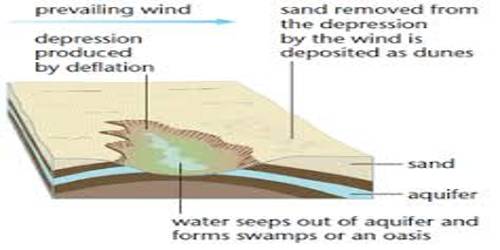
How is deflation hollow formed?
deflation hollow Enclosed depression produced by wind erosion. It may be found both in hot deserts, where wind may scour a hollow in relatively unconsolidated material, and in more …
What is the maximum size of a deflation hollow?
deflation hollow Enclosed depression produced by wind erosion. It may be found both in hot deserts, where wind may scour a hollow in relatively unconsolidated material, and in more …
What are the causes of deflation?
In deflation. …to deflation may result in deflation hollows or blowouts. These may range from 3 m (10 feet) in diameter and less than a metre deep to several kilometres in diameter and several …
What is deflation basin in geology?
Aug 21, 2014 · Deflation Hollow is where wind carries away sand and in return creates depressions within the remaining sand and soil. The appearance is hollow appearing like airy …

What are deflation hollows Class 9?
How does a deflation hollow form?
What is deflation hollows and caves?
What is meant by deflation in geography class 9?
What causes deflation?
Which agent of erosion is the strongest?
What is Ventifact and Dreikanter?
How does a blowout form?
What is a parabolic sand dune?
What is deflation in Archaeology?
What is inflation vs deflation?
How deep is a deflation hollow?
formation by wind. …to deflation may result in deflation hollows or blowouts. These may range from 3 m (10 feet) in diameter and less than a metre deep to several kilometres in diameter and several hundred metres in depth.
How deep is a blowout in deflation?
In deflation. …to deflation may result in deflation hollows or blowouts. These may range from 3 m (10 feet) in diameter and less than a metre deep to several kilometres in diameter and several hundred metres in depth.
How deep is Big Hollow?
The Big Hollow in Wyoming was formed by deflation and is 14.5 km (9….
How deep is a blowout?
formation by wind. In deflation. …to deflation may result in deflation hollows or blowouts. These may range from 3 m (10 feet) in diameter and less than a metre deep to several kilometres in diameter and several hundred metres in depth.
What is the definition of deflation?
Deflation is defined as an economic condition whereby the prices of goods and services go down constantly with the inflation rate turning negative. The situation generally emerges from the contraction of the money supply in the economy. Aggregate Demand Aggregate Demand is the overall demand for all the goods and the services in a country ...
What is a deflation in economics?
Deflation in economics is negative inflation (below 0%) that occurs when a country or an industrial sector experiences a decrease in the price of its products and services due to monetary contraction.
Is deflation worse than inflation?
Deflation is defined as an economic condition whereby the prices of goods and services go down constantly with the inflation rate turning negative. The situation generally emerges from the contraction of the money supply in the economy. Many economists consider deflation worse than inflation as it is usually accompanied by a fall in ...
What are the causes of deflation?
Some major causes of deflation include low credit and money supply in the economy, reduction in the production cost, over supply, inflation controlling contractionary measures, increased savings, and a decline in the aggregate demand.
Is deflation bad for the economy?
Deflation is bad for an economy, even though it increases the purchasing power of money. When prices fall constantly, consumption declines, as people wait for the rates to decrease more to make a cheaper purchase. With more supply and less demand, prices fall further.
What is negative inflation?
Deflation or negative inflation occurs when there is an economic slowdown marked by a sustained downfall in the prices of goods and services within an economy or a specific sector. . During this phase, the level of unemployment shoots up and consumers’ wages go down.
Why does the cost of production go down?
The cost of production steeps down because of technological advancement, discovery of newer and cheaper resources. Overall decline in inputs reduces pricing of goods or service.
What is the definition of deflation?
Deflation, in geology, erosion by wind of loose material from flat areas of dry, uncemented sediments such as those occurring in deserts, dry lake beds, floodplains, and glacial outwash plains. Clay and silt-sized particles are picked up by turbulent eddies in wind and may be carried for hundreds . Deflation, in geology, erosion by wind ...
What is deflation in geology?
Deflation, in geology, erosion by wind of loose material from flat areas of dry, un cemented sediments such as those occurring in deserts, dry lake beds, floodplains, and glacial outwash plains. Clay and silt-sized particles are picked up by turbulent eddies in wind and may be carried for hundreds .
How are clay and silt sized particles picked up?
Clay and silt-sized particles are picked up by turbulent eddies in wind and may be carried for hundreds of kilometres; they later settle to form loessdeposits. Local areas subjected to deflation may result in deflation hollows or blowouts.
How was Big Hollow formed?
The Big Hollow in Wyoming was formed by deflation and is 14.5 km (9 miles) long and 50 m (165 feet) deep. If an area is eroded down to the water table, further deflation is prevented unless the water table is also lowered by evaporation. Some oasesin the Saharawere formed in this manner and may be below sea level.
What is a loess?
Loess, an unstratified, geologically recent deposit of silty or loamy material that is usually buff or yellowish brown in colour and is chiefly deposited by the wind . Loess is a sedimentary deposit composed largely of silt-size grains that are loosely cemented by calcium carbonate.