Things You Must Know about Liabilities in Accounting
- Liabilities Meaning in Accounting. Liabilities in accounting refer to obligations that usually end up in the balance sheet of a company.
- Key Facts about Liabilities in Accounting. ...
- Freshbooks - Best Software Compatible for Liabilities in Accounting. ...
What is liability in accounting?
What is Liability in Accounting? Hub > Accounting. Liabilities in accounting is a company’s financial obligations, like the money a business owes its suppliers, wages payable and loans owing, which can be found on a business’ balance sheet.
What are the different types of liabilities in accounting?
There are many different types of liabilities including accounts payable, payroll taxes payable, and bank notes. Basically, any money owed to an entity other than a company owner is listed on the balance sheet as a liability.
What are liabilities in economics?
owed to another person or company. In other words, liabilities are future sacrifices of economic benefits Economic Value Added (EVA) Economic Value Added (EVA) shows that real value creation occurs when projects earn rates of return above their cost of capital and this increases value for shareholders.
What are the current liabilities of a company?
Current Liabilities: Also called short-term liabilities. These liabilities are due within a year. These include client deposits, interest payable, salaries and wages payable and any amount owing to suppliers. Long-Term Liabilities: Any financial obligation that takes more than a year to pay back, such as a business loan or mortgage.
What is liabilities in accounting with example?
Liabilities are any debts your company has, whether it's bank loans, mortgages, unpaid bills, IOUs, or any other sum of money that you owe someone else. If you've promised to pay someone a sum of money in the future and haven't paid them yet, that's a liability.
What are liabilities?
What Are Liabilities? Broadly speaking, liabilities are things like credit card debts, mortgages and personal loans. A liability is a debt you must pay off, now or in the future.
What is a liability vs asset?
In its simplest form, your balance sheet can be divided into two categories: assets and liabilities. Assets are the items your company owns that can provide future economic benefit. Liabilities are what you owe other parties. In short, assets put money in your pocket, and liabilities take money out!
What is the meaning of liabilities in business?
In business terms, liability is something that the company owes. Generally, it is an obligation or something that you owe somebody. Often times, liabilities are also defined as a company's legal financial debts that arise in the entire course of business operations and growth.
What are 3 types of liabilities?
There are three primary classifications for liabilities. They are current liabilities, long-term liabilities and contingent liabilities. Current and long-term liabilities are going to be the most common ones that you see in your business.
Is cash an asset or liability?
In short, yes—cash is a current asset and is the first line-item on a company's balance sheet. Cash is the most liquid type of asset.
What are 5 examples of liabilities?
Recorded on the right side of the balance sheet, liabilities include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bonds, warranties, and accrued expenses.
Is a house liability or asset?
At a very basic level, an asset is something that provides future economic benefit, while a liability is an obligation. Using this framework, a house could be viewed as an asset, but a mortgage would definitely be a liability. Most people who own a home have a mortgage but also have equity built up in that home.
Why a car is not an asset?
The obvious basic reason why a car is not an asset is that it depreciates in value while at the same time removing money from your pocket. Your car is loosing value every day that you are driving it and at the same time eating into your wallet to maintain it in terms of fuel, service, insurance etc.
Are liabilities debt?
Comparing Liabilities and Debt The main difference between liability and debt is that liabilities encompass all of one's financial obligations, while debt is only those obligations associated with outstanding loans. Thus, debt is a subset of liabilities.
What are assets and liabilities examples?
In other words, assets are items that benefit a company economically, such as inventory, buildings, equipment and cash. They help a business manufacture goods or provide services, now and in the future. Liabilities are a company's obligations—either money owed or services not yet performed.
Is rent a liability or asset?
Rent Payable is a liability account in the general ledger of the tenant which reports the amount of rent owed as the date of the balance sheet.
What are 2 types of liabilities?
Current liabilities (short-term liabilities) are liabilities that are due and payable within one year. Non-current liabilities (long-term liabilities) are liabilities that are due after a year or more.
What are the types of liabilities?
