Full Answer
What is Thomas Malthus' theory of population?
Thomas Malthus’ theory of population proposed that, while the human population grows exponentially, food production grows arithmetically. Hence, at some point humans might face having too few resources to survive. Malthus believed that controlling population growth would help to avoid this catastrophe. Malthus published his theory in 1798.
What is the optimum theory of population?
Optimum Theory Of Population Optimum theory of population implies the ideal size of the population which a country try should possess on the basis of its resources and technology. The word Optimum means the best and the most desirable size of a country’s population. When the population of country is neither too large nor too small, it is called optimum population.
What did Malthus predicted about the human population?
Thomas Robert Malthus (1766–1834) demonstrated perfectly the propensity of each generation to overthrow the fondest schemes of the last when he published An Essay on the Principle of Population (1798), in which he painted the gloomiest picture imaginable of the human prospect. He argued that population, tending to grow at a geometric rate, will ever press against the food supply, which at best increases only arithmetically, and thus poverty and misery are forever inescapable.
What did Malthus think would liimit the population size?
What factors did Thomas Malthus think would eventually limit human population? Competition (war), limited resources (famine), parasitism (disease) + other density dependent factors this is when a population grows in a J curve type of growth patter.

What is the Malthusian theory on population?
The Malthusian theory explained that the human population grows more rapidly than the food supply until famines, war or disease reduces the population. He believed that the human population has risen over the past three centuries.
What is the Malthusian principle of population quizlet?
Malthus argues that population increases exponentially example if a couple have two children and each of those two children have two children the result would be four grandchildren if those four grandchildren each have two children the result to be eight Great grandchildren if a couple have more than two children this ...
What did Thomas Malthus predict about population growth?
In 1798, English economist Thomas Robert Malthus wrote an essay predicting that if humans did not check their fast-growing numbers, mass starvation would result. A debate over Malthus' gloomy outlook ignited during his lifetime and is still going on today.
Why did Malthus believe the population growth would outgrow or surpass the rate of food production quizlet?
What event did Malthus think would curb population growth? What was Malthus conclusion on population growth? Population would eventually surpass available food resources which would cause mass starvation and create in of itself a growth barrier.
What is Malthus moral restraint quizlet?
moral restraint. the only way malthus believed this was a solvable pproblem was if if the world produced lower CBRs or disease, famine, war, or other disasters produced higher CDRs.
Who wrote An Essay on the Principle of Population quizlet?
Malthus - Essay on the Principle on Population.
What does Malthus moral restraint mean?
By moral restraint he meant delayed marriage and sexual abstinence for adults until they were economically able to support their children. While it was generally supposed that Malthus was in favour of contraception, in fact as an Anglican minister he disapproved of it.
Who disagreed with the Malthusian theory?
Karl MarxAnother one of the 19th century critics of Malthusian theory was Karl Marx who referred to it as "nothing more than a schoolboyish, superficial plagiary of De Foe, Sir James Steuart, Townsend, Franklin, Wallace" (in Capital, see Marx's footnote on Malthus from Capital – reference below).
1. Is the Malthusian theory of population applicable today?
Despite the criticism that the theory has faced since it was introduced, the theory does apply to overpopulated countries. One such example is Indi...
2. What is the Malthusian Trap?
The Malthusian Trap, which is also known as the “Malthusian Population Trap” is the idea that increased levels of food production created by modern...
3. State one reason for which The Malthusian Theory of the population is criticized.
The Malthusian Theory of Population was criticized for a variety of reasons. One of the most crucial things for which it was criticized was because...
4. Where can I read more articles like this on other topics of Biology?
The Vedantu website is the ultimate stop for every student to find the free resources that they are looking for. They can easily get a lot of resou...
What is the Malthusian theory?
Based on the principles of the Malthusian theory it can be summarised into the following points: The growth of the human population is much faster than the rate of growth for the means of subsistence such as food, clothing, and other agro-products. As the production rate of agro products is slower it is surpassed by ...
Why Was The Malthusian Theory of Population Criticised?
Since its inception, the Malthusian theory attracted criticism because of its principles. Below is a summary of some of the grounds on which the theory has been criticised.
How many elements are there in Malthusian theory?
There are four major or critical elements of Malthusian theory. These are explained below.
