What stimulates growth hormone?
What amino acids increase HGH levels?
- Glycine. Enjoying the amino acid glycine immediately before training can slightly stimulate the release of growth hormone.
- Arginine, lysine and ornithine. ...
- 5-hydroxy tryptophan derivative of tryptophan. ...
- 4. ...
What supplements help growth hormone?
The 10 Best Human Growth Hormone Supplements in 2021
- Crazy Bulk HGH X2. Injecting HGH injections might sound like a good idea. ...
- HBULK (Brutal Force) Like the previous HGH production booster, the HBULK is an HGH supplement that features a unique formula.
- GenF20 Plus. ...
- HyperGH 14x. ...
- GenFX. ...
- Provacyl. ...
- HGH Energizer. ...
- Onnit Total Human. ...
- Crazy Bulk Growth Hormone Stack. ...
- Max Gains Bulking Stack. ...
What are the uses of human growth hormone?
Injections of hGH can help people with a growth hormone deficiency to:
- increase exercise capacity
- improve bone density
- build muscle mass
- reduce body fat
Does human growth hormone really work?
They do work, they can cause a tremendous change in your physical power and massive increase in muscle mass, and to an extent, even make you look younger. This has been scientifically proved and hence you are suggested to only use HGH releasers as a source of inducing HGH into your body in case you are planning to use it in the near future.

What is the function of growth hormone quizlet?
What does human growth hormone (hGH) do? plays pivotal role in postnatal growth and development. Helps maintain lean body mass and bone density. Helps raise blood glucose and stimulate lipolysis and fat utilization during fasting.
What is human growth hormone and what are its functions?
Human growth hormone, also known as hGH and somatotropin, is a natural hormone your pituitary gland makes and releases that acts on many parts of the body to promote growth in children. Once the growth plates in your bones (epiphyses) have fused, hGH no longer increases height, but your body still needs hGH.
What are the benefits of growth hormone?
GH acts on many tissues throughout the body. In children and adolescents, it stimulates the growth of bone and cartilage. In people of all ages, GH boosts protein production, promotes the utilization of fat, interferes with the action of insulin, and raises blood sugar levels.
Which hormone is also known as growth hormone?
growth hormone (GH), also called somatotropin or human growth hormone, peptide hormone secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. It stimulates the growth of essentially all tissues of the body, including bone.
What is HGH human growth hormone?
Human growth hormone (hGH or GH) is a protein produced in the body that's important not only during childhood but also throughout adulthood. Growth hormone is produced by the pituitary gland, which is known as the "master gland" because it secretes many hormones that control the actions of other glands.
What foods increase growth hormone naturally?
Healthy food keeps the HGH production rate to an optimum, by keeping track of your body fat and insulin levels. To maintain a normal range of human growth hormones in the blood, foods rich in melatonin, such as eggs, fish, mustard seeds, tomatoes, nuts, grapes, and raspberries are highly recommended by experts.
What are the side effects of human growth hormone?
High levels of human growth hormone over a long period can produce irreversible acromegaly, but even smaller doses can lead to complications such as heart disease and diabetes. And because these hormones must be taken as injections, there are further administration risks such as a blood clot or dose error.
How can I increase my human growth hormone?
Here are 11 evidence-based ways to increase human growth hormone (HGH) levels naturally.Lose body fat. ... Fast intermittently. ... Try an arginine supplement. ... Reduce your sugar intake. ... Don't eat a lot before bedtime. ... Take a GABA supplement. ... Exercise at a high intensity. ... Take beta-alanine and/or a sports drink around your workouts.More items...•
What are the functions of growth hormones?
Following are the important growth hormone function: 1 It maintains normal body structure and metabolism. 2 Maintains, builds, and repairs healthy tissue in the brain and other organs. 3 The growth hormone is utilized widely in medicines that heal the growth disorders in children and hormone deficiency in adults. 4 The growth hormone enhances growth in adolescents and children. 5 It also contributes to the regulation of body fluids, fat metabolism, sugar and also the functions of the heart. 6 The growth hormone reduces body fat by increasing bone density and muscle mass. 7 The energy levels rise consequently, along with improved skin tone and bone density. Due to these properties, the growth hormone is utilized by sports players and hence banned by NCAA and IOC.
