
Management
- Establishing whether it is true hyperkalaemia: any doubt warrants an urgent repeat (getting an ABG can provide an almost instant result).
- Determine severity of hyperkalaemia: mild, moderate, severe.
- Get a 12-lead ECG and look for changes as above. ...
When do you treat hyperkalemia?
If you have hyperkalemia—or if you are at risk for getting it— you may need to follow a low-potassium diet. Ask your healthcare provider or dietitian how much potassium is right for you. Eating too much can be harmful, but having too little can cause problems, too. Some people may need a little more; others may need less.
When to treat hyperkalemia?
Dec 14, 2021 · IV sodium bicarbonate. Inhaled albuterol. They start working in minutes by shifting potassium out of the blood and into cells. People with …
How dangerous is hyperkalemia?
Medication management: Many people see improvement after stopping or changing certain blood pressure medications or other drugs that raise potassium levels. Your healthcare provider can determine what medication changes to make.
When to treat hyperkalemia level?
Management of hyperkalemia depends on its severity … Causes and evaluation of hyperkalemia in adults … manifestations, treatment , and prevention of hyperkalemia , as well as a detailed discussion of hypoaldosteronism (an important cause of hyperkalemia ), are presented elsewhere: An understanding of potassium …
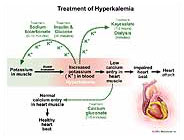
What is the first line treatment for hyperkalemia?
What is the management of potassium?
How is high hyperkalemia treated?
What is the drug of choice for hyperkalemia?
What does Lasix do to potassium?
Do you give insulin or dextrose first for hyperkalemia?
What is the quickest way to lower potassium levels?
How do you give insulin and dextrose for hyperkalemia?
Why is calcium given for hyperkalemia?
Calcium prevents the deleterious cardiac effects of severe hyperkalemia that may occur before the serum potassium level is corrected. Because of its irritating effects when administered parenterally, calcium chloride is generally considered a second choice, after calcium gluconate.Dec 14, 2021
When do you give Kayexalate?
What Is Hyperkalemia (High Blood Potassium levels)?
Hyperkalemia happens when potassium levels in a person’s blood are higher than normal.Normal levels of potassium in the blood are generally between...
Who Can Get Hyperkalemia?
Anyone can get hyperkalemia, but there are some groups who are more at risk. People who have kidney disorders, infants, elderly patients in hospita...
What Are The Symptoms of Hyperkalemia (High Blood Potassium levels)?
A person with high levels of blood potassium may not have any symptoms. However, if symptoms do exist, they may include: 1. Muscle weakness 2. Irre...
What Causes High Blood Potassium Levels?
Hyperkalemia can have a variety of causes: 1. Increased total body potassium 2. Cells releasing extra potassium into the bloodstream 3. Lack of ald...
What Are The Problems Related to Having High Blood Potassium?
The possible problems that have been found in people with hyperkalemia are: 1. Irregular heartbeat 2. Cardiac arrest (heart attack) 3. Changes in n...
Why do you need dialysis for hyperkalemia?
So you might need dialysis to treat your kidney disease -- which also treats hyperkalemia.
What medications lower potassium levels?
Some medications lower potassium slowly, including: 1 Water pills (diuretics), which rid the body of extra fluids and remove potassium through urine 2 Sodium bicarbonate, which temporarily shifts potassium into body cells 3 Albuterol, which raises blood insulin levels and shifts potassium into body cells 4 Sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate), which removes potassium through your intestines before it’s absorbed 5 Patiromer (Veltassa), which binds to potassium in the intestines 6 Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (Lokelma), which binds to potassium in the intestines
What is the best way to remove potassium from the body?
Water pills (diuretics), which rid the body of extra fluids and remove potassium through urine. Sodium bicarbonate, which temporarily shifts potassium into body cells. Albuterol, which raises blood insulin levels and shifts potassium into body cells.
Can you get dialysis for high potassium?
People with very high blood potassium levels may also need dialysis, which uses a special machine to filter the potassium from your blood. Maintenance Medications. Even if hyperkalemia isn’t a crisis, you still need to get your potassium levels down. Some medications lower potassium slowly, including:
Can hyperkalemia be a long term problem?
