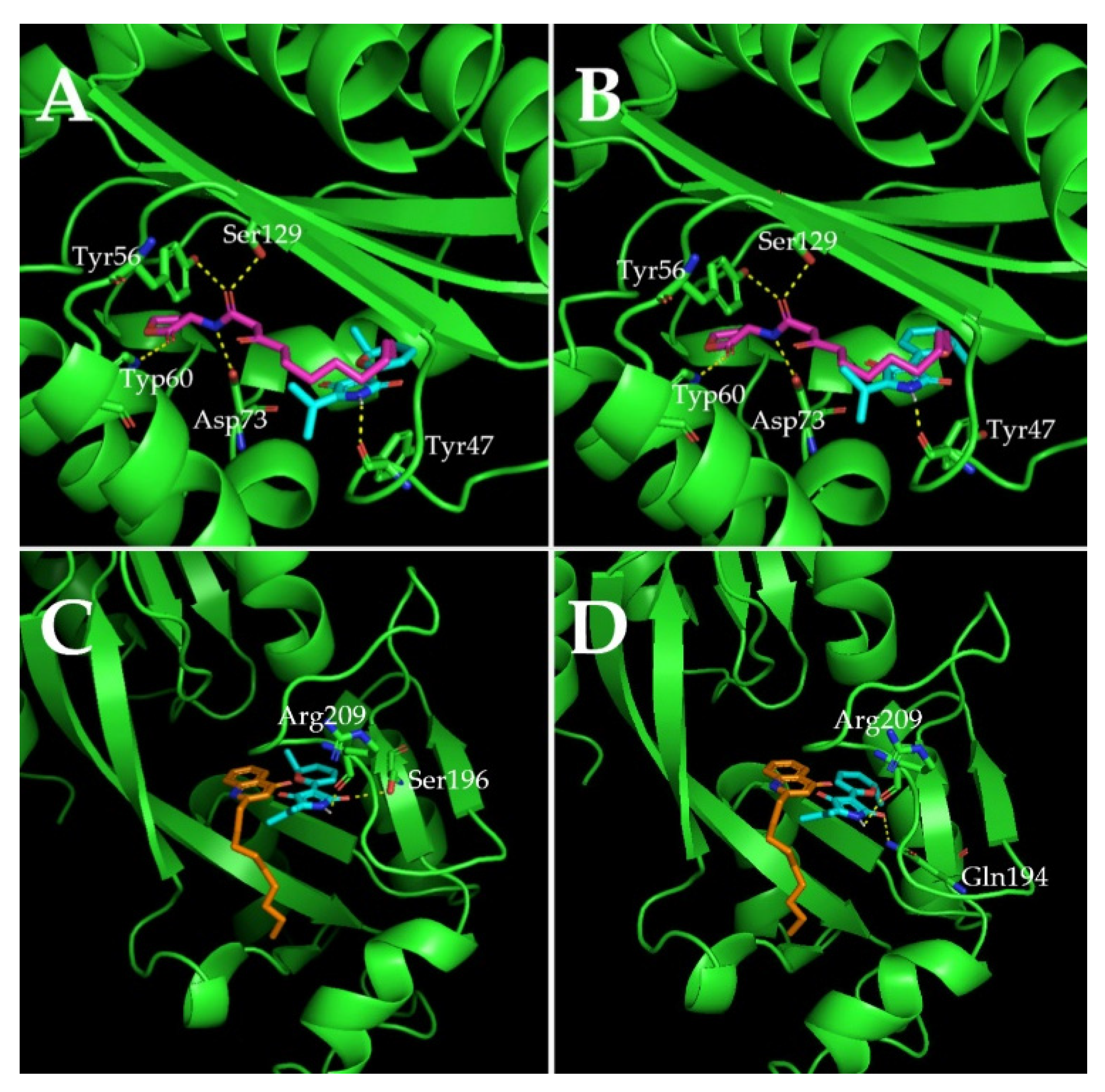
What does it take to be a Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common, free-living, Gram-negative bacterium that can cause significant disease as an opportunistic pathogen. Rapid growth, facile genetics, and a large suite of virulence-related phenotypes make P. aeruginosa a common model organism to study Gram-negative opportunistic pathogens and basic microbiology.
