How do you activate the parasympathetic nervous system?
Method 2 Method 2 of 3: Making Lifestyle Changes Download Article
- Spend time relaxing in nature. Being in nature triggers your body’s calming response, so go outside!
- Use mindfulness instead of multitasking. Mindfulness means being focused on the present, and it can help activate your parasympathetic nervous system.
- Meditate on a calming word for 10 to 30 minutes daily. ...
What does the parasympathetic system stimulate?
The parasympathetic system is responsible for stimulation of "rest-and-digest" or "feed and breed" activities that occur when the body is at rest, especially after eating, including sexual arousal, salivation, lacrimation (tears), urination, digestion and defecation.
How to engage the parasympathetic?
You can try out the following activities to stimulate the PSNS:
- Spend time in the great outdoors or nature.
- Consider getting a massage.
- Meditate regularly.
- Deep abdominal breathing from the diaphragm
- Concentrate on a soothing word like calm or peace.
- Playing or spending quality time with animals or kids
- Exercise
- Practicing yoga, tai chi, or chi kung
- Experiment with progressive relaxation.
What are the functions of the parasympathetic nervous system?
This stands for:
- Salivation: As part of its rest-and-digest function, the PSNS stimulates production of saliva, which contains enzymes to help your food digest.
- Lacrimation: Lacrimation is a fancy word for making tears. ...
- Urination: The PSNS contracts the bladder, which squeezes it so urine can come out.
See more
What is a parasympathetic?
Your parasympathetic nervous system is a network of nerves that relaxes your body after periods of stress or danger. It also helps run life-sustaining processes, like digestion, during times when you feel safe and relaxed.
What is the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic?
The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for the “fight or flight” response during any potential danger. On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system inhibits the body from overworking and restores the body to a calm and composed state.
What is an example of sympathetic?
Example Sentences Adjective He received much help from sympathetic friends. I didn't find the hero in the movie very sympathetic.
What is sympathetic system?
The sympathetic autonomic nervous system (SANS) is one of the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), along with the parasympathetic nervous system (PANS), These systems primarily work unconsciously in opposite ways to regulate many functions and parts of the body.
What is an example of a parasympathetic response?
Examples of parasympathetic responses Salivation: As part of its rest-and-digest function, the PSNS stimulates production of saliva, which contains enzymes to help your food digest. Lacrimation: Lacrimation is a fancy word for making tears. Tears keep your eyes lubricated, preserving their delicate tissues.
What is the role of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic system controls “fight-or-flight” responses. In other words, this system prepares the body for strenuous physical activity. The events that we would expect to occur within the body to allow this to happen do, in fact, occur. The parasympathetic system regulates “rest and digest” functions.
What is a sympathetic person called?
affectionate, caring, compassionate, interested, loving, responsive, sensitive, supportive, thoughtful, warm, bleeding-heart, amenable, appreciative, encouraging, open-minded, receptive, appreciating, benign, benignant, commiserating.
What are the sympathetic effects?
eg, the sympathetic nervous system can accelerate heart rate, widen bronchial passages, decrease motility (movement) of the large intestine, constrict blood vessels, cause pupil dilation, activate goose bumps, start sweating and raise blood pressure.
What is a sympathetic woman?
A sympathetic person is one who's motivated by compassion.
What are the 5 functions of the sympathetic nervous system?
The main functions of the sympathetic nervous system are to dilate blood vessels, increase blood pressure, contract muscles, secrete sweat from sweat glands, dilate bronchi for more oxygen exchange and contraction of heart which helps the body prepare to face emergency situations.
Why is nervous system called sympathetic?
The name of this system can be traced to the concept of sympathy, in the sense of "connection between parts", first used medically by Galen. In the 18th century, Jacob B. Winslow applied the term specifically to nerves.
What are 3 differences between the parasympathetic and the sympathetic division?
The Sympathetic nervous system function is to prepare the body to deal with conditions of fear and stress that respond through a network of interconnected neurons. The Parasympathetic nervous system function is to respond to the body's relaxation, resting and feeding state.
How do you remember the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic?
