
How does probenecid work in the body?
Probenecid - Clinical Pharmacology Probenecid is a uricosuric and renal tubular blocking agent. It inhibits the tubular reabsorption of urate, thus increasing the urinary excretion of uric acid and decreasing serum urate levels.
What is the mechanism of action of probenecid for gout?
Probenecid is also useful in the treatment of gout where the mechanism of action is believed to be focused on the kidney. Probenecid interferes with the kidneys' organic anion transporter (OAT), which reclaims uric acid from the urine and returns it to the plasma. If probenecid (an organic acid) is present,...
What is the mechanism of action of probenecid on avibactam?
Avibactam is a substrate of the renal organic anion transporters (OAT)1 and OAT3; probenecid is a potent inhibitor of these transporters. An in vitro study found probencid blocked 56% to 70% of avibactam uptake by these transporters.
What are the possible drug interactions with probenecid?
Some of the important clinical interactions of probenecid include those with captopril, indomethacin, ketoprofen, ketorolac, naproxen, cephalosporins, quinolones, penicillins, methotrexate, zidovudine, ganciclovir, lorazepam, and acyclovir. In all these interactions, the excretion of these drugs is reduced due to probenecid.

What is the purpose of probenecid?
Probenecid is used in the treatment of chronic gout or gouty arthritis. These conditions are caused by too much uric acid in the blood. The medicine works by removing the extra uric acid from the body. Probenecid does not cure gout, but after you have been taking it for a few months it will help prevent gout attacks.
Does probenecid increase uric acid excretion?
Probenecid is a urate transporter-1 (URAT-1) inhibitor, increasing uric acid excretion via inhibition of tubular reabsorption of oxypurinol, the active metabolite of allopurinol.
What is the mechanism of action of allopurinol and probenecid?
These agents may reduce the amount of uric acid in blood by means of two different ways: (1) by reducing uric acid production through the inhibition of the enzyme xanthine oxidase (as allopurinol); (2) by increasing uric acid clearance through an inhibition of its renal tubular reabsorption (as probenecid), or through ...
How does probenecid lower plasma levels of uric acid?
Probenecid inhibits the tubular reabsorption of urate, thus increasing the urinary excretion of uric acid and decreasing serum urate levels. Probenecid may also reduce plasma binding of urate and inhibit renal secretion of uric acid at subtherapeutic concentrations.
How does probenecid work in gout?
Probenecid is used in the treatment of chronic gout or gouty arthritis. These conditions are caused by too much uric acid in the blood. The medicine works by removing the extra uric acid from the body. Probenecid does not cure gout, but after you have been taking it for a few months it will help prevent gout attacks.
Does probenecid increase blood pressure?
The administration of probenecid (50 mg/kg, ip) induced a significant systolic blood pressure (SBP) decrease, from 167 mmHg to 141 mmHg, within 120 min.
What is the difference between allopurinol and probenecid?
Zyloprim (allopurinol) works well to prevent gout attacks and is cheaper than some alternatives, but it takes a few weeks to start working. Probenecid colchicine (probenecid / colchicine) lessens the redness and swelling that occurs with gout. It lowers uric acid levels associated with gout.
How does probenecid inhibit penicillin excretion?