Is it dangerous to have Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Pseudomonas can be dangerous to people with weakened immune systems. While Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria are of little concern to those who are healthy and strong, they can be deadly for those whose health is not as robust. Indeed, this is one of the reasons why it can cause serious infections among people who are ill and being treated in ...
What does the name Pseudomonas mean?
Pseudomonas is a type of bacteria (germ) that is found commonly in the environment, like in soil and in water. Of the many different types of Pseudomonas, the one that most often causes infections in humans is called Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which can cause infections in the blood, lungs (pneumonia), or other parts of the body after surgery.
How serious is a Pseudomonas infection?
Unfortunately, pseudomonas infections are also increasingly resistant to antibiotics which can make them hard to combat. A pseudomonas infection can impact on a patient in a variety of ways. It can cause pneumonia or sepsis, both of which are serious, life-threatening conditions.
What does Pseudomonas aeruginosa cause in humans?
Of the many different types of Pseudomonas, the one that most often causes infections in humans is called Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which can cause infections in the blood, lungs (pneumonia), or other parts of the body after surgery.
Where is Pseudomonas aeruginosa found in the body?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa commonly inhabits soil, water, and vegetation. It is found in the skin of some healthy persons and has been isolated from the throat (5 percent) and stool (3 percent) of nonhospitalized patients.
What is the best treatment for Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Pseudomonas infection can be treated with a combination of an antipseudomonal beta-lactam (eg, penicillin or cephalosporin) and an aminoglycoside. Carbapenems (eg, imipenem, meropenem) with antipseudomonal quinolones may be used in conjunction with an aminoglycoside.
How does a person get Pseudomonas?
The bacteria can be spread in hospitals via the hands of healthcare workers, or by hospital equipment that is not properly cleaned. Pseudomonas infections are considered opportunistic infections. This means that the organism only causes disease when a person's immune system is already impaired.
How serious is pseudomonas infection?
For many people, a Pseudomonas infection will only cause mild symptoms. However, if a person is in a hospital or has a weakened immune system, the threat becomes very severe. In these situations, a Pseudomonas infection can be life-threatening.
What are the signs and symptoms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Pseudomonas Infection SymptomsEars: pain and discharge.Skin: rash, which can include pimples filled with pus.Eyes:pain, redness, swelling.Bones or joints: joint pain and swelling; neck or back pain that lasts weeks.Wounds: green pus or discharge that may have a fruity smell.Digestive tract: headache, diarrhea.More items...•
What kills Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the lungs?
Chronic lung infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm is cured by L-Methionine in combination with antibiotic therapy.
How can Pseudomonas aeruginosa be prevented?
To prevent spreading Pseudomonas infections between patients, healthcare personnel must follow specific infection control precautions. These precautions may include strict adherence to hand hygiene and wearing gowns and gloves when they enter rooms where patients infected with Pseudomonas are staying.
What does Pseudomonas aeruginosa eat?
Their cells are shaped like tiny rods, and have whip-like tails called flagella that let them swim over everything. Pseudomonas need very little food or water to survive, and are found all over the world. They live in soil and water, and on plants and animals.
How long can a pseudomonas infection last?
The rash in most cases clears in 7 to 10 days. A person who has pus filled lesions on exposed areas should take precautions to avoid direct skin to skin contact with others. Good personal hygiene and hand-washing, especially after handling dressings from draining lesions, should be encouraged.
How quickly does Pseudomonas spread?
Disease progression varies but can rapidly progress and involve the entire cornea within 48 hours, leading to perforation. Fever and systemic symptoms are usually absent.
How serious is Pseudomonas aeruginosa in urine?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic human pathogen, which can cause severe urinary tract infections (UTIs). Because of the high intrinsic antibiotic resistance of P. aeruginosa and its ability to develop new resistances during antibiotic treatment, these infections are difficult to eradicate.
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa part of normal flora?
Although Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a feared hospital pathogen, it is considered to be part of the normal flora in healthy adults.