One of the best ways to remember their differences is to look at the beginning letters of the words. The sympathetic nervous system responds to stress and is your “fight or flight” response. While the parasympathetic nervous system responds to peace and is your “rest and digest” response.
What is the major difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems quizlet?
The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) controls homeostasis and the body at rest and is responsible for the body's "rest and digest" function. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) controls the body's responses to a perceived threat and is responsible for the "fight or flight" response.
Which nerves are sympathetic or parasympathetic?
The sympathetic nervous system is often considered the "fight or flight" system, while the parasympathetic nervous system is often considered the "rest and digest" or "feed and breed" system.
What does parasympathetic and sympathetic have in common?
What do the parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions have in common? Most nerve fibers from both divisions innervate many of the same effectors. Most nerve fibers from both divisions share the same sites of origin. The preganglionic nerve fibers in both divisions are of similar length.
What is the major difference between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems?
The parasympathetic nervous system restores the body to a calm and composed state and prevents it from overworking. The sympathetic nervous system,...
What are the hormones released by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems?
The sympathetic nervous system releases the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine that accelerate the heart rate. The parasympathetic nervous sys...
What actions are controlled by the parasympathetic nervous system?
Salivation, urination, lacrimation, defecation and digestion are the important body activities stimulated by the parasympathetic nervous system.
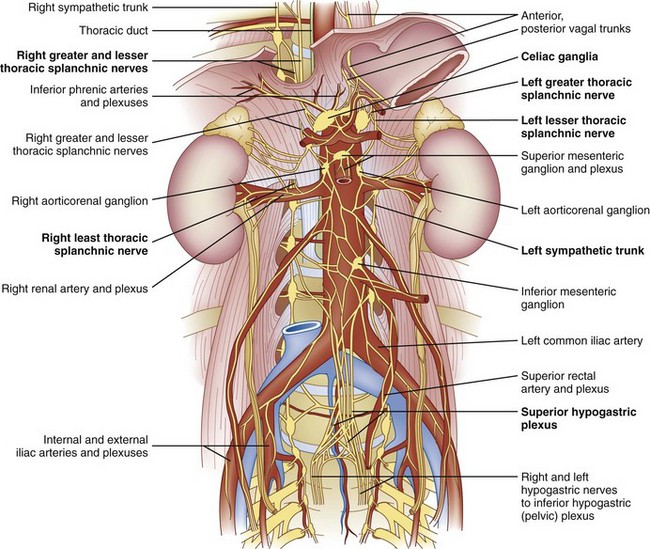
What are parasympathetic ganglia?
These are the autonomic ganglia of the parasympathetic nervous system that lie near or within the organs they innervate.
What are the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system composed of?
The parasympathetic nervous system is composed of cranial and spinal nerves. The sympathetic nervous system comprises cell bodies that lie within t...
1.Is there a major difference between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems?
In addition to providing the body with calm and stability, the parasympathetic nervous system prevents overworking. During a fight or flight respon...
2.What hormones are released by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems?
A heartbeat is accelerated when epinephrine and norepinephrine are released by the sympathetic nervous system.Acetylcholine, a hormone that slows d...
3.What components make up the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems?
Neurons in the parasympathetic nervous system are found in the brain and spine. The sympathetic nervous system consists of cells located within the...
4.What is an example of a sympathetic reaction?
It causes the heart to beat faster, expand bronchial passageways, decrease large intestine motility, constrict blood vessels, increase esophageal p...
5.Breathing is sympathetic or parasympathetic?
Our parasympathetic nervous system is triggered by deep breathing that is slow and steady. Our stress responses can also be managed by taking long,...
6. What is an Autonomous Nervous System?
An autonomous nervous system consists of neurons in the peripheral nervous system that perform specific functions. These neurons control three diff...
7. What are the names of the two parts of the autonomic nervous system? What are their functions?
The two divisions of the autonomic nervous system are the Sympathetic nervous system and Parasympathetic nervous system. The former prepares the bo...
What is Sympathetic And Parasympathetic Nervous System?