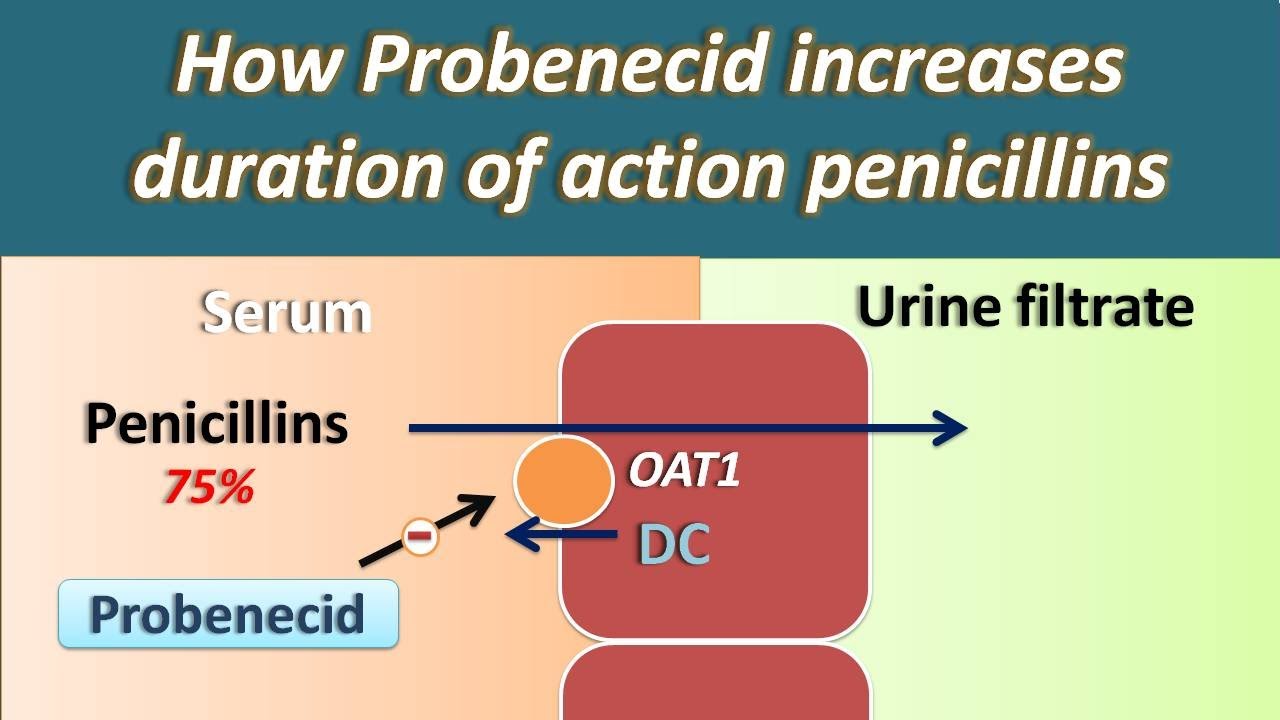
Probenecid has the ability to block the transport of organic acids (e.g. penicillins) across epithelial cells (e.g. renal proximal tubule cells) and its use when combined with penicillins resulted in elevated blood levels of the penicillin and a longer duration of antimicrobial action.
How does probenecid differ from allopurinol?
Probenecid is a uricosuric agent. It works by increasing the excretion of uric acid out of the body. In contrast, allopurinol is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor. It works by decreasing the formation of uric acid in the body.
Does probenecid affect kidney function?
For patients taking probenecid for gout or to help remove uric acid from the body: When you first begin taking probenecid, the amount of uric acid in the kidneys is greatly increased. This may cause kidney stones or other kidney problems in some people.
What is the probable mechanism for the interaction of probenecid with penicillin G?
Mechanism of Action of Probenecid. Probenecid inhibits both the Organic Anion Transporters (OAT) in the basolateral membrane of cells in the proximal tubule. This results in reduced clearance and increased plasma levels of drugs normally secreted by this mechanism (e.g. penicillin).
What are the contraindications for probenecid?
Contraindications / PrecautionsProbenecid hypersensitivity, sulfonamide hypersensitivity. ... Anemia, aplastic anemia, G6PD deficiency, hematological disease, hemolytic anemia. ... Geriatric, renal failure, renal impairment. ... Acid/base imbalance, nephrolithiasis, tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) ... Peptic ulcer disease. ... Pregnancy.More items...
What is probenecid used for?
Probenecid tablets are indicated for the treatment of the hyperuricemia associated with gout and gouty arthritis. As an adjuvant to therapy with penicillin or with ampicillin, methicillin, oxacillin, cloxacillin, or nafcillin, for elevation and prolongation of plasma levels by whatever route the antibiotic is given.
What is the chemical name for probenecid?
The chemical name for Probenecid is 4- [ (dipropylamino) sulfonyl] benzoic acid. It has the following structural formula: Probenecid, USP is a white or nearly white, fine, crystalline powder. Probenecid is soluble in dilute alkali, in alcohol, in chloroform, and in acetone; it is practically insoluble in water and in dilute acids.
What is the effect of probenecid on uric acid?
