
What are the major functions of the limbic system?
The limbic system is a part of the brain that deals with three major functions:
- Emotions
- Memories
- Arousal
What is the limbic system and what is its function?
- Limbic lobe
- Orbitofrontal cortex: a region in the frontal lobe involved in the process of decision-making
- Piriform cortex: part of the olfactory system
- Entorhinal cortex: related to memory and associative components
How to stimulate the limbic system?
Limbic Retraining: 10 Strategies to Improve Limbic System Function
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet. One of the best strategies for improving symptoms of limbic dysfunction is to consume an anti-inflammatory diet.
- Manage Stress Levels. Stress is one of the leading factors in cognitive dysfunction. ...
- Address Chronic Infections. ...
- Avoid Mold Toxicity. ...
- Reduce EMF Exposure. ...
- Increase Omega-3 Intake. ...
- Reduce Toxin Exposure. ...
What is the limbic system responsible for?
The limbic system is responsible for controlling our emotions, along with other important bodily functions. When this system is not working properly, it can cause a variety of emotional and physical problems. The limbic system function is essential for our overall health and well-being.

What are the 3 main functions of the limbic system?
The limbic system functions to facilitate memory storage and retrieval, establish emotional states, and link the conscious, intellectual functions of the cerebral cortex with the unconscious, autonomic functions of the brain stem.
What is the role of the limbic system in emotion?
Emotions: limbic system. The limbic system is a set of structures in the brain that deal with emotions and memory. It regulates autonomic or endocrine function in response to emotional stimuli and also is involved in reinforcing behavior .
How is the limbic system important in behavior?
The limbic system predominantly controls appropriate responses to stimuli with social, emotional, or motivational salience, which includes innate behaviors such as mating, aggression, and defense.
What happens if limbic system is damaged?
Effects of Limbic System Damage on Emotions For example, high levels of the thyrotropin-releasing hormone could cause fatigue and depression, according to the Endocrine Society. Damage to the structures comprising the limbic system may also affect certain emotions, including aggression, anxiety, pleasure, and anger.
Can you live without a limbic system?
It's rare that the entire limbic system will be damaged, but in that case, if the affected individual does survive, he will heavily suffer from many emotional and physical conditions, including memory impairments, epilepsy, anxiety and depression, and will experience continuous emotional stress.
What behaviors are controlled by the limbic system?
The limbic system is the part of the brain involved in our behavioural and emotional responses, especially when it comes to behaviours we need for survival: feeding, reproduction and caring for our young, and fight or flight responses.
How do you strengthen your limbic system?
Train Fitness recommends a fitness regime of 20-30 minutes, 3-5 times a week to help maintain the health of your limbic system. Further research suggests that aerobic exercises such as cardio, swimming, running, walking, and hiking are particularly beneficial to charging up your brainpower.
What are the five F's of the limbic system?
The 'fight or flight' response is how people sometimes refer to our body's automatic reactions to fear.
What is the role of the limbic system quizlet?
Limbic System: involved with regulating many motivational behaviors such as obtaining food, drink, and sex with organizing emotional behaviors such as fear, anger and aggression and with storing memories.
What part of the limbic system controls emotion and memory?
AmygdalaAmygdala: Limbic structure involved in many brain functions, including emotion, learning and memory. It is part of a system that processes "reflexive" emotions like fear and anxiety.
What Does the Limbic System Do?
The limbic system serves a variety of fundamental cognitive and emotional functions. The hippocampi, which lay on the inside edge of the temporal lobes, is essential to memory formation. The amygdalae sit on top of the front portion of each hippocampus. Each amygdala is thought to be important in processing emotion. The amygdala communicates closely with the hippocampus, which helps explain why we remember things that are more emotionally important. The amygdala also communicates closely with the hypothalamus, the area of the brain that is responsible for regulating temperature, appetite, and several other basic processes required for life. The hypothalamus itself is sometimes, but not always, included as part of the limbic system. Through the hypothalamus, as well as some key areas in the brainstem, the limbic system communicates with our autonomic nervous system (which regulates things like heartbeat and blood pressure), endocrine system, and the viscera (or “gut”).
