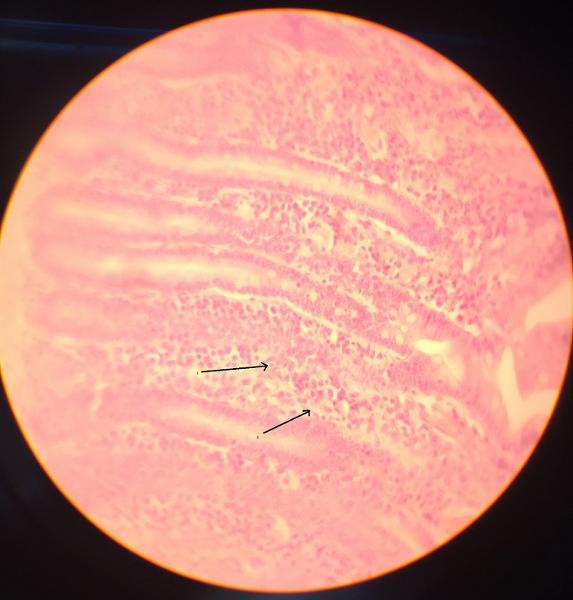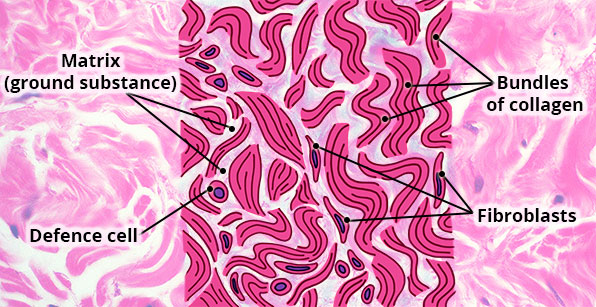
What is dense regular connective tissue?
Feb 03, 2020 · What is the matrix of dense regular connective tissue? Like all connective tissue, dense regular connective tissue is composed of cells, in this case fibroblast cells (fiber …
What is the matrix of connective tissue?
Jan 29, 2016 · The matrix is the most voluminous component of all connective tissues. ... Dense regular connective tissue belongs to the category of connective tissue proper.
Which is the most voluminous component of all connective tissues?
Like all connective tissue, dense regular connective tissue is composed of cells, in this case fibroblast cells (fiber producing cells), fibers (elastin and collagen), as well as a jelly-like …
Which connective tissue has elasticity but is firm in nature?
Mar 16, 2022 · Dense regular connective tissue. Dense regular connective tissue is mainly made up of type I collagen fibers. It is found in areas of the body where large amounts of tensile …
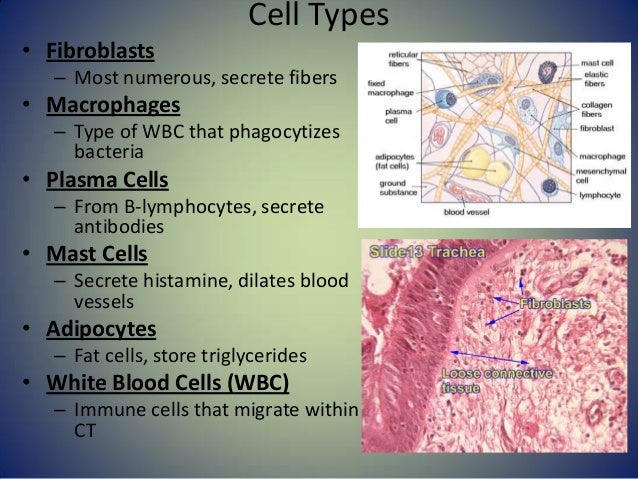
What is the matrix of connective tissues composed of?
What is the matrix of dense regular?
In this type of tissue, the collagen fibres are densely packed, and arranged in parallel. This type of tissue is found in ligaments (which link bone to bone at joints) and tendons (connections between bones or cartilage and muscle).
What does the term regular in dense regular connective tissue refer to?
Dense regular connective tissue: structure. densely packed, parallel arrays of collagen fibers; fibroblasts squeezed between layers; scarce ground substance; greatly reduced blood supply. Dense regular connective tissue: function.
Why is dense regular connective tissue called regular?
What is dense fibrous tissue?
Dense connective tissue, is one of the types of connective tissue also referred to as dense fibrous tissue due to relative abundance of the collagen fibers. It also contains fewer cells and less ground substance in comparison with the other type, loose connective tissue . Dense connective tissue is often further divided into two main categories; dense irregular connective tissue and dense regular connective tissue.
What is connective tissue?
Connective tissue is mainly a supporting tissue that binds and supports organs and the body as a whole. It is comprised of cells and extracellular matrix, including fibers and ground substance. Dense connective tissue, is one of the types of connective tissue also referred to as dense fibrous tissue due to relative abundance of the collagen fibers.
What are fibroblasts in wounds?
In general, fibroblasts become very active during wound repair and healing process, when they proliferate and form fibrous matrix. Specialised form of fibroblasts known as myofibroblasts also appear during wound contraction. The myofibroblasts are characterized by the presence of actin filaments and dense bodies.
What are myofibroblasts characterized by?
The myofibroblasts are characterized by the presence of actin filaments and dense bodies. Overall, these cells exhibit the properties of fibroblasts as well as smooth muscle cells. Learn everything about the dense connective tissue with the following study unit: Dense connective tissue Explore study unit.
What is a tendon?
Tendons are generally resistant to extension, but flexible, meaning that they can be easily distorted around bones and joints. A tendon comprises fascicles of collagen fibers, which run parallel along their axis. In a cross section, a tendon will usually appear round or oval in shape.