Why did Malthus believe that food production would not be able to keep pace with population growth?
One of the major supporting factors behind Malthus’s theory was that food production would not be able to keep pace with population growth due to the operation of diminishing returns in agriculture.
Which theory applies to countries' growth of population rate is more, food production is less and natural calamities are?
Thus the Malthusian theory applies to countries' growth of population rate is more, food production is less and natural calamities are not kept in check. 2.
How many people live below poverty in India?
39% of the population in India lives below the poverty line. The life expectancy of an Indian is 60 years which is comparatively lower than other countries. The death rate is 11 per 1000 and it shows that natural calamities such as floods, diseases, and hunger are not under full control.
Which theory of population is the oldest?
Amongst the well-known theories of population, the Malthusian theory is one of the oldest. Thomas Robert Malthus, an economist explained this theory in his 1798 essay on the ‘Principle of population’. He then modified some parts in the essays next edition in 1803.
What is the Malthusian theory of population?
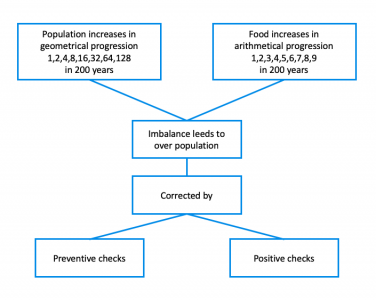
The Malthusian Theory of Population is a theory of exponential population growth and arithmetic food supply growth. Thomas Robert Malthus, an English cleric, and scholar, published this theory in his 1798 writings, An Essay on the Principle of Population. Malthus believed that through preventative checks and positive checks, ...
Why is the Malthusian crisis not achieved?
Even as technological advancement would normally lead to per capita income gains, theorizes Malthus, these gains are not achieved because in practice the advancement also creates population growth. Once the population exceeds what food supplies can support, this supposedly creates a Malthusian crisis with widespread famine as well as rampant ...
What did Malthus believe about the Malthusian catastrophe?
Malthus believed that through preventative checks and positive checks, the population would be controlled to balance the food supply with the population level. These checks would lead to the Malthusian catastrophe.
What were Malthus's measures to correct the imbalance?
These measures include family planning, late marriages, and celibacy.
How has food production increased over the past century?
Thanks to many technological advancements, food production has dramatically increased over the past century. Often, the food production rate has grown higher than the population growth rate. For example, during the 1930s in the US, 25% of the population worked in the agricultural sector while the total GDP was less than $100 billion. Today, less than 2% of the population works in the agricultural sector, while the total GDP is over $14 trillion.
What was the basis for Malthus' theory on food production constraints?
The limited availability of land at the time was the basis for Malthus’ theory on food production constraints. However, thanks to globalization, we can trade goods and services for food, which increases the amount of food a country can consume.
Did population growth create the crisis that Malthus predicted?
The reality, however, has been that population growth has not itself created the crisis that Malthus predicted. We will discuss the ways in which the Malthusian Trap has been disproven in the following section.
What is the Malthusian principle of population?
Notes on Malthusian Principle of Population are as follows: Thomas Malthus’ work Essay on the Principle of Population is considered as the pioneering work on population in which he explicated the fundamental theory of population growth. According to the theory, population grows at a much faster rate than what the natural resources can provide for.
Why did Malthus propose his theory?
Malthus proposed his theory at a time when Europe was experiencing a decline in death rates due to improvements in medicine and an overall industrial growth. Subsequently, there was a rapid growth of population in Europe, but the spread of industry and acquisition of colonies accommodated the growing population.
What was the first country to experience a fall in birth rates around 1800?
France was the first country to experience a fall in birth rates around 1800 and her low fertility rate was considered as one of the reasons for her defeat against Prussia in 1870. Government efforts were made to deal with the problem in 1919 when a separate Council was established as a part of the Ministry of Health to suggest remedial action. The government introduced a number of measures to encourage larger families. Family allowances were granted to assist wage earners with large families. In 1923, the law against abortion was amended to make it more effective.
Why was America concerned about the rise in population?
America was concerned about the rise in population, largely because of the influx of migrants as well as the high rate of fertility among them. America came up with strict immigration policies, which was resented by some European countries, as it closed doors to greater economic opportunities.
What was the pro-natalist movement?