Sympathetic Autonomic Nervous System: It is the part of the autonomic nervous system, located near the thoracic and lumbar regions in the spinal cord. Its primary function is to stimulate the body’s fight or flight response. It does this by regulating the heart rate, rate of respiration, pupillary response and more.
Why is the autonomic nervous system called the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system is named so, because it works autonomously, i.e., without a person’s conscious effort. The primary function of the autonomic nervous system is homeostasis. Apart from maintaining the body’s internal environment, it is also involved in controlling and maintaining the following life processes: Digestion. Metabolism.
What is the role of sympathetic and parasympathetic?
Parasympathetic. Involved in the fight or flight response. Involved in maintaining homeostasis and also, permits the rest and digest response. The sympathetic system prepares the body for any potential danger. The parasympathetic system aims to bring the body to a state of calm.
Where is the parasympathetic nervous system located?
Parasympathetic Autonomic Nervous System: It is located in between the spinal cord and the medulla. It primarily stimulates the body’s “rest and digest” and “feed and breed” response. Read on to explore more differences between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system.
Which system prepares the body for fight and flight response?
The parasympathetic nervous system restores the body to a calm and composed state and prevents it from overworking. The sympathetic nervous system , on the other hand, prepares the body for fight and flight response.
Which system activates the fight or flight response during a threat or perceived danger?
The sympathetic nervous system activates the fight or flight response during a threat or perceived danger, and the parasympathetic nervous system restores the body to a state of calm. Learn more about the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, or other related topics at BYJU’S Biology.
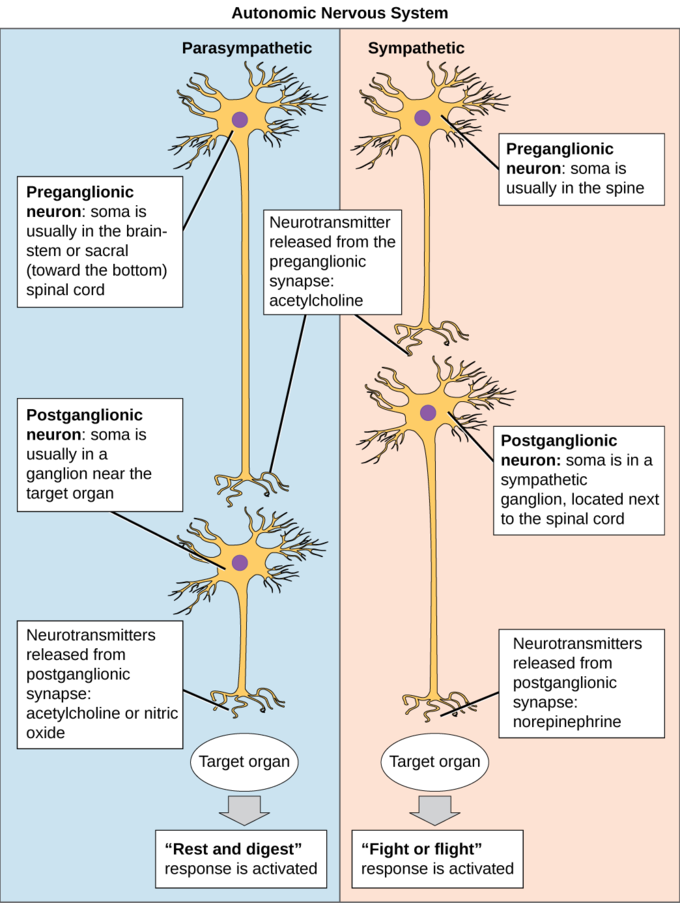
Which system releases acetylcholine?
The sympathetic nervous system releases the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine that accelerate the heart rate. The parasympathetic nervous system releases acetylcholine, the hormone that slows down the heart rate.
What is a Sympathetic Nervous System?
It is the division of the autonomic nervous system which prepares the body for stressful situations and is located near the lumbar and thoracic regions in the spinal cord. A small amount of sympathetic nervous system activity can regulate vital body functions by stimulating the body’s fight or flight response. It responds as a physiological reaction by perceiving a threat or attack to survival. A few examples are regulating the rate of respiration, heart rate and pupillary responses.
