Common Causes
The chance of mastalgia being a symptom of breast cancer is quite low, but it's important to screen women who are at risk. Breast cancer is often painless, but breast pain can be a symptom of the disease. If you do have breast pain, call your doctor for an appointment right away.
Related Conditions
Seek medical attention if you notice the following symptoms:
- Pain that interferes normal day-to-day activities and/or affects sleep
- Pain lasts more than 2 weeks or that is noncyclic
- Bloody or abnormal discharge from the nipples
- Inverted nipple
- Change in the appearance of skin over the breast (orange-peel appearance)
- Hard lump that can be felt on palpation
- Lump that increases in size over time
Is mastalgia a sign of breast cancer?
- Hormones are making your breasts sore. ...
- You have a breast injury. ...
- Your breasts hurt due to an unsupportive bra. ...
- Breast pain is really coming from your chest wall. ...
- Breastfeeding is causing breast tenderness. ...
- You have a breast infection. ...
- Breast pain could be a medication side effect. ...
- You have a painful breast cyst. ...
When to worry about breast pain?
Your Breasts on Menopause
- Tenderness or pain. Why It Happens:Before your period, fluid builds up in your breasts, making them feel more swollen, tender, or painful than other times of the month. ...
- Changes in breast size and shape Why It Happens: As you near menopause, your levels of estrogen drop dramatically. ...
- Lumpy Breasts
What causes shooting pains in the breast?
What causes tender breasts post menopause?
See more

Is mastalgia serious?
For most women, mastalgia is mild-to-moderate rather than severe and often gets better on its own without treatment.
What is the cause of mastalgia?
One cause of noncyclic breast pain is trauma, or a blow to the breast. Other causes can include arthritic pain in the chest cavity and in the neck, which radiates down to the breast.
How do you treat mastalgia?
There are also a few other treatment methods that you can use to help relieve your pain, including:Wearing a well-fitting, supportive bra. ... Taking Vitamin E supplements and other multivitamins.Eliminating caffeine from your diet.Avoiding tobacco products.Using evening primrose oil.More items...•
How long does mastalgia last?
Often, cyclical mastalgia will settle over the course of a few months, returning to “normal” pre-menstrual breast discomfort without any specific treatment. Studies have shown that cyclical breast pain goes away within three months of onset in about 3 in 10 cases.
How is mastalgia diagnosed?
The diagnosis of mastalgia is most often made based on symptoms and a physical breast exam, though imaging studies may be done to further evaluate abnormalities noted during a physical exam. The chance of mastalgia being a symptom of breast cancer is quite low, but it's important to screen women who are at risk.
How can I reduce breast pain?
Steps you can take to minimize sore breasts include:Eliminate caffeine.Eat a low-fat diet.Reduce salt intake.Avoid smoking.Take an over-the-counter pain reliever.Ask your doctor if switching birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy medications may help.
When should you be worried about breast pain?
Talk to your doctor about your breast pain if you are worried, particularly, if you have a lump in the area of pain that does not go away after your period, redness, swelling, drainage from the area (signs of infection), nipple discharge, or if your breast pain is not clearly associated with your menstrual cycle, lasts ...
What vitamins help with breast pain?
Vitamins E and B6 are the most effective and least toxic agents available for the treatment of breast pain [β = 0.807, standard error (SE) = 0.433, P = 0.067].
Why I have pain under my right breast?
Pain under the right breast is rarely a cause for concern and often results from muscles strains or minor injuries. However, it can indicate a more serious condition, such as an infection, chest inflammation, or a gastrointestinal issue.
Which doctor should I consult for breast pain?
It's important to see a healthcare provider—either your primary care physician or your gynecologist—for any new breast or nipple pain. While most cases of breast pain are mild and easily managed, you do not want to delay a diagnosis of breast cancer or a serious non-breast related cause, like a heart condition.
Does breast pain get worse with age?
A woman's menstrual cycle causes hormone fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone. These two hormones can cause a woman's breasts to feel swollen, lumpy, and sometimes painful. Women sometimes report that this pain gets worse as they get older due to increased sensitivity to hormones as a woman ages.
