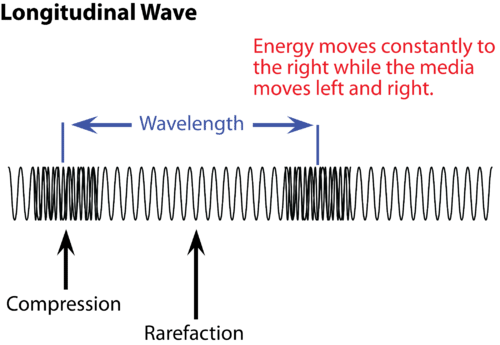
What is the wavelength of a longitudinal wave?
The wavelength of a longitudinal wave is defined as the distance between two consecutive points. These consecutive points lie either between two compressions or between two rarefactions. The maximum displacement of a particle from its rest point is known as its amplitude.
What is amplitude in a longitudinal wave?
In a longitudinal wave, the distance from the equilibrium position in the medium to compression or rarefaction is the amplitude. The time taken by the wave to move one wavelength is known as the period.
What is a mechanical longitudinal wave?
Longitudinal waves are waves in which the displacement of the medium is in the same direction as, or the opposite direction to, the direction of propagation of the wave. Mechanical longitudinal waves are also called compressional or compression waves, because they produce compression and rarefaction when traveling...
What is compression in a longitudinal wave?
In a longitudinal wave, compression is a region in which the particles of the wave are closest to each other.

What is the displacement of a longitudinal wave?
In a longitudinal wave the particle displacement is parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
What is the maximum displacement of a wave called?
amplitudeamplitude, in physics, the maximum displacement or distance moved by a point on a vibrating body or wave measured from its equilibrium position.
What is the highest point in a longitudinal wave?
crestPeak The highest point above the equilibrium position, also called a crest. Rarefaction The region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are farthest apart.
What is the distance of a longitudinal wave?
wavelengthThe wavelength in a longitudinal wave is the distance between two consecutive points that are in phase. The wavelength in a longitudinal wave refers to the distance between two consecutive compressions or between two consecutive rarefactions. The amplitude is the maximum displacement from equilibrium.
How do you find maximum displacement?
The maximum of a motion function occurs when the first derivative of that function equals 0. For example, to find the time at which maximum displacement occurs, one must equate the first derivative of displacement (i.e. velocity) to zero.
When the displacement is maximum?
The displacement of the conductor is maximum when the direction of the current is at right angles to the direction of the magnetic field.
What is the lowest point of a longitudinal wave called?
low point is called the trough. For longitudinal waves, the compressions and rarefactions are analogous to the crests and troughs of transverse waves. The distance between successive crests or troughs is called the wavelength. The height of a wave is the amplitude.
What are the lowest points of a longitudinal waves?
Trough The lowest point of the wave below the rest position. Transverse Waves Examples: 1.
What is the maximum height of a wave?
The maximum ever measured wave height from a satellite is 20.1m during a North Atlantic storm in 2011.
What is the length of longitudinal?
of or relating to longitude or length: longitudinal measurement. extending in the direction of the length of a thing; running lengthwise: a thin, longitudinal stripe. Zoology. pertaining to or extending along the long axis of the body, or the direction from front to back, or head to tail.
How do you calculate longitudinal distance?
The approximation for 1 degree of longitude = cos(Latitude)*degree length of longitude at the equator.
How is longitudinal distance measured?
One of the most common ways to calculate distances using latitude and longitude is the haversine formula, which is used to measure distances on a sphere. This method uses spherical triangles and measures the sides and angles of each to calculate the distance between points.
Is maximum displacement the same as amplitude?
Amplitude—maximum displacement from the equilibrium position of an object oscillating around such equilibrium position. Frequency—number of events per unit of time. Period—time it takes to complete one oscillation.
What is maximum amplitude called?
The variation of (maximum) amplitude over time is called the ENVELOPE of the sound.
What is the maximum wave?
A World Meteorological Organization expert committee has established a new world record significant wave height of 19 meters (62.3 feet) measured by a buoy in the North Atlantic.