How serious is Pseudomonas aeruginosa in urine?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic human pathogen, which can cause severe urinary tract infections (UTIs). Because of the high intrinsic antibiotic resistance of P. aeruginosa and its ability to develop new resistances during antibiotic treatment, these infections are difficult to eradicate.
How do you get Pseudomonas in lungs?
Pseudomonas is a major cause of lung infections in people with cystic fibrosis. The bacteria thrive in moist environments and equipment, such as humidifiers and catheters in hospital wards, and in kitchens, bathrooms, pools, hot tubs, and sinks.
What kills Pseudomonas aeruginosa in lungs?
Chronic lung infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm is cured by L-Methionine in combination with antibiotic therapy.
What is pseudoma aeruginosa?
What Is Pseudomonas Aeruginosa? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention. Pseudomonas is a group of bacteria that can cause various types of infections. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common disease-causing form of this bacteria, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
How Is Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Diagnosed?
aeruginosa, your doctor will perform a physical examination and ask about your symptoms and medical history. Then they’ll send a sample of your blood or other bodily fluid to a lab to test for the bacteria.
How many people died from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in 2017?
Research and Statistics: Who Has Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Being in a healthcare setting puts you at the highest risk of P. aeruginosa. In 2017, P. aeruginosa caused approximately 32,600 infections among patients in hospitals and 2,700 deaths in the United States, according to the CDC.
What happens if you get a pseudomonas infection in your foot?
Pseudomonal infections that enter the bloodstream can also lead to respiratory failure, shock, and death. More on Antibiotics.
Why is it so difficult to treat P. aeruginosa?
aeruginosa infections is becoming more difficult, however, because some bacterial strains show resistance to nearly all classes of powerful antibiotics. Treating these drug-resistant infections requires sending samples to a laboratory to test the bacteria against different antibiotics in hope of finding drugs that are effective against it.
What is the mortality rate for P. aeruginosa?
The mortality rates for P. aeruginosa infections are estimated to range from 18 to 61 percent; more ill patients, such as those with bloodstream infections or cancers of the blood, are at higher risk of dying, per past research.
How is P. aeruginosa spread?
In healthcare settings, P. aeruginosa is spread through improper hygiene, such as from the unclean hands of healthcare workers, or via contaminated medical equipment that wasn't fully sterilized.
What is pseudomonas aeruginosa?
pseudomonas aeruginosa. A normal soil inhabitant and human saprobe/commensal which may contaminate various solutions and fluids in a hospital , causing opportunistic infection in immunocompromised patients. Clinical findings.
How does Pseudonomas aeruginosa infect?
Pathogenesis. Pseudonomas aeruginosa is both invasive and toxicogenic, and infects patients in a 3-step process: 1. Bacterial attachment and colonization—mediated by pili and antiphagocytic effects of the organism’s polysaccharide capsule; 2.
What is the bacterial species that causes blue pus?
Pseu·do·mo·nas ae·ru·gi·no·'sa. a bacterial species found in soil, water, and commonly in clinical specimens (wound infections, infected burn lesions, urinary tract infections); the causative agent of blue pus; occasionally pathogenic for plants; usually causes infections in humans in whom there is a defect in host defense mechanisms. ...
What is the name of the plant that produces blue green pigments?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa. A species that produces a distinctive blue-green pigment, grows readily in water, and may cause life-threatening infections in humans, including nosocomial pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis.
What is a pseudomonas?
A culture dish with Pseudomonas. The word Pseudomonas means "false unit", from the Greek pseudēs ( Greek: ψευδής, false) and ( Latin: monas, from Greek: μονάς, a single unit). The stem word mon was used early in the history of microbiology to refer to germs, e.g., kingdom Monera.
How is pseudomonas spread?
