Key takeaways:
- Quantitative data is data that can be counted or measured in numerical values.
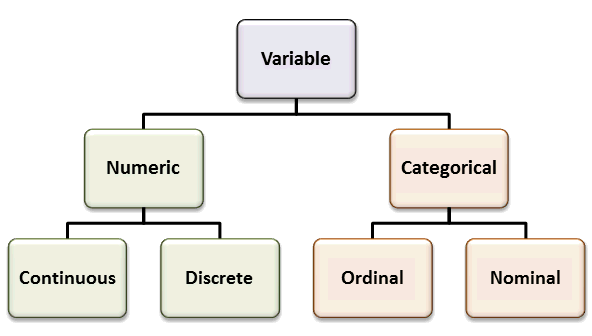
- The two main types of quantitative data are discrete data and continuous data.
- Height in feet, age in years, and weight in pounds are examples of quantitative data.
- Qualitative data is descriptive data that is not expressed numerically.
What are some examples of quantitative data?
Key takeaways:
- Quantitative data is data that can be counted or measured in numerical values.
- The two main types of quantitative data are discrete data and continuous data.
- Height in feet, age in years, and weight in pounds are examples of quantitative data.
- Qualitative data is descriptive data that is not expressed numerically.
What are the different types of quantitative data?
We’ve covered a lot of ground here, so let’s recap on the key points:
- Quantitative data analysis is all about analysing number-based data (which includes categorical and numerical data) using various statistical techniques.
- The two main branches of statistics are descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. ...
- Common descriptive statistical methods include mean (average), median, standard deviation and skewness.
Which data can be classified as quantitative?
Quantitative data may be either discrete or continuous. All data that are the result of counting are called quantitative discrete data. These data take on only certain numerical values. If you count the number of phone calls you receive for each day of the week, you might get values such as zero, one, two, or three.
Which is an example of quantitative data?
Here are some example of quantitative data:
- A jug of milk holds one gallon.
- The painting is 14 inches wide and 12 inches long.
- The new baby weighs six pounds and five ounces.
- A bag of broccoli crowns weighs four pounds.
- A coffee mug holds 10 ounces.
- John is six feet tall.
- A tablet weighs 1.5 pounds.

What is quantitative data and examples?
Quantitative data is data that can be counted or measured in numerical values. The two main types of quantitative data are discrete data and continuous data. Height in feet, age in years, and weight in pounds are examples of quantitative data.
What is qualitative data in statistics?
Qualitative data is information that cannot be counted, measured or easily expressed using numbers. It is collected from text, audio and images and shared through data visualization tools, such as word clouds, concept maps, graph databases, timelines and infographics.
What is quantitative data Short answer?
Quantitative data refers to any information that can be quantified — that is, numbers. If it can be counted or measured, and given a numerical value, it's quantitative in nature. Think of it as a measuring stick. Quantitative variables can tell you "how many," "how much," or "how often."
What are the types of quantitative data in statistics?
There are three types of quantitative data, and each carries valuable information: discrete, continuous, and interval (as compared to ratio) data.
What's the difference between qualitative and quantitative?
As qualitative and quantitative studies collect different data, their data collection methods differ considerably. Quantitative studies rely on numerical or measurable data. In contrast, qualitative studies rely on personal accounts or documents that illustrate in detail how people think or respond within society.
What is qualitative data with examples?
Qualitative data describes qualities or characteristics. It is collected using questionnaires, interviews, or observation, and frequently appears in narrative form. For example, it could be notes taken during a focus group on the quality of the food at Cafe Mac, or responses from an open-ended questionnaire.
What are 5 examples of quantitative data?
Some examples of quantitative data include:Revenue in dollars.Weight in kilograms.Age in months or years.Length in centimeters.Distance in kilometers.Height in feet or inches.Number of weeks in a year.
How do you find quantitative data?
There are several methods by which you can collect quantitative data, which include:Experiments.Controlled observations.Surveys: paper, kiosk, mobile, questionnaires.Longitudinal studies.Polls.Telephone interviews.Face-to-face interviews.
What are the two main types of quantitative data?
Quantitative data is of two types, namely; discrete and continuous data. Continuous data is further divided into interval and ratio data. Quantitative data takes up numeric values with numeric properties.
Why is quantitative data important?