Who suffers from PMS and mastalgia?
Cyclical mastalgia affects up to 40% of women before menopause, most often in their thirties [16]. In approximately 8% of these women had severe pain which interfered with their normal activities. A minority of women with the most severe pain experienced it during menstruation [17].
What vitamins help with breast pain?
Vitamins E and B6 are the most effective and least toxic agents available for the treatment of breast pain [β = 0.807, standard error (SE) = 0.433, P = 0.067].
Why is my left breast pain?
The first thing to do when you have left breast pain is get checked for a heart attack. Left breast pain can come from injuries or conditions that affect the breast tissue and milk ducts. Breast cancer isn't usually painful early on. An exception is inflammatory breast cancer, which also causes redness and swelling.
Why do I keep getting a stabbing pain in my breast?
Shooting pain in the breast is common, and is often the result of hormonal fluctuations in the body. If a person regularly experiences breast pain before a period, they will often find it disappears on its own when their period begins or ends.
Why Does My breast hurt when I press it?
Hormone shifts This sensitivity is known as cyclic mastalgia or fibrocystic changes. Around 50 percent of all women over the age of 30 experience this. Right before your period starts, your breasts may feel especially tender if you press on them, or they may ache.
How long does a cyclical mastalgiamight last?
Cyclical mastalgiamight last for more than 7 days in 11% of women [2].
Where was the cyclical mastalgia trial conducted?
The randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was undertaken through an academic hospital in Iran, with participants being premenopausal, medically well women aged [greater than or equal to] 18 years, with cyclical mastalgiaand a pain score of [greater than or equal to] 3 on the visual analogue scale (VAS).
What is the pain in the breast called?
pain in the breast; called also mammalgiaand mastodynia.
Can oral contraceptives help with mastalgia?
[11-13] Oral contraceptives have shown to be protective in benign breast disorders.
What is the pain of breasts called?
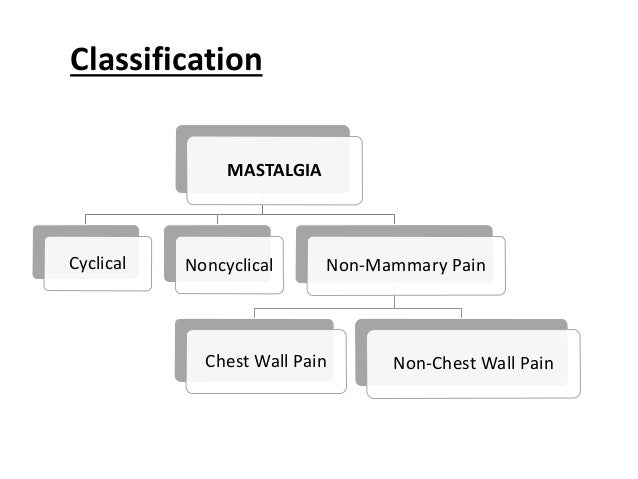
What is mastalgia ? Mastalgia is breast pain. There are 2 main types of mastalgia : Cyclical breast pain. The pain is linked to menstrual periods. Noncyclic breast pain. The pain may come from the breast. Or it may come from somewhere else, such as nearby muscles or joints, and may be felt in the breast.
What is noncyclic breast pain?
Noncyclic breast pain is fairly uncommon, feels different than cyclical mastalgia, and does not vary with the menstrual cycle. Generally, the pain is present all the time and is in only 1 specific location.
What are the treatments for cyclical breast pain?
Treatment for cyclical breast pain will depend on your symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
Can breast pain be radiating?
Or it may be so severe that you can’t wear tight-fitting clothing or handle close contact of any kind. The pain may be felt in only one breast. Or it may be felt as a radiating feeling in the underarm area. Some healthcare providers have women chart their breast pain to figure out if the pain is cyclical or not.
Is noncyclic breast pain hormonal?
It’s more difficult to figure out the best treatment for noncyclic breast pain. That’s because it’s hard to know exactly where the pain is coming from. In addition, the pain is not hormonal. Treatment will depend on your symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
How long does mastalgia last?
