What is the limbic system of the brain responsible for?
What Is the Limbic System?
- Limbic System and Hippocampus Function and Structure. The limbic system sits atop the brain stem, which is believed to be one of the first parts of the brain to develop, ...
- Limbic System Disorders. ...
- Emotional and Psychological Link to the Limbic System. ...
- Essential Oils and the Limbic System. ...
- Interesting Facts and History of the Limbic System. ...
What does the limbic portion of your brain do?
The limbic system is a connection of many brain structures that help control emotions, in addition to memory, learning, motivation, and bodily functions like appetite and sex drive. Subparts of the limbic system include the hippocampus, amygdala and hypothalamus.
Where is the limbic system located in the brain?
- Limbic lobe
- Orbitofrontal cortex: a region in the frontal lobe involved in the process of decision-making
- Piriform cortex: part of the olfactory system
- Entorhinal cortex: related to memory and associative components
What are the 10 parts of the brain?
Brain Part Number Brain Part; 1: amygdala: 4: cerebellum: 2: hippocampus: 5: basal ganglia: 3: language areas (Broca's and Wernicke's area) 6: hypothamalus

What are the 3 main functions of the limbic system?
The limbic system functions to facilitate memory storage and retrieval, establish emotional states, and link the conscious, intellectual functions of the cerebral cortex with the unconscious, autonomic functions of the brain stem.
How does the limbic system affect emotions?
Emotions: limbic system. The limbic system is a set of structures in the brain that deal with emotions and memory. It regulates autonomic or endocrine function in response to emotional stimuli and also is involved in reinforcing behavior .
Where is the limbic area of the brain?
The limbic system is a set of evolutionarily basic or primitive brain structures located on top of the brainstem and buried under the cortex. The limbic system is another subcortical structure that consists of structures and nerve fibers located deep within the cerebrum.
What happens if limbic system is damaged?
Language issues: Some people with limbic lobe damage experience a condition called aphasia, which interferes with their ability to speak, understand language, or both. Changes in mood, personality, or impulse control. Disruptions in autobiographical or working memory that may change personality or behavior.
What disorders are associated with the limbic system?
A dysfunctional limbic system is associated with many clinical manifestations, such as epilepsy, limbic encephalitis, dementia, anxiety disorder, schizophrenia, and autism.
What causes limbic system dysfunction?
Dysfunction, whether from genetics, trauma (physical or emotional), underlying health issues, toxicity, illness, inflammation, or other physical factors, can cause a number of symptoms, including (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6): Strong reactions to mild stimuli from sounds, light, fragrance, touch, stress, etc.
What does limbic mean?
Definition of limbic system : a group of subcortical structures (such as the hypothalamus, the hippocampus, and the amygdala) of the brain that are concerned especially with emotion and motivation.
What does the limbic cortex do?
As a whole, the limbic cortex serves as an association area for behavioral regulation acting to coordinate the exchange of information between higher regions within the neocortex and the subcortical limbic structures.
Which brain part controls emotions?
The limbic system is a group of interconnected structures located deep within the brain. It's the part of the brain that's responsible for behavioral and emotional responses.
How do you fix your limbic system?
Meditation and mindful movement practices, including yoga and Qi Gong, can also facilitate brain and body healing by lowering limbic system activation, enabling the body to enter the parasympathetic “rest, digest, and repair” state that is so essential for healing.
Can a damaged limbic system be repaired?
The amazingly wonderful associated discovery is that our brains are quite capable to “rewire” and recover using the principle of NeuroPlasticity. This literally means that the brain can learn to reroute and reprogram the damaged areas allowing the associated symptoms to lessen and in many cases disappear.
Can you survive without limbic system?
We couldn't live without it. Here are some examples of diseases that can occur if you injure any of the structures that make up this system: Alzheimer's: produced by a degeneration of different brain structures, especially the hippocampus. Causes progressive loss of memory among other symptoms.
What is the limbic system?
