
Does labetalol work immediately?
Labetalol starts to work within 2 hours, but it can take a few days to take full effect. You may not feel any different when you take labetalol, but this doesn't mean it's not working. How long does labetalol last?
Is labetalol an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)?
An Angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) that is indicated for the treatment of hypertension in children younger than 6 years old is : ... A common side effect of cardiovascular beta-blockers such as labetalol (Trandate) is: ... The side effect profile of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) is similar to the side effects of: antiotensin ...
Is labetalol a calcium channel blocker?
labetalol, and propranolol. Bisoprolol and nebivolol eliminated by both liver and kidney, hence a lesser risk of hepatic interactions. No hepatic interactions for atenolol, nadolol, and sotalol. Calcium-channel blockers Bradycardia and heart block, with heart rate-reducing agents (verapamil and diltiazem).
Is labetalol a beta blocker?
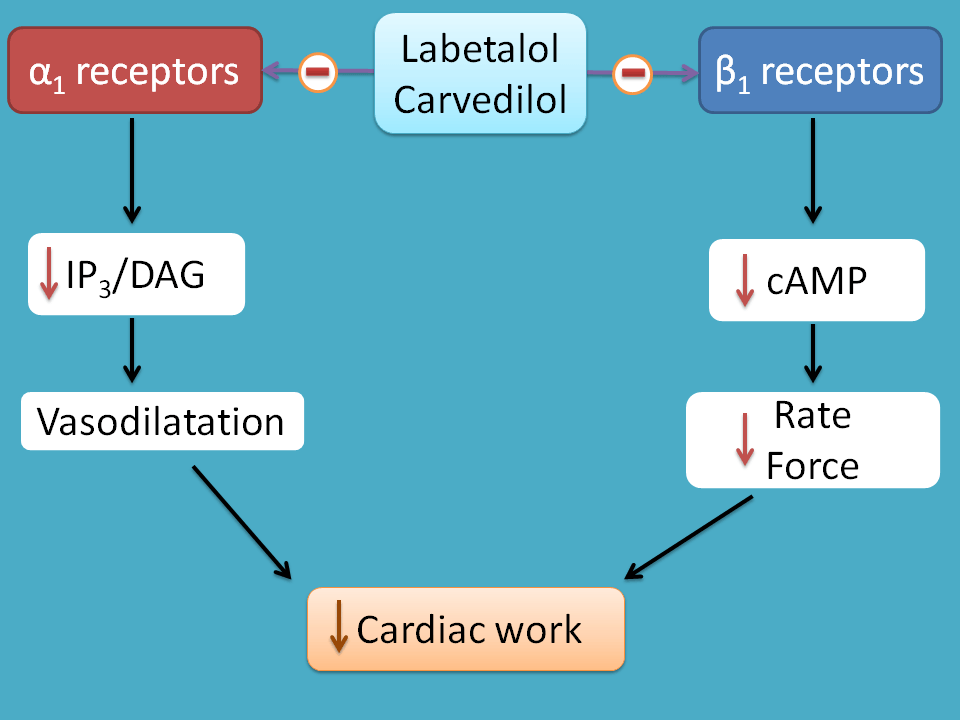
Labetalol is an alpha and beta blocker medication. It lowers blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels (by blocking alpha receptors) and slowing heart rate (by blocking beta receptors). What is labetalol used for? The typical dose for labetalol is 200-400 mg twice a day. Does labetalol work immediately?
What is the primary mechanism of action of beta blockers?
Beta blockers work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. Beta blockers cause the heart to beat more slowly and with less force, which lowers blood pressure.
What type of beta-blocker is labetalol?
Labetalol is a combined alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent for oral and intravenous use in the treatment of hypertension. It is a nonselective antagonist at beta-adrenoceptors and a competitive antagonist of postsynaptic alpha 1-adrenoceptors.
Is labetalol a vasodilator?