However, if no underlying pathology is present, it has high rates of spontaneous remission within three months to 3 years. Factors that are affecting the prognosis include the age of onset and the underlying etiology.
What is the pain in the breast?
Mastalgia is a medical term used for breast pain, one of the most common complaints among women of 15 to 40 years of age (child-bearing age). Approximately two-thirds of women during their reproductive lives suffer from this condition and seek medical help. It is a dull, aching pain while some women may describe it as heaviness, tightness, discomfort, or burning sensation in the breast tissue, which may be unilateral or bilateral. Most often, it is located in the upper outer quadrant of the breast and can sometimes radiate to an ipsilateral arm. It is most common in premenopausal and perimenopausal women, but postmenopausal women can also rarely develop such pain. The breast pain ranges from mild to severe, could be intermittent or constant throughout the day, and may interfere with the female's quality of life.[1][2][3]
Why does my breast hurt during my period?
Breast pain that is associated with the menstrual cycle due to hormonal variation often associated with breast swelling, tenderness, and lumpiness and generally bilateral in nature. Pain intensifies a couple of weeks before the start of periods, decreasing on the day when bleeding starts and subsides over the next few days. Most commonly seen in premenopausal women in the third or fourth decades of life.
What is the pain in the breasts that is not associated with the menstrual cycle?
Breast pain that is not associated with the menstrual cycle and does not vary with hormonal changes in the body. Instead, they are often related to internal anatomical changes, injuries, surgery, infections, or sometimes associated with other breast pathology, i.e., breast cysts or fibroadenoma. These are generally described as a localized sharp, burning breast pain. They are unilateral, constant, or intermittent, affecting one breast with a pinpoint localized area of involvement. Most likely affect women in their 30s and 50s.
How long does it take for breast pain to go away?
Generally, breast pain resolves on its own in 3 to 6 months. If it doesn't, then pharmacological treatment provides promising results in the majority of cases.
Where does extramammary pain come from?
It refers to the breast pain that is originating from a location outside the breast, such as the heart, lung, chest wall , or the esophagus. Extramammary breast pain feels as if it starts in the breast tissue, but in fact, it is a referred pain having its origin somewhere else. For example, pain originating from the chest wall (costochondritis), epigastric pain in GERD, or pain of gallbladder and stomach disease can be referred to give a false impression of breast pain.
Is breast pain a negative thing?
Many females having breast pain reported a negative impact on their life, especially interference with sexual activity (40% females), physical activity (30% females), negative impact on work, and social activities (10% females). [7]
What is mastalgia?
Mastalgia is the medical term for breast pain. There are two main types of mastalgia – cyclic and non-cyclic.
What are the symptoms of mastalgia?
Mastalgia is a symptom rather than a diagnosis, and presents in different ways depending on the type.
Why does cystic mastalgia hurt?
Cyclic mastalgia is thought to be caused by the normal monthly changes in hormones, but the reasons why this should cause pain, or why it affects some women to different degrees, while not affecting others at all are not fully understood. Research is ongoing, with various theories regarding hormone levels.
What is the best treatment for cyclic mastalgia?
For cyclic mastalgia, dietary changes, such as cutting out caffeine, reducing fat intake, and taking vitamin E are sometimes recommended.
What does it mean when your breast hurts?
Most commonly, breast pain is cyclical, meaning that it is related to the normal hormonal fluctuations of the menstrual cycle. Usually it is felt the week before the start of menses, and resolves after the end of menses. Hormonal breast pain tends to be in both breasts, and most severe in the upper and outer aspects of the breast.
How to help a breast pain?
Try Vitamin E . Studies have not consistently shown benefits of vitamin E for treating breast pain, though some women find it helpful. Using vitamin E for a few weeks to see if it will help is unlikely to cause any harm. However, long-term use of vitamin E supplementation is not recommended for breast pain, as there are some studies suggesting this may not be safe.
How to reduce pain in breasts?
Diet: Many patients report that cutting back on caffeine has greatly improved their breast pain. Also, a low-fat, high complex carbohydrate diet has been shown to be helpful in some small studies. Smoking: Smoking might increase breast pain by increasing epinephrine levels in the breast.
How many women have breast pain?
