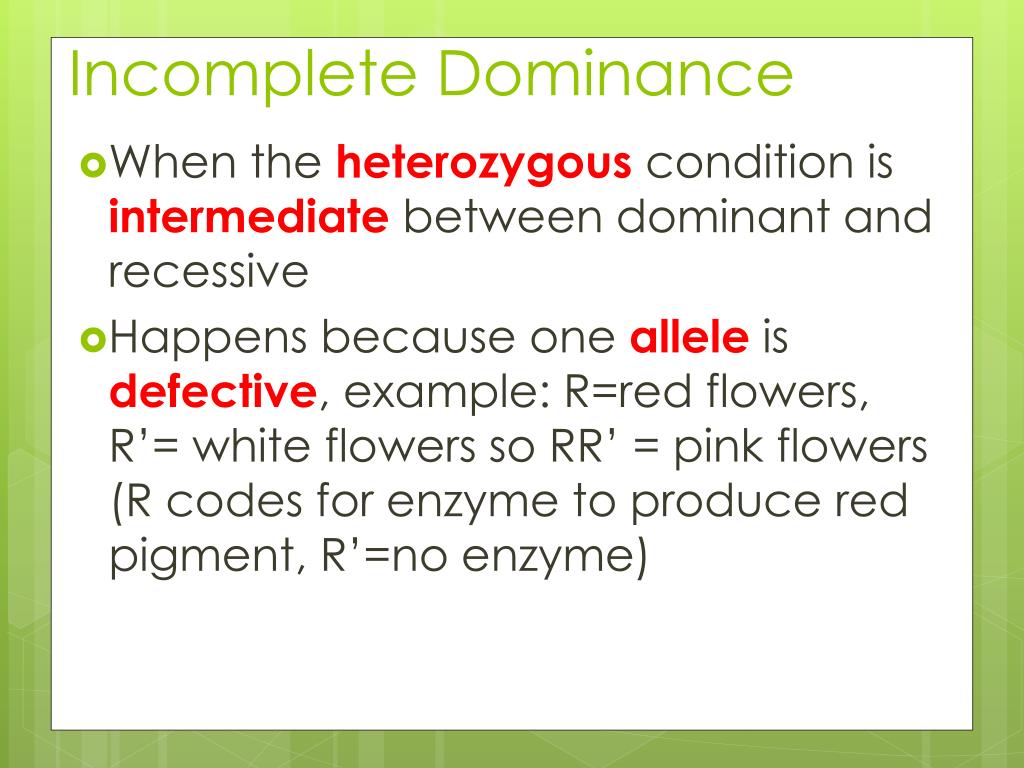
incomplete dominance a pattern of inheritance in which a cross between two phenotypically different parents produces an offspring different from either parent but containing partial features of both. The classic example is in flower colour where, for example, crossing white and red snapdragons produces a pink offspring.
Which statements describe incomplete dominance?
incomplete dominance because both parents' colors are expressed in the offspring incomplete dominance because the fruit color of the offspring is an intermediate form of the parents' fruit color Blood pressure in humans is a phenotype that results from the interaction of many genes, including those for body weight, kidney function, metabolism, and more.
What are characteristics demonstrate incomplete dominance?
Incomplete dominance can be seen in many other physical characteristics such as skin color, height, hand size, and vocal pitch. Carriers of Tay-Sachs disease also show incomplete dominance. Individuals with Tay-Sachs disease lack an enzyme that breaks down lipids, causing too many lipids to accumulate in the brain and other parts of the nervous ...
What does the term incomplete dominance refer to?
The definition of incomplete dominance is the genetic situation when one gene for a characteristic trait does not completely dominate over another gene for the same characteristic trait, and the result is a characteristic trait that is midway between the two.
Which choice describes incomplete dominance?
This type of relationship between alleles, with a heterozygote phenotype intermediate between the two homozygote phenotypes, is called incomplete dominance. We can still use Mendel's model to predict the results of crosses for alleles that show incomplete dominance.
