What is the main role of the atrium?
What is the main function of the atrium? The atria are the 'receiving chambers' for blood to flow through the heart, taking in blood from either the body or the lungs. The atrium is smaller than its counterpart, the ventricle , because it pumps the blood a shorter distance.
What is the function of the atria and the ventricles?
- The right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle.
- The right ventricle pumps the oxygen-poor blood to the lungs.
- The left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle.
What is the function and roles of the right atrium?
Right Atrium: Functions and Definition The right atrium is defined as the chamber that receives deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body and delivers this blood to the right ventricle.
What is the function of the right atrium in the heart?
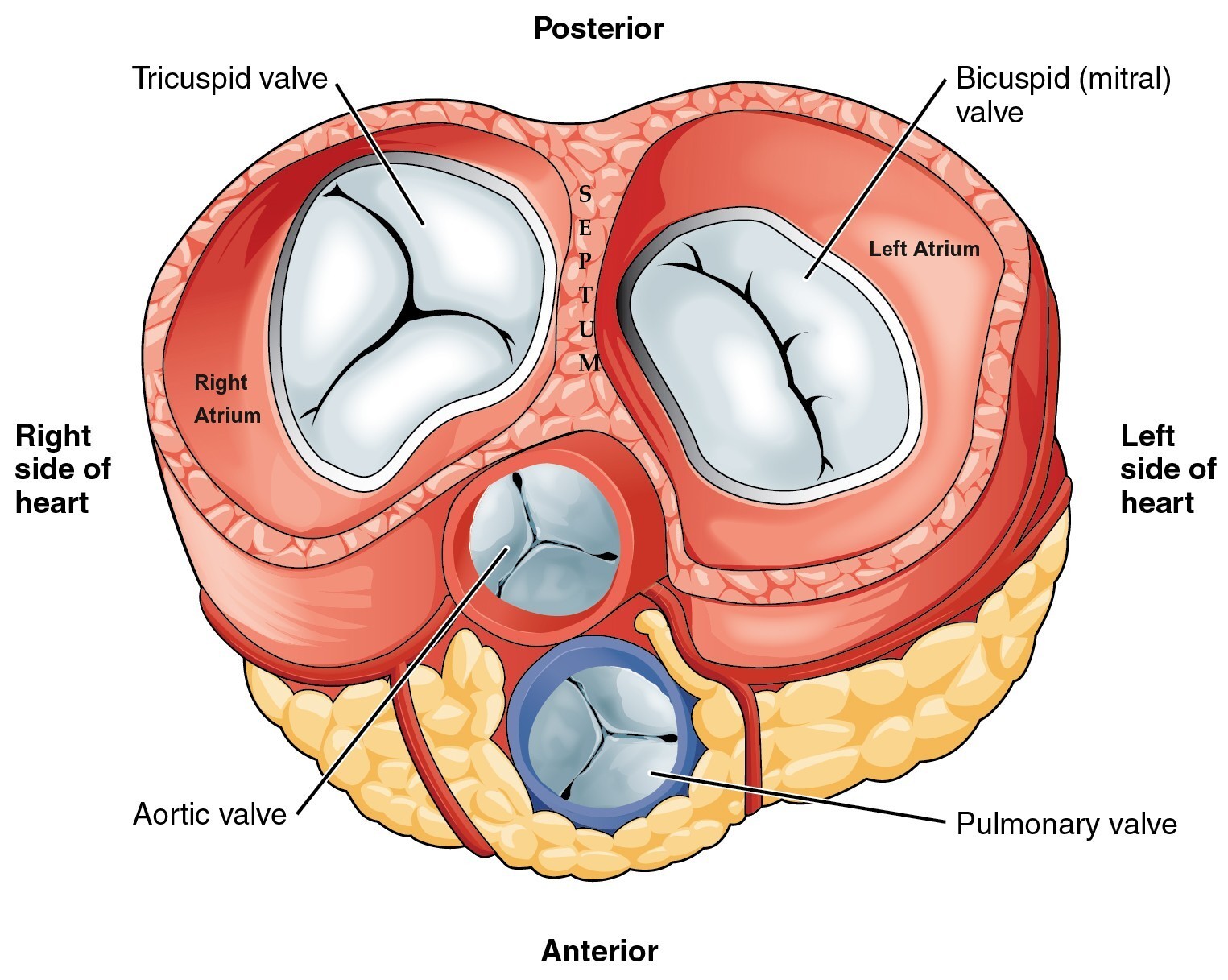
The right atrium is one of the two atria of the heart, which function as receiving chambers for blood entering the heart. It is located to the right of the left atrium and superior to the much larger and more muscular right ventricle. Between the right atrium and right ventricle is a one-way valve known as the tricuspid valve.
See more
nbbj.jpg)
Where is the atrium and what does it do?
atrium, in vertebrates and the higher invertebrates, heart chamber that receives blood into the heart and drives it into a ventricle, or chamber, for pumping blood away from the heart. Fishes have one atrium; amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, two. In humans the atria are the two upper chambers of the heart.