Different types of liabilities in accountingAccounts payable.Income taxes payable.Interest payable.Accrued expenses.Unearned revenue.Mortgage payable.
What are assets and liabilities examples?
Examples of assets and liabilitiesbank overdrafts.accounts payable, eg payments to your suppliers.sales taxes.payroll taxes.income taxes.wages.short term loans.outstanding expenses.
What are liabilities in life?
Liability is a fancy word for debt, or something that you owe. Once you know your total liabilities, you can subtract them from your total assets, or the value of the things you own — such as your home or car — to calculate your net worth.
What are liabilities in accounting?
Liabilities are any debts your company has, whether it’s bank loans, mortgages, unpaid bills, IOUs, or any other sum of money that you owe someone else.
What are long term liabilities?
Some common examples of long-term liabilities include: 1 Principal and interest payments due more than a year from now 2 Bonds, debentures and long-term loans 3 Deferred tax liabilities 4 Lease payments that aren’t due for more than a year 5 Pension obligations 6 Mortgage, equipment and other capital payments that aren’t due for more than a year
What do accountants call debts?
Accountants call the debts you record in your books “liabilities,” and knowing how to find and record them is an important part of bookkeeping and accounting. Here’s everything you need to know about liabilities.
What does it mean when a business has a lower debt ratio?
Generally speaking, the lower the debt ratio for your business, the less leveraged it is and the more capable it is of paying off its debts . The higher it is, the more leveraged it is, and the more liability risk it has.
What does it mean when your balance sheet doesn't balance?
Assets = Liabilities + Equity. If your assets don’t equal your liabilities and equity, the two sides of your balance sheet won’t ‘balance,’ the accounting equation won’t work, and it probably means you’ve made a mistake somewhere in your accounting. These days, the two-column balance sheet format is less popular.
What is current liability?
Current liabilities are debts that you have to pay back within the next 12 months.
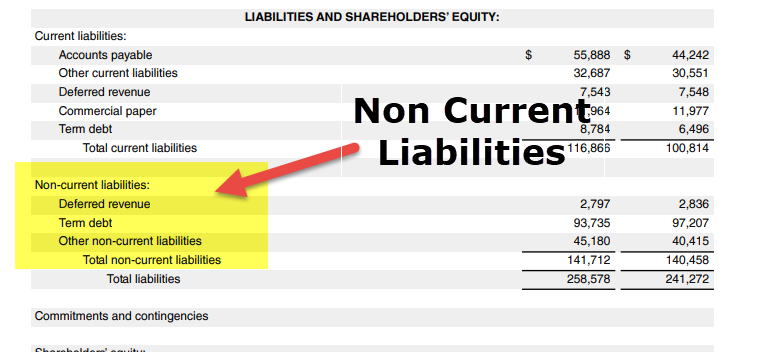
How long are non-current liabilities due?
Also sometimes called “non-current liabilities,” these are any obligations, payables, loans and any other liabilities that are due more than 12 months from now.
What is liability in accounting?
A liability can also mean a legal or regulatory risk or obligation. In corporate accounting, companies book liabilities in opposition to assets.
What does "liability" mean?
Liability can also mean a legal or regulatory risk or obligation.
What Is a Liability?
A liability is something a person or company owes, usually a sum of money. Liabilities are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits including money, goods, or services. Recorded on the right side of the balance sheet, liabilities include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bonds, warranties, and accrued expenses.
How Do I Know If Something Is a Liability?
A liability is something that is owed to or obligated to someone else. It can be real (e.g. a bill that needs to be paid) or potential (e.g. a possible lawsuit).
What Is a Contingent Liability?
A contingent liability is an obligation that might have to be paid in the future, but there are still unresolved matters that make it only a possibility and not a certainty. Lawsuits and the threat of lawsuits are the most common contingent liabilities, but unused gift cards, product warranties, and recalls also fit into this category.
How Are Current Liabilities Different From Long-Term (Noncurrent) Ones?
Current liabilities are due with a year and are often paid for using current assets. Non-current liabilities are due in more than one year and most often include debt repayments and deferred payments.