In contrast to other β-blockers, labetalol should be considered a peripheral vasodilator that does not cause a reflex tachycardia. The dual action of labetalol on both the α1 and β receptors contributes to the decline in blood pressure and systemic vascular resistance.
What is the indication of labetalol?
The FDA-approved indication for labetalol is the treatment of arterial hypertension, which ranges from acute hypertensive crises (urgent/emergency) to stable chronic hypertension.
Why is labetalol used in hypertensive emergency?
Labetalol is a unique alpha- and beta-adrenergic-receptor blocking agent that has recently been approved for the treatment of hypertensive emergencies and urgencies. This agent lowers peripheral vascular resistance by vasodilatation with little or no effect on cardiac output.
What are side effects of labetalol?
Side effects of labetalolFeeling sleepy, dizzy or weak. If labetalol makes you feel dizzy or weak, stop what you're doing and sit or lie down until you feel better. ... Headaches. Make sure you rest and drink plenty of fluids. ... Cold fingers or toes. ... Feeling sick or being sick (nausea or vomiting) ... Diarrhoea. ... Stomach pain.
What does labetalol do to the heart?
This medicine is a beta-blocker. It works by affecting the response to nerve impulses in certain parts of the body, like the heart. As a result, the heart beats slower and decreases the blood pressure.
What is the difference between labetalol and metoprolol?
Labetalol and metoprolol both significantly (p < 0.01) lowered the supine and standing blood pressure from baseline with no significant difference found between the two treatment groups. Both drugs lowered the heart rate; however, the rate-lowering effect was significantly greater with metoprolol (p < 0.01).
How much does labetalol lower BP?
Labetalol tablets need to be given twice a day. Peak concentrations are reached within 5 minutes of labetalol injection. Blood pressure-lowering effects increase with higher dosages. An average lowering of blood pressure of 11/7 mmHg was reported with an initial dosage of 0.25 mg/kg labetalol injection.
What heart rate is too low on beta blockers?
Bradycardia with associated hypotension and shock (systolic BP < 80 mm Hg, heart rate < 60 bpm) defines severe beta-blocker toxicity.
Why is labetalol used in stroke?
Background: Labetalol and nicardipine are antihypertensives commonly used in the management of elevated blood pressure (BP) following an acute stroke, but there is limited evidence to suggest which agent as a continuous infusion should be used preferentially in this setting.
Which is the best medicine for high blood pressure?
In terms of prescriptions written, here are the top 4 high blood pressure medications,the ACE inhibitor lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril) tops the list,followed by amlodipine besylate (Norvasc),a calcium channel blocker, and.generic hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ).
What is the difference between metoprolol and labetalol?
Labetalol and metoprolol both significantly (p < 0.01) lowered the supine and standing blood pressure from baseline with no significant difference found between the two treatment groups. Both drugs lowered the heart rate; however, the rate-lowering effect was significantly greater with metoprolol (p < 0.01).
Is labetalol a Cardioselective beta blocker?
1 The effects of atenolol (100 mg), a cardioselective beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent, and labetalol (300 mg), a combined alpha- and non-selective beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent given in single doses were examined in a double-blind placebo controlled study in 11 asthmatic patients with hypertension.
Is labetalol hard on the kidneys?
Acute renal failure is uncommon in pure beta adrenergic blocker toxicity, but labetalol, with its alpha blockade, can lead to complex hemodynamic changes and can cause acute renal failure at toxic levels.
Will labetalol cause weight gain?
Labetalol may cause heart failure in some patients. Check with your doctor right away if you are having chest pain or discomfort; dilated neck veins; extreme fatigue; irregular breathing; an irregular heartbeat; shortness of breath; swelling of the face, fingers, feet, or lower legs; weight gain; or wheezing .
How to make labetalol hydrochloride?
A 10 mg/mL labetalol hydrochloride oral suspension may be made with tablets and simple syrup. Crush twelve 100 mg tablets in a mortar and reduce to a fine powder. Add a small quantity of simple syrup and mix to a uniform paste; mix while adding the vehicle in incremental proportions to almost 120 mL; transfer to a calibrated bottle, rinse mortar with simple syrup, and add sufficient quantity to make 120 mL. Label "shake well" and "refrigerate." Stable for 4 weeks when stored under refrigeration (preferred) or at room temperature (Nahata 1991; Nahata 2014).
