
Functions of DNA
- Replication and Heredity. Every DNA molecule is distinguished by its sequence of nucleotides. ...
- Transcription. The second important function of genetic material is to direct the physiological activities of the cell.
- Mutation and Evolution. One of the main functions of any hereditary material is to be replicated and inherited. ...
- Genetic Engineering. ...
What is DNA and why is it important?
DNA is the basis for life on planet Earth—every living thing has it. The function of DNA is to store all of the genetic information that an organism needs to develop, function, and reproduce.
What is DNA DNA?
DNA can be described as a long, thin molecule consisting of things called (nucleotides). These nucleotides are linked together by a backbone consisting of both phosphates and the pentavalent sugar, and sometimes the nucleotides are called bases, and there are four types of nucleotides, which are:
What do you need to know about the molecular structure of DNA?
The molecular structure of DNA. In order to understand the biological function of DNA, you first need to understand its molecular structure. This requires learning the vocabulary for talking about the building blocks of DNA, and how these building blocks are assembled to make DNA molecules.
Why is DNA the universal information-storage molecule for life?
The match between DNA structure and the activities of these enzymes is so effective and well-refined that DNA has become, over evolutionary time, the universal information-storage molecule for all forms of life. Nature has yet to find a better solution than DNA for storing, expressing, and passing along instructions for making proteins.
What is the function of DNA?
The function of DNA is to store all of the genetic information that an organism needs to develop, function, and reproduce. Essentially, it is the biological instruction manual found in each of your cells. </span></p> <p style="margin-left:0in; margin-right:0in"><span style="font-size:20px">The instructions in DNA are written in a simple alphabet ...
What are the building blocks of DNA?
As stated above, the basic building blocks of DNA are nucleotides. These nucleotides are composed of a five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The sugars and phosphates link the nucleotides together to form each strand of DNA.
What is the name of the molecule that separates the two strands of DNA?
This RNA polymerase separates the two strands of the DNA helix and copies the DNA of one strand into a molecule called RNA. </span></p> <p style="margin-left:0in; margin-right:0in"><span style="font-size:20px">RNA is very similar to DNA except that instead of thymine (T), it has uracil (U).
How to understand the biological function of DNA?
The molecular structure of DNA. In order to understand the biological function of DNA, you first need to understand its molecular structure. This requires learning the vocabulary for talking about the building blocks of DNA, and how these building blocks are assembled to make DNA molecules.
Why is DNA a good biological molecule?
DNA is well-suited to perform this biological function because of its molecular structure, and because of the development of a series of high performance enzymes that are fine-tuned to interact with this molecular structure in specific ways . The match between DNA structure and the activities of these enzymes is so effective and well-refined that DNA has become, over evolutionary time, the universal information-storage molecule for all forms of life. Nature has yet to find a better solution than DNA for storing, expressing, and passing along instructions for making proteins.
How many letters are in the DNA alphabet?
The English language has a 26 letter alphabet. In contrast, the DNA “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers. They have short and easy to remember names: A, C, T, G. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nucleobase.
Why are nucleobases called nitrogenous bases?
All four of these nucleobases are relatively complex molecules, with the unifying feature that they all tend to have multiple nitrogen atoms in their structures. For this reason, nucleobases are often also called nitrogenous bases.
Which direction does DNA run in?
One strand runs in a 3' to 5' direction while the other runs in a 5' to 3' direction . The nucleotides forming each DNA strand are connected by noncovalent bonds, called hydrogen bonds. Considered individually, hydrogen bonds are much weaker than a single covalent bond, such as a phosphodiester bond.
Which nucleotide has one donor and two acceptors?
Adenine (“A”) and Thymine (“T”) each have one donor and one acceptor, whereas Cytosine (“C”) has one donor and two acceptors, and Guanine (“G”) has one acceptor and two donors. The A nucleotides are always hydrogen bonded to T nucleotides, and C nucleotides are always hydrogen bonded to G nucleotides.
What is the information molecule that stores instructions for making other large molecules called?
DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins . These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.
Why is DNA important in biology?