How Do Liabilities Relate to Assets and Equity?
The accounting equation states that—assets = liabilities + equity. As a result, we can re-arrange the formula to read liabilities = assets - equity. Thus, the value of a firm's total liabilities will equal the difference between the values of total assets and shareholders' equity. If a firm takes on more liabilities without accumulating additional assets, it must result in a reduction in the value of the firm's equity position.
How do liabilities relate to assets?
In accounting, liabilities are opposite to assets. Assets are things a company owns outright or something that's owed to them by another business or entity. Assets can be tangible, like property, buildings, vehicles, machinery or equipment, or intangible, like intellectual property, patents, accounts receivable or interest owed. You use information about a company's liabilities and assets in relation to each other when calculating stockholder equity, by subtracting the amount of liabilities from the amount of assets. It also helps establish the overall health and wellness of a company. You can often find this expressed in two versions of a formula:
What is liability?
Liability essentially is an obligation, financial or service-based, between two parties that aren't yet completed or paid in full. It's the state of being responsible for something. In business and accounting, a liability is a financial obligation a company has, and it often results in sacrificing future economic benefits to other businesses or organizations, like business transactions, sales, events or the exchange of services or assets. Some liabilities, like income taxes payable and accounts payable, are part of regular business operations. Liabilities can also be alternatives to equity for a company's financial funding.
What is an expense vs. a liability?
Expenses are a company's costs of operations used to create revenue and its liabilities are the obligations and debts it owes to others. You can pay expenses immediately or they can become a liability if a company delays payment, like using loans for bills and assets, which also incurs interest as another liability. Another difference is that total expenses help calculate a company's net income and get listed on a company's income statement, whereas its balance sheet lists liabilities.
What is current vs. long-term liability?
Current liabilities are short-term financial obligations due within 12 months or fewer. Long-term liabilities, or non-current liabilities, are obligations not due for a year or more. Sometimes a business can have one liability that falls into both categories. For example, a 30-year mortgage for a factory space taken out by a company is a long-term liability, though the monthly mortgage payments due during the present year are current liabilities, especially for the balance sheet used in the company's accounting documents.
What is a liability in finance?
A liability is a financial obligation of a company that results in the company’s future sacrifices of economic benefits to other entities or businesses. A liability can be an alternative to equity as a source of a company’s financing. Moreover, some liabilities, such as accounts payable.
What is the accounting equation for liabilities?
According to the accounting equation, the total amount of the liabilities must be equal to the difference between the total amount of the assets and the total amount of the equity.
What is accounts payable?
Accounts payable: Accounts Payable Accounts payable is a liability incurred when an organization receives goods or services from its suppliers on credit. Accounts payables are. These are the unpaid bills to the company’s vendors. Generally, accounts payable are the largest current liability for most businesses.
What is interest payable?
Interest Payable Interest Payable is a liability account shown on a company’s balance sheet that represents the amount of interest expense that has accrued. Interest expenses that have already occurred but have not been paid. Interest payable should not be confused with the interest expenses.
Why are legal expenses considered contingent liabilities?
The legal expenses may be recognized as contingent liabilities because: The expenses are probable.
What is a mortgage payable?
Mortgage payable /long-term debt: Long Term Debt Long Term Debt (LTD) is any amount of outstanding debt a company holds that has a maturity of 12 months or longer. It is classified as a non-current liability on the company’s balance sheet.
What is the legal status of a non-human entity that is unable to repay its outstanding debts?
Bankruptcy Bankruptcy is the legal status of a human or a non-human entity (a firm or a government agency) that is unable to repay its outstanding debts. . In addition, liabilities determine the company’s liquidity and capital structure.
What is a liability in accounting?
In the context of accounting, liabilities are seen as the obligation of a business or company drawn from events or financial transactions from the past. Liabilities recognition in financial books is regulated depending on the accounting standards in use. A liability as such is definitely a claim by a creditor on the company's assets. In many instances, liabilities are of two types. This includes long-term and current liabilities in accounting with a difference of about 12 months among them.