What is Growth Hormone?
The growth hormone is produced by the anterior pituitary. It is made up of 191 amino acids that make a long single-chain polypeptide. It is synthesized in somatotropic cells found in the anterior pituitary gland. These cells also store and release the hormone.
What is the name of the hormone that is produced by recombinant DNA?
Somatotropin – growth hormones are otherwise referred by this name and is formed in animals. Somatropin – these are growth hormones that are in the synthetic form produced utilizing recombinant DNA technologies.
How is the secretion of growth hormone regulated?
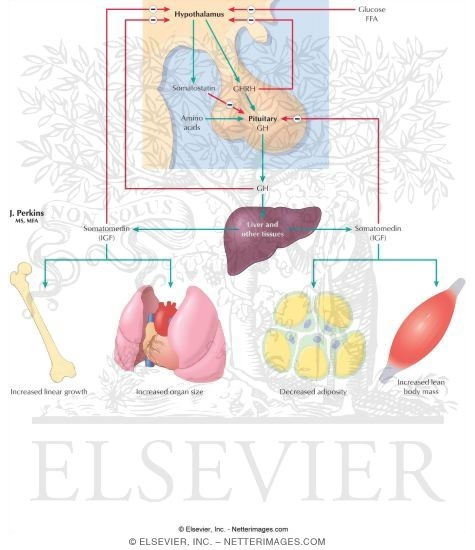
How is the secretion of the growth hormone-regulated? The secretion of the growth hormone is regulated by the hypothalamus and mediators of growth hormone actions. Other factors include- growth hormone-releasing hormone, somatostatin (SRIF), growth hormone-releasing peptide (ghrerin), and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I).
What are the direct effects of growth hormones?
Direct Effects. These are observed when the growth hormone binds with the receptor on the target cells. For eg., fat cells have growth hormone receptors which are stimulated by these hormones to break the triglycerides and suppress their ability to accumulate circulating fats.
Which hormone is released by the hypothalamus?
The formation of growth hormone is regulated by the releasing hormone called somatocrinin along with inhibiting hormone called somatostatin, which is released by the neurosecretory nuclei of the hypothalamus. These regulating hormones are liberated in the hypophysial portal blood that surmounts the pituitary gland.
Where are growth hormones released?
These regulating hormones are liberated in the hypophysial portal blood that surmounts the pituitary gland. The release of a hormone in the pituitary is monitored by these two hormones that are affected by many external inhibitory factors. Various factors stimulate the release of growth hormone, which includes:
Where is growth hormone found?
Growth hormone is a protein, the primary structure of which has been fully established for the human and bovine forms of the hormone. It is probably universally distributed in gnathostomes (vertebrates with jaws), in which it is essential for the maintenance of…
Why is GH important for growth?
GH is vital for normal physical growth in children; its levels rise progressively during childhood and peak during the growth spurt that occurs in puberty. In biochemical terms, GH stimulates protein synthesis and increases fat breakdown to provide the energy necessary for tissue growth.
What gland produces GH?
Growth hormone (GH), also called somatotropin or human growth hormone, peptide hormone secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. It stimulates the growth of essentially all tissues of the body, including bone. GH is synthesized and secreted by anterior pituitary cells called somatotrophs, which release between one and two milligrams ...
How is GH treated?
GH deficiency is most often treated with injections of GH. For decades, however, availability of the hormone was limited, because it was obtained solely from human cadaver pituitaries. In 1985, use of natural GH was halted in the United States and several other countries because of the possibility that the hormone was contaminated with a type of pathogenic agent known as a prion, which causes a fatal condition called Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. That same year, by means of recombinant DNA technology, scientists were able to produce a biosynthetic human form, which they called somatrem, thus assuring a virtually unlimited supply of this once-precious substance.
