
What is an axon terminal and what does it do?
The axon terminal is located on one end of a neuron or nerve cell. It is the final part of a neuron to receive an electrical impulse and is also the area where the impulse is converted to a chemical signal. It transfers information from its neuron into another neuron, though it does not come into physical contact with the other neuron.
What is the function of a presynaptic terminal?
Presynaptic Structure and Function. The presynaptic terminal also contains a network of ion channels and proteins that provide the machinery for vesicular release. As voluntary muscle activation is initiated, a signal travels from the corticospinal pathway to the origin of the motor axon (the anterior horn) selected by the upper motor pathways ...
What's the difference between the axon terminal and a synapse?
As nouns the difference between synapse and axon is that synapse is (neuroanatomy|cytology) the junction between the terminal of a neuron and either another neuron or a muscle or gland cell, over which nerve impulses pass while axon is (cytology) a nerve fibre which is a long slender projection of a nerve cell, and which conducts nerve impulses away from the body of the cell to a synapse.
What does an axon terminal button do?
What Is the Function of the Axon Terminal?
- Dopamine
- Endorphins
- Epinephrine. In addition to these, there are more than 100 neurotransmitters present in the brain at any given time.

What is the function of the axon terminal quizlet?
The axonal terminals are specialized to release the neurotransmitters of the presynaptic cell. The end bulb contains synaptic vesicles which are filled with a neurotransmitter substance.
What happens in the axon terminal?
As the action potential travels down the axon, positive ions continue to flood the cell. Eventually, this influx reaches the very end of the neuron – the axon terminal. When this happens, the positive ions trigger voltage-gated calcium channels to open and let calcium ions into the cell.
Is the axon terminal the synapse?
An axon terminal contains various neurotransmitters that are released at the small gap between two communicating neurons. This gap is called a synapse. The neuron that sends nerve impulses by releasing neurotransmitters via the axon terminal at the synapse is called a presynaptic neuron.
Which occurs at the axon terminal and synapse?
The neurotransmitters are stored in synaptic vesicles located at the axon terminals, which are released when the synaptic vesicles fuse with the neural membrane following an influx of Ca2+ ions. The neurotransmitters then bind with receptors on the postsynaptic cell to carry out the communication.
When nerve impulses reaches the axon terminal?
When the nerve impulse reaches the axon terminal it causes the axon terminal to release a neurotransmitter into the synapse. The synapse is the gap between the axon terminals and the next cell. A neurotransmitter is a chemical that is used to transmit an impulse to another cell.
What is the function of synaptic vesicles inside axon terminals?
Synaptic vesicles (SVs) are small, electron-lucent vesicles that are clustered at presynaptic terminals. They store neurotransmitters and release them by calcium-triggered exocytosis.
What is the difference between axon terminals and dendrites?
Axon originates from the discharging end of Neuron while Dendrite originates from the receiving end of Neuron. You can only find one Axon per Nerve Cell whereas there are various Dendrites within a Nerve Cell. The Axon has the long-tail structure and Dendrite has short, fibrous, root-like structure.
What are terminal branches of axon?
The terminal branches of an axon change electrical impulses or action potentials within a neuron into chemical messages in the form of neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters are released from terminal branches into synapses to relay messages to other neurons or other types of cells like muscle cells.
What are axons in the nervous system?
Axons are part of a neuron that relay action potentials within a neuron and transform them into chemical messages to then be transmitted to other c...
What do terminal branches do?
The terminal branches of an axon change electrical impulses or action potentials within a neuron into chemical messages in the form of neurotransmi...
What is the function of the axon and dendrite?
The dendrite receives input messages from a neuron and other cells, whereas an axon relays output messages away from the neuron towards other cells.
Where is the axon of a neuron?
The axon is located at the distal end of a neuron and relay output messages. The dendrites are located at the proximal end and they receive informa...