The limbic system is a collection of structures involved in processing emotion and memory, including the hippocampus, the amygdala, and the hypothalamus. The limbic system is located within the cerebrum of the brain, immediately below the temporal lobes, and buried under the cerebral cortex (the cortex is the outermost part of the brain).
What are the functions of the limbic system?
These structures are known to be involved in the processing and regulating of emotions, the formation and storage of memories, sexual arousal, and learning.
What are the two structures of the limbic system?
There are two widely accepted structures of the limbic system: the hippocampus and the amygdala. There are differing opinions as to which other structures are included in the system, and what only interacts closely with it.
How many layers are there in the limbic system?
The nerve cells (neurons) within the limbic system are structured differently to those in the cerebral cortex. In the cerebral cortex, the cells are mostly neocortical, meaning they are formed into six layers. Within the limbic system, the cells are either arranged in fewer layers or are more jumbled.
How does the amygdala affect the fight or flight response?
Therefore, the amygdala is also linked with the fight-or-flight response, as stimulating activity in the amygdala can influence the body’s automatic fear response.
What happens if you damage the hippocampus?
Damage to the hippocampus could lead to deficits in being able to learn anything new, as well as affecting memory. Hypothalamus damage can affect the production of certain hormones, including those which can affect mood and emotion. Below is a non-exhaustive list of symptoms associated with limbic system damage:
What is the treatment for limbic impairments?
Alzheimer’s disease. Movement disorders – Huntington’s and Parkinson’s disease. A potential treatment for limbic impairments is deep brain stimulation (DBS). Successful treatment of some cognitive disorders such as anxiety and posttraumatic stress disorder has come from DBS of the amygdala.
What is the name of the brain that contains the limbic system?
The paleopallium or intermediate ("old mammalian") brain, comprising the structures of the limbic system. The neopallium, also known as the superior or rational ("new mammalian") brain, comprises almost the whole of the hemispheres (made up of a more recent type of cortex, called neocortex) and some subcortical neuronal groups.
Where is the limbic system located?
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain. It supports a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, long-term memory, and olfaction.
What are the structures of the limbic system?
The structures and interacting areas of the limbic system are involved in motivation, emotion, learning, and memory. The limbic system is where the subcortical structures meet the cerebral cortex. The limbic system operates by influencing the endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system.
What is the limbic system?
MacLean as a series of cortical structures surrounding the boundary between the cerebral hemispheres and the brainstem. The name "limbic" comes from the Latin word for the border, limbus, and these structures were known together as the limbic lobe.
Which part of the brain is responsible for the limbic system?
Hypothalamus: a center for the limbic system, connected with the frontal lobes, septal nuclei, and the brain stem reticular formation via the medial forebrain bundle, with the hippocampus via the fornix, and with the thalamus via the mammillothalamic fasciculus; regulates many autonomic processes.
Which of the following structures is part of the limbic system?
The following structures are, or have been considered, part of the limbic system: Cortical areas: Limbic lobe. Orbitofrontal cortex: a region in the frontal lobe involved in the process of decision-making. Piriform cortex: part of the olfactory system. Entorhinal cortex: related to memory and associative components.
What is the oldest basal nucleus?
The archipallium or primitive ("reptilian") brain, comprising the structures of the brain stem – medulla, pons, cerebellum, mesencephalon, the oldest basal nuclei – the globus pallidus and the olfactory bulbs. The paleopallium or intermediate ("old mammalian") brain, comprising the structures of the limbic system.
What is the limbic system?
The limbic system is the part of the brain involved in our behavioural and emotional responses, especially when it comes to behaviours we need for survival: feeding, reproduction and caring for our young, and fight or flight responses. You can find the structures of the limbic system buried deep within the brain, ...
Which structure is responsible for the limbic system?
The thalamus, hypothalamus (production of important hormones and regulation of thirst, hunger, mood etc) and basal ganglia (reward processing, habit formation, movement and learning) are also involved in the actions of the limbic system, but two of the major structures are the hippocampus and the amygdala.
What is the role of the amygdala in anxiety?
