The male germ cells which are known as sperms are synthesized in the seminiferous tubules of the male testis, and the female germ cells which are known as ova are synthesized and developed in the female ovaries. Male germ cells are heterozygous with X and Y chromosomes whilst the female germ cells are homozygous XX chromosomes (two X chromosomes).
What is the difference between male and female germ cells?
In females, they are found in the ovaries and in males, in the testes. During oogenesis, germ cells divide to produce ova, or eggs, in females. In males, germ cells undergo spermatogenesis to produce spermatozoa, or sperm cells.
What is the function of germ cells?
Germ cells are cells that create reproductive cells called gametes. Germ cells are located only in the gonads and are called oogonia in females and spermatogonia in males. ... In males, germ cells undergo spermatogenesis to produce spermatozoa, or sperm cells.
Where are germ cells found in the human body?
Germ cells are located only in the gonads and are called oogonia in females and spermatogonia in males. In females, they are found in the ovaries and in males, in the testes. During oogenesis, germ cells divide to produce ova, or eggs, in females.
What is another name for the reproductive germ cell?
In the context of male reproduction, the reproductive germ cell is known as the sperm. Male germs cells are heterozygous with the presence of X and Y chromosomes.
What is the male germ cell called?
The male germ cells are called spermatogonia.
Where are male germ cells?
seminiferous tubulesMale germ cell differentiation occurs continuously in the seminiferous tubules of the testes throughout the life of a normal animal.
What is the germ cell in male and female?
Germ cells are cells that create reproductive cells called gametes. Germ cells are located only in the gonads and are called oogonia in females and spermatogonia in males. In females, they are found in the ovaries and in males, in the testes. During oogenesis, germ cells divide to produce ova, or eggs, in females.
What is the male's germ cell quizlet?
A germ cell produced by a female, which combines with a male germ cell (sperm) to create a fetus; plural, ova. Also called an egg. A germ cell produced by a male, which combines with a female germ cell (ovum) to create a fetus.
Which is the female germ cell?
Mammalian germ cell development begins in the form of PGCs which are the embryonic precursors of gametes [1,2] which on later stages becomes male or female gametes often termed as sperm and oocyte, respectively.
What is another name for a germ cell?
In this page you can discover 5 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for germ-cell, like: somatic-cell, gamete, reproductive cell, idioplasm and sex-cell.
How many germ cells do men have?
After migration primordial germ cells will become oogonia in the forming gonad (ovary). The oogonia proliferate extensively by mitotic divisions, up to 5-7 million cells in humans. But then many of these oogonia die and about 50,000 remain.
Is ovary a female germ cell?
Ovarian germ cell tumors develop from reproductive cells (germ cells) of the ovaries. Your ovaries are two small organs in your pelvis. Ovaries are part of the female reproductive system. They produce eggs and female hormones.
What are the germ cells in the testes?
More than 90% of cancers of the testicle start in cells known as germ cells. These are the cells that make sperm. The main types of germ cell tumors (GCTs) in the testicles are seminomas and non-seminomas. These types occur about equally.
What is a germ cell quizlet?
germ cells. cell type in a diploid organism that carries only one one set of chromosomes and is specialized for sexual reproduction; a sperm or an egg; also called gametes; undergo meiosis to produce haploid gametes; migrate in the embryo to end up at the developing gonads. germ line.
What is the process for producing germ cells in males quizlet?
Spermatogenesis is the production of spermatozoa (haploid) from a diploid primordial germ cell.
What is the purpose of spermatogenesis quizlet?
Spermatogenesis results in the production of four mature gametes (sperm) from a single precursor cell (spermatogonium). For maximum sperm viability, spermatogenesis requires cooler temperatures and adequate testosterone.
Where are germ cells found?
Germ cells are the founder cells of all sexually reproducing organisms. During development, they are set aside from all somatic cells of the embryo. In many species, germ cells form at the fringe of the embryo proper and then traverse through several developing somatic tissues on their journey to the emerging gonad.