The purpose of quantitative research is to attain greater knowledge and understanding of the social world. Researchers use quantitative methods to observe situations or events that affect people. Quantitative research produces objective data that can be clearly communicated through statistics and numbers.
What is quantitative and qualitative data in statistics?
Quantitative data are measures of values or counts and are expressed as numbers. Quantitative data are data about numeric variables (e.g. how many; how much; or how often). Qualitative data are measures of 'types' and may be represented by a name, symbol, or a number code.
What is an example of quantitative and qualitative data?
Start with yourself as an example. To acquire qualitative data, consider identifiers like the color of your clothes, type of hair, and nose shape. For quantitative data, consider measurable values like your height, weight, age, and shoe size.
What are 5 examples of quantitative data?
Some examples of quantitative data include:Revenue in dollars.Weight in kilograms.Age in months or years.Length in centimeters.Distance in kilometers.Height in feet or inches.Number of weeks in a year.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data?
But, to summarize, the differences between quantitative and qualitative data are as follows: Quantitative data is countable or measurable, relating to numbers; qualitative data is descriptive, relating to words. Quantitative data lends itself to statistical analysis; qualitative data is grouped and categorized according to themes.
Why is quantitative data important?
The main advantages of working with quantitative data are as follows: Quantitative data is relatively quick and easy to collect, allowing you to gather a large sample size. And, the larger your sample size, the more accurate your conclusions are likely to be . Quantitative data is less susceptible to bias.
How to collect quantitative data?
Another way to collect quantitative data is through questionnaires and surveys. Nowadays, it’s easy to create a survey and distribute it online—with tools like Typeform, SurveyMonkey, and Qualtrics, practically anyone can collect quantitative data. Surveys are a useful tool for gathering customer or user feedback, and generally finding out how people feel about certain products or services. To make sure you gather quantitative data from your surveys, it’s important that you ask respondents to quantify their feelings—for example, asking them to rate their satisfaction on a scale of one to ten.
What is discrete data?
Discrete data is quantitative data that can only take on certain numerical values. These values are fixed and cannot be broken down. When you count something, you get discrete data. For example, if a person has three children, this is an example of discrete data. The number of children is fixed—it’s not possible for them to have, say, 3.2 children. Another example of discrete quantitative data could be the number of visits to your website; you could have 150 visits in one day, but not 150.6 visits. Discrete data is usually visualized using tally charts, bar charts, and pie charts.
What are some examples of quantitative data?
Examples of quantitative data include numerical values such as measurements, cost, and weight; examples of qualitative data include descriptions (or labels) of certain attributes, such as “brown eyes” or “vanilla flavored ice cream”. Now we know the difference between the two, let’s get back to quantitative data.
What are the two types of data?
Data professionals work with two types of data: Quantitative and qualitative. In simple terms, quantitative data is measurable while qualitative data is descriptive—think numbers versus words. If you plan on working as a data analyst or a data scientist (or in any field that involves conducting research, like psychology), ...
Why is random sampling important?
The use of random sampling helps to ensure that a given dataset is as representative as possible, and protects the sample from bias. This is crucial for drawing reliable conclusions. Quantitative data is analyzed objectively.
What is quantitative data?
Quantitative data is usually collected for statistical analysis using surveys, polls or questionnairessent across to a specific section of a population. The retrieved results can be established across a population. Types of Quantitative Data with Examples. The most common types of quantitative data are as below:
What are the advantages of quantitative data?
Some of advantages of quantitative data, are: Conduct in-depth research:Since quantitative data can be statistically analyzed, it is highly likely that the research will be detailed. Minimum bias:There are instances in research, where personal bias is involved which leads to incorrect results.
What is quantitative data?
Definition of Quantitative Data. Quantitative data is any set of information that can be numerically recognized and analyzed. Quantitative data is the most relevant form of data for use in both mathematics and statistics, as it is the primary type of data that can be measured objectively.
What is continuous data?
Continuous Data. Continuous data include numbers within a range that don’t necessarily have to be whole and may change more frequently in a given time period. Some examples include: The number of kittens up for adoption at your local shelter over the course of a year. Your body temperature throughout the day.
What is the difference between continuous and discrete data?