Which structures are included in the limbic system?
It is still meant to include structures between the cortex and the hypothalamus and brainstem, but different specialists have included different structures as part of the limbic system. The amygdala and hippocampus are widely included, as is the olfactory cortex. From there, however, opinions diverge as to what is considered part ...
What are some examples of paralimbic structures?
Examples of paralimbic structures include the cingulate gyrus, orbitofrontal cortex, temporal pole, and part of the insula.
What are the mammillary bodies and the thalamic nuclei?
The mammillary bodies and some thalamic nuclei are important to the formation of new memories. All of these pathways are intricately connected. The amygdala, for example, communicates to the orbitofrontal pathway through a white matter bundle called the uncinate fasciculus, as does the insula.
What is paralimbic in psychology?
From there, however, opinions diverge as to what is considered part of the limbic system, and what is paralimbic, meaning a structure that interacts closely with the limbic system but is not truly part of it.
Which part of the brain is responsible for communicating with the hippocampus?
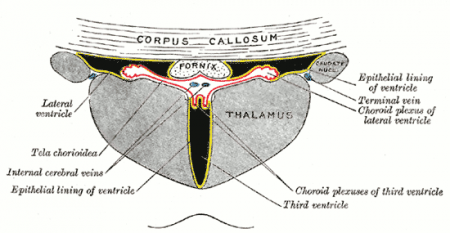
The hippocampus largely communicates through a large white matter pathway called the fornix , which curves around the ventricles of the brain towards the mammillary bodies, sending out branches to the mammillary bodies, thalamus, and cingulate along the way. The limbic system is a heterogeneous group of structures and serves many different functions.
Which part of the brain is considered paralimbic?
The basal forebrain, nucleus accumbens, mammillary bodies and parts of the thalamus (the anterior and mediodorsal nuclei) are also often considered paralimbic structures due to their close interaction with the limbic system. Each of these paralimbic structures has been connected with emotion or basic cognitive processes.
What is the limbic system?
MacLean as a series of cortical structures surrounding the boundary between the cerebral hemispheres and the brainstem. The name "limbic" comes from the Latin word for the border, limbus, and these structures were known together as the limbic lobe.
Where is the limbic system located?
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain. It supports a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, long-term memory, and olfaction.
What is the name of the brain that contains the limbic system?
The paleopallium or intermediate ("old mammalian") brain, comprising the structures of the limbic system. The neopallium, also known as the superior or rational ("new mammalian") brain, comprises almost the whole of the hemispheres (made up of a more recent type of cortex, called neocortex) and some subcortical neuronal groups.
What are the structures of the limbic system?
The structures and interacting areas of the limbic system are involved in motivation, emotion, learning, and memory. The limbic system is where the subcortical structures meet the cerebral cortex. The limbic system operates by influencing the endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system.
Which of the following structures is part of the limbic system?
The following structures are, or have been considered, part of the limbic system: Cortical areas: Limbic lobe. Orbitofrontal cortex: a region in the frontal lobe involved in the process of decision-making. Piriform cortex: part of the olfactory system. Entorhinal cortex: related to memory and associative components.
Which system is involved in lower order emotional processing of input from sensory systems?
With a primordial structure, the limbic system is involved in lower order emotional processing of input from sensory systems and consists of the amygdaloid nuclear complex ( amygdala ), mammillary bodies, stria medullaris, central gray and dorsal and ventral nuclei of Gudden.
Where does the term limbic come from?
The term limbic comes from the Latin limbus, for "border" or "edge", or, particularly in medical terminology, a border of an anatomical component. Paul Broca coined the term based on its physical location in the brain, sandwiched between two functionally different components. The limbic system is a term that was introduced in 1949 by ...
What is the limbic system?
Although not empirically proven, the limbic system is a functional concept which may be employed to explain various brain functions .[1]
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for emotion?