Changes to your diet and medication often resolve mild cases of hyperkalemia. With the right care, most people don’t have long-term complications from hyperkalemia. Your healthcare provider may order more frequent blood tests to ensure your potassium levels stay within a healthy range.
Can hyperkalemia cause long term complications?
With the right care, most people don’t have long-term complications from hyperkalemia. Your healthcare provider may order more frequent blood tests to ensure your potassium levels stay within a healthy range.
What does high potassium mean?
Hyperkalemia (High Potassium) People with hyperkalemia have high potassium levels in their blood. Signs like fatigue and muscle weakness are easy to dismiss. A low-potassium diet and medication changes often bring potassium numbers to a safe level. An extremely high potassium level can cause a heart attack and requires immediate medical care.
Can high potassium cause a heart attack?
A low-potassium diet and medication changes often bring potassium numbers to a safe level. An extremely high potassium level can cause a heart attack and requires immediate medical care.
What happens if you have too much potassium in your blood?
Potassium is an essential nutrient found in foods. This nutrient helps your nerves and muscles function. But too much potassium in your blood can damage your heart and cause a heart attack. You can’t always tell when your potassium levels are high.
What are the symptoms of high potassium levels?
Dangerously high potassium levels affect the heart and cause a sudden onset of life-threatening problems. Hyperkalemia symptoms include: Abdominal (belly) pain and diarrhea. Chest pain. Heart palpitations or arrhythmia (irregular, fast or fluttering heartbeat). Muscle weakness or numbness in limbs. Nausea and vomiting.
How to get rid of high potassium in urine?
Options include: Diuretics: Also called water pills, these drugs make you pee more often. Your body gets rid of potassium mainly in urine. Intravenous (IV) therapy: Extremely high potassium levels need immediate treatment. You’ll receive an IV infusion of calcium to protect your heart.
Is a surgical intervention needed for hyperkalemia?
Surgical Therapy. Surgical intervention generally is not needed for the care of a patient with hyperkalemia. Patients with metabolic acidosis and consequent hyperkalemia due to ischemic gut obviously require exploration.
What is the FDA approved treatment for hyperkalemia?
Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (Lokelma) was approved by the FDA in May 2018 to treat hyperkalemia in adults. It preferentially captures potassium in exchange for hydrogen and sodium, which reduces the free potassium concentration in the lumen of the GI tract, and thereby lowers the serum potassium level.
Is hyperkalemia aggressive?
The aggressiveness of therapy for hyperkalemia is directly related to the rapidity with which the condition has developed, the absolute level of serum potassium, and the evidence of toxicity. The faster the rise in the potassium level, the higher it has reached, and the greater the evidence of cardiotoxicity, the more aggressive therapy should be. ...
Can you be hospitalized for hyperkalemia?
After emergency management and stabilization of hyperkalemia, the patient should be hospitalized. Once the potassium level is restored to normal, the potassium-lowering therapies can be discontinued, and the serum potassium level can be monitored. Continuous cardiac monitoring should be maintained.
How long after hyperkalemia can you measure potassium?
Measurement of potassium levels at least 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 hours after identification and treatment of hyperkalemia is recommended. [ 64] Discontinue any potassium-sparing drugs or dietary potassium. If the patient is taking digoxin, look for evidence of digitalis toxicity.
Can sodium zirconium be used for hyperkalemia?
Like patiromer, sodium zirconium cyclosilicate should not be used as an emergency treatment for life-threatening hyperkalemia because of its delayed onset of action. Approval was based on the HARMONIZE clinical trial in patients with serum potassium levels of 5.1 mEq/L or higher.
Can potassium be increased with cation exchange resin?
If the patient has only a moderate elevation in potassium level and no electrocardiographic (ECG) abnormalities, excretion can be increased by using a cation exchange resin or diuretics, and the source of excess potassium (eg, increased intake or inhibited excretion) can be corrected. [ 63]
How does hyperkalemia occur?