It inhibits the tubular reabsorption of urate, thus increasing the urinary excretion of uric acid and decreasing serum urate levels. Effective uricosuria reduces the miscible urate pool, retards urate deposition, and promotes resorption of urate deposits.
How many mg of probenecid are in a USP?
How is Probenecid Supplied. Probenecid Tablets, USP are available containing 500 mg of Probenecid, USP. The tablets are capsule shaped, film-coated yellow, debossed LCI on one side and 1367 on the other side. They are available as follows:
Does sulindac affect probenecid?
Probenecid given concomitantly with sulindac had only a slight effect on plasma sulfide levels, while plasma levels of sulindac and sulfone were increased. Sulindac was shown to produce a modest reduction in the uricosuric action of Probenecid, which probably is not significant under most circumstances.
Does probenecid increase penicillin?
When Probenecid is used to elevate plasma concentrations of penicillin or other beta-lactams, or when such drugs are given to patients taking Probenecid therapeutically, high plasma concentrations of the other drug may increase the incidence of adverse reactions associated with that drug.
Can probenecid be used for renal failure?
Use with caution in patients with a history of peptic ulcer. Probenecid has been used in patients with some renal impairment , but dosage requirements may be increased. Probenecid may not be effective in chronic renal insufficiency particularly when the glomerular filtration rate is 30 mL/minute or less.
What is probenecid used for?
Medical uses. Probenecid is primarily used to treat gout and hyperuricemia . Probenecid is sometimes used to increase the concentration of some antibiotics and to protect the kidneys when given with cidofovir. Specifically, a small amount of evidence supports the use of intravenous cefazolin once rather than three times a day when it is combined ...
What was the purpose of Probenecid in World War II?
During World War II, probenecid was used to extend limited supplies of penicillin; this use exploited probenecid's interference with drug elimination (via urinary excretion) in the kidneys and allowed lower doses of penicillin to be used.
Does probenecid help with gout?
Probenecid probably has several pharmacological targets, including blocking pannexins. Probenecid is also useful in the treatment of gout where the mechanism of action is believed to be focused on the kidney. Probenecid interferes with the kidneys' organic anion transporter (OAT), which reclaims uric acid from the urine and returns it to the plasma. If probenecid (an organic acid) is present, the OAT binds preferentially to it (instead of to uric acid), preventing reabsorption of the uric acid. Hence, the urine retains more uric acid, lowering uric acid concentration in the plasma. This is a good example of a medical usage for competition between substrates transported across cell membranes. This same effect, however, alters excretion of acidic drugs by the kidney, leading to the many drug interactions noted above.
What is the role of sodium independent organic anion transmembrane transporter?
Specific Function. Plays an important role in the excretion/detoxification of endogenous and exogenous organic anions, especially from the brain and kidney. Involved in the transport basolateral of steviol, fexofenad...
Does Lisinopril lower the excretion rate of Probenecid?
Lisinopril may decrease the excretion rate of Probenecid which could result in a higher serum level . Probenecid may decrease the excretion rate of Lithium carbonate which could result in a higher serum level. Lithium citrate may decrease the excretion rate of Probenecid which could result in a higher serum level.
Does probenecid reduce uric acid?
Probenecid inhibits the tubular reabsorption of urate, thus increasing the urinary excretion of uric acid and decreasing serum urate levels. Probenecid may also reduce plasma binding of urate and inhibit renal secretion of uric acid at subtherapeutic concentrations.
Does ropivacaine increase metabolism?
The metabolism of Roflumilast can be increased when combined with Probenecid. The metabolism of Romidepsin can be increased when combined with Probenecid. Ropivacaine may decrease the excretion rate of Probenecid which could result in a higher serum level.
Does probenecid increase pimozide?
Probenecid may decrease the excretion rate of Picosulfuric acid which could result in a higher serum level. The metabolism of Pimavanserin can be increased when combined with Probenecid. The metabolism of Pimozide can be increased when combined with Probenecid.
Does Colesevelam affect probenecid?
Colesevelam can cause a decrease in the absorption of Probenecid resulting in a reduced serum concentration and potentially a decrease in efficacy. Colestipol. Colestipol can cause a decrease in the absorption of Probenecid resulting in a reduced serum concentration and potentially a decrease in efficacy.