Is the maximum distance of a wave?
The amplitude is the maximum distance the particles in a medium move from their rest position as the wave passes through the medium.
The longitudinal wave formula is given by the equation _____.
y(x,t)=y o cos[w(t-x/c)]
List the characteristics of sound?
The characteristics of the sound are as follows: Loudness Pitch Quality
What happens when a pebble is dropped into a pond with still water?
When a pebble is dropped into a pond with still water, there is the formation of ripples on the surface of the water. These ripples are in the circ...
State true or false: Mechanical waves are also known as elastic waves.
The given statement is true. Mechanical waves are also known as elastic waves because they depend on the elastic property of the waves.
Name the condition in which sound waves can travel through the gas.
For a sound wave to travel through the gas, the required condition is an adiabatic condition. This is because when the sound waves travel they prod...
What is a mechanical wave?
A mechanical wave is a type of wave that is generated by the oscillation matter, which transmits energy through the propagating medium.
What are the two types of mechanical waves?
Longitudinal waves and transverse waves are the two types of mechanical waves.
What is meant by a longitudinal wave?
A longitudinal wave is a type of wave in which the medium’s vibration is parallel to the direction of the wave, and the medium’s displacement is in...
What are the main characteristics of a longitudinal wave?
Compression, rarefaction, wavelength, amplitude, period and frequency are the main characteristics of a longitudinal wave.
1. What are Three Examples of Longitudinal Waves?
Examples of longitudinal waves: Sound waves, Vibration in spring, Tsunami waves, etc.
2. What are the Characteristics of Longitudinal Waves?
Characteristics of longitudinal waves, just like in the transverse waves the following properties can be defined for longitudinal waves: wavelength...
3. What do you understand about wave velocity ?
When the distance is travelled in a motion per unit time in a cyclic or periodic manner in any direction, it is known as Wave velocity. The common...
What is longitudinal wave?
To define longitudinal waves, it is the type of disturbance, such that the particles will be executing the to and fro motion about their mean position will have longitudinal waves.
What media can longitudinal waves propagate through?
Longitudinal waves can propagate through any media, such as the longitudinal can propagate through a gas medium, air medium, water, solids, etc...
What are some examples of longitudinal waves?
The best example of longitudinal waves is the sound wave, in order to receive the sound wave we definitely require a medium which is generally an air medium. This is the main reason why the sound waves can not propagate in a vacuum. In this article, we will discuss what are longitudinal waves, examples of longitudinal waves, formation of longitudinal waves, etc…
Why are people afraid of tsunamis?
We know that tsunamis are dangerous natural disasters that may lead to severe loss to human beings. Tsunamis cause damage to coastal regions (sea shore) and that’s the reason why people residing in coastal regions are afraid of them. Most people think that sea waves are transverse waves as they keep travelling in to and fro motion i.e., they go up and down continuously. However, water or sea waves, including Tsunami, are an example of both transverse as well as a longitudinal wave. When the waves reach the shore or remote areas, they become comparatively smaller and thinner, and water molecules move parallel to the wave, hence making it a longitudinal wave.
Why do animals use sound waves?
Sound waves are used by many animals to detect danger, warning them of possible attacks before they happen .
Is a sound wave longitudinal?
Yes, the sound waves are longitudinal in nature. When we speak, the sound wave propagates through the air medium and reaches the audience. The sound waves are the best example of a longitudinal wave and are produced by vibrating or disturbing the motion of the particles that travel through a conductive medium. An example of sound waves in a longitudinal direction of propagation is the tuning fork. In sound waves, the amplitude of the wave is always the difference between the maximum pressure caused by the wave and the pressure of the undisturbed air. The propagation speed of sound depends upon the type, composition of the medium, and temperature through which it will propagate.
Can animals sense earthquakes?
It is said that animals can sense earthquake waves much before humans. They have the ability to sense the seismic P waves, which travel only in the interior of the earth. Even humans can experience a little bump and rattle of these waves, but they are mostly unnoticeable to us. The P waves are the fastest waves, and they require a medium to travel either solid or liquid. The P waves cause the interior of the earth i.e., tectonic plates to move back and forth (in other words to oscillate) in a longitudinal manner, which leads to the surface waves i.e., seismic S waves, which we can feel.