Paul Pierre Broca in 1878 spoke of ‘le grand lobe limbique’or the great limbic lobe and applied the term “limbic” (from the Latin limbusfor border) to the curved rim of the cortex which incudes the cingulate and the parahippocampal gyri. However, its putative role in emotion was elaborated by the American physician, James Papez in 1937 in the seminal paper titled ‘A proposed mechanism of emotion’. This anatomical model is referred to as the Papez circuit.[2] Yakovlev in 1948 proposed Yakovlev's circuit in the control of emotion involving the orbitofrontal, insular and anterior temporal lobe cortex, the amygdala and the dorsomedial nucleus of thalamus.[3] In 1952, Paul D. MacLean coined the term “limbic system” to describe Broca's limbic lobe and related subcortical nuclei as the collective neural substrate for emotion.[1] MacLean was also instrumental in proposing and defining the Triune concept of the brain. MacLean's evolutionary “Triune brain theory” proposed that the human brain was in reality three brains in one: the R-complex (reptilian complex), the limbic system and the neocortex.[4] The concept of the limbic system has since been further expanded and developed by Nauta, Heimer and others.
Which gyrus is associated with the corpus callosum?
The cingulate gyrus (Latin = Belt ridge) dorsal to the corpus callosum is heavily interconnected with the association areas of the cerebral cortex. The parahippocampal gyrus in the medial temporal lobe contains several distinct regions, the most important being the entorhinal cortex (ERC). The ERC funnels highly processed cortical information to the hippocampal formation and serves as its major output pathway.[5]
Which lobe is located at the inferomedial aspect of the cerebral hemispheres?
The limbic lobe situated at the inferomedial aspect of the cerebral hemispheres, consists of two concentric gyri surrounding the corpus callosum. Broca proposed that the larger outer gyrus be named “limbic gyrus” and the smaller inner one “the intralimbic gyrus”. The limbic gyrus (limbic lobe) consists of the isthmus of the cingulate gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus (both of which are continuous via a bundle of white matter called “cingulum”) and the subcallosal area.[6]
How many zones are there in the hippocampal lobe?
Hippocampal formation in the temporal lobe has three distinct zones:
Where is the amygdala located?
Identified by Burdach in the early 19thcentury, amygdala, an almond-shaped structure deep within the temporal lobe, is a collection of nuclei lying beneath the uncus. Lying at the anterior end of the hippocampal formation and the anterior tip of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle, it merges with the periamygdaloid cortex, which forms part of the surface of the uncus. The amygdaloid complex is structurally diverse and comprises of approximately 13 nuclei. These are further divided into subdivisions that have extensive internuclear and intranuclear connections. The major groups are:
Which part of the brain is responsible for relaying information about social signals?
This circuit is relayed via the basolateral amygdala. This circuit consists of the orbitofrontal and anterior temporal cortex, amygdala (especially the basolateral amygdala) and magnocellular division of the dorsomedial nucleus of the thalamus (frontothalamic pathway), which relays back to the orbitofrontal cortex.[11] This circuit encodes information about social signals and social plans for social acts. The circuit has been proposed as a substrate for the human ability to infer the intentions of others from their language, gaze and gestures (Theory of mind and social cognition)[Figure 6].[12]
What are the functions of the limbic system?
These structures are known to be involved in the processing and regulating of emotions, the formation and storage of memories, sexual arousal, and learning.
Why is the limbic system important?
The limbic system is thought to be an important element in the body’s response to stress, being highly connected to the endocrine and autonomic nervous systems . If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations.
What are the two structures of the limbic system?
There are two widely accepted structures of the limbic system: the hippocampus and the amygdala. There are differing opinions as to which other structures are included in the system, and what only interacts closely with it.
How many layers are there in the limbic system?
The nerve cells (neurons) within the limbic system are structured differently to those in the cerebral cortex. In the cerebral cortex, the cells are mostly neocortical, meaning they are formed into six layers. Within the limbic system, the cells are either arranged in fewer layers or are more jumbled.
What happens if you damage the hippocampus?
Damage to the hippocampus could lead to deficits in being able to learn anything new, as well as affecting memory. Hypothalamus damage can affect the production of certain hormones, including those which can affect mood and emotion. Below is a non-exhaustive list of symptoms associated with limbic system damage:
What is the effect of the basal ganglia on the limbic system?
In relation to the limbic system, the basal ganglia may also contribute to depression (Stathis et al., 2007).