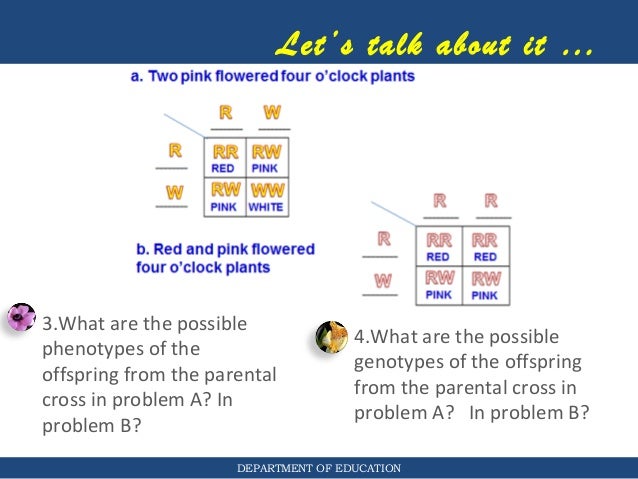
What is incomplete dominance example?
Incomplete dominance occurs when neither trait is truly dominant over the other. This means that both traits can be expressed in the same regions, resulting a blending of two phenotypes. If a white and black dog produce a gray offspring, this is an example of incomplete dominance.
What is the meaning of complete dominance?
Complete dominance is when one allele is fully dominant over the other. The trait displayed will be dominant if the child is monohybrid (AA) or dihybrid (Aa). A trait is the characteristic that appears, such as hair color. This is also called a phenotype. A genotype is the allele combination (AA, Aa, aa).
What is incomplete dominance vs codominance?
Codominance and Incomplete dominance are two types of genetic inheritance. Codominance essentially means that no allele can block or mask the expression of the other allele. On the other hand, incomplete dominance is a condition in which a dominant allele does not completely mask the effects of a recessive allele.
What are the 3 types of dominance?
There are different types of dominance: incomplete dominance, co-dominance and complete dominance.
What is complete dominance example?
A classic example of complete dominance is the inheritance of seed shape (pea shape) in peas. Peas may be round (associated with allele R) or wrinkled (associated with allele r). In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, rr, Rr. RR and rr are homozygous and Rr is heterozygous.
What is dominance with example?
dominance, in genetics, greater influence by one of a pair of genes (alleles) that affect the same inherited character. If an individual pea plant with the alleles T and t (T = tallness, t = shortness) is the same height as a TT individual, the T allele (and the trait of tallness) is said to be completely dominant.
What is complete dominance gene action?
Complete dominant gene action: A type of gene action whereby one allele is expressed more strongly than the other in the production of qualitative phenotypes: the allele that is expressed more strongly is called the “dominant allele,” and the other is called the “recessive allele.” A gene that exhibits complete ...
What is Incomplete Dominance?
Incomplete dominance is a form of Gene interaction in which both alleles of a gene at a locus are partially expressed, often resulting in an intermediate or different phenotype. It is also known as partial dominance.
Why is incomplete dominance a phenotype?
Incomplete dominance occurs because neither of the two alleles is completely dominant over the other. This results in a phenotype that is a combination of both. Gregor Mendel conducted experiments on pea plants. He studied on seven characters with contrasting traits and all of them showed a similar pattern of inheritance.
What is dominance in genetics?
In genetics, Dominance is a relationship between alleles of one gene. In order to understand the concept of the dominance of alleles, we need to know more about genes. So far we know that genes are a hereditary unit in organisms which exist as a pair of alleles in diploid organisms. These pair of alleles may or may not be similar.
What blood type shows codominance?
The humans with AB blood type also show codominance where the alleles for both blood types A and B are expressed.
Why is one trait dominant over the other?
When we say one trait is dominant over the other, there can be two reasons: either it is non-functional, or. is less active than the normal allele.
Is incomplete dominance the same as codominance?
Incomplete dominance and codominance are different from each other.
COMPARE COMMONLY CONFUSED WORDS
These are smilar words, and share related meanings, but their uses are very different. Click on the buttons to learn more about these commonly confused words.
How to use incomplete dominance in a sentence
In the meantime, most of the detailed studies are incomplete in one way or another.