Suppressing or stimulating activity in the amygdala can influence the body’s automatic fear response, which kicks in when something unpleasant happens, such as a startling noise. Through this research, QBI scientists have identified receptors in the amygdala that could help to develop new types of anti-anxiety drugs.
Why is the hippocampus important?
The hippocampus is also important for spatial orientation and our ability to navigate the world. The hippocampus is one site in the brain where new neurons are made from adult stem cells. This process is called neurogenesis, and is the basis of one type of brain plasticity.
What is the shape of the hippocampus?
The hippocampus, like many other structures in the brain, comes as a pair, one in each hemisphere of the brain. It resembles the shape of a curvy seahorse (and is named after its scientific genus) and is essentially the memory centre of our brains.
What is the role of the amygdala in our emotional response?
Located right next to the hippocampus, the left and right amygdalae play a central role in our emotional responses, including feelings like pleasure, fear, anxiety and anger.
Does the amygdala modify memories?
Memories that have strong emotional meaning tend to stick. The amygdala doesn't just modify the strength and emotional content of memories; it also plays a key role in forming new memories specifically related to fear. Fearful memories are able to be formed after only a few repetitions.
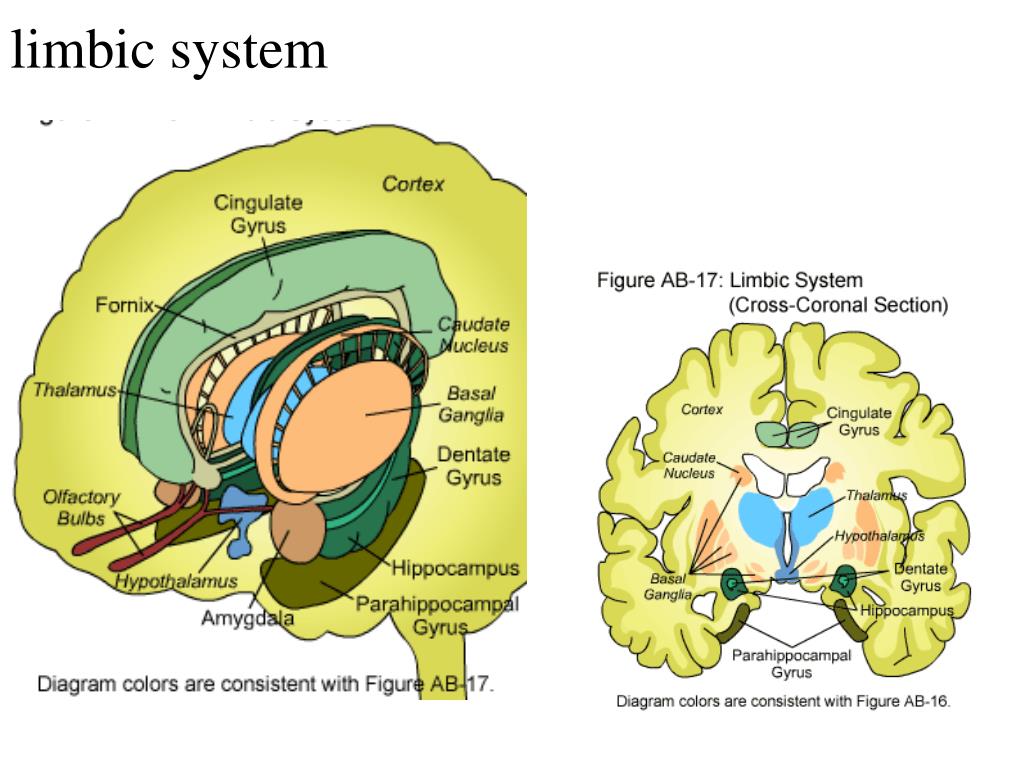
What are the parts of the limbic system?
Parts of the Limbic System. The limbic system is the portion of the brain that deals with three key functions: emotions, memories and arousal (or stimulation). This system is composed of several parts, which are found above the brainstem and within the cerebrum. The limbic system connects parts of the brain that deal with high and low functions.