What is the hypersensitivity to labetalol?
Hypersensitivity to labetalol or any component of the formulation ; severe bradycardia; heart block greater than first degree (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker); cardiogenic shock; bronchial asthma or a history of obstructive airway disease; uncompensated cardiac failure; conditions associated with severe and prolonged hypotension
Is labetalol safe for pregnancy?
Oral labetalol is considered appropriate for the treatment of chronic hypertension in pregnancy (ACOG 203 2019; Magee 2014). Intravenous labetalol is recommended for use in the management of acute onset, severe hypertension (systolic BP ≥160 mm Hg or diastolic BP ≥110 mm Hg) in pregnant and postpartum women.
Can beta blockers cause arterial insufficiency?
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) and Raynaud disease: Beta blockers may precipitate or aggravate symptoms of arterial insufficiency in patients with PVD and Raynaud disease; use with caution and monitor for progression of arterial obstruction.
Can beta blockers be withdrawn?
Abrupt withdrawal: Beta-blocker therapy should not be withdrawn abruptly (particularly in patients with CAD), but gradually tapered to avoid acute tachycardia, hypertension, and/or ischemia. Severe exacerbation of angina, ventricular arrhythmias, and myocardial infarction (MI) have been reported following abrupt withdrawal of beta-blocker therapy. Temporary but prompt resumption of beta-blocker therapy may be indicated with worsening of angina or acute coronary insufficiency.
Is acebutolol a beta blocker?
Cardioselective beta-blockers (eg, acebutolol, atenolol, metoprolol, and penbutolol) may be safer than nonselective beta-blockers. All beta-blockers appear to mask tachycardia as an initial symptom of hypoglycemia. Ophthalmic beta-blockers are probably associated with lower risk than systemic agents. Monitor therapy.
Does beta blocker work on grass pollen?
More specifically, Beta-Blockers may inhibit the ability to effectively treat severe allergic reactions to Grass Pollen Allergen Extract (5 Grass Extract) with epinephrine. Some other effects of epinephrine may be unaffected or even enhanced (e.g., vasoconstriction) during treatment with Beta-Blockers.
How does Labetalol work?
It works by blocking the activation of β-receptors and α-receptors. Labetalol was patented in 1966 and came into medical use in 1977. It is available as a generic medication. In 2017, it was the 211th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than two million prescriptions.
What is labetalol used for?
Key:SGUAFYQXFOLMHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Y. (verify) Labetalol is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and in long term management of angina. This includes essential hypertension, hypertensive emergencies, and hypertension of pregnancy. In essential hypertension it is generally less preferred than a number of other blood pressure medications.
What is the first drug to combine alpha and beta receptors?
Labetalol was the first drug created that combined both alpha- and beta- adrenergic receptor blocking properties. It was created to potentially fix the compensatory reflex issue that occurred when blocking a single receptor subtype, i.e. vasoconstriction after blocking beta-receptors or tachycardia after blocking alpha receptors. Because the reflex from blocking the single receptor subtypes acted to prevent the lowering of blood pressure, it was postulated that weak blocking of both alpha- and beta- receptors could work together to decrease blood pressure.
What is the fourth isomer of labetalol?
The fourth isomer, the ( R, R )-isomer which is also known as dilevalol, is a mixed nonselective β blocker and selective α 1 blocker. Labetalol is typically given as a racemic mixture to achieve both alpha and beta receptor blocking activity. Stereoisomers of labetalol. ( R, R )-Labetalol.
What is the ratio of alpha to beta blockade?
The amount of alpha to beta blockade depends on whether labetalol is administered orally or intravenously (IV). Orally, the ratio of alpha to β blockade is 1:3 . Intravenously, alpha to β blockade ratio is 1:7.