What is Sympathetic and Parasympathetic?
As defined above, the two main divisions of Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) are:
How does the ANS respond to the external environment?
When the ANS receives information about the external environment and the body, it responds by stimulating varied body processes, through the sympathetic nervous system, or can also inhibit the body systems through the parasympathetic nervous system. There are two nerve cells in an autonomic nerve pathway, one cell is situated in ...
What are the functions of the autonomic nervous system?
Functions of the Autonomic Nervous System 1 Blood pressure 2 Body temperature 3 Heart and breathing rates 4 Digestion 5 Metabolism and body weight 6 Keeping a balance of water and electrolytes like Na (Sodium) and Ca (Calcium) 7 Production of body fluids such as saliva, tears, and sweat 8 Defecation 9 Urination 10 Sexual response
What is the autonomous nervous system?
Ans: An autonomous nervous system consists of neurons in the peripheral nervous system that perform specific functions. These neurons control three different types of cells, the first being smooth muscle cells present in all structures all over the body that are controlled by different neurons. The two big parts of the autonomic nervous system are ...
How does the sympathetic nervous system regulate vital body functions?
A small amount of sympathetic nervous system activity can regulate vital body functions by stimulating the body’s fight or flight response. It responds as a physiological reaction by perceiving a threat or attack to survival. A few examples are regulating the rate of respiration, heart rate and pupillary responses.
What happens when ANS doesn't work?
When ANS doesn't function properly, disorders may arise leading to affected body parts or processes, which are often progressive. However, some of the autonomic nervous system disorders can be reversed. [Image will be Uploaded soon]
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
The parasympathetic nervous system is part of the autonomic nervous system. It originates in the spinal cord and the medulla and controls homeostasis, or the maintenance of the body's systems. The parasympathetic nervous system controls the "rest and digest" functions of the body.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates visceral functions, i.e. functions of the internal organs such as the heart, stomach and intestines. The ANS is part of the peripheral nervous system and also has control over some muscles within the body. The functions of the ANS are involuntary and reflexive, e.g. the beating of the heart, expansion or contraction of blood vessels or pupils, etc. — which is why we are seldom conscious of it. The parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems, along with the enteric nervous system make up the ANS.
What is the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems?
Sympathetic Nervous System. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) controls homeostasis and the body at rest and is responsible for the body's "rest and digest" function. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) controls the body's responses to a perceived threat and is responsible for the "fight or flight" response.
What are the functions of the ANS?
The functions of the ANS are involuntary and reflexive, e.g. the beating of the heart, expansion or contraction of blood vessels or pupils, etc. — which is why we are seldom conscious of it. The parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems, along with the enteric nervous system make up the ANS.
What happens to the body when the sympathetic nervous system is shut down?
With sympathetic nervous responses, the body speeds up, tenses up and becomes more alert. Functions that are not essential for survival are shut down. Following are the specific reactions of sympathetic nervous system:
Which system controls the body's responses to a perceived threat?
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) controls the body's responses to a perceived threat and is responsible for the "fight or flight" response. The PNS and SNS are part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which is responsible for the involuntary functions of the human body.
Which system is responsible for involuntary functions?
The PNS and SNS are part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which is responsible for the involuntary functions of the human body.
Sympathetic Nervous System: Fight or Flight
The ANS directs your body’s rapid and involuntary response to strain, such as danger, disease, and exercise. It sends messages to organs, muscles, and glands to increase heart rate, dilate the bronchial tubes to your lungs, increase perspiration, and cause pupil dilation.
Parasympathetic Nervous System: Rest and Digest
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) works in opposition to the sympathetic system, controlling the body’s ability to relax. It mainly functions to downregulate the body using the vagus nerve, which sends impulses from the brain to the body and back.
Autonomic Nervous System and Heart Rate Variability
Heart rate variability (HRV) is a measure of how the SNS and PSNS affect your heart beat. When your nervous system is balanced, your heart is constantly being told to beat slower by your parasympathetic system, and to beat faster by your sympathetic system. These mixed messages result in a constant state of variation in your heart rate.