What are some examples of liabilities in accounting?
For instance, accounts payable come up once services and goods are purchased by a business on credit from manufacturers or suppliers. As the business begins to pay the money owed to the supplier or manufacturer, the accounts payable of the business will then decrease.
What is contingent liability?
Among list of liabilities in accounting are contingent liabilities, which refer potential losses or potential liabilities. Contingent liabilities are dependent on the occurrence or not of an event in days to come. For example, if a business is notified of a lawsuit filed against it, indeed a potential loss or contingent liability is imminent ...
When does accounts payable come up?
For instance, accounts payable come up once services and goods are purchased by a business on credit from manufacturers or suppliers. As the business begins to pay the money owed to the supplier or manufacturer, the accounts payable of the business will then decrease. Deferred revenues and deposits by customers are other liabilities in accounting ...
Is estimated liability contingent liability?
Note that estimated liabilities differ from contingent liabilities. For instance, since such expenses as repairs, cover premiums, property taxes and energy consumed, among others are owed with absolute clarity because delivery of goods and services actually happened, they cannot be termed as contingent liability. Nevertheless, their amounts were not known during the preparation of financial statements and estimated amounts needed to be used.
Is the place of liabilities in a balance sheet?
In financial statements, the place of liabilities is almost assured. In balance sheets it's at the heart of the transactions and makes a fundamental element of financial accounting. In fact, every balance sheet is based on an equation that has liabilities at the scheme of things, where Assets are equal to Liabilities plus the Owner's Equity.
Is a liability enforceable?
It's worth remembering that all liabilities in accounting can be enforceable legally, but in virtually every business once a liability obligation has come up it's usually recognized and dealt with. In financial statements, the place of liabilities is almost assured. In balance sheets it's at the heart of the transactions and makes a fundamental element of financial accounting. In fact, every balance sheet is based on an equation that has liabilities at the scheme of things, where Assets are equal to Liabilities plus the Owner's Equity.
What are Liabilities?
Liabilities are legally binding obligations that are payable to another person or entity. Settlement of a liability can be accomplished through the transfer of money, goods, or services. A liability is increased in the accounting records with a credit and decreased with a debit. A liability can be considered a source of funds, since an amount owed to a third party is essentially borrowed cash that can then be used to support the asset base of a business. Examples of liabilities are:
What are some examples of liabilities?
Examples of liabilities are: Accounts payable. Accrued liabilities. Deferred revenue.
What is provision in accounting?
A provision is a liability or reduction in the value of an asset that an entity elects to recognize now, before it has exact information about the amount involved. For example, an entity routinely records provisions for bad debts , sales allowances, and inventory obsolescence .
What is contingent liability?
A contingent liability is a potential liability that will only be confirmed as a liability when an uncertain event has been resolved at some point in the future. Only record a contingent liability if it is probable that the liability will occur, and if you can reasonably estimate its amount.
When is a liability considered a current liability?
You would classify a liability as a current liability if you expect to liquidate the obligation within one year. All other liabilities are classified as long-term liabilities. If there is a long-term note or bond payable, that portion of it due for payment within the next year is classified as a current liability.
Which is the largest of the preceding liabilities?
Of the preceding liabilities, accounts payable and notes payable tend to be the largest. Liabilities are aggregated on the balance sheet within two general classifications, which are current liabilities and long-term liabilities.
Can a company have a negative liability?
It is possible to have a negative liability, which arises when a company pays more than the amount of a liability, thereby theoretically creating an asset in the amount of the overpayment. Negative liabilities tend to be quite small.
What is liability in accounting?
Home » Accounting Dictionary » What are Liabilities? Definition: A liability is a debt owed from one company to a person or company that is not an owner of business. In other words, liabilities are debts owed to non-owners or creditors.
What Does Liability Mean?
Basically, any money owed to an entity other than a company owner is listed on the balance sheet as a liability.
Why is sales tax considered a liability?
The sales tax expense is considered a liability because the company owed the state the money. Liabilities are split into two main categories on the balance sheet: current and long-term. Current liabilities consist of debts that will become due in the next year.
