Why must profits be zero in long-run competitive equilibrium?
As a result according to the zero profit condition, competitive firms in the long run equilibrium are compensated for their opportunity costs. That means there is no superior alternative for them so they have no incentive to go out of business. On the contrary, they may still generate substantial accounting profits.
What is long run equilibrium in perfect competition?
The long-run equilibrium point for a perfectly competitive market occurs where the demand curve (price) intersects the marginal cost (MC) curve and the minimum point of the average cost (AC) curve. Perfect Competition in the Long Run: In the long-run, economic profit cannot be sustained. Click to see full answer.
What is long run perfect competition?
Perfect competition, in the long run, is a hypothetical benchmark. For market structures such as monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly, which are more frequently observed in the real world than perfect competition, firms will not always produce at the minimum of average cost, nor will they always set price equal to marginal cost.
When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium,?
In the long run, the economic profits for a monopolistically competitive firm will be the same as the profits for a purely competitive firm. In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms make normal profits because they are forced to operate at the minimum point on their average total cost curve.
What happens in the long run in perfect competition?
In a perfectly competitive market, firms can only experience profits or losses in the short run. In the long run, profits and losses are eliminated because an infinite number of firms are producing infinitely divisible, homogeneous products.
What is meant by long run equilibrium?
In economics, the long-run is a theoretical concept in which all markets are in equilibrium, and all prices and quantities have fully adjusted and are in equilibrium. The long-run contrasts with the short-run, in which there are some constraints and markets are not fully in equilibrium.
How do you find long run equilibrium price in perfect competition?
0:368:18Perfect Competition: Long-run Equilibrium - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipProduct equals marginal cost equals average cost and the firm is producing where average cost isMoreProduct equals marginal cost equals average cost and the firm is producing where average cost is minimized as we're going to see the skin this is one of the keys for long-run equilibrium.
What is short and long run equilibrium?
Short-run equilibrium is when the aggregate amount of output is the same as the aggregate amount of demand. Long-run equilibrium is when prices adjust to changes in the market and the economy functions at its full potential.
What is the meaning of long run?
a long period of timeDefinition of the long run : a long period of time after the beginning of something investing for the long run Your solution may cause more problems over the long run. It may be our best option in the long run. This deal will cost you more in the long run.
What is the long run equilibrium price?
The long-run equilibrium price is simply MC(q∗)=2q∗ = 2 · 4 = 8. The market quantity is determined through the market demand, Qd(p∗) = 24 − p∗ = 24 − 8 = 16. The number of firms in the long-run n∗ = 16/4 = 4.
What is long run equilibrium graph?
6:5610:33Long-run Equilibrium in the AD-AS Model - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOr government spending increased I could cause our aggregate demand curve to shift out. Cause aMoreOr government spending increased I could cause our aggregate demand curve to shift out. Cause a short-run increase in the equilibrium level of output.
What is long run equilibrium quizlet?
the condition for a firm in long-run equilibrium in a perfectly competitive industry can be summarized as. P=MR=MC=ATC= minimum LARC, where LARC is the long-run average cost curve. if market demand increases or shifts to the right. market price rises.
What is the long run equilibrium?
The long-run equilibrium then refers to the situation when free and full adjustment in the capital equipment as well as in the number of firms has been allowed to take place.
What are the two conditions for a firm to be in long-run equilibrium?
It, therefore, follows that for a perfectly competitive firm to be in long-run equilibrium, the following two conditions must be fulfilled. 1. Price — Marginal Cost.
What happens if the price is lower than the OP?
If price is lower than OP, the average and marginal revenue curve will lie below the average cost curve so that the marginal cost and price will be equal at the point where the firm is making losses. Therefore, there will be tendency for some of the firms in the industry to go out with the result that price will rise and the firms left in the industry make normal profits.
What happens if the price is greater than the average cost?
If the price is greater than the average cost, the firms will earn more than normal profits. These supernormal profits will attract outer firms into the industry.
What is the long run?
The long run is a period of time which is sufficiently long to allow the firms to make changes in all factors of production. In the long run, all factors are variable and none fixed. The firms, in the long run, can increase their output by changing their capital equipment; they may expand their old plants or replace the old lower-capacity plants by ...
Why is it beneficial to work at optimum size?