Where are the female germ cells made?
The female germ cells or eggs are made in the uterus.
Is ovary a female germ cell?
Ovarian germ cell tumors develop from reproductive cells (germ cells) of the ovaries. Your ovaries are two small organs in your pelvis. Ovaries are part of the female reproductive system. They produce eggs and female hormones.
gamete
1. one of two haploid reproductive cells, male ( spermatozoon) and female ( oocyte ), whose union is necessary in sexual reproduction to initiate the development of a new individual.
gamete
Genetics A mature ♀ or ♂ reproductive cell–sperm or ovum/egg with a haploid set of chromosomes–23 for humans. See Chromosome, Haploid, Macrogamete, Microgamete, Nullisomic gamete.
gamete
A cell, such as a sperm or ovum, possessing half the normal number of chromosomes (haploid) and capable of fusing with another gamete in the process of fertilization, so that the full (diploid) number of chromosomes is made up. From the Greek gamos , marriage.
germ cell
a specialized HAPLOID cell that fuses with a gamete from the opposite sex (or mating type) to form a diploid ZYGOTE. In simple organisms, the process is called isogamy (see ISOGAMETE ), and OOGAMY in more complex organisms. In animals where oogamy occurs male gametes are called sperm, the female gametes eggs.
Where do germ cells originate?
In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads. There, they undergo meiosis, followed by cellular differentiation into mature gametes, either eggs or sperm. Unlike animals, plants do not have germ cells designated in early development.
What is the lineage of germ cells?
The lineage of germ cells is called germ line. Germ cell specification begins during cleavage in many animals or in the epiblast during gastrulation in birds and mammals. After transport, involving passive movements and active migration, germ cells arrive at the developing gonads.
Why are germ cells not susceptible to mutation?
As germ cells are quiescent and therefore not dividing, they are not susceptible to mutation. Since the germ cell lineage is not established right away by induction, there is a higher chance for mutation to occur before the cells are specified.
What are the end products of the germ cell cycle?
The end-products of the germ cell cycle are the egg or sperm. Under special conditions in vitro germ cells can acquire properties similar to those of embryonic stem cells (ES). The underlying mechanism of that change is still unknown. These changed cells are then called embryonic germ cells (EG).
How do germ cells establish their lineage?
Specification. There are two mechanisms to establish the germ cell lineage in the embryo. The first way is called preformistic and involves that the cells destined to become germ cells inherit the specific germ cell determinants present in the germ plasm (specific area of the cytoplasm) of the egg (ovum).
What is the name of the cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually?
Germ cell . A germ cell is any biological cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads.
Where does spermatogenesis occur?
Mammalian spermatogenesis is representative for most animals. In human males, spermatogenesis begins at puberty in seminiferous tubules in the testicles and go on continuously. Spermatogonia are immature germ cells. They proliferate continuously by mitotic divisions around the outer edge of the seminiferous tubules, next to the basal lamina. Some of these cells stop proliferation and differentiate into primary spermatocytes. After they proceed through the first meiotic division, two secondary spermatocytes are produced. The two secondary spermatocytes undergo the second meiotic division to form four haploid spermatids. These spermatids differentiate morphologically into sperm by nuclear condensation, ejection of the cytoplasm and formation of the acrosome and flagellum.
Overview
Germ cells are cells that populate the gonads and develop into sperm in males and ova in females. They are called germ cells, which is short for “germinate,” a term that means “to grow or develop.”
What are germ cell tumors?
Germ cell tumors are benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous) growths that arise from specialized cells called germ cells, which develop in a baby before birth (a fetus). Germ cells form within the yolk sac, a structure that helps to nourish a fetus before the placenta forms.
What causes germ cell tumors?
Doctors aren’t sure what causes germ cell tumors, but some people who have rare inherited conditions affecting the sex chromosomes (X and Y) or reproductive organs may be at increased risk of the condition.