What is a long term debt?
Long-term liabilities consist of debts that have a due date greater than one year in the future. The most common long-term debts include bank notes and bonds. Long-term liabilities are listed after current liabilities on the balance sheet because they are less relevant to the current cash position of the company.
Is a long term liability a current liability?
Portions of long-term liabilities can be listed as current liabilities on the balance sheet. Most often the portion of the long-term liability that will become due in the next year is listed as a current liability because it will have to be paid back in the next 12 months. A. B. C.
Is sales tax a liability?
If the company does not remit the sales tax at the end of the month, it would record a liability until the taxes are paid. The sales tax expense is considered a liability because the company owed the state the money.
What is liability in financial reporting?
Defined by the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Framework: “A liability is a present obligation of the enterprise arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the enterprise of resources embodying economic benefits.”
What are the three types of liabilities?
There are three primary types of liabilities: current, non-current, and contingent li abilities. Liabilities are legal obligations or debt. Senior and Subordinated Debt In order to understand senior and subordinated debt, we must first review the capital stack. Capital stack ranks the priority of different sources of financing.
What is contingent liability?
Contingent liabilities#N#Contingent Liability A contingent liability is a potential liability that may or may not occur. The relevance of a contingent liability depends on the probability of the contingency becoming an actual liability, its timing, and the accuracy with which the amount associated with it can be estimated.#N#are liabilities that may occur, depending on the outcome of a future event. Therefore, contingent liabilities are potential liabilities. For example, when a company is facing a lawsuit of $100,000, the company would incur a liability if the lawsuit proves successful.
Why should current liabilities be closely watched?
Current liabilities should be closely watched by management to ensure that the company possesses enough liquidity from current assets. Current Assets Current assets are all assets that a company expects to convert to cash within one year. They are commonly used to measure the liquidity of a.
What is a short term liability?
Current liabilities (short-term liabilities) are liabilities that are due and payable within one year. Non-current liabilities (long-term liabilities) are liabilities that are due after a year or more. Contingent liabilities are liabilities that may or may not arise, depending on a certain event.
Why are long term liabilities important?
Long-term liabilities are crucial in determining a company’s long-term solvency.
What is residual income?
The Residual Income technique that serves as an indicator of the profitability on the premise that real profitability occurs when wealth is. that an entity is required to make to other entities due to past events or past transactions.

What Is Liability in Financial Accounting?
- A liability is an obligation, financial or service-based, between two parties that hasn’t yet been fulfilled or paid in full. It's the state of being responsible or liable for something. Some liabilities, like income taxes payable and accounts payable, are part of regular business operations. Liabilities can also be alternatives to equity for a com...
Common Types of Liabilities
- While there are many types of liabilities a company may assume, the most common types of liabilities include: 1. Mortgages or rent 2. Loans 3. Bonds 4. Warranties 5. Accrued expenses 6. Deferred revenues 7. Accounts payable 8. Income taxes payable Related: Complete Guide for Liabilities: Definition and Examples
What Is Current vs. Long-Term Liability?
- Liabilities in business often center on two categories, current liabilities and long-term liabilities. Current liabilities are short-term financial obligations due within 12 months or sooner. Long-term liabilities, or non-current liabilities, are obligations not due for a year or more. Sometimes a business can have one liability that falls into both categories. For example, a 30-year mortgage f…
How Do Liabilities Relate to Assets?
- In accounting, liabilities are opposite to assets. Assets are things a company owns outright or something that's owed to them by another business or entity. Assets can be tangible, like property, buildings, vehicles, machinery or equipment, or intangible, like intellectual property, patents, accounts receivable or interest owed. You use information about a company's liabilities and ass…
What Is An Expense vs. A Liability?
- Expenses are a company's cost of operation used to create revenue, and its liabilities are the obligations and debts it owes to others. You can pay expenses immediately or they can become a liability if a company delays payment, like using loans for bills and assets, which also incurs interest as another liability. Another difference is that total expenses help calculate a company's …