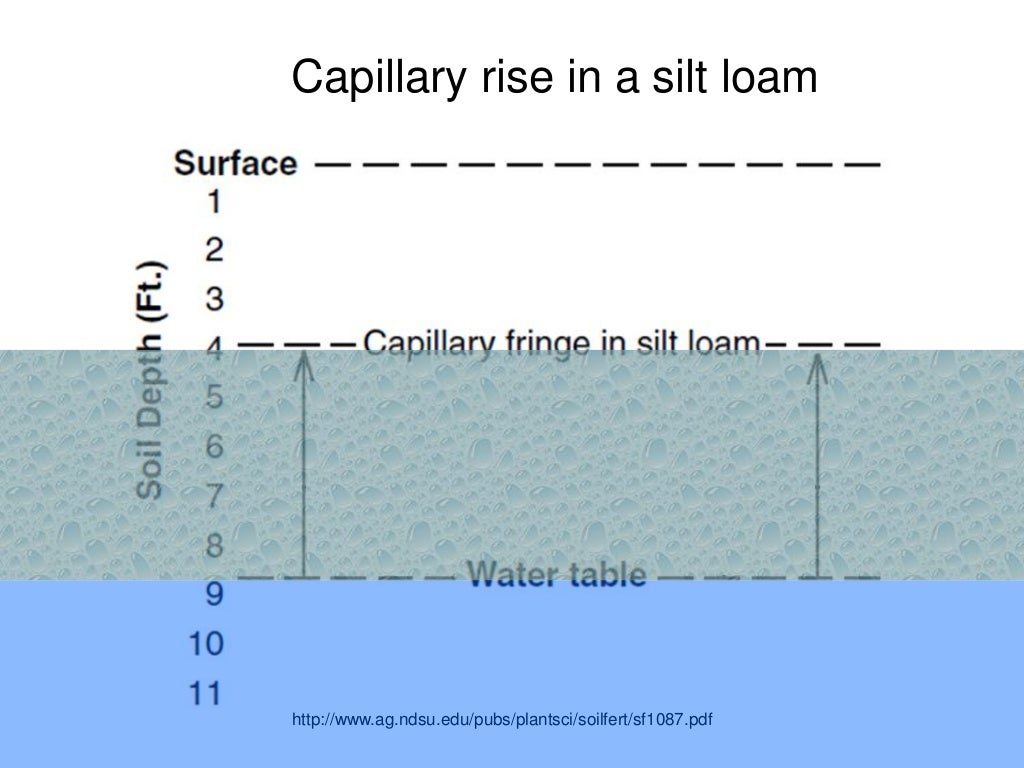
Which soil has high water retaining capacity?
However, large pores do not have a great ability to hold water. As a result, sandy soils drain excessively. On the other hand, clayey soils have small particles and small pores. Since small pores have a greater ability to hold water, clayey soils tend to have high water holding capacity.
How can you increase soils ability to hold water?
Organic Soil Amendments
- Sphagnum peat moss (please note that Sphagnum peat may not be a sustainably harvested amendment)
- Compost
- Coir dust (a byproduct of coconut harvest)
- Aged manure (may have high salt content)
- Other organic materials such as grass clippings and straw
Is result of too much water given to soil?
Too much water in the soil is often caused by construction and planting practices, such as the improper use of irrigation systems. However, some locations are naturally susceptible to saturated soil because of soil type, terrain, heavy rains, flooding, or a high water table.
How much water should soil ideally hold?
Unfortunately there is no general rule because much depends on the type of soil. In this science activity you will see how much water soil can hold by practicing with readily available kitchen substitutes for dirt. Once you understand some general principles, you should be better equipped to tackle the real problem of watering wisely.

Why is water retention important in soil?
Water holding capacity is important to soil health. Soils that can retain a balanced amount of water are able to nourish crops and keep soil organic matter alive. Healthy soil structure forms into aggregates, lessening the density in the soil to create more pores, where water can filter in and out.
What is meant by water retention?
Water retention, also known as fluid retention or edema, occurs when excess fluids build up in your body. Water retention occurs in the circulatory system or within tissues and cavities. It may cause swelling in your hands, feet, ankles, and legs. There are several potential causes, including: Hormonal changes.