Pseudomonas can be spread by equipment that gets contaminated and is not properly cleaned or on the hands of healthcare workers. Pseudomonas can, in rare circumstances, cause community-acquired pneumonias, as well as ventilator -associated pneumonias, being one of the most common agents isolated in several studies. Pyocyanin is a virulence factor of the bacteria and has been known to cause death in C. elegans by oxidative stress. However, salicylic acid can inhibit pyocyanin production. One in ten hospital-acquired infections is from Pseudomonas. Cystic fibrosis patients are also predisposed to P. aeruginosa infection of the lungs due to a functional loss in chloride ion movement across cell membranes as a result of a mutation. P. aeruginosa may also be a common cause of "hot-tub rash" ( dermatitis ), caused by lack of proper, periodic attention to water quality. Since these bacteria thrive in moist environments, such as hot tubs and swimming pools, they can cause skin rash or swimmer's ear. Pseudomonas is also a common cause of postoperative infection in radial keratotomy surgery patients. The organism is also associated with the skin lesion ecthyma gangrenosum. P. aeruginosa is frequently associated with osteomyelitis involving puncture wounds of the foot, believed to result from direct inoculation with P. aeruginosa via the foam padding found in tennis shoes, with diabetic patients at a higher risk.
What is the name of the bacteria that is blue?
The names pyocyanin and pyoverdine are from the Greek, with pyo-, meaning "pus", cyanin, meaning "blue", and verdine, meaning "green". Hence, the term "pyocyanic bacteria" refers specifically to the "blue pus" characteristic of a P. aeruginosa infection. Pyoverdine in the absence of pyocyanin is a fluorescent-yellow color.
How does P. aeruginosa grow?
P. aeruginosa is a facultative anaerobe, as it is well adapted to proliferate in conditions of partial or total oxygen depletion. This organism can achieve anaerobic growth with nitrate or nitrite as a terminal electron acceptor. When oxygen, nitrate, and nitrite are absent, it is able to ferment arginine and pyruvate by substrate-level phosphorylation. Adaptation to microaerobic or anaerobic environments is essential for certain lifestyles of P. aeruginosa, for example, during lung infection in cystic fibrosis and primary ciliary dyskinesia, where thick layers of lung mucus and bacterially-produced alginate surrounding mucoid bacterial cells can limit the diffusion of oxygen. P. aeruginosa growth within the human body can be asymptomatic until the bacteria form a biofilm, which overwhelms the immune system. These biofilms are found in the lungs of people with cystic fibrosis and primary ciliary dyskinesia, and can prove fatal.
How many P. aeruginosa core proteins are present in 1811?
The same comparative study (494 Pseudomonas strains, of which 189 are P. aeruginosa) identified that 41 of the 1811 P. aeruginosa core proteins were present only in this species and not in any other member of the genus, with 26 (of the 41) being annotated as hypothetical.
What does the suffix ruginosa mean?
Another assertion from 1956 is that aeruginosa may be derived from the Greek prefix ae- meaning "old or aged", and the suffix ruginosa means wrinkled or bumpy. The names pyocyanin and pyoverdine are from the Greek, with pyo-, meaning "pus", cyanin, meaning "blue", and verdine, meaning "green".
What is the color of aeruginosa?
The species name aeruginosa is a Latin word meaning verdigris ("copper rust"), referring to the blue-green color of laboratory cultures of the species. This blue-green pigment is a combination of two metabolites of P. aeruginosa, pyocyanin (blue) and pyoverdine (green), which impart the blue-green characteristic color of cultures. Another assertion from 1956 is that aeruginosa may be derived from the Greek prefix ae- meaning "old or aged", and the suffix ruginosa means wrinkled or bumpy.
Where is Pseudomonas aeruginosais found?
Pseudomonas aeruginosais commonly found in the environment, particularly in freshwater. Reservoirs in urban communities include hot tubs, jacuzzis, and swimming pools. It can cause a wide array of community-acquired infections like folliculitis, puncture wounds leading to osteomyelitis, pneumonia, otitis externa, and many others. It is commonly an opportunistic pathogen and is also an important cause of nosocomial infections like ventilator-associated pneumonia, catheter-associated urinary tract infections, and others. Reservoirs in the hospital setting include potable water, taps, sinks, toothbrushes, icemakers, disinfecting solutions, sanitizers, soap bars, respiratory therapy equipment, endoscopes, and endoscope washers. [1][2]
What is pseudomonasfolliculitis?
