
reverse fault [ rĭ-vûrs ′ ] A geologic fault in which the hanging wall has moved upward relative to the footwall. Reverse faults occur where two blocks of rock are forced together by compression.
What is a real life example of a reverse fault?
The Himalayan Mountains in India, Nepal, and Pakistan are the most spectacular example of what a reverse fault can do. Many millions of years ago the plate that India is on was not connected to the rest of Asia. It slowly crashed into its current position, pushing up the mountains.
What is an example for a reverse fault?
Reverse faults are a type of dip-slip fault that result from compression or pushing together of rocks. The Sierra Madre in southern California is an example. Thrust faults are a type of reverse ...
What does reverse fault mean?
A reverse fault, or thrust fault, is due to compression when the rock is being pushed towards itself. One plate is thrust upwards, vertically, above the fault line. A strike-slip fault is where one or both plates move horizontally beside the other. The best known example of this is the San Andreas Fault in California.
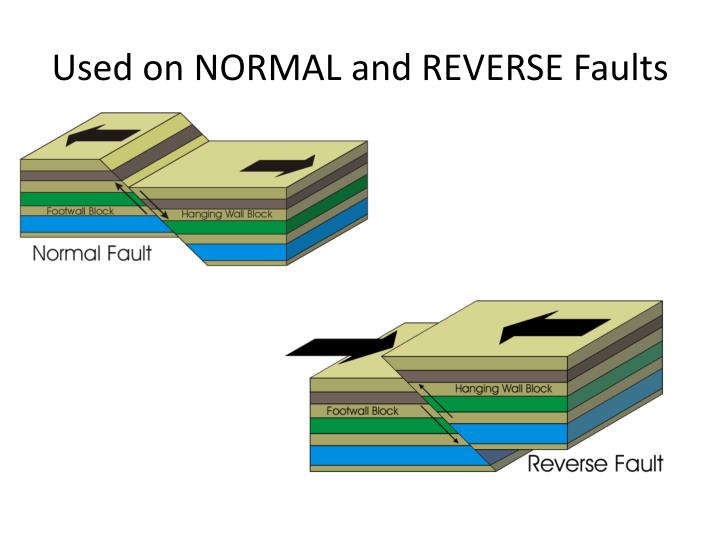
How do normal faults differ from reverse faults?
The main difference between normal fault and reverse fault is that normal fault describes the downward movement of one side of the fault with respect to the other side whereas reverse fault refers to the upward movement of one side of the fault with respect to the other side.
What are examples of reverse faults?
Some famous reverse faults include:Glarus thrust (Switzerland) - thrust fault in the Swiss Alps.Longmenshan Fault (China) - thrust fault at the Longmen mountains, between the Eurasian and Indian-Australian plates.Lusatian Fault (Germany) - overthrust fault between the Elbe valley and Giant Mountains.More items...
What is another name for a reverse fault?
overthrust faultAlternate Synonyms for "reverse fault": thrust fault; overthrust fault; inclined fault.
Where do you find reverse faults?
Reverse faults occur commonly at plate boundaries. The type of movement seen in reverse faults is the result of compression. The hanging wall isn't going to move up and over the foot wall against the force of gravity without a push. When one plate pushes up against another, we get a reverse fault and mountains.
What does a reverse fault make?
(A) Reverse faults display severe damage in the form of landslides over the fault trace caused by the inability of the hanging wall to support the overhang caused by the fault displacement, folds, and compression features within the fractured hanging wall, and compressional block tilting.
What is a normal and reverse fault?
A normal fault is one in which the rocks above the fault plane, or hanging wall, move down relative to the rocks below the fault plane, or footwall. A reverse fault is one in which the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall.
What is a reverse earthquake?
If the rock mass above an inclined fault moves down, the fault is termed normal, whereas if the rock above the fault moves up, the fault is termed reverse.
What are the 3 fault types?
There are three main types of fault which can cause earthquakes: normal, reverse (thrust) and strike-slip. Figure 1 shows the types of faults that can cause earthquakes.
What type of plate boundary is a reverse fault?
Reverse faults often form along convergent plate boundaries. Strike-slip Faults: Sometimes referred to as a lateral fault, this type forms when the blocks of rock on either side of a vertical (or nearly vertical) fracture move past each other.
What type of stress causes strike-slip faults?
Strike-slip faults are distinct from the previous two because they don't involve vertical motion. They form via shear stress.
How does a reverse fault get its name?
Before understanding how a reverse fault gets its name, we should first look at its opposite: a normal fault. In a normal fault, one side of the fault slides down. Think about how the earth should move based on gravity - it should go down, not up, right? So when one side of the fault does go up instead of down, it is called a reverse fault. It is working against gravity.
What are some examples of reverse faults?
The Himalayan Mountains in India, Nepal, and Pakistan are the most spectacular example of what a reverse fault can do. Many millions of years ago the plate that India is on was not connected to the rest of Asia. It slowly crashed into its current position, pushing up the mountains. Coal Mining Terms.
What is a fault in the Earth?
The Faults in Our Earth. A fault is a rupture or fracture in the earth's crust, its outer layer. The Earth's crust moves along these faults, which are everywhere, both on land and on the crust under the oceans. There are different types of faults, categorized by how the earth on either side of the fault moves.
What is thrust fault?
A thrust fault is a reverse fault that is at an incline of less than 45 degrees. The terms we use to describe dip-slip faults, those that move vertically, come from coal mining. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account.
What type of movement is seen in reverse faults?
The type of movement seen in reverse faults is the result of compression. The hanging wall isn't going to move up and over the foot wall against the force of gravity without a push. When one plate pushes up against another, we get a reverse fault and mountains.
What is the difference between thrust and reverse fault?
A reverse fault is one in which one side of the fault, the hanging wall, moves up and over the other side , the foot wall. This movement is caused by compression and is common at tectonic plate boundaries. A thrust fault is a reverse fault that is at an incline of less than 45 degrees.
What is the angle of incline of a thrust fault?
It moves in the same way as a reverse fault, in that the hanging wall moves up relative to the foot wall, but the angle of incline is less than 45 degrees. Subduction zones, where the edge of one of the earth's tectonic plates rises over the edge of another, are thrust faults.
What is reverse fault?
A geologic fault in which the hanging wall has moved upward relative to the footwall. Reverse faults occur where two blocks of rock are forced together by compression. Compare normal fault. See Note and illustration at fault.
Why is the word "sinister" Latin?
The word "sinister" is Latin for "left," because left-handed people were often thought of as suspicious, evil, or demonic.