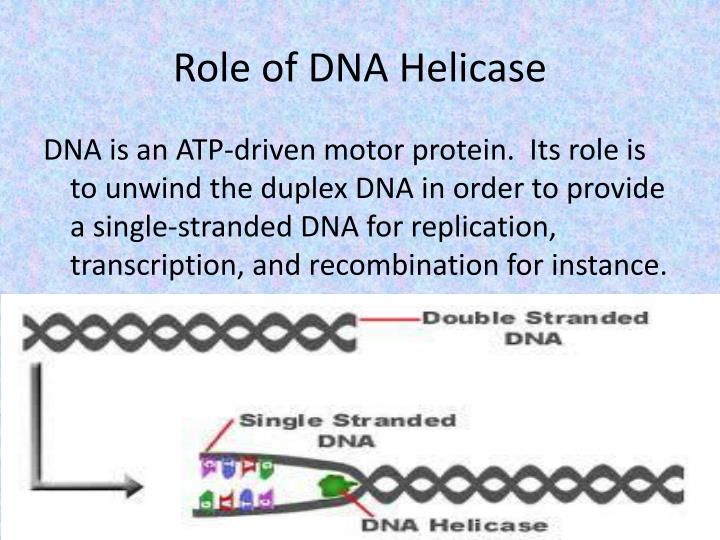
How does helicase actually "unwind" DNA?
- The first step in DNA replication is to ‘unzip’ the double helix structure of the DNA molecule.
- This is carried out by an enzyme called helicase which breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the complementary bases of DNA together (A with T, C with G).
- The separation of the two single strands of DNA creates a ‘Y’ shape called a replication ‘fork’. ...
- 1. ...
What is the function of topoisomerases in DNA?
What is Topoisomerase?
- It was first found by J.C. Wang in the 1970s while working on Escherichia coli. ...
- As the name suggests, it helps in changing the DNA topology. ...
- It can also be called DNA topoisomerase as it only acts on DNA strands.
- It doesn’t work on RNA.
- It breaks the phosphodiester bond that is present in the backbone of DNA strands. ...
Does DNA Helicase or topoisomerase actually "unwind" DNA?
The short answer is yes, helicase unwinds DNA. The unwinding causes supercoiling in the opposite direction. In a net sense and for the sake of your question, the amount of "winding" in the entire helix is unchanged before and after helicase, although this is such an oversimplification that it's very nearly incorrect.
What does helicase do in transcription?
What enzymes are involved in replication transcription and translation?
- DNA Helicase I. Unzips the DNA (replication)
- DNA Polymerase I/II/III, Ligase. Completes the complementary strands of DNA (replication)
- DNA Polymerase III. Corrects mistakes in the DNA (replication)
- DNA Transcriptase, DNA Helicase II.
- RNA Polymerase.
- Aminoacyl tRNA Synthetase.
- Peptidyl Transferase.

What is the main function of DNA helicase in DNA replication quizlet?
What is the function of helicase in DNA replication? It untwists the double helix and separates the two DNA strands. -By pulling apart and untwisting the DNA strands, helicase makes them available for replication.
What is the main function of DNA replication?
DNA replication is the process by which the genome's DNA is copied in cells. Before a cell divides, it must first copy (or replicate) its entire genome so that each resulting daughter cell ends up with its own complete genome.
What is an example of DNA helicase?
Certain DNA helicases (for example, WRN, BLM, FANCJ and PIF1) unwind G4 DNA substrates in vitro149.
What are the 4 main functions of DNA?
The four roles DNA plays are replication, encoding information, mutation/recombination and gene expression.
What is the purpose of DNA replication quizlet?
The sole purpose of DNA replication is to generate identical DNA molecules, as they are the blueprint that makes life possible. There are reasons that there DNA replication goes through a slightly different process to repair damage. However, not all the DNA damages can be repaired accurately.
What DNA replication means?
Listen to pronunciation. (… reh-plih-KAY-shun) The process by which a copy of the DNA in a cell is made before the cell divides.
What are the 3 functions purposes of DNA?
DNA now has three distinct functions—genetics, immunological, and structural—that are widely disparate and variously dependent on the sugar phosphate backbone and the bases.
Which subunits bind to DNA sequence?
b. Two ribosomal subunits bind to the DNA sequence.
Is DNA single strand or double strand?
a. It would be a single strand instead of the original double-stranded D NA.