Can mecamylamine be used in combination with probenecid?
The risk or severity of adverse effects can be increased when Probenecid is combined with Mecamylamine. The therapeutic efficacy of Mecasermin can be increased when used in combination with Probenecid. Probenecid may decrease the excretion rate of Meclofenamic acid which could result in a higher serum level.
How is probenecid administered?
Probenecid is administered orally. The drug distributes throughout the body tissues and is 75% to 95% plasma protein-bound, predominantly to albumin. Probenecid undergoes hepatic metabolism resulting in active metabolites. Both parent drug and active metabolites are eliminated renally, mainly by tubular secretion. Small amounts of unchanged probenecid are filtered at the glomeruli. The parent drug is nearly completely reclaimed via tubular reabsorption; minor amounts of metabolites undergo tubular reabsorption. The plasma half-life of probenecid is dose-dependent. Half-life ranges from 3 to 8 hours for a 500 mg dose and 6 to 12 hours for larger doses. Both unchanged drug and its metabolites are excreted in the urine; the unchanged drug is reabsorbed. [42116]
What is probenecid used for?
Probenecid is a uricosuric and renal tubular blocking agent. It inhibits the tubular reabsorption of urate, thus increasing the urinary excretion of uric acid and decreasing serum urate levels. Effective uricosuria reduces the miscible urate pool, retards urate deposition, and promotes resorption of urate deposits. Probenecid also competitively inhibits the active reabsorption of uric acid at the proximal convoluted tubule, facilitating urinary excretion of uric acid and decreasing plasma urate concentrations. The drug does not affect the glomerular filtration rate or reabsorption of glucose, arginine, urea, sodium, potassium, and chloride. The tubular reabsorption of phosphorus is inhibited in hypoparathyroid but not in euparathyroid individuals.
Can probenecid interfere with glucose?
Probenecid may cause laboratory test interference. A reducing substance may appear in the urine of patients receiving probenecid that may interfere with certain urine tests for glucose that are not specific. This disappears with the discontinuance of therapy. Suspected glycosuria should be confirmed by using a test specific for glucose. [42116] Also, falsely high readings for theophylline have been reported in an in vitro study, using the Schack and Waxler technique, when therapeutic concentrations of theophylline and probenecid were added to human plasma. [42116]
Can probenecid be used during lactation?
The label for probenecid does not note any particular cautions for the use of probenecid during lactation. Data are limited regarding use of probenecid during breast-feeding; however, one case report has documented probenecid excretion into human milk. In this report, a 30-year-old lactating mother was administered probenecid (500 mg PO four times daily) in combination with cephalexin for a breast infection. After 16 days of treatment, 12 milk samples were collected. The average probenecid milk concentration was 964 mcg/L, corresponding to a relative infant dose 0.7% of the maternal weight-adjusted dose. Symptoms of severe diarrhea, discomfort, and crying were observed in the infant, and these were determined by the authors to be possibly related to probenecid, but more probably associated with cephalexin. [32196]
Can probenecid be used for peptic ulcers?
Probenecid should be used with caution in patients with peptic ulcer disease, because of a possible increase in gastrointestinal adverse reactions. Gastric intolerance during probenecid therapy may be indicative of the dose being too high, and may be corrected by decreasing the dosage.
Is probenecid contraindicated for sulfonamide?
Probenecid is contraindicated in patients with known probenecid hypersensitivity. Rarely, severe allergic reactions and anaphylaxis have been reported with the use of probenecid. Most of these have been reported to occur within several hours after readministration following prior usage of the drug. The appearance of hypersensitivity reactions requires cessation of therapy with probenecid. It may be prudent to monitor patients with a known history of sulfonamide hypersensitivity for allergic-type reactions when initiating probenecid. Although it contains a sulfonamide side chain, probenecid and other nonantibiotic sulfonamides do not contain the N4 aromatic amine or the N1-substituent that are present in sulfonamide antibiotics and thought to be responsible for hypersensitivity-type adverse reactions. The risk of cross-sensitivity in patients taking a nonantibiotic sulfonamide that have a history of sulfonamide hypersensitivity is low and has been confirmed by recent observational studies. In general, patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any drug are predisposed for subsequent hypersensitivity reactions to other drugs. Because of this, patients with a history of sulfonamide hypersensitivity should be monitored for hypersensitivity reactions to other drugs, including probenecid; however, treatment with a nonantibiotic sulfonamide may not need to be withheld in patients with a sulfonamide allergy as long as patients are monitored appropriately, especially if alternative therapies are not available.
