What are the main causes of corrosion?
Causes Of Corrosion • Some of the main and popular causes of corrosion are as follows: • Too much humidity or condensation of water vapour on metal surfaces are the primary causes of corrosion. • Corrosive gases such as chlorine, hydrogen oxides, ammonia, sulfur oxides, amongst others can result in corrosion of parts of electronic equipment, etc. Corrosion can also occur due to hydrogen ...
Is corrosion bad for the environment?
The Dangers of Corrosion When materials interact with the environment around them, deterioration caused by corrosion can occur. In commercial applications, this usually pertains to damage to steel, iron, or metal from road, rail, and bridge maintenance, warehouse cylinders and tanks, utilities, and pipework.
What caused the corrosion?
Corrosion Causes Uncontrolled humidity and corrosive gases are the primary causes of corrosion in industrial environments. Condensation of water vapor on metal surfaces and corrosive gases such as ammonia, chlorine, hydrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, etc. can result in corrosion of electronic equipment, rusty corners, and corroded parts.
Are corrosion and oxidation the same thing?
While oxidation is often called corrosion, they are not exactly the same thing. Oxidation simply means combining one material with oxygen to make a new compound. The process can be fast, like burning, or slow, like rusting, depending upon the materials and conditions.Obviously, oxidation can be a very useful process.

What is corrosion explain theories and mechanism?
What Does Corrosion Theory Mean? Corrosion refers to the gradual destruction of objects, typically metals, caused by environment and chemical reaction. It accurately refers to electrochemical metal oxidation with oxygen as oxidant. One of the best examples of this phenomenon is iron oxide formation, or rusting.
How many types of corrosion mechanisms are there?
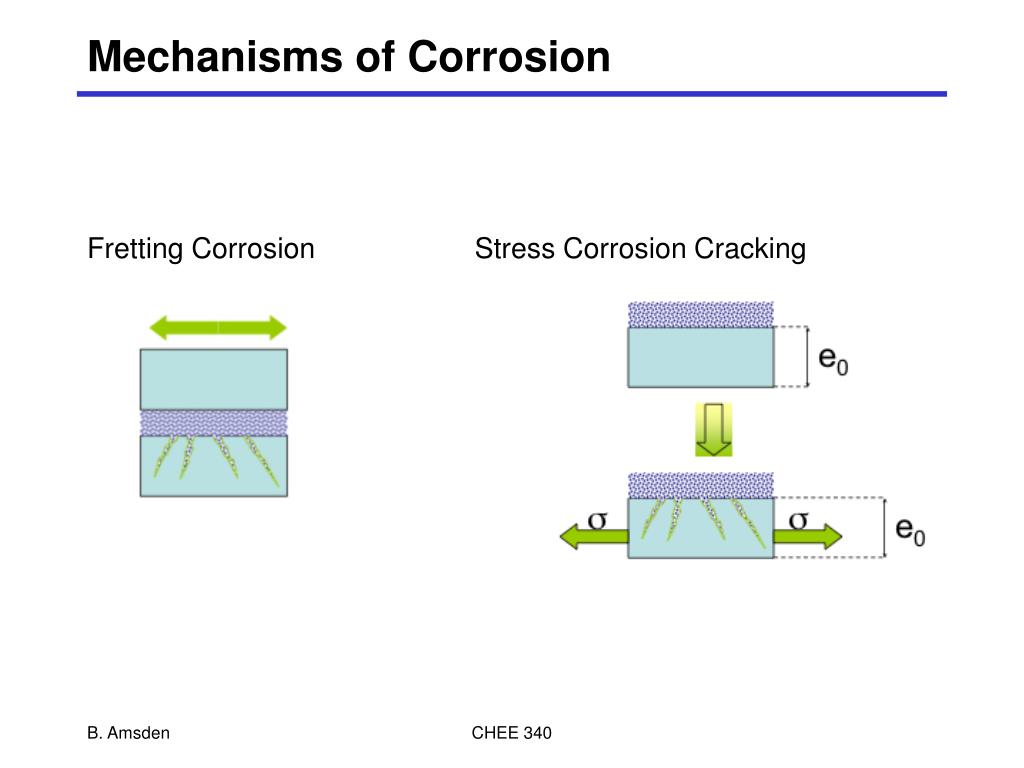
There are many different types of corrosion that are visible to the naked eye: uniform corrosion, pitting, crevice corrosion, filiform corrosion, galvanic corrosion, environmental cracking, and fretting corrosion, to name a few.