How are germ cell tumors diagnosed?
If a child or teen has a suspected germ cell tumor, the doctor will gather information about their medical history, examine them during an office visit, and send them for tests that can confirm the presence of a tumor.
How are germ cell tumors treated?
Children and teens with germ cell tumors typically undergo surgery to remove the tumor. If a biopsy shows that the tumor is benign, removal of the tumor should be the only treatment.
What is the outlook for people with germ cell tumors?
The good news is that most children and teens with malignant germ cell tumors can be treated successfully.
Where are germline stem cells located in Drosophila?
In Drosophila, the male germline stem cells reside in a germinal proliferation center, located at the apical tip of the testis. Surrounding the germ stem cells is another group of stem cells, called cyst progenitor cells ( Figure 3) . The cyst cells give rise to somatic cells that are in a sense the counterparts of the mammalian Sertoli cells; they accompany the male germ cells throughout spermatogenesis. The second group of somatic cells, called the hub cells, also surrounds each germline stem cell. The process of spermatogenesis is initiated when a germline stem cell divides asymmetrically to yield two daughter cells, one a stem cell and the other a cell committed to differentiation. Generally, the cell that moves away from the central hub of apical cells is the one destined to become a primary spermatogonium. The primary spermatogonial cell then undergoes four rounds of mitotic divisions with incomplete cytokinesis to yield 16 interconnected cells that enter meiosis ( Figure 3 ).
How many PGCs are there in a mouse?
By E12.5–13.5 in the mouse, there are about 25,000–30,000 PGCs. Subsequently, proliferation of PGCs ceases but apoptosis continues. During this period of quiescence the germ cells are referred to as gonocytes ( Figure 4) . The gonocytes are positioned in the center of the seminiferous tubule (
What is the process of spermatogenesis?
The process of spermatogenesis is poorly understood generally, and the mechanisms governing the decision by male germ cells to proliferate or differentiate is among the least understood elements of it. As in most other biological systems, direct cell-cell interactions or interactions mediated through local extracellular signals play essential roles. The special environmental organization in which stem cells exist is normally referred to as a niche, a microenvironment that supports the survival and proliferation of the stem cell (
Where are female germ cells developed?
Location of Synthesis. Male germ cells are developed in seminiferous tubules of the male testis. Female germ cells are developed in the female ovaries.
How do germ cells form?
Male and female germ cells unite to form a zygote through a process known as fertilization. This is a key step in human reproduction. The sperm, male germ cell is composed of four (04) distinct structures including disc-shaped flattened head, neck, mid piece and tail. At the tip region of the head, consists of a modified lysosome known as acrosome which consists of hydrolytic vesicles which involve in the degeneration of the wall of the ovum. The ovum is a spherical structure with different layers of cell linings which covers the ovum. The nucleus is located eccentrically. Both cells are haploid (n) with 23 chromosomes. The key difference between the male and female germ cells is Male germ cells are heterozygous with X and Y chromosomes whereas the female germ cells are homozygous with two X chromosomes.
Why don't sperms reach the ovum?
They don’t have the ability to reach the ovum and fertilize due to lack of motility. The human sperms are haploid (n) which consist of 23 chromosomes. The human sperm consists of four distinct parts which include, head, neck, mid piece and the tail.
What is the process of a sperm cell forming a zygote?
Both cells fuse in a process called fertilization which then develops into a structure known as the zygote. The zygote then will develop into an embryo which then divides into the development of an organism. The male germ cells which are known as sperms are synthesized in the seminiferous tubules of the male testis, ...
How many chromosomes are in a female germ cell?
The key difference between the male and female germ cells is Male germ cells are heterozygous with X and Y chromosomes whereas the female germ cells are homozygous with two X chromosomes.
What is the structure of sperm called?