Can probenecid be used for gout?
Probenecid has been used in patients with some renal impairment, as some degree of renal impairment may be present in patients with gout. Use a reduced initial dosage in patients with renal impairment and titrate to response. A total daily dosage of 1,000 mg/day may be adequate.
What is the mechanism of action of uricosuric drugs?
Mechanism of Action: Uric acid is freely filtered by the glomerulus, secreted & normally 90% is reabsorbed by anionic active transport sites in the proximal tubule. Uricosuric drugs are organic acids that inhibit anionic transport sites of the renal tubule.
Does probenecid help arthritis?
Tophaceous deposits of urate can be reabsorbed, with relief of arthritis and re-mineralization of bone. Mechanism of Action of Probenecid. Probenecid inhibits both the Organic Anion Transporters (OAT) in the basolateral membrane of cells in the proximal tubule. This results in reduced clearance and increased plasma levels ...
Does Probenecid affect methotrexate?
Probenecid interferes with the renal secretion of penicillin, other beta-lactam antibiotics, and methotrexate, thereby decreasing their renal clearance, increasing their half-life, and elevating their plasma concentrations (if dosage adjustments are not made).
Does probenecid increase uric acid?
In addition, probenecid also inhibits Urate Transporters (URAT) in the apical membrane of the proximal tubule, which decreases uric acid reabsorption, resulting in an increased urinary excretion of uric acid, which is beneficial in patients with gout. Indications:
Is probenecid good for ocular syphilis?
Based on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, probenecid in combination with proc aine penicillin G is an effective and recommended alternative regimen in the treatment neurosyphilis, including ocular syphilis.
Does probenecid increase NAPQI?
Acetaminophen: Probenecid may increase the serum concentration of Aceta minophen . Probenecid may also limit the formation of at least one major non-toxic metabol ite, possibly increasing the potential for formation of the toxic NAPQI metabolite. Consider therapy modification
Does probenecid increase methotrexate?
Methotrexate: Probenecid may increase the serum concentration of methotrexate. Avoid concomitant use of probenecid and methotrexate if possible. If used together, consider lower methotrexate doses and monitor for methotrexate toxicity.
What is the purpose of probenecid?
Probenecid is a highly lipid-soluble benzoic acid derivative that was discovered in a search for acidic agents effective in blocking the renal excretion of penicillin at a time when penicillins were in short supply Beyer et al (1951). Probenecid has the ability to block the transport of organic acids (e.g. penicillins) across epithelial cells (e.g. renal proximal tubule cells) and its use when combined with penicillins resulted in elevated blood levels of the penicillin and a longer duration of antimicrobial action. The inhibition of renal secretion of numerous drugs (e.g. methotrexate) and drug metabolites (e.g. glucuronides of non-steroidal antiinflammatory agents) has also been reported. Inhibition of acidic agents from the spinal subarachnoid space to blood and from liver into bile has also been reported Insel (1996). Probenecid has also been reported to have effects on the formation of some Phase II metabolites which could prolong the pharmacological effect of the drug.
What are the interactions between penicillin and probenecid?
Perhaps the most widely appreciated drug interaction is that of penicillin and probenecid, first noted over five decades ago, in which coadministration of probenecid resulted in elevated penicillin serum levels, representing a beneficia l drug–drug interaction (Burnell and Kirby 1951 ). Studies have shown that the high renal clearance of penicillins can be decreased by inhibition of OAT-mediated transport on the basolateral membrane of proximal tubular cells with coadministration of probenecid ( Table 8) ( Jariyawat et al. 1999 ). Similarly, competitive interactions can also be beneficial when they lead to decreased proximal tubular uptake of nephrotoxins, which is the presumptive explanation for the nephroprotective actions of probenecid and NSAIDs against toxicity from adefovir and cidofovir, cephaloridine, ochratoxin A, and mercury ( Aslamkhan et al. 2003; Groves et al. 1998; Lacy et al. 1998; Mulato et al. 2000; Tune 1997 ). In addition, effects of probenecid coadministration have now been extended to other anionic drugs such as angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and HIV antiviral drugs ( Ayrton and Morgan 2001 ).