Discrete data can only be one numeric value, but continuous data are made up of several different numeric values within a range. Think of discrete data as separate, individual points of data, whereas continuous data looks more like connected dots or lines that mark each subtle transition in the numerical value over time.
What is discrete data?
Discrete data are whole numbers that can be counted and don’t change within a given time period. Some examples include: The number of kittens up for adoption at your local shelter on a given day. Your body temperature when you first woke up this morning. The number of students in your third grade class.
Can qualitative data be used at the same time as quantitative data?
While researchers can and often do collect qualitative data at the same time as quantitative data, it’s important that your quantitative methods are direct and limit the range of responses to achieve objective measurements.
What is quantitative data?
Quantitative data is information that can be counted or measured—or, in other words, quantified—and given a numerical value.
What are examples of quantitative data?
Quantitative data is anything that can be counted in definite units and numbers. So, among many, many other things, some examples of quantitative data include:
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative data?
There are many differences between qualitative and quantitative data —each represent very different data sets and are used in different situations. Often, too, they’re used together to provide more comprehensive insights.
Characteristics of quantitative data
Quantitative data is made up of numerical values and has numerical properties, and can easily undergo math operations like addition and subtraction. The nature of quantitative data means that its validity can be verified and evaluated using math techniques.
When should I use quantitative or qualitative research?
Quantitative and qualitative research can both yield valuable findings, but it’s important to choose which type of data to collect based on the nature and objectives of your research.
What are the pros and cons of quantitative data?
Quantitative data is most helpful when trying to understand something that can be counted and expressed in numbers.
How do you collect quantitative data?
There are many ways to collect quantitative data, with common methods including surveys and questionnaires. These can generate both quantitative data and qualitative data, depending on the questions asked.
How to collect quantitative data?
To collect quantitative data, you will often need to use operational definitions that translate abstract concepts (e.g., mood) into observable and quantifiable measures (e.g., self-ratings of feelings and energy levels). Control or manipulate an independent variable to measure its effect on a dependent variable.
What is quantitative research?
Revised on February 15, 2021. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting ...
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research?
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analyzing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
Why is quantitative research important?
Quantitative research is often used to standardize data collection and generalize findings. Strengths of this approach include: Replication. Repeating the study is possible because of standardized data collection protocols and tangible definitions of abstract concepts. Direct comparisons of results.
What can you use to visualize data?
You can also use graphs, scatter plots and frequency tables to visualize your data and check for any trends or outliers. Using inferential statistics, you can make predictions or generalizations based on your data. You can test your hypothesis or use your sample data to estimate the population parameter.
What is operationalization in psychology?
Operationalization means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations. For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioral avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
What is experimental research?
In experimental research, you systematically examine whether there is a cause-and-effect relationship between variables. Correlational and experimental research can both be used to formally test hypotheses, or predictions, using statistics.

What Is Quantitative Data?
What Is The Difference Between Quantitative and Qualitative Data?
- It’s hard to define quantitative data without comparing it to qualitative data—so what’s the difference between the two? While quantitative data can be counted and measured, qualitative data is descriptive and, typically, unstructured. It usually takes the form of words and text—for example, a status posted on Facebook or an interview transcript are both forms of qualitative da…
How Is Quantitative Data collected?
- Now we know what quantitative data is, we can start to think about how analysts actually work with it in the real world. Before the data can be analyzed, it first needs to be generated or collected. So how is this done? Researchers (for example, psychologists or scientists) will often conduct experiments and studies in order to gather quantitative data and test certain hypothese…
How Is Quantitative Data analyzed?
- A defining characteristic of quantitative data is that it’s suitable for statistical analysis. There are many different methods and techniques used for quantitative data analysis, and how you analyze your data depends on what you hope to find out. Before we go into some specific methods of analysis, it’s important to distinguish between descriptive and inferential analysis.
What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative Data?
- As with anything, there are both advantages and disadvantages of using quantitative data. So what are they? Let’s take a look.
Key Takeaways and Further Reading
- In this post, we explained what quantitative data is, how it differs from qualitative data, and how it’s collected and analyzed. To recap what we’ve learned: 1. Quantitative data is data that can be quantified.It can be counted or measured, and given a numerical value. 2. Quantitative data lends itself to statistical analysis,while qualitative data is grouped according to themes. 3. Quantitativ…