On another level, DNA’s role as genetic material and an understanding of its chemistry allows us to manipulate it and use it to enhance quality of life. For example, genetically modified crops that are pest or drought resistant have been generated from wild type varieties through genetic engineering. A lot of molecular biology is dependent on the isolation and manipulation of DNA, for the study of living processes.
What is DNA in biology?
DNA Definition. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. DNA is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction of the cell. Large compressed DNA molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, ...
What are the four types of nucleotides in DNA?
The nitrogenous bases in DNA are of four types – adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine. The phosphate and the deoxyribose sugars form a backbone-like structure, with the nitrogenous bases extending out like rungs of a ladder.
How was DNA discovered?
DNA was isolated and discovered chemically before its functions became clear. DNA and its related molecule, ribonucleic acid (RNA), were initially identified simply as acidic molecules that were present in the nucleus. When Mendel’s experiments on genetics were rediscovered, it became clear that heredity was probably transmitted through discrete particles, and that there was a biochemical basis for inheritance. A series of experiments demonstrated that among the four types of macromolecules within the cell (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids ), the only chemicals that were consistently transmitted from one generation to the next were nucleic acids.
Which strand of DNA is involved in transcription?
Only one of the two strands of DNA is involved in transcription. This is called the template strand and the other strand is called the coding strand . Since transcription is also dependent on complementary base pairing, the RNA sequence is nearly the same as the coding strand.
Where is DNA found?
Large compressed DNA molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, are mostly present inside the nucleus. Some cytoplasmic organelles like the mitochondria also contain DNA molecules. DNA is usually a double-stranded polymer of nucleotides, although single-stranded DNA is also known.
Who discovered DNA?
DNA was first chemically isolated and purified by Johann Friedrich Miescher who was studying immunology. Specifically, he was trying to understand the biochemistry of white blood cells. After isolating the nuclei from the cytoplasm, he discovered that when acid was added to these extracts, stringy white clumps that looked like a tufts of wool, separated from the solution. Unlike proteins, these precipitates went back into solution upon the addition of an alkali. This led Miescher to conclude that the macromolecule was acidic in nature. When further experiments showed that the molecule was neither a lipid nor a protein, he realized that he had isolated a new class of molecules. Since it was derived from the nucleus, he named this substance nuclein.
What are the components of DNA?
The DNA molecule is made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains three different components — a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. The sugar in DNA is called 2’-deoxyribose. These sugar molecules alternate with the phosphate groups, making up the “backbone” of the DNA strand.
What is DNA made of?
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It’s made up of units of biological building blocks called nucleotides. DNA is a vitally important molecule for not only humans, but for most other organisms as well. DNA contains our hereditary material and our genes — it’s what makes us unique.
What happens when your cells divide?
The cells of your body divide as a normal part of growth and development. When this happens, each new cell must have a complete copy of DNA.
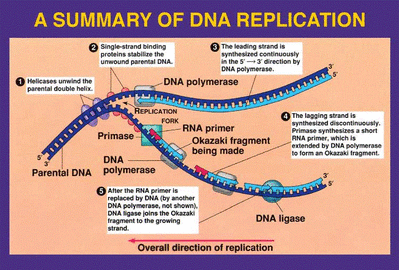
How does DNA get split?
In order to achieve this, your DNA must undergo a process called replication. When this occurs, the two DNA strands split apart. Then, specialized cellular proteins use each strand as a template to make a new DNA strand. When replication is completed, there are two double-stranded DNA molecules.
What part of DNA is responsible for aging?
Another part of DNA that may be involved in aging are telomeres. Telomeres are stretches of repetitive DNA sequences that are found at the ends of your chromosomes. They help to protect DNA from damage, but they also shorten with each round of DNA replication.
Why do cells read the code 3 bases at a time?
Your cells read this code three bases at a time in order to generate proteins that are essential for growth and survival. The DNA sequence that houses the information to make a protein is called a gene. Each group of three bases corresponds to specific amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
Why is DNA damaged?
In fact, it’s estimated that tens of thousands of DNA damage events occur every day in each of our cells. Damage can occur due to things like errors in DNA replication, free radicals, and exposure to UV radiation. But never fear!