What is short stature and GH deficiency?
In addition, short stature and GH deficiency are often found in children diagnosed with psychosocial dwarfism, which results from severe emotional deprivation. When children with this disorder are removed from the stressing, nonnurturing environment, their endocrine function and growth rate normalize.
Why is GH high?
Serum GH concentrations are high because of the absence of the inhibitory action of IGF-1 on GH secretion. Dwarfism may also be caused by insensitivity of bone tissue and other tissues to IGF-1, resulting from decreased function of IGF-1 receptors.
How does GH affect the body?
GH may act directly on tissues, but much of its effect is mediated by stimulation of the liver and other tissues to produce and release insulin-like growth factors, primarily insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1; formerly called somatomedin). The term insulin-like growth factor is derived from the ability of high concentrations of these factors to mimic the action of insulin, although their primary action is to stimulate growth. Serum IGF-1 concentrations increase progressively with age in children, with an accelerated increase at the time of the pubertal growth spurt. After puberty the concentrations of IGF-1 gradually decrease with age, as do GH concentrations.
What is growth hormone-releasing hormone?
Growth hormone-releasing hormone is a hormone produced in the hypothalamus . The main role of growth hormone-releasing hormone is to stimulate the pituitary gland to produce and release growth hormone into the bloodstream. This then acts on virtually every tissue of the body to control metabolism and growth. Growth hormone stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor 1in the liver and other organs, and this acts on tissues in the body to control metabolism and growth. In addition to its effect on growth hormone secretion, growth hormone-releasing hormone also affects sleep, food intake and memory.
Which hormone is produced by the hypothalamus to prevent the release of growth hormones?
The action of growth hormone-releasing hormone on the pituitary gland is counteracted by somatostatin, a hormone also produced by the hypothalamus, which prevents growth hormone release.
What is growth hormone testing?
When a deficiency of growth hormone is suspected, a ‘growth hormone stimulating test’ is performed using growth hormone-releasing hormone or other substances, in order to determine the ability of the pituitary gland to release growth hormone. Childhood-onset growth hormone deficiency is associated with growth failure and delayed physical maturity. ...
What happens if the hypothalamus produces too little growth hormone?
If the hypothalamus produces too little growth hormone-releasing hormone, the production and release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland is impaired, leading to a lack of growth hormone ( growth hormone deficiency ' data-content='1276' >adult-onset growth hormone deficiency).
What causes too much growth hormone?
Too much growth hormone-releasing hormone production may be caused by hypothalamic tumours or by tumours located in other parts of the body (ectopic tumours). The consequence of too much growth hormone-releasing hormone is a rise in growth hormone levels in the bloodstream and, in many cases, enlargement of the pituitary gland.
Why is my baby so tall?
An increase in growth hormone before children reach their final height can lead to excessive growth of long bones, resulting in the child being abnormally tall. This is commonly known as gigantism. However, in most cases, growth hormone overproduction is caused by pituitary tumours that produce growth hormone; only in very rare occasions is excess ...
What hormones stimulate the production of insulin-like growth factor 1?
Growth hormone stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor 1in the liver and other organs, and this acts on tissues in the body to control metabolism and growth. In addition to its effect on growth hormone secretion, growth hormone-releasing hormone also affects sleep, food intake and memory. The action of growth hormone-releasing hormone ...
What hormone stimulates the production of somatomedins?
Growth Hormone: Functions. -Increases production of somatomedins (i.e. IGF-1) by the liver. -Stimulates and regulates growth in most tissues. -Stimulates amino acid uptake and then synthesis into proteins. -Inhibits the breakdown of proteins. -Increases lipolysis and the release of fatty acids into the blood.
What is the function of IGF-1?
Tap card to see definition 👆. -Increases production of somatomedins (i.e. IGF-1) by the liver. -Stimulates and regulates growth in most tissues. -Stimulates amino acid uptake and then synthesis into proteins. -Inhibits the breakdown of proteins. -Increases lipolysis and the release of fatty acids into the blood.