Hyperkalemia results either from the shift of potassium out of cells or from abnormal renal potassium excretion. Cell shift leads to transient increases in the plasma potassium concentration, whereas decreased renal excretion of potassium leads to sustained hyperkalemia. Impairments in renal potassium excretion can be the result of reduced sodium delivery to the distal nephron, decreased mineralocorticoid level or activity, or abnormalities in the cortical collecting duct. In some instances, all 3 of these perturbations are present. Excessive intake of potassium can cause hyperkalemia but usually in the setting of impaired renal function. We discuss the clinical manifestations of hyperkalemia and outline an approach to its diagnosis and treatment.
What are the symptoms of hyperkalemia?
Severe elevation in potassium can give rise to an ascending paralysis with eventual flaccid quadriplegia. Typically, the trunk, head, and respiratory muscles are spared, and respiratory failure is rare.
What is the difference between hyperkalemia and potassium?
Hyperkalemia results either from the shift of potassium out of cells or from abnormal renal potassium excretion. Cell shift leads to transient increases in the plasma potassium concentration, whereas decreased renal excretion of potassium leads to sustained hyperkalemia. Impairments in renal potassium excretion can be the result ...
What is the role of potassium in the body?
Maintenance of total-body potassium content is primarily the job of the kidneys, with a small contribution by the gastrointestinal tract. 1, 2 Hyperkalemia is most commonly encountered in patients with decreased kidney function.
What foods cause hyperkalemia?
Foods naturally rich in potassium include bananas (a medium-sized banana contains 451 mg or 12 mmol of potassium) and potatoes (844 mg or 22 mmol in a large baked potato with skin).
Does clay cause hypokalemia?
White clay consumption causes hypokalemia due to potassium binding in the gastrointestinal tract. Red clay or river bed clay, on the other hand, is enriched in potassium (100 mmol of potassium in 100 g of clay) and can cause life-threatening hyperkalemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. 8.
What happens to potassium after a meal?
After a meal, release of insulin not only regulates the plasma glucose concentration, it also causes potassium to move into cells until the kidneys have had sufficient time to excrete the dietary potassium load and reestablish total-body potassium content. Exercise, beta-blockers.
Why does hyperkalemia occur?
Hyperkalemia may occur when one of these mechanisms is impaired because of renal failure, renal hypoper fusion (e.g., volume depletion, congestive heart failure), or hypoaldosteronism.
What is the cause of hyperkalemia?
Hyperkalemia is a potentially life-threatening metabolic problem caused by inability of the kidneys to excrete potassium, impairment of the mechanisms that move potassium from the circulation into the cells, or a combination of these factors. Acute episodes of hyperkalemia commonly are triggered by the introduction of a medication affecting ...
Is hyperkalemia life threatening?
The presence of typical electrocardiographic changes or a rapid rise in serum potassium indicates that hyperkalemia is potentially life threatening. Urine potassium, creatinine, and osmolarity should be obtained as a first step in determining the cause of hyperkalemia, which directs long-term treatment.
Which acid enters cells in exchange for potassium, causing hyperkalemia?
Amino acids*. Lysine, arginine, or epsilon-aminocaproic acid enters cells in exchange for potassium, causing hyperkalemia. ARBs and ACE inhibitors. Decreases aldosterone synthesis; hyperkalemia often can be reduced by concomitant diuretic use; ARBs less likely to cause hyperkalemia than ACE inhibitors.
Does lysine cause hyperkalemia?
Lysine, arginine, or epsilon-aminocaproic acid enters cells in exchange for potassium, causing hyperkalemia. ARBs and ACE inhibitors. Decreases aldosterone synthesis; hyperkalemia often can be reduced by concomitant diuretic use; ARBs less likely to cause hyperkalemia than ACE inhibitors. Azole antifungals.
Can mannitol cause hyperkalemia?
Hyperkalemia may occur with continuous infusions or with boluses of hypertonic glucose. May be present with hypertonicity caused by other agents such as mannitol (Osmitrol) as well. Heparins. Can cause hyperkalemia in patients with decreased renal function; inhibits adrenal aldosterone synthesis.
Can hyperkalemia be fatal?
ECG changes in a patient with hyperkalemia are an ominous portent of potentially fatal arrhythmias. However, hyperkalemia can be life threatening even if the ECG is normal, 25, 26 and about one half of patients with potassium levels exceeding 6.0 mEq per L have a normal ECG. 1.