Is water retention good for soil?
Stronger plants grow from soil with improved water retention. This is because, when soil is thicker and rightly packed, plants can extend deeper, thicker, and healthier roots.
What causes retaining water?
You can experience water retention in the legs, ankles, or feet as well as the face and hands. It's caused by fluid buildup in body tissues. Sitting for a long time during the workday or on plane flights, hormone changes during pregnancy, and even standing for too long can all cause this to happen.
What are the main causes of water retention?
Causes of fluid retention Gravity – standing up for long periods of time allows fluid to 'pool' in the tissues of the lower leg. Hot weather – the body tends to be less efficient at removing fluid from tissues during the summer months. Burns – including sunburn.
Which type of soil has high soil water retention?
clay-rich soilsGenerally speaking, clay-rich soils have the largest pore space, hence the greatest total water holding capacity.
What is the best soil to retain water?
Clay soil has small, fine particles, which is why it retains the most amount of water. Sand, with its larger particles and low nutritional content, retains the least amount of water, although it is easily replenished with water.
Which soil has highest water retention capacity?
The water holding capacity of a soil is a very important agronomic characteristic. ... The water holding capacity is highest in clayey soil because it is made up of very small tightly packed particles that do not allow water to percolate.Hence The water holding capacity is the highest in Clayey soil.More items...
What is water retention in soil?
Water retention in soil can be understood as the water retained by the soil after it runs through the soil pores to join water bodies such as groundwater or surface streams. Pores in the soil can be defined as the air-spaces that exist in between soil particles. Water retention is mainly dependant on the particle size of the soil.
Why is water retention important for plants?
The water retention by soil is critical for plants and acts as the chief source of moisture for it in almost all habitats . Other than percolation through the soil, soil moisture can also deplete due to evaporation directly from the soil and by transpiration by plants.
Why is soil not able to hold water?
The physical problems can involve soil that is not able to contain much water due to lack of cohesion or due to a rigidity that can occur owing to encrustation, or a very clayey surface . Shallow depth of soil, soil that is too clayey, or the presence of hard opaque surfaces underneath can also present problems to water retention ...
Which type of material retains the most water?
i) Clay – the particles are microscopic to sub-microscopic and exhibit plasticity, allowing it to retain the most water. ii) Silt – the particles are fine grains, but exhibit less plasticity, making this form retain lesser water. iii) Sand and Gravel – aggregates of comparably larger particles that are coarse and loosely bound thus lacking cohesion.
Is green manure good for agriculture?
Among a large gamut of solutions and applications, the most common one is the use of ecologically beneficial green manure. Agricultural soil should also be frequently and properly drained to achieve effects such as the leaching of saline moisture in soils.
What is soil water retention?
The most fundamental concept to understand about soil water retention is that soil water content is positively related to soil matric potential. As soil water content decreases, matric potential also decreases, becoming more negative. When all the pores in a soil are filled with water, the soil is at its saturated water content (θ s) ...
How does hysteresis affect soil water retention?
This phenomenon has a number of important effects on soil water dynamics. For example, hysteresis in the water retention curve can increase the amount of water that is stored near the soil surface after an infiltration and drainage event [21]. Hysteresis can also slow the rate of solute leaching in soil under natural rainfall conditions with greater effects in coarse-textured than fine-textured soils [22]. In subsequent chapters, we will further consider the effects of hysteresis. For now, we will examine its nature and causes.
What is the contact angle of organic soil?
Organic soils and mineral soils in which much of the surface area becomes covered with organic coatings can have contact angles >90°, making them hydrophobic, i.e. tending to repel water. To visualize contact angle hysteresis and how it may affect soil water retention, a thought experiment may help.
Why is soil hydraulics important?
Soil hydraulic properties are essential in irrigation and drainage studies for closing water balance equation, for predicting leaching of nutrients, for water supply to plants, and for other agronomical and environmental applications. Soil hydraulic properties reflect the structure of the soil porous system comprising pores ...
Does soil moisture depend on topography?