WHOOP Calculates HRV to Help Monitor Your ANS
WHOOP monitors your heart rate and calculates your HRV on a nightly basis using a dynamic average during sleep. It is weighted towards your last stage of slow wave sleep when you’re in your deepest period of sleep and your body is most at rest.
Casey Meserve
Casey Meserve is a writer at WHOOP. Prior to joining WHOOP, they were an SEO Strategist at TechTarget, an editor at Patch.com, and a reporter for the Old Colony Memorial in Plymouth, Mass.
Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic
The difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic is that while the sympathetic nervous system controls, regulates, and influences the body’s response to fight or flight, while parasympathetic, on the other hand, induces the body to rest and digest and/or to feed and breed.
What is Sympathetic?
The sympathetic autonomous nervous system plays a vital role in the survival of the human body.
What is Parasympathetic?
The parasympathetic system of nerves forms the other half of the autonomic nervous system present in the human anatomy.
Main Differences Between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
SNS forms half of ANS that is responsible for flight or fight reaction. PNS forms another half of ANS that plays a role in controlling and regulating body processes while at rest.
Conclusion
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) forms a part of the human anatomy that is in charge of specific and selected body processes. This includes circulation of blood, digestion, breathing, urination, heartbeat, etc. ANS functions take place independently with no active effort from the human being.
What happens when you switch from negative to positive?
Another is that the switch from negative to positive emotions quiets your sympathetic nervous system – which triggers the fight-or-flight response – and activates the parasympathetic system, which acts more like a brake on strong emotions. — The Conversation, oregonlive, 29 Dec. 2020 Another is that the switch from negative to positive emotions quiets your sympathetic nervous system – which triggers the fight-or-flight response – and activates the parasympathetic system, which acts more like a brake on strong emotions. — The Conversation, oregonlive, 29 Dec. 2020 Another is that the switch from negative to positive emotions quiets your sympathetic nervous system – which triggers the fight-or-flight response – and activates the parasympathetic system, which acts more like a brake on strong emotions. — The Conversation, oregonlive, 29 Dec. 2020 Another is that the switch from negative to positive emotions quiets your sympathetic nervous system – which triggers the fight-or-flight response – and activates the parasympathetic system, which acts more like a brake on strong emotions. — The Conversation, oregonlive, 29 Dec. 2020 Another is that the switch from negative to positive emotions quiets your sympathetic nervous system – which triggers the fight-or-flight response – and activates the parasympathetic system, which acts more like a brake on strong emotions. — The Conversation, oregonlive, 29 Dec. 2020 Another is that the switch from negative to positive emotions quiets your sympathetic nervous system – which triggers the fight-or-flight response – and activates the parasympathetic system, which acts more like a brake on strong emotions. — The Conversation, oregonlive, 29 Dec. 2020 Recent Examples on the Web: Noun Parasympathetic has two other states though- the rest and digest and according to the Polyvagal Theory, the ventral vagal branch of the parasympathetic which is social engagement. — Womensmedia, Forbes, 15 Apr. 2021 But purposeful breathing can trigger your parasympathetic system, or the part of your autonomic nervous system that opposes the fight-flight-freeze response. — Emily Shiffer, SELF, 3 Nov. 2020 Those two arms are the parasympathetic and the sympathetic nervous systems, says Lawrence Creswell, a cardiac surgeon in Jackson, Miss., who studies sports cardiology. — Charles Wallace, WSJ, 25 June 2017
What is adjective yoga?
Recent Examples on the Web: Adjective Yoga is a parasympathetic activation exercise that helps with digestion, blood flow and more. — Womensmedia, Forbes, 15 Apr. 2021 Another is that the switch from negative to positive emotions quiets your sympathetic nervous system – which triggers the fight-or-flight response – and activates ...
What is the definition of parasympathetic?
Definition of parasympathetic. (Entry 1 of 2) : of, relating to, being, or acting on the parasympathetic nervous system.
What is parasympathetic nerve?
noun. Medical Definition of parasympathetic (Entry 2 of 2) 1 : a parasympathetic nerve this sacral group of parasympathetics supplies fibers to the external genitalia — A. C. Guyton. 2 : parasympathetic nervous system.