Pseudomonasfolliculitis is characterized by a maculopapular pruritic rash, axillary lymphadenopathy, breast tenderness, and fever. It is associated with the use of hot tubs, jacuzzis, and pools. [4]
Can a hot tub grow Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Lesion culture from patients with folliculitis after the use of hot tubs frequently grow Pseudomonas aeruginosa.[4] In puncture wounds and malignant otitis externa, clinicians should look for early signs of deep tissue involvement. Imaging may be needed to exclude soft tissue, bone, and joint involvement.[5] In systemic infections, routine laboratory and imaging workup are needed in addition to blood, urine, and tissue cultures if necessary. Due to the high prevalence of antibiotic resistance, the determination of sensitivity to different antimicrobials in pseudomonal infections is extremely important as they guide therapy.
Is pseudomonal coverage needed for cystic fibrosis?
In cystic fibrosis exacerbations, pseudomonal coverage is always needed . Chronic infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosaoccurs in more than 60% of adults with cystic fibrosis and is linked to higher mortality. [2][6]
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa an immunocompromised disease?
Pseudomonas aeruginosainfections are common in individuals with an immunocompromised state such as cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, neutropenia, burns, cancer, AIDS, organ transplant, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, and ICU admissions. Individuals with invasive devices e.g., indwelling catheters or endotracheal tubes, are also at risk due to the organism's unique ability to form biofilms that are difficult to detect. [2]
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa gram negative?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a gram-negative, aerobic, non-spore forming rod that is capable of causing a variety of infections in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised hosts.[1] Its predilection to cause infections among immunocompromised hosts, extreme versatility, antibiotic resistance, and a wide range of dynamic defenses makes it an extremely challenging organism to treat in modern-day medicine.[2]
Is pseudomonal osteomyelitis self-limited?
Fortunately, some pseudomonal infections are self-limited e.g., hot tub folliculitis.[4] Others may be more challenging but still have good outcomes, as is the case with pseudomonal osteomyelitis secondary to puncture wounds. However, long-term radiographic evidence persists in those cases.[5] In cases of pneumonia requiring mechanical ventilation, septic shock, and burn infections, the prognosis varies and is largely dependant on the severity of the underlying disease process and the availability of antimicrobial agents that remain with pseudomonal activity. [11]
Where is Pseudomonas aeruginosa found?
Like other members of the genus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a free-living bacterium, commonly found in soil and water. However, it occurs regularly on the surfaces of plants and occasionally on the surfaces of animals.
What does it mean if your Pseudomonas aeruginosa result is too high?
High levels of Pseudomonas aeruginosa may indicate increased intestinal inflammatory activity and may cause abdominal cramping and loose stools. Some strains of P. aeroginosa may produce toxins that can damage cells.
What is the most common gram negative bacteria?
Pseudomonas species are gram-negative bacteria found widely in the environment. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common species causing infection and can affect every portion of the intestine.
What is the simplest medium for growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
In the laboratory, the simplest medium for growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa consists of acetate as a source of carbon and ammonium sulfate as a source of nitrogen.
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa Gram negative?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative rod measuring 0.5 to 0.8 µm by 1.5 to 3.0 µm. Almost all strains are motile by means of a single polar flagellum. The bacterium is ubiquitous in soil and water, and on surfaces in contact with soil or water.
Is Pseudomonas a bacterium?
The typical Pseudomonas bacterium in nature might be found in a biofilm, attached to some surface or substrate, or in a planktonic form, as a unicellular organism, actively swimming by means of its flagellum. Pseudomonas is one of the most vigorous, fast-swimming bacteria seen in hay infusions and pond water samples.
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant to salts?
It is resistant to high concentrations of salts and dyes, weak antiseptics, and many commonly used antibiotics. - Pseudomonas aeruginosa has a predilection for growth in moist environments, which is probably a reflection of its natural existence in soil and water.
How many MBp is Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Published in Nature (Stover et al. 406:959-964, 2000), it was the largest bacterial genome sequenced to that time. The 6.3-Mbp genome contains 5570 predicted genes on one chromosome.