Firstly, working at optimum size implies that the resources of the society are being utilised in the most efficient way. Secondly, it signifies that the consumers are getting the goods at the lowest possible price.
When is a firm in equilibrium?
As explained above, a firm is in equilibrium under perfect competition when marginal cost is equal to price. But for the firm to be in long-run equilibrium, besides marginal cost being equal to price, the price must also be equal to average cost.
How many equilibrium states does a competitive firm have?
Therefore, a competitive firm has four equilibrium states based on its period of operation. These are: Short-run equilibrium of a competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium of a competitive firm. Short-run equilibrium of a competitive industry.
How does perfect competition affect price?
Under Perfect Competition, we know that a firm is unable to affect the price of a product even if it modifies the quantity of its output. Also, in this market structure, the input and cost conditions are given. Therefore, a firm can change the quantity of the output of a product without affecting its price. The cost and revenue conditions of a firm determine its equilibrium state (maximum profits). In this article, we will talk about a firm’s long-run equilibrium under Perfect Competition.
What is the price of a firm's product?
The price of the firm’s product is equal to its optimum cost of production. If this price is OP1 with the average revenue curve AR 1 and the marginal revenue curve MR 1, then we can see that
What are the four equilibrium states?
Answer: The four equilibrium states are: Short-Run equilibrium of a Competitive Firm. Long-Run equilibrium of a Competitive Firm. Short-Run equilibrium of a Competitive Industry.
What is the long term of a firm?
Long-term is the period in which the firm can vary all of its inputs. There are no fixed costs and therefore, the AFC or Average Fixed Cost curve vanishes. Also, the Average Cost (AC) curve represents the Average Total Cost (ATC) curve. Further, since the firm can vary all its inputs, it can close own and leave the industry.
What is the long run of an AC curve?
We know that in the long-run, the AC curve which is formed by its short-run AC curves is also U-shaped. This means that up to a certain limit, the firm experiences increasing returns and the AC curve slopes downwards. A phase of constant returns follows in which the AC curve neither rises nor falls.
Which axis does AR curve run parallel to?
Further, its AR curve runs parallel to the X-axis and the MR curve coincides with it.
What is the difference between monopoly and long run equilibrium?
In long-run equilibrium under perfect competition, the price of the product becomes equal to the minimum long-run average cost (LAC) of the firm. In monopoly, on the other hand, long- run equilibrium occurs at the point of intersection between the monopolist’s marginal revenue (MR) and long-run marginal cost (LMC) curves.
What is the value of the marginal unit of the good to the consumer?
11.14 that at q = q*, the consumer is willing to pay p*, i.e., the value of the marginal unit of the good to the consumer is p* which is greater than the cost of production of the marginal unit , Eq*. Therefore, for the sake of efficiency, the good should be produced in a larger quantity till p reduces from p* to p c and output increases from q* to q c at the p = MC point, S, on the demand curve.
Is efficiency achieved at the long run equilibrium point of the competitive firm?
We may conclude, therefore, that efficiency from the point of view of society is achieved at the long-run equilibrium point of the competitive firm, and it is not achieved at the long-run equilibrium point of the monopolist. The reason is obvious. The latter possesses market power while the former does not.
Is p MC output efficient?
As we have seen, from the point of view of the society as a whole, the p = MC output, q c, is efficient and the MR = MC output, q*, is inefficient. Therefore, for the benefit of the society as a whole, the firm should produce q c and not q* of output. In order to ascertain this, let us suppose that the firm produces an output q = q*.
Is demand price equal to marginal cost?
In other words, in the long-run equilibrium, price is equal to marginal cost for the competitive firm and price is greater than marginal cost for the monopolistic firm. Now, under certain conditions, demand price for a commodity represents its marginal social valuation.
