
What are intradermal injections typically used for?
Intradermal injections are typically used in skin sensitivity tests, such as for allergens and tuberculosis, in which a quick reaction can be measured.
How to give an intradermal injection?
Where can I give an intramuscular injection?
- Thigh: Look at your thigh and divide it into 3 equal parts. The middle third is where the injection will go. ...
- Hip: Have the person getting the injection lie on his or her side. ...
- Upper arm muscle: Completely expose the upper arm. You will give the injection in the center of an upside down triangle. ...
- Buttocks: Expose one side of the buttocks. ...
What is the difference between intradermal and intramuscular?
What is the difference between intradermal and intramuscular vaccination? Intramuscular vaccination is given deep into the deltoid (upper arm) muscle in adults and into the anterolateral area of the thigh in infants. Intradermal vaccination is given into the upper skin area over the deltoid muscle in adults or lateral thigh area of infants.
What is the difference between intradermal and subcutaneous?
is that intradermal is in medicine, injections or infusions fall into the parenteral category of drug/substance delivery methods intradermal means within, about, or below a dermal tissue layer (typically the skin) and describes the location of administration while subcutaneous is pertaining to the fatty layer under the skin.
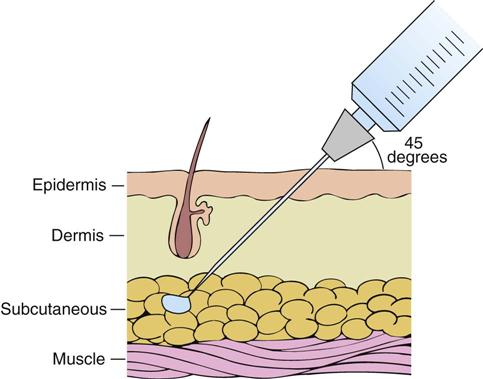
What is meant by intradermal injection?
Intradermal injection, often abbreviated ID, is a shallow or superficial injection of a substance into the dermis, which is located between the epidermis and the hypodermis. This route of administration is relatively rare compared to injections into the subcutaneous tissue or muscle.
What is an example of intradermal injection?
These types of injections are used for sensitivity testing because the patient's reaction is easy to visualize and the degree of reaction can be assessed. Examples of intradermal injections include tuberculosis (TB) and allergy testing.
Why intradermal injection is given?
AN INTRADERMAL injection may be given for diagnostic purposes, such as allergy or tuberculosis testing. Medication injected into the dermis is absorbed slowly because of this skin layer's limited blood supply.
What is intradermal in medical terms?
Medical Definition of intradermal : situated, occurring, or done within or between the layers of the skin also : administered by entering the skin intradermal injections.
What are the 3 types of injections?
What are the different types of injections?Intravenous (IV) injections. An IV injection is the fastest way to inject a medication and involves using a syringe to inject a medication directly into a vein. ... Intramuscular (IM) injections. ... Subcutaneous (SC) injections. ... Intradermal (ID) injections.
What needle is used for intradermal injection?
Intradermal injections (ID) are administered into the dermis just below the epidermis. Use a tuberculin syringe, calibrated in tenths and hundredths of a milliliter, with a needle length of 1/4 inches to 1/2 inches and a gauge of 25 – 27 Page 2 ID injections may be given on the inner aspect of the forearm.
What are the 5 injection sites?
IM injections are administered in five potential sites: deltoid (commonly used for adult vaccinations), dorsogluteal, ventrogluteal, rectus femoris, and vastus lateralis3,10,11 (Figure 1).
How do you give an intradermal?
0:331:46Administering Intradermal Injections - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipUp stretch the skin taut at the injection site by pulling gently with the thumb and forefinger ofMoreUp stretch the skin taut at the injection site by pulling gently with the thumb and forefinger of your non-dominant. Hand hold the needle very close to the patient's skin insert.
Why is intradermal injection painful?
However, because the pH of lidocaine solution is about 6, it is weakly acidic and inevitably causes pain during injection.
What degree is intradermal injection?
The angle of administration for an ID injection is 5 to 15 degrees. Once the ID injection is completed, a bleb (small blister) should appear under the skin. Checklist 56 outlines the steps to administer an intradermal injection.
How many types of injection are there?
Learn about the 4 types of injection: intradermal, subcutaneous, intravenous and intramuscular injections, and what they are used for in Singapore.
How do you inject a ID?
Place the needle almost flat against the patient's skin, bevel side up, and insert needle into the skin. Insert the needle only about 1/4 in, with the entire bevel under the skin. Keeping the bevel side up allows for smooth piercing of the skin and induction of the medication into the dermis.
What is the most commonly used site for intradermal injection quizlet?
Abdomen. Inner surface of the forearm. Rationale:Common sites to administer intradermal injections are the inner surface of the forearm or the upper back, under the scapula. The deltoid muscle is used for intramuscular injections, and the abdomen and thigh are used for subcutaneous injections.