What is corrosion explain mechanism of corrosion and give methods to stop the corrosion?
By connecting metal to a more electropositive metal As long as the more electropositive metal is present, the given metal will not get corroded. For instance, you can protect iron from corrosion by connecting it to a block/plate of zinc or magnesium. This method of protection is known as cathodic protection.
What are the 3 main causes of corrosion?
Causes of Corrosion Metal corrodes when it reacts with another substance such as oxygen, hydrogen, an electrical current or even dirt and bacteria.
What is mechanical corrosion?
Mechanically assisted corrosion (MAC) encompasses the most dangerous forms of corrosion, often leading to catastrophic failures. They occur due to a combination of mechanical factors (e.g. applied and/or residual stresses, cyclic loading, wear) and electrochemical corrosion.
What are the four 4 main types of corrosion?
In certain environments, metals may be exposed to various types of local corrosion including pitting, crevice, intergranular, stress, and galvanic corrosion.
What are the 3 types of corrosion?
CORROSION TYPES And PreventionUniform Corrosion. Uniform corrosion is considered an even attack across the surface of a material and is the most common type of corrosion. ... Pitting Corrosion. ... Crevice Corrosion. ... Intergranular Corrosion. ... Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) ... Galvanic Corrosion. ... Conclusion.
What is corrosion explain the mechanism of rusting of iron?
The overall rusting involves the following steps: Oxidation occurs at the anodes of each electrochemical cell. Therefore, at each anode neutral iron atoms are oxidized to ferrous ions. 1- At anode: Thus, the metal atoms in the lattice pass into the solution as ions, leaving electrons on the metal itself.
What is corrosion explain its effect and give its example?
Corrosion Definition: Corrosion (from the Latin word corrodes, meaning "to gnaw") is the irreversible damage or destruction of living tissue or material due to a chemical or electrochemical reaction. Example: A prime example of corrosion is rusting of iron or steel. Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph.
What is corrosion and its causes?
Corrosion is a phenomenon of oxidation of metal in the presence of oxygen when it is exposed to external environmental factors which include moisture, acid rain, etc., and chemicals like acids, bases, etc. For example - Rusting of Iron, tarnishing of Silver wares, green coating on Copper vessels.
What causes corrosion and its effect?
Corrosion is the process of decay on a material caused by a chemical reaction with its environment. Corrosion of metal occurs when an exposed surface comes in contact with a gas or liquid, and the process is accelerated by exposure to warm temperature, acids, and salts.
What are the factors of corrosion?
Introduction. There are several factors influencing the rate of corrosion including diffusion, temperature, conductivity, type of ions, pH value and electrochemical potential.
What are the 6 main types of corrosion?
6 Types of Corrosion That Take Some Examination To Accurately...Erosion Corrosion. Erosion corrosion occurs when a corrosive fluid runs past a metal surface. ... Intergranular Corrosion. ... Fretting Corrosion. ... Cavitation Corrosion. ... De-Alloying (Selective Leaching) ... Exfoliation Corrosion.
What are the 3 types of corrosion?
CORROSION TYPES And PreventionUniform Corrosion. Uniform corrosion is considered an even attack across the surface of a material and is the most common type of corrosion. ... Pitting Corrosion. ... Crevice Corrosion. ... Intergranular Corrosion. ... Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) ... Galvanic Corrosion. ... Conclusion.