It is obvious that soil moisture content depends not only on topography, but also on some physical and hydraulic characteristics of soils, such as soil texture and soil water retention (Lin, 2012 ).
What is the soil water retention function?
The soil water retention function determines the relation between the volume of water retained by the soil, expressed by θ, and the governing soil matric, or suction forces ( Dane and Hopmans, 2002 ). These suction forces are typically expressed by the soil water matric head (strictly negative) or soil suction (strictly positive). These suction forces increase as the size of the water-filled pores decreases, as may occur by drainage, water uptake by plant roots, or soil evaporation. Also known as the soil water release or soil water characteristic function, this soil hydraulic property describes the increase of θ and the size of the water-filled pores with an increase in matric potential, as occurs by infiltration. Since the matric forces are controlled by pore-size distribution, specific surface area, and type of physico-chemical interactions at the solid–liquid interfaces, the soil water retention curve is very soil specific and highly nonlinear. It provides an estimate of the soil's capacity to hold water after irrigation and free drainage (field capacity), minimum soil water content available to the plant (wilting point), and root zone water availability for plants. The soil water retention curve exhibits hysteresis, that is, the θ value is different for wetting (infiltration) and drying (drainage).
Why is water retention important?
The water retention relation is important in quantifying soil moisture dynamics, as discussed later. Another area in which it is important is in soil–plant–water relations. Often termed matric potential because it is representative of the energy state of the soil water, ψ indicates the work that must be done by plant roots to extract water from the unsaturated soil. Plants wilt from inadequate soil moisture not in direct response to low θ, but rather because at low θ, ψ is low. In soil that is too dry, ψ is so highly negative that a plant is incapable of overcoming this energy barrier. Typically, the minimum ψ is about −15 atm for agricultural plants, though much lower in some plants, especially those native to arid regions.
What is the water retention capacity of a colloid?
The colloid has water retention capacity, which can make a certain amount of water fixed in the colloidal network structure skeleton lose fluidity. The mass fraction (90%) of the colloid is water, so as to give full play to the role of water fire extinguishing.
How do mycorrhizal fungi affect soil water retention?
Mycorrhizal fungi play a subtle but important role in shaping the hydraulic properties of soils through multiple direct and indirect mechanisms related to mycorrhizal-induced changes in soil structure and organic matter content. A majority of studies report that the presence and/or abundance of mycorrhizal mycelia correlates positively with soil water-retention capacity, hydraulic conductivity, and infiltration capacity, and negatively with soil water erodibility, although further research in this area is warranted. Direct mechanisms include mycorrhizal enhancement of soil aggregation and porosity, enhanced soil organic matter accumulation resulting from hyphal carbon inputs to soil and protection of labile soil organic matter pools inside aggregates, mycorrhizal inhibition of soil organic matter decomposition through competitive interactions with other soil microbial guilds, and mycorrhizal regulation of soil water repellency. At the ecosystem scale, indirect (plant-mediated) mechanisms may be even more important than direct mechanisms, given that mycorrhizal enhancement of plant growth and plant community diversity and productivity stimulates soil organic matter accumulation and soil aggregation, porosity, and water retention.
What is the purpose of natural water retention measures?
This alternative design proposes multifunctional measures, starting with Natural Water Retention Measures (http://nwrm.eu/ ), with the aim of “protecting and managing water resources and addressing water-related challenges by restoring or maintaining ecosystems as well as natural features and characteristics of water bodies using natural means and processes.” This is proposed as a system that aims to control flood damage and at the same time manages to preserve and improve the water-retention capacity of aquifers, soil, and ecosystems in order to restore their status.
What is the importance of theoretical water retention time?
The importance of the theoretical water retention time, RT, was delineated in Section 6.1.3. In accordance with the outlined relations, the categories of reservoirs given in Table 6.4 can be distinguished. It is stressed that the reservoirs of the first two categories are so different in their water quality conditions that the use of standard empirical relations for estimating their water quality conditions cannot be used, or have to be highly modified.
How do mycorrhizal fungi affect soil?
Mycorrhizal fungi play a subtle but important role in shaping the hydraulic properties of soils through multiple direct and indirect mechanisms related to mycorrhizal-induced changes in soil structure and organic matter content.