Is labetalol a sympathomimetic drug?
Labetalol possesses intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. In particular, it is a partial agonist at beta2- receptors located in the vascular smooth muscle. Labetalol relaxes vascular smooth muscle by a combination of this partial beta2- agonism and through alpha1- blockade.
Is labetalol a beta blocker?
Thus, the labetalol can be thought to be a beta-blocker with some al pha-blocking effects. By comparison, labetalol is a weaker β-blocker than propranolol, and has a weaker affinity for alpha-receptors compared to Phentolamine. Labetalol possesses intrinsic sympathomimetic activity.
What is a review of labetalol?
Labetalol: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, clinical uses and adverse effects.
Does labetalol lower blood pressure?
Unlike conventional beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs without intrinsic sympathomimetic activity, labetalol, when given acutely, produces a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance and blood pressure with little alteration in heart rate or cardiac output.
Is labetalol a beta adrenoceptor?
Labetalol is more potent at beta that at alpha 1 adrenoceptors in man; the ratio of beta-alpha antagonism is 3:1 after oral and 6.9:1 after intravenous administration. Labetalol is readily absorbed in man after oral administration, but the drug, which is lipid soluble, undergoes considerable hepatic first-pass metabolism ...
Does labetalol cause dizziness?
In addition, preliminary studies indicate that labetalol may be of value in the management of ischemic heart disease. The most troublesome side effect of labetalol therapy is posture-related dizziness. Other reported side effects of the drug include gastrointestinal disturbances, tiredness, headache, scalp tingling, skin rashes, ...
Does labetalol cause gastrointestinal problems?
Other reported side effects of the drug include gastrointestinal disturbances, tiredness, headache, scalp tingling, skin rashes, urinary retention and impotence. Side effects related to the beta-adrenoceptor blocking effect of labetalol, including asthma, heart failure and Raynaud's phenomenon, have been reported in rare instances.
Is labetalol a diuretic?
Labetalol administered alone or with a diuretic is often effective when other antihypertensive regimens have failed. Studies have shown that labetalol is effective in the treatment of essential hypertension, renal hypertension, pheochromocytoma, pregnancy hypertension and hypertensive emergencies.
How is Labetalol hydrochloride infused?
Labetalol hydrochloride injection is prepared for continuous intravenous infusion by diluting the vial contents with commonly used intravenous fluids (see below). Examples of two methods of preparing the infusion solution are:
How long does it take for Labetalol to lower blood pressure?
Labetalol HCl administered as a continuous intravenous infusion, with a mean dose of 136 mg (27 mg to 300 mg) over a period of 2 to 3 hours (mean of 2 hours and 39 minutes), lowered the blood pressure by an average of 60/35 mmHg.
How long should you stay supine after a labetalol injection?
It is not a disclosure of all possible adverse or intended effects. During and immediately following (for up to 3 hours ) Labetalol hydrochloride injection, the patient should remain supine.
Is lbetalol hydrochloride contraindicated?
Labetalol hydrochloride injection is contraindicated in bronchial asthma, overt cardiac failure, greater-than-first-degree heart block, cardiogenic shock, severe bradycardia, other conditions associated with severe and prolonged hypotension, and in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any component of the product (see WARNINGS ).
Does Labetalol HCl lower blood pressure?
Both the alpha- and beta-blocking actions of orally administered Labetalol HCl contribute to a decrease in blood pressure in hypertensive patients.
Is labilel HCl a racemic?
Dilevalol, the R,R' stereoisomer, makes up 25% of racemic Labetalol. Labetalol HCl is a white or off-white crystalline powder, soluble in water. Labetalol hydrochloride injection is a clear, colorless to light yellow, aqueous, sterile, isotonic solution for intravenous (IV) injection. It has a pH range of 3.0 to 4.5.
Is lab work required before or after a lab test?
Routine laborator y tests are ordinarily not required before or after intravenous Labetalol. In patients with concomitant illnesses, such as impaired renal function, appropriate tests should be done to monitor these conditions.