Sperms are developed with the ability of motility in order to reach the female germ cell; ovum and penetrate it which completes the process of fertilization and then develops into a structure known as the zygote. Some sperms are nonmotile, and they are referred to as spermatium.
What is the difference between sperm and ovum?
Sperm is a small cell with the presence of distinct structures; disc-shaped flattened head, neck, mid piece and tail. Ovum is a comparatively larger cell with a spherical structure that consists of a centrally located nucleus. The cytoplasm is thick due to the presence of yolk. Male germ cells are usually motile.
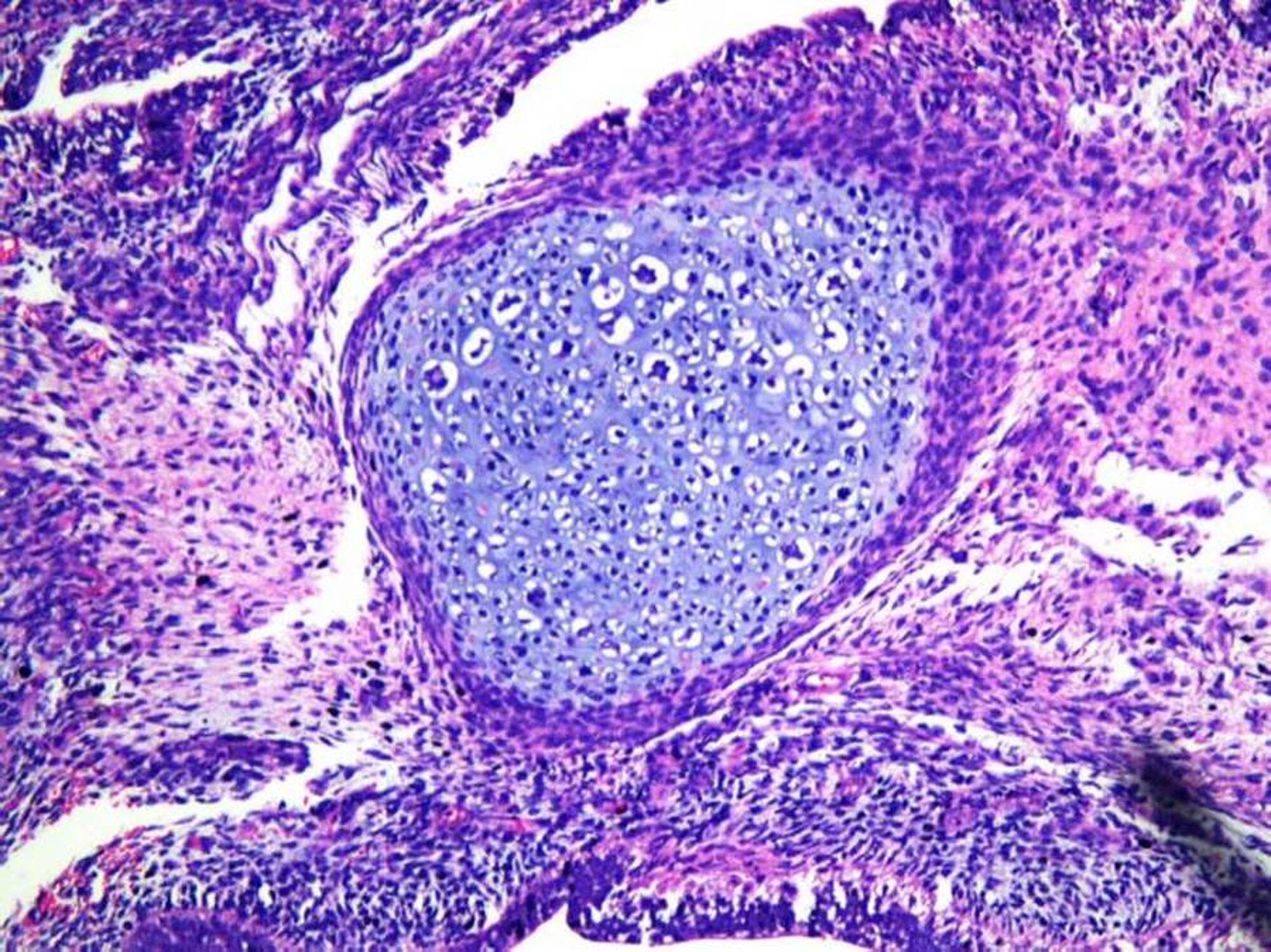
What is a germ cell tumor?