What are Longitudinal Waves?
Longitudinal waves are waves that consist of a periodic disturbance or vibration that takes place in the same direction as the direction of the travel of the wave.
What is the required condition for a sound wave to travel through a gas?
Ans: The required condition, for a sound wave to travel through the gas, must be an adiabatic condition as when the sound waves travel they produce compressions and rarefactions resulting in the generation of heat. Therefore, the temperature must be constant for the waves to travel through the gas. Thus, the ideal condition would be an adiabatic condition.
What is a tuning fork?
Ans: A sound wave is a type of longitudinal wave that is produced by the vibrating motion of particles traveling through a conductive medium. A tuning fork is an example of sound waves. In Sound waves, the difference between the maximum pressure produced by the wave and the pressure of the undisturbed air is referred to as the amplitude of the wave. The propagation speed of sound depends upon the type of medium, the composition of the medium, and the temperature through which it is propagating.
What is a sound wave?
A sound wave is a type of longitudinal wave that is produced by the vibrating motion of particles traveling through a conductive medium. A tuning fork is an example of sound waves.
What is rarefaction in physics?
Rarefaction refers to a region in a longitudinal wave where the wave’s particles are farthest apart from each other.
What are the two types of mechanical waves?
Depending on the type of motion, the mechanical waves are classified into two types, i.e. longitudinal wave and transverse wave. The longitudinal waves are found when the energy is transmitted inside the medium whereas the transverse waves are formed at the surface. Here, we will discuss longitudinal waves in detail along with some important questions.
What is compression wave?
Compression refers to a region in a longitudinal wave where the wave’s particles are closest to each other.
What is the difference between mechanical longitudinal waves and pressure waves?
Mechanical longitudinal waves are also called compressional or compression waves, because they produce compression and rarefaction when traveling through a medium, and pressure waves, because they produce increases and decreases in pressure. Sound travels through longitudinal waves.
What is longitudinal wave?
Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propag ation. Mechanical longitudinal waves are also called compressional or compression waves, ...
How does sound travel?
Sound travels through longitudinal waves. Sound travels through transversal waves in 90 degrees. The other main type of wave is the transverse wave, in which the displacements of the medium are at right angles to the direction of propagation. Transverse waves, for instance, describe some bulk sound waves in solid materials (but not in fluids);
What is transverse wave?
Transverse waves, for instance, describe some bulk sound waves in solid materials ( but not in fluids); these are also called "shear waves" to differentiate them from the (longitudinal) pressure waves that these materials also support.
What are L waves and T waves?
While these two abbreviations have specific meanings in seismology (L-wave for Love wave or long wave) and electrocardiography (see T wave ), some authors chose to use "l-waves" (lowercase 'L') and "t-waves" instead, although they are not commonly found in physics writings except for some popular science books.
What is the amplitude of a sound wave?
For sound waves, the amplitude of the wave is the difference between the pressure of the undisturbed air and the maximum pressure caused by the wave. Sound's propagation speed depends on the type, temperature, and composition of the medium through which it propagates.
What is the difference between the pressure of the undisturbed air and the maximum pressure caused by the wave?
For sound waves, the amplitude of the wave is the difference between the pressure of the undisturbed air and the maximum pressure caused by the wave.
What is the displacement of a transverse wave?
The wave displacement of a transverse wave is perpendicular to the direction of the wave's travel, as the material itself does not travel along with the wave. For a wave moving in the negative x direction, we change the subtraction sign in the equation to an addition sign.
What is displacement in a wave?
As a wave travels through a medium, it creates a displacement in it, which is a change in position of that medium from its starting position before the wave traveled through it.
What degree does Damien have?
Damien has a master's degree in physics and has taught physics lab to college students. As a transverse wave travels, it affects the material it is traveling through. We can learn more about how it affects that material by exploring wave displacement and learning how to calculate it. Create an account.