Does Probenecid inhibit organic ion transport?
Probenecid has biological effects unrelated to inhibition of organic ion transport, and acivicin pretreatment can fail to protect against haloalkene (e.g., hexachloro-1,3-butadiene) nephrotoxicity even when it is known that glutathione and/or cysteine conjugates of the parent haloalkene are nephrotoxicants.
What is probenecid used for?
Probenecid is a uricosuric and renal tubular blocking agent and is used in combination with colchicine to treat chronic gouty arthritis when complicated by frequent, recurrent acute attacks of gout. It inhibits the reabsorption of urate at the proximal convoluted tubule, thus increasing the urinary excretion of uric acid and decreasing serum urate levels. Effective uricosuria reduces the miscible urate pool, retards urate deposition, and promotes resorption of urate deposits. At the proximal and distal tubles, probenecid competitively inhibits the secretion of many weak organic acids including penicillins, most cephalosporins, and some other β-lactam antibiotics. This results in an increase in the plasma concentrations of acidic drugs eliminated principally by renal secretion, but only a slight increase if the drug is eliminated mainly by filtration. Thus, the drug can be used for therapeutic advantages to increase concentrations of certain β-lactam antibiotics in the treatment of gonorrhea, neurosyphilis, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
What is the effect of probenecid on kidneys?
Probenecid competitively inhibits the active reabsorption of urate at the proximal tubule in the kidney thereby increasing urinary excretion of uric acid and lowering serum urate concentrations.
What is adjuvant in medicine?
Adjuvants, Pharmaceutic. Agents that aid or increase the action of the principle drug (DRUG SYNERGISM) or that affect the absorption, mechanism of action, metabolism, or excretion of the primary drug (PHARMACOKINETICS) in such a way as to enhance its effects . (See all compounds classified as Adjuvants, Pharmaceutic .)
Is probenecid a uricosuric?
Probenecid is a uricosuric agent used for the treatment of gout usually in combination with other agents. Probenecid has been associated with minor serum aminotransferase elevations and very rarely with hypersensitivity reactions which, even more rarely, can be accompanied by acute liver injury.
Does probenecid increase uric acid?
Probenecid inhibits the tubular reabsorption of urate, thus increasing the urinary excretion of uric acid and decreasing serum urate levels. Probenecid may also reduce plasma binding of urate and inhibit renal secretion of uric acid at subtherapeutic concentrations. The mechanism by which probenecid inhibits renal tubular transport is not known, but the drug may inhibit transport enzymes that require a source of high energy phosphate bonds and/or nonspecifically interfere with substrate access to protein receptor sites on the kidney tubules.
Probenecid Description
Probenecid - Clinical Pharmacology
- Probenecid is a uricosuric and renal tubular blocking agent. It inhibits the tubular reabsorption of urate, thus increasing the urinary excretion of uric acid and decreasing serum urate levels. Effective uricosuria reduces the miscible urate pool, retards urate deposition, and promotes resorption of urate deposits. Probenecid inhibits the tubular s...
Indications and Usage For Probenecid
- Probenecid tablets are indicated for the treatment of the hyperuricemia associated with gout and gouty arthritis. As an adjuvant to therapy with penicillin or with ampicillin, methicillin, oxacillin, cloxacillin, or nafcillin, for elevation and prolongation of plasma levels by whatever route the antibiotic is given.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to Probenecid. Children under 2 years of age. Not recommended in persons with known blood dyscrasias or uric acid kidney stones. Therapy with Probenecid should not be started until an acute gouty attack has subsided.