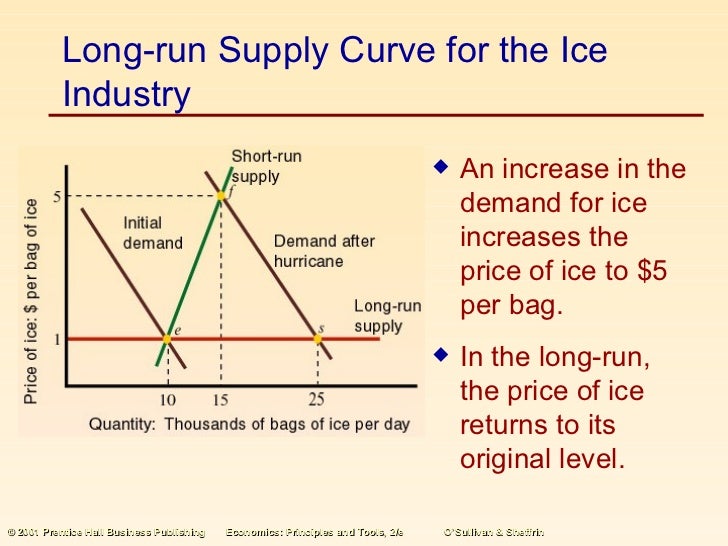
Where is the initial short run equilibrium?
i. The figure shows that initial short run equilibrium is at point e 1 where short run supply curve (S 1 S 2) intersects demand curve (D 1 D 2 ). At this point, equilibrium price is OP 1 and industry supply is OQ 1. This is also initial long run equilibrium and, hence, will be represented by a point on the long run supply curve.
How to find equilibrium of a firm?
There are two methods of finding equilibrium of a firm – TR-TC method and MR-MC method. Price determination in industry takes place through price mechanism, i.e., through interaction of demand and supply forces.
Why does the SMC curve above the SAVC curve only form its supply curve?
Now the question arises, why the SMC curve above the SAVC curve will only form its supply curve and why not the entire SMC curve? It is because of the fact that equilibrium is found where SMC = MR (= P). If the price is less than SAVC, firm will stop production and, hence, its supply will be zero. Thus, a firm’s market supply will be represented only by the SMC curve above the SAVC curve.
What is the equilibrium price of a market?
Demand is depicted as D 1 D 2 curve. The equilibrium market price is OP 1 in short period (as also in very short period) where the demand and supply intersects. The price so determined (OP 1) is followed by both the firms to find out their respective equilibrium.
How does the long run adjustment process affect the demand of inputs and, hence their prices?
The long run adjustment process will affect the demand of inputs and, hence their prices. If input demand increases, supply remaining the same, their respective price will rise leading a firm’s MC curve to shift to its left. It implies that firm will produce same output at a higher marginal cost.
What happens to industry supply when the firms are earning super normal profits in short run?
As a result, industry supply will increase pushing down the price. This will wipe out the super normal profits and ultimately all the firms will earn only normal profit at long run equilibrium.
What is initial equilibrium?
i. Initial equilibrium, interaction of demand (D 1 D 2) and supply (S 1 S 2) curves, is at point e 1 where the industry supply is OQ 1 at OP 1 price. It is the equilibrium applicable to both the short run and long run, to start with.
What is the long run?
The long run is a period of time which is sufficiently long to allow the firms to make changes in all factors of production. In the long run, all factors are variable and none fixed. The firms, in the long run, can increase their output by changing their capital equipment; they may expand their old plants or replace the old lower-capacity plants by the new higher-capacity plants
What is equilibrium in economics?
Equilibrium is a useful concept for predicting (or explaining) changes - unplanned and uncontrolled systems, such as free markets, move toward equilibrium, jus
What is the best level of output for a monopolist firm?
In case, the output is increased beyond OB, the MR < SMC. Hence, the increased outputs beyond OB adds more to total cost than to total receipts. This causes profits to decrease. So the best level of output for the monopolist firm is that where SMC curve cuts the MC curve from below.
What is the OE of a monopoly?
At point K both the equilibrium conditions are fulfilled. As a result, therefore, OE is monopoly price and OB, the monopoly output. At the monopoly output OB, the average total cost OF = BN. The profit per unit is FE. The short run monopoly profit is ETNF, It is represented by the area of shaded rectangle in figure 16.3.
How does a monopolist maximize profit?
A monopolist will maximize profit or minimize losses by producing that output for which marginal cost (MC) equals marginal revenue (MR). Whether a profit or loss is made or not depends upon the relation between price and average total cost (ATC). It may be made clear here that a monopolist does not necessarily makes profit. He may earn super profit or normal profit or even produce at a loss in the short ran.
How does a monopolist increase the price of a product?
In the short period, if the demand for the product is high, a monopolist increase the price and the quantity of output. He can increase the, output by hiring more labor, using more raw material, increasing working hours etc. However, he cannot change his fixed plant and equipment. In case, the demand for the product falls, he then decreases the use of variable inputs, (like labor, material etc.).