What is the function of the atrium quizlet?
What is the function of the atria? The atria receive blood returning to the heart from other areas of the body. R atrium: receives deoxygenated blood returning to the heart from the superior and inferior venae cavae. L atrium: receives oxygenated blood returning to the heart from the pulmonary veins.
What is the definition atrium?
: an anatomical cavity or passage especially : a chamber of the heart that receives blood from the veins and forces it into a ventricle or ventricles.
What does atrium stand for?
atrium (plural atria or atriums) (architecture) A central room or space in ancient Roman homes, open to the sky in the middle; a similar space in other buildings. (architecture) A square hall lit by daylight from above, into which rooms open at one or more levels. (anatomy) A cavity, entrance, or passage.
What is atrium in respiratory system?
The Atria Are the Heart's Entryways for Blood The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood returning from other parts of the body. Valves connect the atria to the ventricles, the lower chambers. Each atrium empties into the corresponding ventricle below.
What is the function of the left atrium EMT quizlet?
The left atrium receives blood from pulmonary veins and delivers it to the left ventricle. One of two (right and left) lower chambers of the heart. The left ventricle receives blood from the left atrium (upper chamber) and delivers blood to the aorta.
What is the main function of the heart quizlet?
The function of the heart is to contract and pump oxygenated blood to the body and deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Why is it important for a fetus to have lungs?
This is significantly important to a fetus’ circulatory health. While in the womb, the fetus draws oxygenated blood from its mother. Once born, lungs become necessary and the connection between the two atria closes. Last medically reviewed on April 19, 2018.
What is the right atrium?
The right atrium is one of the four chambers of the heart. The heart is comprised of two atria and two ventricles. Blood enters the heart through the two atria and exits through the two ventricles. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium through the inferior and superior vena cava. The right side of the heart then pumps this deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary arteries around the lungs. There, fresh oxygen enters the blood stream, and the blood moves to the left side of the heart, where it is then pumped to the rest of the body. There is a major difference between the heart of a developing fetus and that of a fully mature adult: a fetus will have a hole in the right atrium. This allows blood to flow straight through to the left atrium. This is significantly important to a fetus’ circulatory health. While in the womb, the fetus draws oxygenated blood from its mother. Once born, lungs become necessary and the connection between the two atria closes.
Where does oxygen go in the heart?
There, fresh oxygen enters the blood stream, and the blood moves to the left side of the heart, where it is then pumped to the rest of the body. There is a major difference between the heart of a developing fetus and that of a fully mature adult: a fetus will have a hole in the right atrium.
What causes a patent foramen ovale?
The pathogenesis can be narrowed down to one of the following problems: 1 Abnormal absorption of the septum primum where the incorrect part or too much of the septum was reabsorbed can give rise to a patent foramen ovale. An abnormally large foramen ovale can also persist due to the fact that it will not be adequately occluded by the remaining septum primum . 2 Failure of the septum secundum to form adequately and occlude the ostium secundum may result in the defect persisting into extrauterine life. 3 If the endocardial cushions fail to fuse, then the ostium primum will remain patent since the septum primum has nothing to merge with. This is the most likely cause of endocardial cushion defects with ostium primum .
Why are the atria important?
While each aspect of the heart plays an important role in the circulatory system, the atria are particularly important as they help to fill the ventricles prior to ventricular contraction. As such, the goal of this article is to discuss the embryology, anatomy, and blood supply of the atria of the heart. Furthermore, the physiological function, as ...
How does the autonomic nervous system work?
The autonomic nervous system works in tandem to regulate the activities of the sinuatrial node. The heart is said to be in sinus rhythm as long as there are coordinated atrial contractions, followed by normal ventricular contractions. This can be demonstrated on an electrocardiograph by a P-wave preceding each QRS-complex, with normal intervals.
How does atrial dilation affect the heart?
Atrial dilatation and ischaemic tissue facilitate the development of re-entrant circuits. The dilatation results in stretching of the electrical pathway, which slows down the propagation of an action potential through a particular loop. As a result, some of the tissues exit the normal post action potential refractory period (i.e. completing repolarization) and can, therefore, be prematurely depolarized by an ectopic beat. The myocardium heals by forming fibrous tissue, which is a poor conductor of electricity. Consequently, the action potential has to find an alternative (possibly longer) route to travel; which leads to a similar situation described above.
What is the upper chamber of the heart called?
Each pump contains an upper chamber that functions as a receptacle for incoming blood, called the atrium , and a lower chamber that is responsible for pushing blood out of the heart called the ventricle. The heart is located in the mediastinum within a region known as the cardiac box; the boundaries of which include:
What is the cardiac atrium?
Much like the wide, open architectural atrium that functions as receiving sites for incoming guests, the cardiac atrium is a pair of chambers situated at the upper part of the heart that receives systemic and pulmonary blood.
Which atrium is larger, the right or the left?
The left atrium. The left atrium is positioned slightly above and behind the right atrium. Although it is smaller in terms of the amount of blood it can hold, the left atrium has a thicker myocardial wall when compared to the right atrium.