The pro- natalist measures related well to the Fascist and Nazi propaganda of the time and took on ethnic and racist hues. Considerations of race and science led to the emergence of eugenics, a political movement and a philosophy that dominated Europe in the early twentieth century, particularly in Germany under Hitler.
What is the Malthusian theory of population growth?
Resource production can even be accelerated through industrialization, as Malthus was seeing during his own lifetime. This was more or less consistent with other philosophers' descriptions of the world around them. However, Malthus went on to explain that population growth was exponential and that populations would , at some point grow too fast for their society to sustain them.
What is the Malthusian theory?
What is Malthusian theory? The Malthusian theory of population growth is a sociological theory originally proposed by Thomas Robert Malthus to explain what he saw as the dangers of overpopulation. Malthus first published his influential essay on population growth in 1798. Since that time, Malthusianism has been both praised and criticized for its approach to population theory.
What is the importance of Malthusian theory?
Works like The Population Bomb brought Neo-Malthusian thought into the mainstream and have had real-world consequences. Despite widespread criticism and the failure of the proposed point of crisis to materialize, Malthusianism continues to be a pervasive force in the popular imagination, with many people blaming population growth for environmental issues without reference to things like wealthy countries' disproportionate energy consumption or the dangers of violent checks on the population.
What did Thomas Malthus believe?
On the contrary, he believed that many things could be done to prevent it by curbing population growth. He proposed two kinds of checks on the population. The first were called positive checks. These were any natural or incidental phenomena that lowered populations. For example, Malthus considered warfare, disease, and famine to be positive checks on the population. He also described preventative checks, which he described as behavioral modifications that could be made to discourage people from reproducing. Most importantly, Malthus encouraged moral restraint, or the delaying of marriage and reproduction until one was financially able to support a family. He also encouraged celibacy.
What did Malthus believe about the point of crisis?
He believed that this was what England and other nations were heading towards if they did not slow their population growth. He also believed that following the point of crisis, society would collapse and people would be forced to revert to a simpler, less industrialized way of life with a smaller population to reduce the strain on resources. This idea was contrary to popular conceptions of the future as a realm of progress and prosperity.
What was Malthus concerned about?
Looking at the rapidly changing world around him, Malthus became concerned about population growth. He noted that population growth was, or was quickly becoming, exponential, while the growth of resources and people's ability to produce them was essentially arithmetic. How industrialization was going to impact the world was a question that many intellectuals at the time were asking, but Malthus's answer to that question has been one of the most enduring.
What is the problem with Malthus's theory?
The other major problem with Malthus's theory in the real world is that when it comes to resource consumption, heavily industrialized and wealthy nations have far higher per capita resource consumption than poorer or less industrialized countries, regardless of population and population growth. Population growth does not seem to be the major factor in resource consumption; wealth does. Additionally, Malthus's calculations of resource increase as arithmetic rather than exponential seem to be lacking in detail and, while they may have been applicable to England in 1798, they do not seem to be applicable on a worldwide scale, especially in a globalized world that functions on international trade.
What is the Neoclassical Theory of Migration?
Neoclassical Theory of Migration One of the oldest and most commonly used theory used to explain migration is the Neoclassical theory of Migration. Neoclassical Theory (Sjaastad 1962; Todaro 1969) proposes that international migration is connected to the global supply and demand for labor. Nations with scarce labor supply and high demand will have high wages that attract immigrants from nations with a surplus of labor. The main assumption of neoclassical theory of migration is led by the push factors which cause person to leave and the pull forces which draw them to come to that nation. The Neoclassical theory states that the major cause of migration is different pay and access to jobs even though it looks at other factors contributing to the departure, the essential position is taken by individual higher wages benefit element.
What is the basis of the exponential growth model?
Although the exponential growth model is the basis of this model, population ecologists have developed this to model the reality of limited resources. This model illustrates how a population may increase exponentially until it reaches the carrying capacity (the number of individuals of a particular species than an environment can support) of its environment. The logistic growth model looks like this when it is illustrated
What is the demographic transition?