Which part of the limbic system is responsible for producing multiple chemical messengers?
Next, we have the hypothalamus, which is a vital portion of the limbic system that is responsible for producing multiple chemical messengers, called hormones. These hormones control water levels in the body, sleep cycles, body temperature and food intake. The hypothalamus is located beneath the thalamus.
What are the roles of amygdalae in the development of memories?
Both amygdalae are responsible for preparing the body for emergency situations , such as being 'startled,' and for storing memories of events for future recognition. Amygdalae assist in the development of memories, particularly those related to emotional events and emergencies. The amygdalae are also involved specifically with the development ...
Which part of the temporal lobe is responsible for converting short term memories into long term memories?
The hippocampus is another section of the temporal lobe that is responsible for converting short-term memories into long-termed memories. The hippocampus is thought to work with the amygdala for memory storage, and damage to the hippocampus may lead to amnesia (or memory loss).
Where is the hypothalamus located?
The hypothalamus is located beneath the thalamus. The cingulate gyrus, meanwhile, serves as a pathway that transmits messages between the inner and outer portions of the limbic system. The amygdala is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nerve cells in the temporal (or side) lobe of the cerebrum.
Which system controls emotion, memories, and arousal?
Lesson Summary. The limbic system is a set of structures in the brain that controls emotion, memories and arousal. It contains regions that detect fear, control bodily functions and perceive sensory information (among other things).
Which system deals with instincts?
Therefore, many of the functions of the limbic system deal with instincts, rather than learned behaviors. (Note: This does not mean that memories will not play a role in learned behaviors, but it does mean that the primary functions will be instinctive.)
What is the limbic system?
The limbic system was once thought to be a discrete set of brain structures, but now we know that the limbic system involves a complex range of brain structures, as well as the hormones that affect these structures.
How does the limbic lobe work?
How the Limbic Lobe Works With Other Structures. The limbic lobe and the various brain organs and regions it involves relies heavily on sensory input. Indeed, without such input, the limbic lobe can do little. Some of the myriad complicated ways it interacts with other regions of the body include:
What are the components of the limbic lobe?
Key components of the limbic lobe include the amygdala, hippocampus, mamillary body, and cingulate gyrus. Other structures that are often attributed to the limbic lobe include: paraterminal gyrus. subcallosal area. parahippocampal gyrus. dentate gyrus. subiculum.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for the development of unconscious associations?
Processing sensory input from the eyes, ears, mouth, and skin, and applying meaning to that input. The limbic lobe also helps with the development of unconscious associations, such as the unconscious association between certain sights and smells and danger, pleasure, or other emotions.
Which lobe of the brain is a C-shaped region that crosses the brain hemispheres within
For this reason, a number of references may use the two terms interchangeably. The limbic lobe is a C-shaped region that crosses brain hemispheres within the cortex, including portions of the temporal, parietal, and frontal lobes. All mammals have a limbic lobe. Which parts of the brain make up the limbic lobe is a subject for some debate, ...
Which lobe of the brain is a discrete set of brain structures?
So too can a scent, a sound, or a visual image that calls to mind a memory. The limbic lobe, by contrast, is a discrete set of brain structures—the same structures once thought to constitute the entirety of the limbic system. For this reason, a number of references may use the two terms interchangeably. The limbic lobe is a C-shaped region that ...
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for memory, learning, motivation, and emotion?
Limbic Lobe. The limbic lobe is not a single brain structure, but rather an interacting group of brain structures that includes portions of each lobe of the cerebral cortex. This C-shaped brain region is vital for the functioning of memory, learning, motivation, and emotion, as well as endocrine functions and some autonomic—automatic, ...
Where is the limbic cortex located?
The limbic cortex is located in the medial temporal lobe of the brain. It is closely related to memory. Specifically, with the consolidation and recovery of declarative memories: both episodic and semantic. In addition, like the fornix, it plays an important role in sending information between different brain structures.