What are the 5 injection sites?
IM injections are administered in five potential sites: deltoid (commonly used for adult vaccinations), dorsogluteal, ventrogluteal, rectus femoris, and vastus lateralis3,10,11 (Figure 1).
What are IM injections examples?
An intramuscular injection is an injection into a muscle....Examples of medicines given using an IM injectionantibiotics.contraceptive hormones such as Depo-Provera.vaccines.EpiPen (adrenaline injections for severe allergic reactions)antipsychotics (read more about depot antipsychotics).
Which of the following is a common site for intradermal injection quizlet?
Which of the following is a common site for intradermal injection? Forearm (Intradermal injections are commonly given on the forearm because it is relatively hair-free, and test results are easy to examine at that location.)
What is intradermal injection?
Intradermal injection, often abbreviated ID, is a shallow or superficial injection of a substance into the dermis, which is located between the epidermis and the hypodermis. This route is relatively rare compared to injections into the subcutaneous tissue ...
Where is the ID injection located?
Intradermal injection, often abbreviated ID, is a shallow or superficial injection of a substance into the dermis, which is located between the epidermis and the hypodermis. This route is relatively rare compared to injections into the subcutaneous tissue or muscle. Due to the more complex use, ID injections are not the preferred route ...
How many degrees is the mantoux injection?
The traditional procedure of ID injection ( Mantoux Procedure) involves injecting at angle of administration of 5 to 15 degrees angle, almost against the skin. With bevel (opening) side up, the needle is inserted about 1⁄8 inch (3 mm) with the entire bevel inside and injected while watching for a small wheal or blister to appear.
How long is a syringe?
The dosage given is usually less than 0.5 mL, less than given subcutaneously or intramuscularly. A 1⁄4 -to- 1⁄2 -inch-long (6 to 13 mm ) and 26 or 27 gauge thick needle is used.
What is intravenous injection?
intravenous injection an injection made into a vein. Intravenous injections are used when rapid absorption is called for, when fluid cannot be taken by mouth, or when the substance to be administered is too irritating to be injected into the skin or muscles.
What is an injection?
injection. [ in-jek´shun] 1. congestion. 2. the forcing of a liquid into a part, as into the subcutaneous tissues, the vascular tree, or an organ. 3. a substance so forced or administered; in pharmacy, a solution of a medicament suitable for injection. Immunizing substances, or inoculations, are generally given by injection.
What is the dynamic study of 30 min immediately after intradermal injection?
The dynamic study of 30 min immediately after intradermal injectionwas used to study the uptake/excretion pattern of the compound in lymph nodes and other organs of interest.
How long should a needle be for a muscle injection?
As a general rule, not more than 5 ml is given in an intramuscular injection for an adult.
Why do you give a sciatic nerve injection in the buttocks?
They should be given with extreme care, especially in the buttock, because the sciatic nerve may be injured or a large blood vessel may be entered if the injection is not made correctly into the upper, outer quadrant of the buttock.
Where is subcutaneous injection given?
Subcutaneous injections may be given wherever there is subcutaneous tissue, usually in the upper outer arm or thigh. A 25-gauge needle about 2 cm long is usually used, held at a 45-degree angle to the skin, and the amount injected should not exceed 2 ml in an adult. Subcutaneous insulin injections may be given at a 90-degree angle with an insulin syringe. Called also hypodermic injection.
Where are injections made?
In addition to the most common types of injections described below, injections are sometimes made into arteries, bone marrow, the spine, the sternum, the pleural space of the chest region, the peritoneal cavity, and joint spaces. In sudden heart failure, heart-stimulating drugs may be injected directly into the heart (intracardiac injection).
What gauge needle do you use for insulin?
Use a short (10mm) 26-27 gauge needle with a short bevel and a 1ml insulin syringe
How far should a bevel be from the epidermis?
Insert the bevel into the dermis with the bevel facing upwards, to a distance of approx. 2mm. The bevel should be visible through the epidermis
Is mantoux intradermally administered?
Mantoux and Q Fever tests are also performed intradermally. Hepatitis B vaccine is usually given by the IM route however there is a small percentage of the population who do not mount a protective immune response to the IM course of hepatitis B vaccines.
What is intravenous injection?
intravenous injection an injection made into a vein. Intravenous injections are used when rapid absorption is called for, when fluid cannot be taken by mouth, or when the substance to be administered is too irritating to be injected into the skin or muscles.
What is an injection?
injection. [ in-jek´shun] 1. congestion. 2. the forcing of a liquid into a part, as into the subcutaneous tissues, the vascular tree, or an organ. 3. a substance so forced or administered; in pharmacy, a solution of a medicament suitable for injection. Immunizing substances, or inoculations, are generally given by injection.
How long should a needle be for a gluteus maximus injection?
The needle should be long enough to insure that the medication is injected deep into the muscle tissue. The gauge of the needle depends on the viscosity of the fluid being injected. As a general rule, not more than 5 ml is given in an intramuscular injection for an adult. The maximum for an infant is 0.5 ml, and the injection is made into the vastus lateralis muscle. The needle is inserted at a 90-degree angle to the skin. When the gluteus maximus muscle is the site chosen for the injection, the patient should be in a prone position with the toes turned in if possible. This position relaxes the muscle and makes the injection less painful.
How long should a needle be for a muscle injection?
As a general rule, not more than 5 ml is given in an intramuscular injection for an adult.
Why do they inject medicine into the tongue?
The injection of medicines into the tongue, usually done as an emergency measure when a vein suitable for use is not available because of circulatory collapse.
Where is subcutaneous injection given?
Subcutaneous injections may be given wherever there is subcutaneous tissue, usually in the upper outer arm or thigh. A 25-gauge needle about 2 cm long is usually used, held at a 45-degree angle to the skin, and the amount injected should not exceed 2 ml in an adult. Subcutaneous insulin injections may be given at a 90-degree angle with an insulin syringe. Called also hypodermic injection.
Where to inject intramuscular injection?
intramuscular injectioninjection into the substance of a muscle, usually the muscle of the upper arm, thigh, or buttock. Intramuscular injections are given when the substance is to be absorbed quickly. They should be given with extreme care, especially in the buttock, because the sciatic nerve may be injured or a large blood vessel may be entered if the injection is not made correctly into the upper, outer quadrant of the buttock. The deltoid muscle at the shoulder is also used, but less commonly than the gluteus muscle of the buttock; care must be taken to insert the needle in the center, 2 cm below the acromion.
Examples of intradermal in a Sentence
Recent Examples on the Web Zydus Cadila said its vaccine would be administered using a needle-free applicator, thus ensuring painless intradermal vaccination. — Ramakrishnan Narayanan, Forbes, 29 Aug.
Medical Definition of intradermal
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!
What are the different types of injections?
When ‘type’ of injection is mentioned, ‘type’ usually refers to the body tissue or path by which a medication is injected. The ‘type’ of injection describes its route of administration.
Where is the best place to get an injection?
The best site on your body to receive an injection depends on factors such as the medication being given, what you are treating, how quickly or slowly the medication needs to work, and the type of injection you are receiving.
Rotate your injection sites - the best spot is not always the same spot
If you are receiving SC and IM injections regularly it’s recommended to rotate the site of your injections. Injecting in the same spot each time can cause the skin in that area to become lumpy or sunken.
5 steps to follow when giving injections at home
Some people are prescribed injectable medications that they need to administer regularly at home. Often injections given at home are SC injections, but sometimes IM injections also need to be given at home.
Tips to help with needle phobia
A fear of needles or injections is very common, affecting about 1 in 10 people. It can cause your heart to race, your stomach to churn, and your blood pressure to increase then rapidly drop. It can make you faint or simply feel faint. A fear of injections may cause embarrassment, but it’s nothing to be ashamed of.
Sources
Infusion Associates. How Does an IV Work? [Accessed November 2, 2021]. Available from: https://infusionassociates.com/how-does-an-iv-work/.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.

Overview
Intradermal injection, often abbreviated ID, is a shallow or superficial injection of a substance into the dermis, which is located between the epidermis and the hypodermis. This route of administration is relatively rare compared to injections into the subcutaneous tissue or muscle. Due to the more complex use, ID injections are not the preferred route of administration for injection and therefore used for certain therapies only, such as tuberculosis tests and allergy tests. Specific benefits are a …
Injection sites
Common injection sites include the inner surface of the forearm and the upper back, under the shoulder blade.
Equipment
Equipment include syringes calibrated in tenths and hundredths of a milliliter. The dosage given is usually less than 0.5 mL, less than given subcutaneously or intramuscularly. A 1⁄4-to-1⁄2-inch-long (6 to 13 mm) and 26 or 27 gauge thick needle is used.
Mantoux procedure
The traditional procedure of ID injection known as the Mantoux procedure (as used in the Mantoux test) involves injecting at angle of administration of 5 to 15 degrees angle, almost against the skin. With bevel (opening) side up, the needle is inserted about 1⁄8 inch (3 mm) with the entire bevel inside and injected while watching for a small wheal or blister to appear.
Intradermic needles
Traditionally hypodermic needles are used for intradermal injections, instead of intradermic needles. Various microneedle technology researchers worldwide develop new devices and therapies to overcome typical usability issues associated with the traditional Mantoux procedure. Most intradermic needles require a change in injection technique or instruction to use, for example a perpendicular intradermal injection.
See also
• Subcutaneous injection
• Intramuscular injection
• Intravenous injection