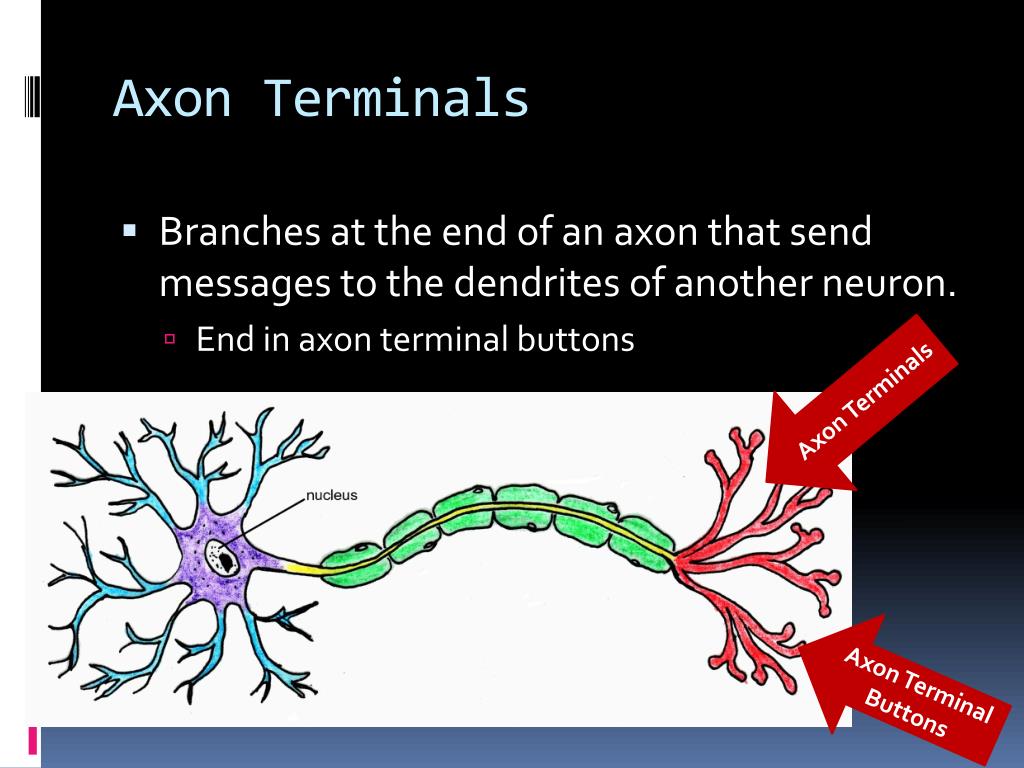
What is the axon terminal?
Axon Terminals: An axon divides into many little branches towards the end of the neuron into axon terminals. It is described in more detail below.
How does an axon work?
An axon is a cable that transmits messages away from the cell body or soma towards the dendrites of other neurons or the sensory receptors of other types of cells to impact them directly. Each axon typically has multiple branches coming off the main branch of the axon known as axon collaterals, which then split into terminal branches. And each axon terminal has an output receptor at the end of it known as a synaptic terminal. The synaptic terminal transmits chemical messages and release neurotransmitters onto other cells. The space between the synaptic terminal and the input receptor of the next cell is known as a synapse. Electrical signals are used within the neuron itself in the form of action potentials.
What is the collateral of an axon?
An axon collateral is a branch that comes off an axon. This allows for a neuron to increase its output to even more numbers and types of cells. While dendrites typically branch frequently, it is more rare for axons to branch out into axon collaterals. Furthermore, axon collaterals typically branch out at an almost right or 90 degree angle. They similarly carry electrical impulses or messages down the axonal branch towards other cells.
What is the fatty tissue that encapsulates an axon?
Myelin Sheath: Myelin sheath consists of clusters of fatty tissue encapsulating an axon which allows for insulation and faster conduction of electrical impulses down an axon. There are two types of axons: myelinated and unmyelinated. Glial cells myelinate an axon in the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. Schwann cells are a type of glial cell found in the peripheral nervous system.
How many axons are there in a neuron?
While a neuron can have many dendrites to receive impulses, there is typically only one axon per neuron. An axon from a motor neuron can have a synapse onto a muscle cell which would either signal the muscle fiber to fire and move a muscle or relax and cease any movement, depending on which kind of neurotransmitter or electrical impulse is transmitted. Similarly, an axon from a sensory neuron can have a synapse with a sensory receptor in the fingertip which would eventually allow the brain to sense a specific touch or temperature being perceived at that fingertip.
What is the main branch of the axon?
The main branch of axons are also typically coated with a fatty tissue known as a myelin sheath, which greatly increases the speed of conductance of the electrical impulse or message down the axon by acting as an insulator. An axon can be thinner than the width of the human hair. Axons can vary in length anywhere from 1 mm in the brain to over 1 meter in the spinal cord.
What is the function of the initial segment?
Initial segment: The main function of the initial segment is to initiate an output action potential to be carried away from the body towards another cell via the axon and axon terminal. This part is unmyelinated and very short in length (20-60 micrometers). It is also a very excitable region of the axon as it contains a high density of voltage-gated sodium channels to help quickly initiate and transmit an action potential. A longer initial segment translates to greater excitability.
What is the function of axons?
A neuron is responsible for receiving sensory input, sending motor commands to your muscles, and transforming and relaying the electrical signals throughout these processes. Every neuron has one axon that connects it with other neurons or with muscle or gland cells.