Why is the limbic system called the limbic lobe?
The first time the limbic system was discussed, though in a less conceptualized and more primitive way than we do now, it was because Paul Broca named an area near the pineal gland. Out of “limb” or border, he called it the area of “the great limbic lobe”. Hence the logic of its name, because it is situated in the limbo or edge ...
What are the functions of the limbic system?
As we said before, not all neurologists and neuropsychologists agree on the composition of the limbic system, since its functions are so complex. Therefore, some professionals may also include the following structures in an explanation of its operation: 1 Circumvolution of the cingulate: provides a pathway from the thalamus to the hippocampus and is associated with olfactory memory and the memory of pain. 2 Septal area: participates in the inhibition of the limbic system and the alert level when selective attention requires it. It also seems to intervene to relate memory, motivation, emotion, and alertness, modulating pleasurable sensations and external activation states. 3 Ventral tegmental area: considered one of the centers of reinforcement par excellence, thus intervening in the regulation of pleasure and addictions.
What is the arc of the hippocampus?
Fornix. The fornix is a bundle of axons in the shape of an arc that connects the hippocampus with other brain regions. It plays a role in the limbic system and connects to the mammillary bodies and the hippocampus. Thus, this arc is the main structure responsible for transmitting information between the most important structures ...
Why is the hypothalamus important?
Because it is responsible for our autonomic nervous system and our endocrine system. It also organizes the most important behaviors linked to the survival of the species: fight, flight, feeding, and reproduction. One of the most important structures of the hypothalamus when it comes to the functioning of the limbic system are the mammillary bodies.
What did MacLean think of the limbic system?
MacLean expanded the number of structures that make up the limbic system. He considered that the development of the cerebral cortex was just as important in our evolution as the development of our emotional brain. “Happiness is a mental state activated by the limbic system.”. -Antonio Damasio-.
Which area of the brain is associated with olfactory memory and the memory of pain?
Circumvolution of the cingulate: provides a pathway from the thalamus to the hippocampus and is associated with olfactory memory and the memory of pain. Septal area: participates in the inhibition of the limbic system and the alert level when selective attention requires it.

Overview
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.
It supports a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it critically aids the formation of memo…
Structure
The limbic system was originally defined by Paul D. MacLean as a series of cortical structures surrounding the boundary between the cerebral hemispheres and the brainstem. The name "limbic" comes from the Latin word for the border, limbus, and these structures were known together as the limbic lobe. Further studies began to associate these areas with emotional and motivational processes and linked them to subcortical components that were then grouped into the limbic sys…
Function
The structures and interacting areas of the limbic system are involved in motivation, emotion, learning, and memory. The limbic system is where the subcortical structures meet the cerebral cortex. The limbic system operates by influencing the endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system. It is highly interconnected with the nucleus accumbens, which plays a role in sexual arousal and the "high" derived from certain recreational drugs. These responses are heavil…
Evolution
Paul D. MacLean, as part of his triune brain theory, hypothesized that the limbic system is older than other parts of the forebrain, and that it developed to manage circuitry attributed to the fight or flight first identified by Hans Selye in his report of the General Adaptation Syndrome in 1936. It may be considered a part of survival adaptation in reptiles as well as mammals (including humans). MacLean postulated that the human brain has evolved three components, that evolve…
History
The term limbic comes from the Latin limbus, for "border" or "edge", or, particularly in medical terminology, a border of an anatomical component. Paul Broca coined the term based on its physical location in the brain, sandwiched between two functionally different components.
The limbic system is a term that was introduced in 1949 by the American physician and neuroscientist, Paul D. MacLean. The French physician Paul Broca first called this part of the brai…
See also
• Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (LHPA axis)
• Emotional memory
• Fundamentals of Neuroscience at Wikiversity
• Paralimbic cortex
External links
• Media related to Limbic system at Wikimedia Commons
• http://biology.about.com/od/anatomy/a/aa042205a.htm
• https://qbi.uq.edu.au/brain/brain-anatomy/limbic-system