What is the difference between displacement and distance?
Do you remember the difference between displacement and distance? It might seem like it, but they aren't the same thing. Distance is how far an object has traveled, and displacement is a measurement of the change in an object's starting position.
How does angular frequency differ from standard frequency?
Angular frequency and angular wavenumber only differ from standard frequency ( f) and wavenumber (or nu bar) by a factor of 2 * pi. We can see this by comparing their formulas:
What is the difference between frequency and amplitude?
Amplitude is defined as the height of the wave's crests and troughs. Frequency is the number of waves that pass by a point in a certain time frame. Finally, wavenumber is the number of wavelengths that appear in a wave over a given distance. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account.
How to see separation of wave movement?
You can see an extreme example of the separation of wave movement and what it travels through by using a jump rope. You just need two people to do this experiment. Have each person hold one end of the jump rope. One person holds still as the other moves their arm up and down in a quick motion. You can see a wave travel down the rope, but the rope itself isn't traveling along with the wave. In this lesson, we're going to learn a bit about how waves affect the material they travel through by digging into wave displacement.
What happens when phase difference is equal to 0?
occurs at points where the phase difference is equal to 0, waves traveling in the same direction combine and the resulting amplitude is greater than any individual wave amplitude
What causes particles of the material to vibrate in SHM in a direction parallel to the direction of the motion of?
a disturbance causes the particles of the material to vibrate in SHM in a direction parallel to the direction of the motion of the wave
What is the point on a periodic wave that is at equal displacements fromt their rest position?
points on a periodic wave that are at equal displacements fromt their rest position and are experiencing identical movements, that is , are moving in the same direction toward or away from rest position
When two points of equal frequency and amplitude whose phase difference is 180 meet at a point, what happens?
occurs when two points of equal frequency and amplitude whose phase difference is 180 meet at a point; waves traveling in opposite directions combine and the resulting amplitude is less than any individual wave amplitude
What is vibration of an object at its natural frequency caused by?
the vibration of an object at its natural frequency caused by a vibrating source of the same frequency
What does bending mean in waves?
bending of a wave when it enters a medium where its speed is different

Overview
Sound waves
In the case of longitudinal harmonic sound waves, the frequency and wavelength can be described by the formula
where:
• y is the displacement of the point on the traveling sound wave;
• x is the distance from the point to the wave's source;
Nomenclature
"Longitudinal waves" and "transverse waves" have been abbreviated by some authors as "L-waves" and "T-waves", respectively, for their own convenience. While these two abbreviations have specific meanings in seismology (L-wave for Love wave or long wave ) and electrocardiography (see T wave), some authors chose to use "l-waves" (lowercase 'L') and "t-waves" instead, although they are not commonly found in physics writings except for some popular science books.
Pressure waves
The equations for sound in a fluid given above also apply to acoustic waves in an elastic solid. Although solids also support transverse waves (known as S-waves in seismology), longitudinal sound waves in the solid exist with a velocity and wave impedance dependent on the material's density and its rigidity, the latter of which is described (as with sound in a gas) by the material's bulk modulus.
Electromagnetics
Maxwell's equations lead to the prediction of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum, which is strictly transverse waves, due to the fact that they would need particles to vibrate upon, the electric and magnetic fields of which the wave consists are perpendicular to the direction of the wave's propagation. However plasma waves are longitudinal since these are not electromagnetic waves but density waves of charged particles, but which can couple to the electromagnetic field.
See also
• Transverse wave
• Sound
• Acoustic wave
• P-wave
• Plasma waves
Further reading
• Varadan, V. K., and Vasundara V. Varadan, "Elastic wave scattering and propagation". Attenuation due to scattering of ultrasonic compressional waves in granular media - A.J. Devaney, H. Levine, and T. Plona. Ann Arbor, Mich., Ann Arbor Science, 1982.
• Schaaf, John van der, Jaap C. Schouten, and Cor M. van den Bleek, "Experimental Observation of Pressure Waves in Gas-Solids Fluidized Beds". American Institute of Chemical Engineers. New York, N.Y., 1997.