What is the failure of one or other of two alleles to exert a dominant effect with the result that the?
Failure of one or other of two ALLELES to exert a dominant effect with the result that the PHENOTYPE has a form somewhere in between those of the two phenotypes that would be produced were either gene homozygous.
What is it called when both alleles are partially expressed?
A heterozygous condition in which both alleles at a gene locus are partially expressed, often producing an intermediate phenotype. Also called partial dominance.
What is the pattern of inheritance in which a cross between two phenotypically different parents produces an offspring?
The classic example is in flower colour where, for example, crossing white and red snapdragons produces a pink offspring. Compare CODOMINANCE. See also DOMINANCE (1).
Do incomplete dominance, epistasis, and pleiotropy affect genetic control?
Even considering the effects of incomplete dominance, epistasis, and pleiotropy as modifiers of genetic control, the possible phenotypes change only in degree or number of discrete possibilities.
What is the difference between dominant and recessive heredity?
In dominant and recessive heredity, dominant alleles are those that require only one copy to be displayed. Recessive alleles, however, require two alleles in order to show up in the organism. So under most circumstances, an individual with one dominant and one recessive allele (called a heterozygote) will only express the dominant version. However, this is not the case when it comes to incomplete dominance.
When two alleles are simultaneously exhibited together?
Incomplete dominance: When two alleles are simultaneously exhibited together.

Mechanisms of Incomplete Dominance
- Many genes show complete dominance. This means that if an individual is heterozygous for a particular gene, the dominant allele will completely mask the recessive allele. Many of the properties that the Austrian monk Gregor Mendel studied in his famous pea plants were controll…
Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
- Incomplete dominance is not the same as codominance. In codominance, both alleles can be seen in the phenotype at the same time. Instead of being uniformly pink, a flower with red and white alleles that show codominance will have patches of red and patches of white. As with incomplete dominance, the F2 generation from heterozygous plants will have a ratio of 1:2:1 of r…
Examples of Incomplete Dominance
- In Humans
A child born to a parent with straight hair and a parent with curly hair will usually have wavy hair, or hair that is a little curled, due to the expression of both curly and straight alleles. Incomplete dominance can be seen in many other physical characteristics such as skincolor, height, hand si… - In Other Animals
The Andalusian chicken, a type of chicken native to the Andalusia region of Spain, shows incomplete dominance in its feather color. A white male and a black female will often produce offspring that have blue-tinged feathers. This is caused by a dilution gene that partially dilutes th…
Related Biology Terms
- Allele– A certain form of a gene.
- Dominant– An allele that masks the phenotype of a recessive allele for the same gene.
- Phenotype– Observable physical characteristics from genes and the environment.
- Punnett square– A diagram that shows the possible outcomes of breeding between two individuals.
Quiz
- 1. Which is NOT an example of incomplete dominance? A. A pink flower produced from red and white flowers B. A flower that is both red and white produced from red and white flowers C. Curly-haired and straight-haired individuals producing wavy-haired offspring D.A highly spotted dog and a non-spotted dog producing puppies with a few spots 2. A rose shows incomplete dominance; …
What Is Incomplete Dominance?
Mechanism of Incomplete Dominance
- Incomplete dominance occurs because neither of the two alleles is completely dominant over the other. This results in a phenotype that is a combination of both. Gregor Mendel conducted experiments on pea plants. He studied on seven characters with contrasting traits and all of them showed a similar pattern of inheritance. Based on this, he generalized the law of inheritance. Lat…
Concept of Dominance
- In genetics, Dominance is a relationship between alleles of one gene. In order to understand the concept of the dominance of alleles, we need to know more about genes. So far we know that genes are a hereditary unit in organisms which exist as a pair of alleles in diploid organisms. These pair of alleles may or may not be similar. That is, a heterozygous gene has two dissimilar …
Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
- Incomplete dominance and codominance are different from each other. In codominance, both the alleles present on a gene are expressed in the phenotype. A flower showing codominance will have patches of red and white instead of a uniformly pink flower. In incomplete dominance, the F2 generation from heterozygous plants will have a ratio of 1:2:1 with the phenotypes red, white an…