What is labetalol used for?
Labetalol is a combined α- and β-adrenergic receptor blocker that currently is approved for both oral and intravenous use in the treatment of hypertension. Labetalol lowers blood pressure by decreasing systemic vascular resistance by α1 -blockade and at the same time counteracts the reflex tachycardia from vasodilation through its β-blocker effect. 28,29 Labetalol reduces peripheral vascular resistance while maintaining cerebral, renal, and coronary blood flow. Unlike other β-blockers, labetalol does not reduce cardiac output. When administered intravenously it has a rapid onset of action (2 to 5 minutes), with peak hypotensive effect occurring within 5 to 10 minutes and the effect lasting 2 to 4 hours. 30 The drug is metabolized primarily by the liver and has a plasma elimination half-life of approximately 5 hours. 28
What are the adverse effects of labetalol?
Most adverse effects of labetalol are manifestations of the combined beta and alpha-1 adrenoceptor blockade or its intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. Orthostatic hypotension is a common adverse effect. Other adverse cardiovascular effects include bradycardia/tachycardia, arrhythmias, cold extremities, heart failure, and edema.
How much labetalol should I take for BP?
However, several other investigators used doses as high as 500 to 1200 mg to achieve BP control. 50 The initial dose should be 200 mg followed by hourly 200-mg doses to a maximal dose of 1200 mg.
How long does labetalol last?
The onset of action is observed within 2 to 15 minutes after IV administration of labetalol and may last for about 2 to 6 hours. The longer duration of action and variability in pharmacokinetics may make labetalol extremely difficult to titrate as a continuous infusion.
How long does it take for labetalol to be eliminated?
Labetalol has a maximal onset time of 20 minutes and no active metabolites, and the elimination half-life is approximately 6 hours.
Is labetalol bad for asthma?
Adverse effects of labetalol include orthostatic hypotension, bronchospasm (the drug should be avoided in asthma patients), heart failure, and significant bradycardia (it should be avoided in the presence of sinus bradycardia or heart block greater than first degree).
Is labetalol a vasodilator?
In contrast to other β-blockers, labetalol should be considered a peripheral vasodilator that does not cause a reflex tachycardia.
What is the purpose of lbetalol hydrochloride?
Labetalol hydrochloride is used in the management of hypertension. The drug has been used as monotherapy or in combination with other classes of antihypertensive agents. The drug is at least as effective as pure beta-adrenergic blocking agents, thiazide diuretics, methyldopa, or clonidine. ...
How long does it take for labetalol to be bioavailable?
100mg and 200mg oral doses of labetalol have a T max of 20 minutes to 2 hours. Bioavailability may be as low as 11% or as high as 86% and may increase in older patients or when taken with food.
How much radiolabelled labetalol is recovered in urine?
Route of Elimination. Radiolabelled doses of labetalol are 55-60% recovered in the urine and 12-27% recovered in the feces. Volume of Distribution.
Is labetalol a metabolite?
The metabolism of labetalol has not been fully described in the literature but studies in sheep show an N-dealkylation to 3-amino-1-phenyl butane. This metabolite may be further metabolized to benzylacetone and 3-amino- (4-hydroxyphenyl)butane. Labetalol in humans is mainly metabolized to glucuronide metabolites such as the O-phenyl-glucuronide and the N-glucuronide.
Does IV labetalol lower blood pressure?
Iv labetalol appears to adequately reduce blood pressure in about 80-90% of patients with severe hypertension or hypertensive emergencies, irrespective of etiology, and may be useful even when other drugs have failed. / Labetalol hydrochloride /.
Is labetalol an antihypertensive?
Labetalol is an antihypertensive agent with both alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptor blocking activity. Labetalol has been linked to several cases of clinically apparent drug induced liver disease, some of which have been severe and even fatal.
Is labetalol hydrochloride a base?
The drug is physically and/or chemically incompatible with 5% sodium bicarbonate injection; labetalol hydrochloride solutions containing 1.25-3.75 mg/ml in 5% sodium bicarbonate have a pH of 7.6-8 and form a white precipitate, probably the free base, within 6 hrs after admixture. / Labetalol hydrochloride /.
Labetalol
A mixed alpha/beta Adrenergic antagonist, Antihypertensive (pregnancy-induced hypertension).
Home Delivery for Labetalol in Your City
Medicine India is just a publishing medium for medicine related information and does not provide services or sales of medicines including labetalol.

Overview
Pharmacology
Labetalol's dual alpha and beta adrenergic antagonism has different physiological effects in short- and long-term situations. In short-term, acute situations, labetalol decreases blood pressure by decreasing systemic vascular resistance with little effect on stroke volume, heart rate and cardiac output. During long-term use, labetalol can reduce heart rate during exercise while maintaining cardiac output by an increase in stroke volume.
Medical uses
Labetalol is effective in the management of hypertensive emergencies, postoperative hypertension, pheochromocytoma-associated hypertension, and rebound hypertension from beta blocker withdrawal.
It has a particular indication in the treatment of pregnancy-induced hypertension which is commonly associated with pre-eclampsia.
Side effects
• Neurologic: headache (2%), dizziness (11%)
• Gastrointestinal: nausea (6%), dyspepsia (3%)
• Cholinergic: nasal congestion (3%), ejaculation failure (2%)
• Respiratory: dyspnea (2%)
Contraindications
Labetalol is contraindicated in people with overt cardiac failure, greater-than-first-degree heart block, severe bradycardia, cardiogenic shock, severe hypotension, anyone with a history of obstructive airway disease including asthma, and those with hypersensitivity to the drug.
Chemistry
The minimum requirement for adrenergic agents is a primary or secondary amine separated from a substituted benzene ring by one or two carbons. This configuration results in strong agonist activity. As the size of the substituent attached to the amine becomes greater, particularly with respect to a t-butyl group, then the molecule typically is found to have receptor affinity without intrinsic activity, and is, therefore, an antagonist. Labetalol, with its 1-methyl-3-phenylpropyl subs…
History
Labetalol was the first drug created that combined both alpha- and beta- adrenergic receptor blocking properties. It was created to potentially fix the compensatory reflex issue that occurred when blocking a single receptor subtype, i.e. vasoconstriction after blocking beta-receptors or tachycardia after blocking alpha receptors. Because the reflex from blocking the single receptor subtypes acted to prevent the lowering of blood pressure, it was postulated that weak blocking …
External links
• "Labetalol". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
• "Labetalol hydrochloride". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
Administration
- Dosage Form: injection Labetalol HCl administered as a continuous intravenous infusion, with a mean dose of 136 mg (27 mg to 300 mg) over a period of 2 to 3 hours (mean of 2 hours and 39 minutes), lowered the blood pressure by an average of 60/35 mmHg. When the patient is started on Labetalol hydrochloride tablets following adequate control of blood pressure with Labetalol h…
Mechanism of action
- Labetalol hydrochloride injection is an adrenergic receptor blocking agent that has both selective alpha1-adrenergic and nonselective beta-adrenergic receptor blocking actions in a single substance. Labetalol HCl combines both selective, competitive, alpha1-adrenergic blocking and nonselective, competitive, beta-adrenergic blocking activity in a si...
Chemistry
- Labetalol hydrochloride (HCl) is a racemate chemically designated as 2-hydroxy-5-[1-hydroxy-2-[(1-methyl-3-phenylpropyl)amino]ethyl]benzamide monohydrochloride and it has the following structure: Labetalol HCl has the empirical formula C19H24N2O3HCl and a molecular weight of 364.9. It has two asymmetric centers and therefore exists as a molecular complex of two diaste…
Description
- Labetalol HCl is a white or off-white crystalline powder, soluble in water. Labetalol hydrochloride injection is a clear, colorless to light yellow, aqueous, sterile, isotonic solution for intravenous (IV) injection. It has a pH range of 3.0 to 4.5. Each mL contains 5 mg Labetalol hydrochloride USP, 45 mg anhydrous dextrose, 0.10 mg edetate disodium; 0.80 mg of methylparaben and 0.10 mg of p…
Effects
- Labetalol HCl produces dose-related falls in blood pressure without reflex tachycardia and without significant reduction in heart rate, presumably through a mixture of its alpha- and beta-blocking effects. Hemodynamic effects are variable, with small, nonsignificant changes in cardiac output seen in some studies but not others, and small decreases in total peripheral resistance. Elevate…
Signs and symptoms
- Due to the alpha1-receptor blocking activity of Labetalol HCl, blood pressure is lowered more in the standing than in the supine position, and symptoms of postural hypotension can occur. During dosing with intravenous Labetalol HCl, the contribution of the postural component should be considered when positioning the patient for treatment, and the patient should not be allowed to …
Pharmacology
- In a clinical pharmacologic study in severe hypertensives, an initial 0.25 mg/kg injection of Labetalol HCl administered to patients in the supine position decreased blood pressure by an average of 11/7 mmHg. Additional injections of 0.5 mg/kg at 15 minute intervals up to a total cumulative dose of 1.75 mg/kg of Labetalol HCl caused further dose-related decreases in blood …
Results
- Similar results were obtained in the treatment of patients with severe hypertension who required urgent blood pressure reduction with an initial dose of 20 mg (which corresponds to 0.25 mg/kg for an 80 kg patient) followed by additional doses of either 40 mg or 80 mg at 10 minute intervals to achieve the desired effect, or up to a cumulative dose of 300 mg.
Side effects
- Exacerbation of angina and, in some cases, myocardial infarction and ventricular dysrhythmias have been reported after abrupt discontinuation of therapy with beta-adrenergic blocking agents in patients with coronary artery disease. Abrupt withdrawal of these agents in patients without coronary artery disease has resulted in transient symptoms, including tremulousness, sweating, …
Medical uses
- Although beta-adrenergic receptor blockade is useful in the treatment of angina and hypertension, there are also situations in which sympathetic stimulation is vital. For example, in patients with severely damaged hearts, adequate ventricular function may depend on sympathetic drive. Beta-adrenergic blockade may worsen A-V block by preventing the necessary facilitating effects of sy…
Uses
- Labetalol hydrochloride injection is indicated for control of blood pressure in severe hypertension.
Contraindications
- Labetalol hydrochloride injection is contraindicated in bronchial asthma, overt cardiac failure, greater-than-first-degree heart block, cardiogenic shock, severe bradycardia, other conditions associated with severe and prolonged hypotension, and in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any component of the product (see WARNINGS). Beta-blockers, even those w…
Treatment
- In patients with latent cardiac insufficiency, continued depression of the myocardium with beta-blocking agents over a period of time can, in some cases, lead to cardiac failure. At the first sign or symptom of impending cardiac failure, patients should be fully digitalized and/or be given a diuretic, and the response should be observed closely. If cardiac failure continues despite adequ…
Risks
- Several deaths have occurred when Labetalol hydrochloride injection was used during surgery (including when used in cases to control bleeding).
Interactions
- A synergism between Labetalol HCl and halothane anesthesia has been shown (see PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions). Drugs possessing beta-blocking properties can blunt the bronchodilator effect of beta-receptor agonist drugs in patients with bronchospasm; therefore, doses greater than the normal antiasthmatic dose of beta-agonist bronchodilator drugs may be …
Prevention
- Since Labetalol hydrochloride injection may be administered to patients already being treated with other medications, including other antihypertensive agents, careful monitoring of these patients is necessary to detect and treat promptly any undesired effect from concomitant administration.
Adverse effects
- In one survey, 2.3% of patients taking Labetalol HCl orally in combination with tricyclic antidepressants experienced tremor as compared to 0.7% reported to occur with Labetalol HCl alone. The contribution of each of the treatments to this adverse reaction is unknown, but the possibility of a drug interaction cannot be excluded.