Germ cell tumors are growths that form from reproductive cells. Tumors may be cancerous or noncancerous. Most germ cell tumors that are cancerous occur as cancer of the testicles (testicular cancer) or cancer of the ovaries (ovarian cancer). Some germ cell tumors occur in other areas of the body, such as the abdomen, brain and chest, ...
Where do germ cell tumors occur?
Some germ cell tumors occur in other areas of the body, such as the abdomen, brain and chest, though it's not clear why. Germ cell tumors that occur in places other than the testicles and ovaries (extragonadal germ cell tumors) are very rare. Germ cell tumors tend to respond to treatment and many can be cured, even when diagnosed at a late stage.

Overview
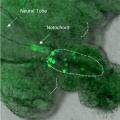
Migration
Primordial germ cells, germ cells that still have to reach the gonads (also known as PGCs, precursor germ cells or gonocytes) divide repeatedly on their migratory route through the gut and into the developing gonads.
In the model organism Drosophila, pole cells passively move from the posterior end of the embryo to the posterior midgut because of the infolding of the blastoderm. Then they actively move thro…
Introduction
Multicellular eukaryotes are made of two fundamental cell types. Germ cells produce gametes and are the only cells that can undergo meiosis as well as mitosis. These cells are sometimes said to be immortal because they are the link between generations. Somatic cells are all the other cells that form the building blocks of the body and they only divide by mitosis. The lineage of germ cells is called the germline. Germ cell specification begins during cleavage in many animals or in the ep…
Specification
There are two mechanisms to establish the germ cell lineage in the embryo. The first way is called preformistic and involves that the cells destined to become germ cells inherit the specific germ cell determinants present in the germ plasm (specific area of the cytoplasm) of the egg (ovum). The unfertilized egg of most animals is asymmetrical: different regions of the cytoplasm contain different amounts of mRNA and proteins.
Gametogenesis
Gametogenesis, the development of diploid germ cells into either haploid eggs or sperm (respectively oogenesis and spermatogenesis) is different for each species but the general stages are similar. Oogenesis and spermatogenesis have many features in common, they both involve:
• Meiosis
• Extensive morphological differentiation
Oogenesis
After migration primordial germ cells will become oogonia in the forming gonad (ovary). The oogonia proliferate extensively by mitotic divisions, up to 5-7 million cells in humans. But then many of these oogonia die and about 50,000 remain. These cells differentiate into primary oocytes. In week 11-12 post coitus the first meiotic division begins (before birth for most mammals) and remains arrested in prophase I from a few days to many years depending on the …
Spermatogenesis
Mammalian spermatogenesis is representative for most animals. In human males, spermatogenesis begins at puberty in seminiferous tubules in the testicles and go on continuously. Spermatogonia are immature germ cells. They proliferate continuously by mitotic divisions around the outer edge of the seminiferous tubules, next to the basal lamina. Some of these cells stop proliferation and differentiate into primary spermatocytes. After they proceed through the fi…
Diseases
Germ cell tumor is a rare cancer that can affect people at all ages. As of 2018, germ cell tumors account for 3% of all cancers in children and adolescents 0–19 years old.
Germ cell tumors are generally located in the gonads but can also appear in the abdomen, pelvis, mediastinum, or brain. Germ cells migrating to the gonads may not reach that intended destination and a tumor can grow wherever they end up, but the exact cause is still unknown. Th…