What is the limbic system?
The limbic system is a collection of structures involved in processing emotion and memory, including the hippocampus, the amygdala, and the hypothalamus. The limbic system is located within the cerebrum of the brain, immediately below the temporal lobes, and buried under the cerebral cortex (the cortex is the outermost part of the brain).
Why is the limbic system important?
Because subparts of the limbic system ultimately regulate important aspects of our conscious and unconscious patterns — including our emotions, perceptions, relationships, behaviors and motor control — it’s easy to see why damage to this region can cause serious problems. Disorders or behaviors that are related to limbic system dysfunction, or sometimes limbic system damage due to things like traumatic injuries or aging, include: ( 4)
What is the limbic system?
The limbic system is one hard-working region of the brain, as you can tell. Some specific limbic system functions include: Controlling emotions like anger and fear. Regulating eating, hunger and thirst. Responding to pain and pleasure.
How does the limbic system affect the body?
One important way that the limbic system impacts emotional health is through carrying sensory input from the environment to the hypothalamus and then from the hypothalamus to other parts of the body. The hypothalamus acts like the “regulator” of hormone control, helps the body maintain homeostasis and send signals to the pituitary/thyroid/adrenal glands. It receives information from many body parts, including the heart, vagus nerve, gut/digestive system and skin.
How to maintain homeostasis in the limbic system?
In order to maintain homeostasis and feel your best, the goal is to balance activities of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. Too much activation of one causes high amounts of anxiety, but too much of the other causes low motivation and symptoms like fatigue.
How does essential oil affect limbic function?
This is true because the strong fragrances they hold, which are found inside volatile molecules that can make their way into your bloodstream, travel directly through the blood/brain barrier very quickly.
What is the function of the hippocampus?
Functions of the hippocampus include: ( 3) Forming short-term and long-term memories through consolidating information. Learning new skills from reward, punishment, reinforcement and failure.
Which system controls emotions?
While the entire central nervous system helps control our emotions, as you’ll learn, activities in the limbic system and autonomic nervous system are especially influential over our emotional health. The entire limbic system — including subparts like the hippocampus, hypothalamus and amygdala — helps control numerous emotional, voluntary, ...
What are the functions of the limbic system?
As we said before, not all neurologists and neuropsychologists agree on the composition of the limbic system, since its functions are so complex. Therefore, some professionals may also include the following structures in an explanation of its operation: 1 Circumvolution of the cingulate: provides a pathway from the thalamus to the hippocampus and is associated with olfactory memory and the memory of pain. 2 Septal area: participates in the inhibition of the limbic system and the alert level when selective attention requires it. It also seems to intervene to relate memory, motivation, emotion, and alertness, modulating pleasurable sensations and external activation states. 3 Ventral tegmental area: considered one of the centers of reinforcement par excellence, thus intervening in the regulation of pleasure and addictions.
Why is the limbic system called the limbic lobe?
The first time the limbic system was discussed, though in a less conceptualized and more primitive way than we do now, it was because Paul Broca named an area near the pineal gland. Out of “limb” or border, he called it the area of “the great limbic lobe”. Hence the logic of its name, because it is situated in the limbo or edge ...
What are the main structures of the limbic system?
The limbic system is composed of many brain structures, all interconnected. This makes it difficult to determine precisely what structures form it and the concrete job of each structure. However, studies suggest that the structures that make up the limbic system and its functions are the following:
What is the arc of the hippocampus?
Fornix. The fornix is a bundle of axons in the shape of an arc that connects the hippocampus with other brain regions. It plays a role in the limbic system and connects to the mammillary bodies and the hippocampus. Thus, this arc is the main structure responsible for transmitting information between the most important structures ...
What are the most important structures of the hypothalamus?
One of the most important structures of the hypothalamus when it comes to the functioning of the limbic system are the mammillary bodies. The mammillary bodies are a profusion of the fundus of the encephalon at ...
What did MacLean think of the limbic system?
MacLean expanded the number of structures that make up the limbic system. He considered that the development of the cerebral cortex was just as important in our evolution as the development of our emotional brain. “Happiness is a mental state activated by the limbic system.”. -Antonio Damasio-.