What is the shape of a tendon?
In a cross section, a tendon will usually appear round or oval in shape. Where a tendon attaches to a bone, there is a transition from cartilage to mineralised cartilage to bone. Meanwhile, aponeuroses are flat sheets of collagen fibers that normally comprise numerous layers.
How do ligaments form?
Ligaments form from thick bundles of connective tissue, mainly forming from collagen. Despite their density, ligaments can still be fairly elastic. Ligaments need to be strong as they connect bones together, and hold joints in place.
What are the different types of connective tissue?
Connective tissues aren't, as the name suggests, merely just tissues that connect tissues or organs to one another; they are also responsible for anchoring, separating, and encasing other tissues and organs within the body. Within the category of connective tissue there are six types: 1 Loose (which are 'loosely' packed tissues that appear to have spaces) 2 Blood 3 Bone 4 Cartilage 5 Adipose (also known as fat) 6 Fibrous connective tissues
What is the extracellular matrix?
All connective tissue has an extracellular matrix of proteins, water, and carbohydrate molecules that forms something called ground substance. Ground substance, is very flexible and can take the shape of anything, but when it sets, it is firm while still remaining pliable.
Why do fibroblasts have flat nuclei?
They appear as having long flat nuclei because they are literally squished between the many layers of densely packed fibers.
What is collagen fiber?
Collagen fibers are very thick wide fibers that provide the tissue with a high degree of stretch (due to the undulating pattern of fibers that can stretch straight) and a very high level of tensile strength, meaning that they can resist tearing when the fibers are pulled on length-wise.
What is the most abundant tissue in the human body?
Connective tissue is the most abundant tissue in the human body and forms all tendons and ligaments, but is also found throughout the body in fibrous membrane coverings. These coverings encase and surround things like bone, cartilage, nerve fibers, and muscle fibers. Let's review.
How does elastin work?
Elastin fibers work like elastic bands. The tissue can actually be stretched to 150% of its original length and still bounce back to its original shape, just like a rubber band. The proportions of these two fibers vary based on the elastic needs of the location where dense regular connective tissue is found.
What is dense regular connective tissue?
Dense regular connective tissue fibers are parallel to each other, enhancing tensile strength and resistance to stretching in the direction of the fiber orientations. Ligaments and tendons are made of dense regular connective tissue. In dense irregular connective tissue, the direction of fibers is random.
What is the matrix of connective tissue?
The matrix usually includes a large amount of extracellular material produced by the connective tissue cells that are embedded within it . The matrix plays a major role in the functioning of this tissue. Two major components of the matrix are ground substance and protein fibers.
What are the different types of connective tissue?
Identify and distinguish between the types of connective tissue: loose, dense, cartilage, bone, and blood. As may be obvious from its name, one of the major functions of connective tissue is to connect tissues and organs.
What is reticular tissue?
Reticular tissue is a mesh-like, supportive framework for soft organs such as lymphatic tissue, the spleen, and the liver (Figure 4.8). Reticular cells produce the reticular fibers that form the network onto which other cells attach. It derives its name from the Latin reticulus, which means “little net.”. Figure 4.8.
What are the two types of bone tissue?
There are two types of bone tissue: compact and spongy. Picture shown is of compact bone tissue. This is most common and has the appearance of the matrix forming concentric rings around cavities for blood vessels. The osteocytes (bone cells) position themselves within the concentric rings.
What are the three types of fibers that fibroblasts secrete?
Three main types of fibers are secreted by fibroblasts: collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers . Collagen fiber is made from fibrous protein subunits linked together to form a long and straight fiber.
What is ground substance made of?
All of these fiber types are embedded in ground substance. Secreted by fibroblasts, ground substance is made of water, polysaccharides, specifically hyaluronic acid, and proteins. These combine to form a proteoglycan with a protein core and polysaccharide branches.
What is connective tissue made of?
Connective tissue is made up of a few cells present in the intercellular framework of protein fibres secreted by the cells, known as collagen or elastin. The cells also secrete a thin gel of polysaccharides, which together with fibres make matrix or ground substance.
What is dense irregular tissue?
Dense irregular tissue: There are many fibres including collagen, which are oriented irregularly or randomly. The irregular arrangement gives uniform strength in all directions. Fibres may form a mesh-like network. This type of tissue is present in the dermis of the skin.
What are the different types of tissues?
There are mainly four different types of tissues present in our body. Epithelial- provides covering or lining. Muscular- helps in movement.
What are the three types of connective tissue?
Connective tissues contain three types of fibres: collagen, elastic and reticular. Collagen fibres are the most widespread and made up of fibrous protein, collagen. Collagen fibres are flexible and have high tensile strength (comparable to steel). Elastic fibres form a network and can be stretched like a rubber band.
What are collagen fibres made of?
Collagen fibres are the most widespread and made up of fibrous protein, collagen. Collagen fibres are flexible and have high tensile strength (comparable to steel). Elastic fibres form a network and can be stretched like a rubber band. They are made up of protein elastin.
What is the function of adipose tissue?
Adipose Tissue: They are present under the skin and store fat. It acts as a shock absorber and helps in maintaining body temperature in colder environments. White adipose tissues protect kidneys and are also found at the back of the eye, in the hump of camels, blubber of whales, etc.
What is the function of fibroblasts?
In the dense connective tissue, fibroblast cells and fibres are compactly packed. Their main function is to support and transmit mechanical forces. They are somewhat less flexible than loose connective tissue. On the basis of the arrangement of collagen fibres, they are divided into two types: