What is another name for leiomyoma?
Fibroma, plural, leiomyomata or, incorrect, but increasingly popular, leiomyomas A benign, well-circumscribed smooth muscle tumor most common in the uterus and stomach. See Fibroid, Fibroma, Intestinal leiomyoma.
What is uterine leiomyomata?
Uterine Leiomyomata - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Uterine fibroids or leiomyomata are the most common benign tumor affecting women. An early 2003 study by Baird et al. showed that the estimated incidence of fibroids in women by age 50 was 70% for white women and reached over 80% black women.[1]
What is metastatic leiomyoma?
Metastatic leiomyoma are an extremely rare complication after surgery to remove the uterus for uterine fibroids. The most frequent sites of occurrence are the lungs and pelvis. The lesions are hormonally responsive.
What is leiomyoma polycythemia?
A leiomyoma, also known as fibroids, is a benign smooth muscle tumor that very rarely becomes cancer (0.1%). They can occur in any organ, but the most common forms occur in the uterus, small bowel, and the esophagus. Polycythemia may occur due to increased erythropoietin production as part of a paraneoplastic syndrome . The...

What is the meaning of Leiomyomata uteri?
Uterine fibroids (also called leiomyomas) are growths made up of the muscle and connective tissue from the wall of the uterus. These growths are usually not cancerous (benign). Your uterus is an upside down pear-shaped organ in your pelvis. The normal size of your uterus is similar to a lemon.
What kind of tumor is leiomyoma?
Leiomyomas, also known as fibroids, are a group of benign smooth muscle tumors commonly present in premenopausal women. These tumors are of monoclonal origin which arises from the smooth muscle of the uterus.
What causes Leiomyomata?
What causes fibroids? The cause of fibroids is not known. Research suggests each tumor develops from an abnormal muscle cell in the uterus and multiplies rapidly when encountering the estrogen hormone, which promotes the tumor's growth.
Is leiomyoma a tumor?
Leiomyomas are benign tumors arising from smooth muscle, most commonly seen in uterine myometrium, gastrointestinal tract, skin and lower extremities of middle-aged women.
Is leiomyoma serious?
Leiomyomas may enlarge to cause significant distortion of the uterine surface or cavity. Although they are benign, they commonly result in severe symptoms, such as heavy, irregular, and prolonged menstrual bleeding as well as anemia.
How fast do leiomyomas grow?
It grows quickly and can double in size in as little as one month.
Can I get pregnant with fibroids?
Many women who have fibroids can get pregnant naturally. Treatment may not even be necessary for conception. In some cases, however, fibroids can impact your fertility.
Are Leiomyomas painful?
Leiomyomas are often painful.
Which medicine is best for fibroids?
GnRH Agonists (Lupron) GnRH agonists are a class of medications that temporarily shrink fibroids and stop heavy bleeding by blocking production of the female hormone, estrogen. Lupron is the most well known of these drugs.
Can leiomyoma be removed?
Myomectomy (my-o-MEK-tuh-me) is a surgical procedure to remove uterine fibroids — also called leiomyomas (lie-o-my-O-muhs). These common noncancerous growths appear in the uterus. Uterine fibroids usually develop during childbearing years, but they can occur at any age.
Where can leiomyomas be found?
Leiomyoma are benign tumors of smooth muscle origin. They are most commonly found in the female genital tract, but they can also be found in the retroperitoneum and the urinary bladder.
What is a common complication of leiomyomas?
COMPLICATIONS. Clinical problems associated with leiomyomas are related to pregnancy, infertility, abnormal bleeding, large masses, pain, and sarcomatous changes.
Is uterine leiomyoma benign or malignant?
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are benign smooth muscle tumors of the uterus. These common tumors affect approximately 20 percent of women by the age of 40. Most cases of uterine fibroids do not cause symptoms (asymptomatic) and do not require treatment.
Is leiomyoma and fibroid same?
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the uterus that often appear during childbearing years. Also called leiomyomas (lie-o-my-O-muhs) or myomas, uterine fibroids aren't associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer and almost never develop into cancer.
What causes leiomyoma of uterus?
One of the main risk factors associated with leiomyoma (AKA uterine fibroids) are genetic mutations in the smooth muscle cells. Additionally, the female steroid hormones estrogen and progesterone can be associated with fibroid growth, due to their effect on cell division and increasing certain growth factors.
Can leiomyomas turn malignant?
They affect 20–30 % of women older than 35 years. Leiomyomas can undergo various degenerative changes including malignant degeneration.
What is a leiomyomata?
What is Leiomyomata? Leiomyomata which is also known by various other names like Uterine Fibroids, Uterine Myoma, Leiomyoma, and Fibromyoma is a pathological condition in which there is growth of benign lesions in the muscle tissue of the uterus of a female. Leiomyomata is quite a common condition and about 50% of females ...
Where is the leiomyomata located?
Leiomyomata is primarily of four types which have been described below. They are classified based on their location in the uterus. Subserosal Leiomyomata: The lesion or fibroid in this type of Leiomyomata is found in the outer portion of uterus and their growth is also in that direction. Intramural Leiomyomata: This is by far ...
What are the Chances of Recurrence of Leiomyomata Post Surgical Removal?
Myomectomy is the procedure which is done for treatment of Leiomyomata but post treatment by this method there is also a chance of recurrence of Leiomyomata. It is a bit difficult to judge the exact percentage of recurrence, studies have suggested a recurrence rate of 10% in a five year time frame when myomectomy is done using laparotomy. There is a greater chance of recurrence after a laparoscopic myomectomy. This means that if a female has frequent or recurrent Leiomyomata then the chances of that female getting pregnant or carrying her pregnancy to term is quite bleak post myomectomy for treatment of Leiomyomata.
How long does it take for fibroids to go away after hysteroscopic myomectomy?
There is no harm done to the uterus. The patient can return to normal functioning within two days of the procedure.
How long does it take to recover from leiomyomata?
This is usually done in an outpatient setting and the recovery time is usually three days.
How long does it take to recover from a laparoscopic myomectomy?
It uses a laparoscope for removal of the fibroids and is done in an outpatient setting and the patient requires at least a couple of weeks to fully recover from the procedure.
Can leiomyomata cause pain?
As stated, many cases of Leiomyomata may not cause any problems but in some cases certain symptoms can be experienced especially if a female has submucosal type of Leiomyomata. These symptoms are: Heavy and prolonged menstrual periods. Severe pain behind the legs. Experiencing pressure or pain in the pelvic region.
What is a leiomyoma tumor?
leiomyoma. [ li″o-mi-o´mah] a benign tumor derived from smooth muscle, most often of the uterus (leiomyoma uteri). bizarre leiomyoma epithelioid leiomyoma. leiomyoma cu´tis one arising from cutaneous or subcutaneous smooth muscle fibers, found singly or multiply, usually as lesions arising from arrectores pilorum muscles;
Where is a leiomyoma found?
A benign tumour of smooth muscle found most commonly in the womb (uterus). Leiomyomas often contain much fibrous tissue. Also known as FIBROID, fibromyoma or leiomyofibroma.
What is a benign tumor composed of muscle tissue?
A benign tumor composed of muscle tissue. Leiomyomas in the uterus are sometimes called fibroids.
What is epithelioid leiomyoma?
epithelioid leiomyoma one in which the cells are polygonal rather than spindle shaped, usually found in the stomach. Called also bizarre leiomyoma and leiomyofibroma. leiomyoma u´teri ( uterine leiomyoma) leiomyoma of the uterus; called also uterine myoma and, colloquially, fibroids. It is the most common of all tumors found in women.
What is a fibroma?
Fibroma, plural, leiomyomata or, incorrect, but increasingly popular, leiomyomas A benign, well-circumscribed smooth muscle tumor most common in the uterus and stomach. See Fibroid, Fibroma, Intestinal leiomyoma.
When do leiomyomas occur?
Leiomyomas usually occur during the third and fourth decades, and are often multiple, although a single tumor may occur. They are usually small but may grow quite large and occupy most of the uterine wall; after menopause, growth usually ceases. Symptoms vary according to the location and size of the tumors.
Can a leiomyoma cause abortion?