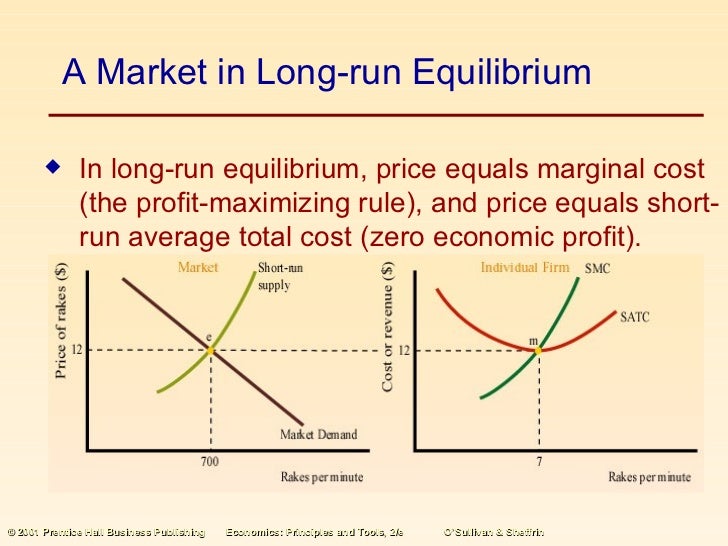
Why is the industry in equilibrium?
At the price P the industry is in equilibrium because profits are normal and all costs are covered so that there is no incentive for entry or exit. That the firms earn just normal profit (neither excess profits nor losses) is shown by the equality
What Is Perfect Competition?
An industry or market is said to be operating under perfect competition if the following conditions are satisfied:
When is industry in equilibrium?
In the long-run, industry is in equilibrium when there is no tendency to expansion or contraction. So all the firms should be earned just a normal profit. In this situation, all firms will be operating at the minimum point of the LAC curve.
What happens to the price of a product if the firms make losses inside the long-run?
If the firms make losses inside the long-run they may go away the industry. As a result, the price will rise and the demand curve will shift upward. The cost will go down and price curves shift downward. These changes will continue until the remaining corporations attain the minimum factor of the LAC curve.
What happens to firms that make losses in the short run?
Under the prevailing market price, the firms can make excess profit or losses. So the firms that make losses in the short-run will make necessary adjustments. Otherwise, they will close down the firm in the long-run. The firms that earn excess profit will expand the size of the firms to maximize their profit.
What happens if the SAC is below the price at the equilibrium?
If the SAC is below the price at the equilibriu m, the firm earns an excess profi t. But, if the SAC is highe r than the price at the equilibrium, the firm makes losses.
What happens if the price falls below the PW?
If the price falls below the Pw, (this price is equal to the minimum variable cost) the firm cannot cover all its variable cost, and hence, it will close down whereby minimizing the losses.
Can a firm make an excess profit in the short run?
However, it does not mean that the firms necessarily earn excess profit in the short-run. It depends on the level of the SAC (short-run average cost) in the short-run equilibrium.
Meaning of Industry
The group of firms producing homogenous products is called industry. Such firms are found only under perfect competition. An industry is in equilibrium when it has no tendency in change its size.
Equilibrium of an industry can be studies under two heads
The industry is in equilibrium at that price at which quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. But for industry to be in full equilibrium, in the short run, is very rare. Full equilibrium position is possible only when all firms earn just normal profit.

Equilibrium Under Perfect Competition – II
A Firm’S Long-Run Equilibrium Under Perfect Competition
- Long-term is the period in which the firm can vary all of its inputs. There are no fixed costs and therefore, the AFC or Average Fixed Cost curve vanishes. Also, the Average Cost (AC) curve represents the Average Total Cost (ATC) curve. Further, since the firm can vary all its inputs, it can close own and leave the industry. We know that in the long-run, the AC curve which is form…
Solved Question on Perfect Competition
- Q1. What are the four equilibrium states of a competitive firm? Answer: The four equilibrium states are: 1. Short-Run equilibrium of a Competitive Firm 2. Long-Run equilibrium of a Competitive Firm 3. Short-Run equilibrium of a Competitive Industry 4. Long-Run equilibrium of a Competitive Industry Q4. What is the long-run equilibrium of a competitive firm? Answer: In long-run equilibri…