Warnings
- Exacerbation of gout following therapy with Probenecid may occur; in such cases colchicine or other appropriate therapy is advisable. Probenecid increases plasma concentrations of methotrexate in both animals and humans. In animal studies, increased methotrexate toxicity has been reported. If Probenecid is given with methotrexate, the dosage of methotrexate should be r…
Precautions
- General
Hematuria, renal colic, costovertebral pain, and formation of uric acid stones associated with the use of Probenecid in gouty patients may be prevented by alkalization of the urine and a liberal fluid intake (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). In these cases when alkali is administered, t… - Drug Interactions
When Probenecid is used to elevate plasma concentrations of penicillin or other beta-lactams, or when such drugs are given to patients taking Probenecid therapeutically, high plasma concentrations of the other drug may increase the incidence of adverse reactions associated wit…
Adverse Reactions
- The following adverse reactions have been observed and within each category are listed in order of decreasing severity. Central Nervous System:headache, dizziness. Metabolic:precipitation of acute gouty arthritis. Gastrointestinal:hepatic necrosis, vomiting, nausea, anorexia, sore gums. Genitourinary:nephrotic syndrome, uric acid stones with or without hematuria, renal colic, costov…
Probenecid Dosage and Administration
- Gout
Therapy with Probenecid should not be started until an acute gouty attack has subsided. However, if an acute attack is precipitated duringtherapy, Probenecid may be continued without changing the dosage, and full therapeutic dosage of colchicine, or other appropriate therapy, should be giv… - Probenecid and Penicillin Therapy
Adults:The recommended dosage is 2000 mg (4 tablets of Probenecid) daily in divided doses. This dosage should be reduced in older patients in whom renal impairment may be present. Children:2-14 years of age: Initial dose: 25 mg/kg body weight (or 0.7 g/square meter body surfa…
How Is Probenecid Supplied
- Probenecid Tablets, USP are available containing 500 mg of Probenecid, USP. The tablets are capsule shaped, film-coated yellow, debossed LCI on one side and 1367 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0527-1367-01 bottles of 100 tablets NDC 0527-1367-10 bottles of 1000 tablets STORE AT 20°-25°C (68°-77°F)[See USP Controlled Room Temperature] PROTECT …
Principal Display Panel
- NDC 71626-999-08 Medstone Pharma LLC Probenecid TABLETS, USP 500 mg Rx Only 8 TABLETS Medical Disclaimer
Overview
Probenecid, also sold under the brand name Probalan, is a medication that increases uric acid excretion in the urine. It is primarily used in treating gout and hyperuricemia.
Probenecid was developed as an alternative to caronamide to competitively inhibit renal excretion of some drugs, thereby increasing their plasma concentr…
Medical uses
Probenecid is primarily used to treat gout and hyperuricemia.
Probenecid is sometimes used to increase the concentration of some antibiotics and to protect the kidneys when given with cidofovir. Specifically, a small amount of evidence supports the use of intravenous cefazolin once rather than three times a day when it is combined with probenecid.
It has also found use as a masking agent, potentially helping athletes using performance-enhanc…
Adverse effects
Mild symptoms such as nausea, loss of appetite, dizziness, vomiting, headache, sore gums, or frequent urination are common with this medication. Life-threatening side effects such as thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, leukemia and encephalopathy are extremely rare. Theoretically probenecid can increase the risk of uric acid kidney stones.
Drug interactions
Some of the important clinical interactions of probenecid include those with captopril, indomethacin, ketoprofen, ketorolac, naproxen, cephalosporins, quinolones, penicillins, methotrexate, zidovudine, ganciclovir, lorazepam, and acyclovir. In all these interactions, the excretion of these drugs is reduced due to probenecid, which in turn can lead to increased concentrations of these.
Pharmacodynamics
In gout, probenecid competitively inhibits the reabsorption of uric acid through the organic anion transporter (OAT) at the Proximal tubules. This leads to preferential reabsorption of probenecid back into plasma and excretion of uric acid in urine. Thus, reducing blood uric acid levels and reducing its deposition in various tissues.
Probenecid also inhibits Pannexin 1. Pannexin 1 is involved in the activation of inflammasomes a…
Pharmacokinetics
In the kidneys, probenecid is filtered at the glomerulus, secreted in the proximal tubule and reabsorbed in the distal tubule.
History
During World War II, probenecid was used to extend limited supplies of penicillin; this use exploited probenecid's interference with drug elimination (via urinary excretion) in the kidneys and allowed lower doses of penicillin to be used.
Probenecid was added to the International Olympic Committee's list of banned substances in January 1988.
See also
• Probenecid and colchicine