assisted living and looking into memory care or a nursing home might be the best option.
How long does dementia last?
Others succumb to another disease, such as heart disease or cancer. End-stage dementia lasts approximately 1 to 3 years.
How long does a person live with vascular dementia?
Average life expectancy for a person with vascular dementia is 5 years following diagnosis. Dementia prognosis and life expectancy can vary greatly. Taking steps to improve your overall health may slow the progression of symptoms. Your healthcare provider will help you manage dementia with medicine to preserve mental function ...
How long does it take to live with Lewy body dementia?
Life expectancy for a person with Lewy body dementia is approximately 2 to 8 years after the onset of noticeable symptoms.
What is the prognosis of vascular dementia?
Vascular dementia is caused by changes to the brain’s blood supply. It can be caused by a series of small strokes over time. Vascular dementia is the second most common cause of dementia after Alzheimer’s disease.
What is the role of caregivers in dementia?
Your healthcare provider will help you manage dementia with medicine to preserve mental function and help with behavioral changes. At the end of mid-stage dementia, most people need round-the-clock care, so the caregiver plays an important role at the end of life.
How long does it take to live with Alzheimer's?
According to the Alzheimer’s Association, on average, a person with Alzheimer’s lives 4 to 8 years after diagnosis. However, some people live with dementia for 20 years.
What is the end stage of dementia?
In the end-stage of dementia, most people rely on others to dress and bathe them; assistance with eating is also necessary and some patients have trouble swallowing food and drink. They are susceptible to infection, including pneumonia and urinary tract infections.
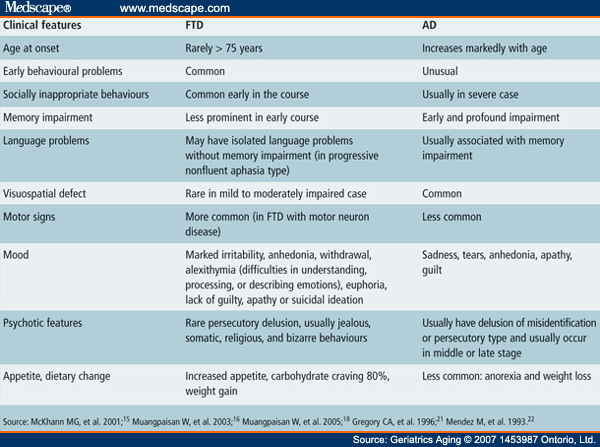
What Is Frontal Lobe Dementia?
Signs and Symptoms?
Life Expectancy and Treatment