They may also cause spontaneous abortion and death of the fetus. Small leiomyomas are usually left undisturbed and are checked at frequent intervals. Larger tumors may be removed surgically, sometimes accompanied by a hysterectomy, or medication may be prescribed to induce a temporary menopause. Leiomyoma of the uterus.
What is a leiomyoma?
leiomyomas, leiomyomata. Uterine lipoleiomyoma, a type of leiomyoma. H&E stain. Specialty. Oncology. A leiomyoma, also known as fibroids, is a benign smooth muscle tumor that very rarely becomes cancer (0.1%). They can occur in any organ, but the most common forms occur in the uterus, small bowel, and the esophagus.
What is the plural of "leiomyomas"?
The word is from leio- + myo- + -oma, "smooth-muscle tumor". The plural form can be either the English leiomyomas or the classical leiomyomata.
Where does leiomyoma enucleate?
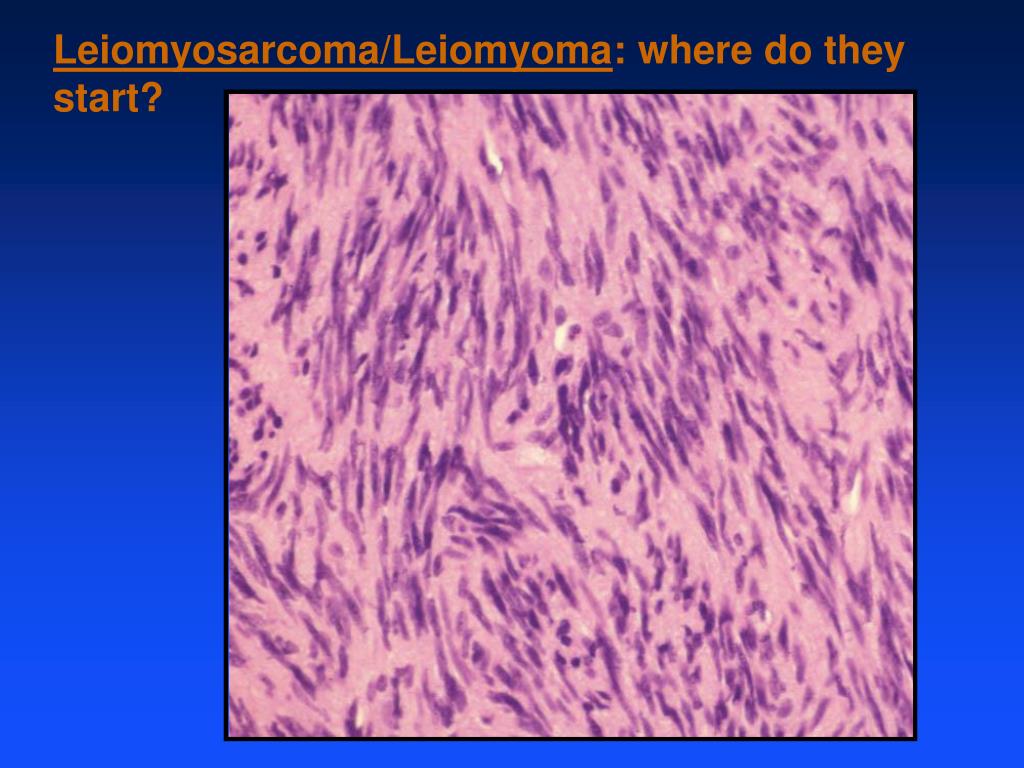
Leiomyoma enucleated from a uterus. External surface on left; cut surface on right. Micrograph of a small, well-circumscribed colonic leiomyoma arising from the muscularis mucosae and showing fascicles of spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and elongated, cigar-shaped nuclei. Uterine fibroids are leiomyomata of the uterine smooth muscle.
What is a cutaneous leiomyoma?
Solitary cutaneous leiomyoma. Multiple cutaneous (or pilar) leiomyomas arising from the arrectores pilorum muscles. Angioleiomyomas (Vascular leiomyomas) that are thought to arise from vascular smooth muscle. Dartoic (or genital) leiomyomas originating in the dartos muscles of the genitalia, areola, and nipple.
What are the symptoms of a 10 cm leiomyoma?