What do axons do?
Simply put, axons allow nerve cells to send electrical and chemical messages to other nerve, gland, and muscle cells using this internal communication process.
How does myelin protect the axon?
Myelin insulates an axon by surrounding the thin fiber with a layer of fatty substance protection. This layer is located between the axon and its covering (the endoneurium).
How many axons does a neuron have?
Quantity: A neuron may have just one axon, while it may have more than one set of dendrites.
Where are axons located?
Cell location: Axons are found at the specialized location on a cell body called the axon hillock. Dendrites are seen as branching away from the cell body into what’s called dendritic trees due to their appearance.
What is the meaning of axons?
The University of Queensland. Axons: the cable transmission of neurons.
What is the term for the attack of the immune system on myelin in the brain and spinal cord?
Multiple sclerosis (MS): MS occurs when the immune system attacks myelin in the brain and spinal cord. 9
Why must an axon be an axon?
This must be an axon, because by definition only axons generate action potentials.
What would happen if calcium ion channels were blocked in the axon terminal?
Blocking calcium ion channels in the axon terminal would inhibit exocytosis of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. This would shut off synaptic transmission between two neurons.
What is the difference between excitatory and inhibitor postsynaptic potential?
An excitatory postsynaptic potential creates a local depolarization in the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron that brings it closer to threshold. An inhibitor postsynaptic potential does the opposite; it hyperpolarizes the membrane and brings it farther away from threshold.
What is the function of inhibitory synapses?
Inhibitory synapses perform several functions, including preventing antagonist muscles from contracting while agonist muscles are simultaneously contracting. When inhibitory synapses are prevented by tetanospasmin, antagonist and agonist muscles contract at the same time. This leads to painful muscle contractures, a situation in which all muscles are in spasm and movement is impossible.
Which summate prevents action potentials from being generated in affected neurons?
The inhibitory potentials summate, which prevents action potentials from being generated in affected neurons, effectively putting them "to sleep."
How many axons does a PNS have?
This is a pseudounipolar neuron, in which it has two axons, a central process and a peripheral process. Both processes are capable of generating action potentials, and so both are axons. A damaged axon in the PNS may be able to regenerate only if the cell body is intact.
What are the roles of anchor neurons and blood vessels?
Anchor neurons and blood vessels, maintain extracellular environment around neurons, assist in formation of the blood-brain barrier.
What is the axonal terminal?
The axonal terminals are specialized to release the neurotransmitters of the presynaptic cell.
What is the name of the space where a neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules?
At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. the synaptic cleft helps to decode the message. When the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic ending, it is translated into a chemical message that then diffuses across the synaptic cleft to the postsynaptic cell.
What is the name of the projection of a nerve cell?
nerve fiber, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials, away from the nerve cell body.
What is the function of the nodes of Ranvier?
The nodes of Ranvier allow for ions to diffuse in and out of the neuron, propagating the electrical signal down the axon. Since the nodes are spaced out, they allow for saltatory conduction, where the signal rapidly jumps from node to node.
What is the function of a junction between two nerve cells?
a junction between two nerve cells, consisting of a minute gap across which impulses pass by diffusion of a neurotransmitter.The function of this is to transfer electric activity (information) from one cell to another.
What is the purpose of myelin?
It is made up of protein and fatty substances. The main purpose of myelin is to increase the speed at which electrical impulses propagate along the myelinated fiber.
Structure
Function
- Axons help with the cable transmission between neurons. They form side branches called axon collaterals so they can send messages to several neurons at once.2 These branches split into smaller extensions known as axon terminal branches, or nerve terminals. Each terminal holds a synapse where neurotransmitters send their messages and where messages ...
Types
- A nerve contains bundles of nerve fibers, either axons or dendrites, surrounded by connective tissue.3Different types of nerves contain different types of fibers.
Damage
- Acute axon damage is serious and life changing. Severe and diffuse axonal injuries can explain why people with head injury may be limited by a vegetative state. Axonal tears have been linked to lesions responsible for loss of consciousness in people who experience mild head injuries or concussions. Axon damage can result in axon degeneration (loss) and can eventually kill the un…
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the axon hillock?
In the nervous system, the axon hillock is a specialized location on a cell body (soma) where the neuron connects to an axon. It controls the firing of neurons. - What are axon terminals?
Axon terminals are located at the end of an axon. This is where messages from neurotransmitters are received.
Summary
- An axon is a thin fiber that extends from a neuron, or nerve cell, and is responsible for transmitting electrical signals to help with sensory perception and movement. Each axon is surrounded by a myelin sheath, a fatty layer that insulates the axon and helps it transmit signals over long distances.