The Demographic Transition is indicated by population changes of demographic patterns which are the birth rate, death rate and growth rates as a nation undergoes development from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic state. Each phase is characterized by a specific relationship between birth rate ( number of live births per one thousand population in an area) and mortality rate (number of annual deaths per one thousand people). The changing of the rates has an essential impact on the total population of a nation. Each country will experience a transition from one phase to the next in accordance with the country 's social and economic development. Based on demographer point of view, there are four stages of classical demographic transition, as follows: 1.
What is industrialization in sociology?
According to Indergraard (2007), industrialization is “the process by which an economy shifts from an agricultural to a manufacturing base during a period of sustained change and growth, eventually creating a higher standard of living”. Within sociology, the three founding fathers, particularly Karl Marx and Émile Durkheim, were interested in studying what the causes of industrialization and the consequences of it on the development of society. This essay will compare the ways in which Marx and Durkheim shared similar ideas about industrialisation within society as well as contrast the aspects of their theories which have different ideological roots and conclusions. The essay with then go on to conclude that whilst there were some key differences
What is the point of Malthus's view on the increasing gap between the population and resources?
In his opinion, the increasing gap between the population and resources shall ultimately lead to the point where misery and poverty shall become inevitable. According to Malthus, postponement of marriage was and would continue to be the chief preventive.
What did Malthus say about the capitalist system?
Malthus defends the capitalistic set-up of society on the ground that if the capital was to be distributed among poor, it will not be available for investment on the mode of production. Thus, the rich will continue to grow richer and the poor constituting the labour class poorer.
What did Malthus see as a major cause of the misery of much of the humanity?
Malthus saw the tension between population and resources as a major cause of the misery of much of the humanity.
What were Malthus' checks?
So, while Malthus’ ‘positive’ checks included wars, disease, poverty, and especially lack of food, his ‘preventive’ checks included principally ‘moral restraint’, or the postponement of marriage, and ‘vice’ in which he included adultery, birth control and abortion.
What did Malthus say about the poor?
He stressed the negative correlation between one’s social rank or position in life and number of children and, in order to induce in the lower classes the self-control and social responsibility which he saw in the middle classes, Malthus asserted that the poor should be better paid and educated.
What will happen to the population of the world if the gap between population and subsistence is widening?
The widening gap between population and subsistence will increase a man’s tendency to press upon the means of subsistence. With the result, the society gets divided into two sets of people the rich (haves) and the poor (have not’s) giving rise to capitalistic set-up.
Who is Robert Malthus Thomas?
Robert Malthus Thomas, the English economist and demographer, is well-known for his theory of population growth.
What is Thomas Malthus' example of population growth doubling?
Thomas Malthus' example of population growth doubling was based on the preceding 25 years of the brand-new United States of America. Malthus felt that a young country with fertile soil like the U.S. would have one of the highest birth rates around.
Why did Malthus argue that the poor should give birth to more children?
Malthus argued that this only encouraged the poor to give birth to more children as they would have no fear that increased numbers of offspring would make eating any more difficult. Increased numbers of poor workers would reduce labor costs and ultimately make the poor even poorer.
What college did Thomas Malthus attend?
In 1784 he attended Jesus College and graduated in 1788; in 1791 Thomas Malthus earned his master's degree. Thomas Malthus argued that because of the natural human urge to reproduce human population increases geometrically (1, 2, 4, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, etc.). However, food supply, at most, can only increase arithmetically (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, ...
What were the main ideas of Thomas Malthus?
The ideas that Thomas Malthus developed came before the industrial revolution and focuses on plants, animals, and grains as the key components of the diet. Therefore, for Malthus, available productive farmland was a limiting factor in population growth.
What would happen if the population increased faster than the production?
As well, since population increases faster than production, the supply would essentially be stagnant or dropping so the demand would increase and so would price. Nonetheless, he suggested that capitalism was the only economic system that could function.
When was the second edition of Principles of Population published?
Thomas Malthus printed the second edition of his Principles of Population in 1803 and produced several additional editions until the sixth edition in 1826.
Who wrote the pamphlet on population?
In 1798, a 32-year-old British economist anonymously published a lengthy pamphlet criticizing the views of the Utopians who believed that life could and would definitely improve for humans on earth. The hastily written text, An Essay on the Principle of Population as it Affects the Future Improvement of Society, with Remarks on the Speculations of Mr. Godwin, M. Condorcet, and Other Writers, was published by Thomas Robert Malthus.