The symptoms for a 30 year old male with a 10 cm leiomyoma included "dead leg" pains. Tumor was intertwined with quadricep muscles, making identification and excision difficult. Tumor was successfully excised with only minor rehabilitation required.
What is familial leiomyoma?
Familial leiomyoma. Associated with papillary variant of renal cell carcinoma and multiple cutaneous leiomyoma. Defect is in the fumarate hydratase gene in the long arm of chromosome 1.
Is fibromyoma a benign breast neoplasm?
Fibromyoma of the breast is an extremely rare benign breast neoplasm. Most reports in literature mention a history of hysterectomy for uterine fibroids, although the question of whether these fibromyomas are possibly metastases of the uterine fibroids has not been investigated.
What are the symptoms of a leiomyoma?
Common presenting symptoms include metrorrhagia, menorrhagia , or a combination of the two. Less common presenting symptoms include dyspareunia, pelvic pain, bowel problems, urinary symptoms, or signs and symptoms related to anemia. Most of the less frequent symptoms are a reflection of the mass effect produced by leiomyomas on surrounding structures. Patients may also be completely asymptomatic with an incidental finding of fibroids on imaging.
Is myomectomy a surgical procedure?
Myomectomy. An invasive surgical option for those who desire fertility preservation. There is no large randomized controlled trial showing that myomectomy can improve fertility for patients. [2][10]Furthermore, the outcome is highly dependent on the location and size of the fibroid. [8][20]Nevertheless, it can be an effective treatment option in those wishing to avoid hysterectomy.
Is uterine leiomyomata benign?
Uterine leiomyomata or fibroids are an extremely common benign neoplasm in women of reproductive age. Although they are benign, they can have a significant impact on the everyday physical and mental well-being of women with this condition. This activity outlines the presentation, evaluation, and management options of fibroids, and reviews the role of the healthcare team in diagnosis and treatment options for patients with this condition.
What is leiomyoma of the uterus?
Better known as uterine fibroids, leiomyomas are benign, fibrous uterine tumors. “ Leio ” means ‘smooth’, ” myo ” means ‘muscle’, and ” oma ” means ‘tumor’.
What are the most important facts to know about leiomyoma of the uterus?
To summarize, leiomyoma of the uterus, also known as uterine fibroids, are the most common gynecological tumors. Leiomyomas are almost always benign, and can range from small, barely visible tumors to larger, palpable ones. Their growth is associated with genetic mutations in smooth muscle cells, and risk factors include hormones like estrogen and progesterone. The different types of leiomyoma are categorized according to their location: subserosal leiomyomas arise under the perimetrium, intramural leiomyomas are found within the walls of the uterus, and submucosal leiomyomas can be found beneath the endometrium.
How do you diagnose leiomyoma of the uterus?
Since leiomyomas are usually asymptomatic, they’re often found incidentally upon routine examination in the obstetrics and gynecology ward. Palpation and either abdominal or transvaginal ultrasound are both common techniques that lead to the discovery of leiomyomas. Some individuals may get additional imaging testing, such as MRI, which can aid in localization of the leiomyoma when planning surgical intervention or if malignancy is suspected. Finally, in rare cases, especially if there’s abnormal vaginal bleeding, a biopsy can be done to rule out sarcoma .
What are subserosal uterine leiomyomas of the uterus?
Subserosal leiomyomas can extend out of the uterus and even attach to other surrounding organs, receiving blood supply from them.
What is the most common gynecological tumor?
Leiomyoma is the most common gynecological tumor. They affect 30–50% of the female population in reproductive age, and are predominantly found among individuals of African descent. Leiomyomas are benign tumors that originate in smooth muscle cells of the myometrium, which is the thick middle layer of the uterine wall that contracts ...
What is intramural leiomyoma?
Intramural leiomyomas arise within the wall of the uterus. They are the most common type of leiomyomas, and can be associated with infertility, miscarriage, fetal malpresentation, and preterm birth.
What are the risks of developing leiomyoma?
Therefore, the higher the levels of these hormones, the higher the risk of developing leiomyomas. Higher levels of female steroid hormones are associated with breastfeeding, perimenopausal, and pregnant individuals. People that have never been pregnant (AKA “nulliparous” individuals) are also at higher risk for leiomyoma.