Which part of the brain is responsible for emotions?
Within the limbic system, the amygdala is the captain of our emotions. Not only that, but in conjunction with the hippocampus it also generates emotional memories. And then, together with the hypothalamus, it impregnates our basic processes with emotional color.
What Is the Limbic System?
As the term implies, the Limbic system is a set of structures in the brain that impacts emotions, learning, memory, and other behavioral patterns. Specific hormones that regulate the autonomic nervous system are also linked to this system. The brain structures are a part of the control system that resonates with the feelings and emotions connected to hunger, thirst, motivation and reward, and the fight or flight responses.
How Does Limbic Calming or Retraining Aid Development?
Limbic calming can help you help your child break the loop that promotes extreme emotional responses. Aggression, eating disorders, meltdowns, tantrums, fight or flight responses, stress, anxiety, fear, and many other issues can be handles from childhood itself. Small lifestyle changes can help retrain the child's emotional response so that he/she can avoid a physiological expression that leads to unwanted behavior patterns.
How does limbic training affect children?
Stress, depression, anxiety, and fear responses can damage the psychological reactions of the child, and limbic training can help reduce if not removing unwanted responses of the neuro-emotional nature. It could lead to the hope of near-normal social and emotional responses that could help your child develop naturally.
How to help a child break the limbic loop?
Meditation, both guided and non-guided, can also help your child break the limbic loop. Praying aloud, if that's something you practice in your home, can also help. Take a few minutes in the morning and at bedtime to practice this for best results.
What is the emotional nervous system?
Primitive emotion and higher mental functionality are combined into a single system that is often referred to as the emotional nervous system . The pleasure that you derive from eating, for example, comes from this 'pleasure center' in the brain. The emotional reaction to pain is also monitored by the Limbic system and helps in regulating aggressive behavior.
Which system controls stress and can be the catalyst for diseases like hypertension?
Sexual arousal and drug-induced 'highs' are felt through the function of the limbic system. This system also controls stress, and it can be the catalyst for diseases like hypertension.
What is neuroplasticity in therapy?
It is the route used by therapists to retrain the brain to form new neuronal networks to alter emotional responses. The process involves rewiring the neuronal pathways to change the physiological response to stress stimuli.
Overview
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.
It supports a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it critically aids the formation of memo…
Structure
The limbic system was originally defined by Paul D. MacLean as a series of cortical structures surrounding the boundary between the cerebral hemispheres and the brainstem. The name "limbic" comes from the Latin word for the border, limbus, and these structures were known together as the limbic lobe. Further studies began to associate these areas with emotional and motivational processes and linked them to subcortical components that were then grouped into the limbic sys…
Function
The structures and interacting areas of the limbic system are involved in motivation, emotion, learning, and memory. The limbic system is where the subcortical structures meet the cerebral cortex. The limbic system operates by influencing the endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system. It is highly interconnected with the nucleus accumbens, which plays a role in sexual arousal and the "high" derived from certain recreational drugs. These responses are heavil…
Evolution
Paul D. MacLean, as part of his triune brain theory, hypothesized that the limbic system is older than other parts of the forebrain, and that it developed to manage circuitry attributed to the fight or flight first identified by Hans Selye in his report of the General Adaptation Syndrome in 1936. It may be considered a part of survival adaptation in reptiles as well as mammals (including humans). MacLean postulated that the human brain has evolved three components, that evolve…
History
The term limbic comes from the Latin limbus, for "border" or "edge", or, particularly in medical terminology, a border of an anatomical component. Paul Broca coined the term based on its physical location in the brain, sandwiched between two functionally different components.
The limbic system is a term that was introduced in 1949 by the American physician and neuroscientist, Paul D. MacLean. The French physician Paul Broca first called this part of the brai…
See also
• Amygdala Hijack
• Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA axis)
• Emotional memory
• Fundamentals of Neuroscience at Wikiversity
External links
• Media related to Limbic system at Wikimedia Commons
• http://biology.about.com/od/anatomy/a/aa042205a.htm
• https://qbi.uq.edu.au/brain/brain-anatomy/limbic-system