Where does Pseudomonas live?
Pseudomonas normally resides in the soil, marshes, and coastal marine habitats. It can survive under conditions that few other organisms can tolerate, it produces a slime layer that resists phagocytosis (engulfment), and it is resistant to most antibiotics.
What is the blue pus bacteria?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The versatile "blue-green pus bacteria" that opportunistically infects people, especially those who are immunocompromised. Pseudomonas rarely causes infection in healthy individuals but it is a major cause of hospital acquired (nosocomial) infections. It tends to infect people with immunodeficiency or burns ...
Can pseudomonas cause sepsis?
It tends to infect people with immunodeficiency or burns and those with indwelling catheters or on respirators. Infection with pseudomonas can lead to urinary tract infections, sepsis (blood stream infection), pneumonia, pharyngitis, and many other medical problems.
Can pseudomonas multiply?
Pseudomonas can multiply in an extraordinary assortment of environments including eyedrops, soaps, sinks, anesthesia and resuscitation equipment, fuels, humidifiers and even stored distilled water. It has also been reported in kidney dialysis machines.
What is the name of the infection caused by pseudomonas?
Blood. A bacterial infection of the blood is called bacteremia. A blood infection is one of the most severe infections caused by pseudomonas. Symptoms may include: fever. chills. fatigue. muscle and joint pain.
Where are pseudomonas found?
The bacteria are found widely in the environment, such as in soil, water, and plants. They usually do not cause infections in healthy people. If an infection does occur in a healthy person, it is generally mild. More severe infections occur in people who are ...
What is a pathogen in a hospital?
A pathogen is a microorganism that causes disease. Infections acquired in a hospital are called nosocomial infections. Infections can occur in any part of the body. Symptoms depend on which part of the body is infected. Antibiotics are used to treat the infections. Pseudomonas infection could be fatal in people who are already very ill.
What is the most common species of pseudomonas?
Only a few of the many species cause disease. The most common species that causes infection is called Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Trusted Source.
What is it called when a bacterium infects the skin?
When this bacterium infects the skin, it most often affects the hair follicles. This is called folliculitis. Symptoms may include:
How to test for pseudomonas?
They may take a sample of pus, blood, or tissue, and send it to a laboratory. The laboratory will then test the sample for the presence of pseudomonas.
Is a pseudomonade a pathogen?
More severe infections occur in people who are already hospitalized with another illness or condition, or people who have a weak immune system. Pseudomonades are fairly common pathogens involved in infections acquired in a hospital setting. ...
What Are Pseudomonas Infections?
Pseudomonas infections are infections caused by a kind of bacteria called Pseudomonas that’s commonly found in soil, water, and plants. The type that typically causes infections in people is called Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Some healthy people even have strains of it growing on their skin in moist parts of their body, like their armpits or genital area.
What are the signs of Pseudomonas?
Pseudomonas can infect any part of your body, such as your blood, lungs, stomach, urinary tract, or tendons. Pressure sores, wounds, and burns can also become infected. Places where infection occurs -- and their signs -- may include: Ears: pain and discharge. Skin: rash, which can include pimples filled with pus.
What to do after pseudomonas surgery?
After surgery, be on the lookout for signs of infection . If you run a fever, have pain or see redness or discharge at your surgery site, call your doctor right away. Pseudomonas Infection Outlook. In most cases, antibiotics can clear the infection, but it’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions and focus on prevention.
Can pseudomonas cause a rash?
If you’re in good health, you could come into contact with pseudomonas and not get sick. Other people only get a mild skin rash or an ear or eye infection. But if you’re sick or your immune system is already weakened, pseudomonas can cause a severe infection. In some cases, it can be life-threatening.
Can you take more than one antibiotic for pseudomonas?
Every pseudomonas bacteria is slightly different, and strains are constantly changing, so these types of infections can be hard to treat. Many times, you may need to take more than one kind of antibiotic. You can lower your risk of getting sick by trying to avoid coming into contact with this type of bacteria.
Can pseudomonas grow on fruits?