A survey of women found that almost half had mild breast pain, and about 1 in 5 had severe breast pain, although most had not reported these symptoms to their doctor. Breast pain is the most common breast-related symptom for which patients seek medical treatment, and accounts for about half of breast-related office visits.
What causes pain in the pectoralis muscle?
Other medications can also contribute to pain, including some antidepressants, cardiovascular agents, and antibiotics. Chest wall pain: This is most commonly from irritation of the pectoralis major muscle. Examples of activities that can cause this muscle pain include waterskiing, raking, rowing, and shoveling.
Is it normal for breast pain to be in both breasts?
Hormonal breast pain tends to be in both breasts, and most severe in the upper and outer aspects of the breast. Minor cyclical breast discomfort is very normal. However, in a small number of women, this cyclical pain can be moderate to severe, affecting day-to-day activities.
What Is Mastalgia?
Mastalgia is a medical term for breast pain. It’s a common affliction in women, with discomfort ranging in intensity from relatively mild to severely distressing. Breast pain may originate in a single spot, in several locations, or be referred from another part of the body, typically the chest, rib cage, or underarms. Mastalgia has a variety of causes, sometimes linked to hormone production and sometimes independent of it. The source of the pain is typically benign and often clears up on its own; cancer is only rarely involved.
How many forms of mastalgia are there?
There are two primary forms of mastalgia, and their symptoms vary accordingly:
What doctor can diagnose mastalgia?
For more information about mastalgia diagnosis and treatment, schedule an appointment with your primary care physician or gynecologist.
Is noncyclical mastalgia a menstrual cycle?
Noncyclical mastalgia occurs without any relation to the menstrual cycle. It is most frequent in women after menopause. The pain may be continual or episodic. Noncyclical breast pain appears to have a number of potential causes, including costochondritis, which is an inflammation of the interface between bone and cartilage in the rib cage.
What medications can cause mastalgia?
Medications: Certain medications, including infertility treatments, birth control pills, and over-the-counter antidepressants, may contribute to mastalgia.
Can breast pain affect both breasts?
Localized pain affecting only one breast (hormone-driven pain tends to affect both).
Can mastalgia be diagnosed?
The diagnosis of mastalgia will be made if no other cause for breast pain can be identified.
What does it mean when your breast hurts?
Breast pain (mastalgia) can be described as tenderness, throbbing, sharp, stabbing, burning pain or tightness in the breast tissue. The pain may be constant or it may occur only occasionally, and it can occur in men, women and transgender people. Breast pain can range from mild to severe. It may occur:
What does it mean when your breasts are swollen?
Described as dull, heavy or aching. Often accompanied by breast swelling, fullness or lumpiness. Usually affects both breasts, particularly the upper, outer portions, and can radiate to the underarm. Intensifies during the two weeks leading up to the start of the menstrual period, then eases up afterward.
What causes extramammary pain?
Pulling a muscle in the chest, for example, can cause pain in the chest wall or rib cage that spreads (radiates) to the breast. Arthritis that involves the cartilage in the chest, also known as costochondritis, can also cause pain.
How to stop breast pain from getting worse?
The following steps may help prevent the causes of breast pain, although more research is needed to determine their effectiveness. Avoid hormone therapy if possible. Avoid medications that are known to cause breast pain or make it worse. Wear a properly fitted bra, and wear a sports bra during exercise.
Why does my breast hurt after surgery?
Breast surgery. Breast pain associated with breast surgery and scar formation can sometimes linger after incisions have healed. Fatty acid imbalance. An imbalance of fatty acids within the cells may affect the sensitivity of breast tissue to circulating hormones. Medication use.
Why do my breasts hurt every month?
Throughout the month, not related to a menstrual cycle. In men, breast pain is most commonly caused by a condition called "gyne comastia" (guy-nuh-koh-MAS-tee-uh).
Does breast pain go away after menopause?
Most times, breast pain signals a noncancerous (benign) breast condition and rarely indicates breast cancer. Unexplained breast pain that doesn't go away after one or two menstrual cycles, or that persists after menopause, or breast pain that doesn't seem to be related to hormone changes needs to be evaluated.