Which hormones are binding in uterine leiomyomataand in normal uterine tissues?
Estrakial and progesterone binding in uterine leiomyomataand in normal uterine tissues.
What is the procedure that removes fibroids?
The choice depends on the size of the fibroids and other factors such as previous births and previous surgeries. Myomectomy. In this surgical procedure only the fibroids are removed; the uterus is repaired and left in place. This is the surgical procedure many women choose if they are not finished with childbearing.
Overview
There are three major types of uterine fibroids. Intramural fibroids grow within the muscular uterine wall. Submucosal fibroids bulge into the uterine cavity. Subserosal fibroids project to the outside of the uterus. Some submucosal or subserosal fibroids may be pedunculated — hanging from a stalk inside or outside the uterus.
Symptoms
Many women who have fibroids don't have any symptoms. In those that do, symptoms can be influenced by the location, size and number of fibroids.
Causes
Doctors don't know the cause of uterine fibroids, but research and clinical experience point to these factors:
Risk factors
There are few known risk factors for uterine fibroids, other than being a woman of reproductive age. Factors that can have an impact on fibroid development include:
Complications
Although uterine fibroids usually aren't dangerous, they can cause discomfort and may lead to complications such as a drop in red blood cells (anemia), which causes fatigue, from heavy blood loss. Rarely, a transfusion is needed due to blood loss.
Prevention
Although researchers continue to study the causes of fibroid tumors, little scientific evidence is available on how to prevent them. Preventing uterine fibroids may not be possible, but only a small percentage of these tumors require treatment.

Overview
A leiomyoma, also known as a fibroid, is a benign smooth muscle tumor that very rarely becomes cancer (0.1%). They can occur in any organ, but the most common forms occur in the uterus, small bowel, and the esophagus. Polycythemia may occur due to increased erythropoietin production as part of a paraneoplastic syndrome.
Uterus
Uterine fibroids are leiomyomata of the uterine smooth muscle. As other leiomyomata, they are benign, but may lead to excessive menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia), often cause anemia and may lead to infertility.
A rare form of these tumors is uterine lipoleiomyoma—benign tumors consisting of a mixture of adipocytes and smooth muscle cells. Uterine lipoleiomyomata ha…
Gallbladder
Mesenchymal neoplasms of the gallbladder are rare and in particular leiomyomas of the gallbladder have been rarely reported, all of them in patients with immune system disorders. Although, recently, a case was reported in absence of associated immunodeficiency at Monash Hospital in Melbourne Australia in a healthy 39-year-old woman with no symptoms.
Skin
Leiomyomas of the skin are generally (1) acquired, and (2) divided into several categories:
• Solitary cutaneous leiomyoma
• Multiple cutaneous (or pilar) leiomyomas arising from the arrectores pilorum muscles
• Angioleiomyomas (Vascular leiomyomas) that are thought to arise from vascular smooth muscle
Esophagus, stomach and small intestines
Leiomyoma is the most common benign mesenchymal tumor of esophagus and second most common benign tumor of the small bowel (with gastrointestinal stromal tumor as most common). Although leiomyoma is the most common benign esophageal tumor, malignant carcinoma is still 50 times more likely. Approximately 50% of cases are found in the jejunum, followed by the ileum in 31% of cases. Almost one half of all lesions are less than 5 centimeters.
Other locations, metastatic leiomyoma
• Metastatic leiomyoma are an extremely rare complication after surgery to remove the uterus for uterine fibroids. The most frequent sites of occurrence are the lungs and pelvis. The lesions are hormonally responsive.
• Fibromyoma of the breast is an extremely rare benign breast neoplasm. Most reports in literature mention a history of hysterectomy for uterine fibroids, although the question of whether these fibromyomas are possibly metastases of the uterine fibroids has not b…
Familial leiomyoma
• Associated with papillary variant of renal cell carcinoma and multiple cutaneous leiomyoma. Defect is in the fumarate hydratase gene in the long arm of chromosome 1.
See also
• Leiomyosarcoma
• Elagolix/estradiol/norethindrone acetate