Pseudomonas Infection Causes and Risk Factors. You can get pseudomonas in many different ways. It can grow on fruits and vegetables, so you could get sick from eating contaminated food. It also thrives in moist areas like pools, hot tubs, bathrooms, kitchens, and sinks. The most severe infections occur in hospitals.
What is a pseudomona?
1 capitalized : a genus (the type of the family Pseudomonadaceae) comprising short rod-shaped motile gram-negative bacteria including some saprophytes, a few animal pathogens, and numerous important plant pathogens — see burkholderia. 2 plural pseudomonades ˌsüd-ə-ˈmō-nə-ˌdēz.
What bacteria can cause Legionnaires disease?
Along with legionella bacteria, which can cause Legionnaires’ disease, the routine testing of the water system revealed pseudomonas bacteria, which can lead to severe infections in people with weakened immune systems. — Washington Post, 18 Oct. 2019 The hospital discovered the infection, caused by the pseudomonas bacteria, in July, according to Van Stone, and the deaths happened in the past two months. — Theresa Waldrop And Elizabeth Joseph, CNN, 7 Oct. 2019 The cases of pseudomonas infection were contained in the NICU and have not been reported in other parts of the hospital. — CBS News, 7 Oct. 2019 Lab tested to kill 99.99 percent of illness-causing bacteria such as staphylococcus, salmonella, pseudomonas, and MRSA. — Necee Regis, BostonGlobe.com, 23 July 2019 Streptococcus A is the bacteria that causes most cases of nectrotizing fasciitis, but Shamoon noted that other types of bacteria, including staph, clostridium, E.coli, and pseudomonas, also can lead to the infection. — Kristen Jordan Shamus, Detroit Free Press, 4 July 2019

Overview
Nomenclature
The word Pseudomonas means "false unit", from the Greek pseudēs (Greek: ψευδής, false) and (Latin: monas, from Greek: μονάς, a single unit). The stem word mon was used early in the history of microbiology to refer to germs, e.g., kingdom Monera.
The species name aeruginosa is a Latin word meaning verdigris ("copper rust"), …
Biology
The genome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa consists of a relatively large circular chromosome (5.5–6.8 Mb) that carries between 5,500 and 6,000 open reading frames, and sometimes plasmids of various sizes depending on the strain. Comparison of 389 genomes from different P. aeruginosa strains showed that just 17.5% is shared. This part of the genome is the P. aeruginosa core genome.
Pathogenesis
An opportunistic, nosocomial pathogen of immunocompromised individuals, P. aeruginosa typically infects the airway, urinary tract, burns, and wounds, and also causes other blood infections.
It is the most common cause of infections of burn injuries and of the outer ear (otitis externa), and is the most frequent colonizer of medical devices (e.g., cath…
Diagnosis
Depending on the nature of infection, an appropriate specimen is collected and sent to a bacteriology laboratory for identification. As with most bacteriological specimens, a Gram stain is performed, which may show Gram-negative rods and/or white blood cells. P. aeruginosa produces colonies with a characteristic "grape-like" or "fresh-tortilla" odor on bacteriological media. In mixed cultures, i…
Treatment
Many P. aeruginosa isolates are resistant to a large range of antibiotics and may demonstrate additional resistance after unsuccessful treatment. It should usually be possible to guide treatment according to laboratory sensitivities, rather than choosing an antibiotic empirically. If antibiotics are started empirically, then every effort should be made to obtain cultures (before admini…
Research
In 2013, João Xavier described an experiment in which P. aeruginosa, when subjected to repeated rounds of conditions in which it needed to swarm to acquire food, developed the ability to "hyperswarm" at speeds 25% faster than baseline organisms, by developing multiple flagella, whereas the baseline organism has a single flagellum. This result was notable in the field of experimental evolution in that it was highly repeatable.
Distribution
As of 2019 the East African Community considers P. aeruginosa to be a quarantine concern. The presence of Phaseolus vulgaris-pathogenic strains of P. aeruginosa in Kenya for the rest of the area. A pest risk analysis by the EAC was based on this bacterium's CABI's Crop Protection Compendium listing, following Kaaya & Darji 1989's initial detection in Kenya.