What are the 2 types of corrosion?
Broadly speaking, corrosion can be separated into two distinct types: generalized and localized.
What are the forms of corrosion?
Forms of corrosionUniform corrosion. Uniform or general corrosion are defined as a type of corrosion attack that is more or less distributed over the entire exposed surface of a metal. ... Galvanic corrosion. ... Concentration cells. ... Crevice corrosion. ... Pitting corrosion. ... Selective corrosion. ... Erosion corrosion. ... Cavitation corrosion.More items...•
What is the science of corrosion?from corrosion-doctors.org
Modern corrosion science has its roots in electrochemistry and metallurgy. Electrochemistry contributes an understanding of the mechanism that is basic to the corrosion of all metallic objects. Metallurgy provides a knowledge of the characteristics of metals and their alloys as well as the methods of combining the various metals and working them into the desired shapes.
How does corrosion prevent corrosion?from sciencedirect.com
Corrosion products are formed close to the metal surface, unlike the case in aqueous corrosion, and they may prevent further corrosion by acting as a physical barrier between the metal surface and environment, particularly if they are insoluble as in the case of copper or lead. The following is a simplified mechanism of aqueous corrosion ...
What is the mechanism of corrosion in AlMgSi?from sciencedirect.com
The primary corrosion mechanism in AlMgSi alloys, when exposed to corrosive conditions, is intergranular corrosion. Intergranular corrosion is the selective dissolution of the grain boundary zone, while the bulk grain is not attacked. Intergranular corrosion is caused by the action of micro-galvanic cells at the grain boundaries. Grain boundaries are preferred sites for segregation and precipitation, which makes them physically and chemically different from the matrix. Furthermore, a zone adjacent to the grain boundary is depleted of the solute elements. Consequently, a ‘galvanic cell’ is formed. If, for example, the grain boundary precipitates are electro-chemically nobler than the aluminium matrix, the depleted zone becomes electrochemically active, i.e. is preferentially dissolved. But also the opposite case is possible (Svenningsen, 2003 ). The susceptibility to intergranular corrosion is influenced by:
How is anode destroyed?from corrosion-doctors.org
The anode is destroyed by the corrosion reaction, leaving the cathode intact. This technique is still used extensively to protect underground gas and water pipelines. Concentration cellsmay also be formed where there are differences in metal ion concentration.
What is the process of pitting?from sciencedirect.com
The process of pitting once initiated become autocatalytic . The electron released in oxidation, Fe+3Cl − → FeCl 3 + 3 e, flows through steel to the cathode, FeCl 3 + 3OH − → Fe (OH) 3 +3Cl −, which results in an increase in the concentration of chloride ion and reduction of pH. The above process would only proceed if the chloride concentration is higher than the hydroxyl ion (OH -) concentration. If OH - ion concentration is higher, the ferrous oxide film would convert to ferric oxide (γ-FeOOH) and passivity would be preserved. A higher oxygen concentration would also promote the conversion of ferrous hydroxide to ferric oxide and the passivation of the reinforcement. Carbon dioxide and chloride ions are basically the two ingredients responsible for corrosion of reinforcement. The mechanism of corrosion of reinforcement by these two components is shown in Fig. 12.13. Other factors, such as the moisture content, temperature of oxygen, potential difference, concrete cover, act by either reducing or increasing the ease of penetration of the corrosion inducing species in concrete. The key factor is maintaining of alkalinity, as under alkaline conditions corrosion cannot take place because of the passive state of the reinforcement in this condition.
Why are there anodic and cathodic sites on metal?from corrosion-doctors.org
The existence of anodic and cathodic sites on the surface of a piece of metal implies that differences in electrical potential are found on the surface. These potential differences have a number of causes. One important mechanism is oxygen concentration cell corrosion, in which the oxygen concentration in the electrolyte varies from place to place. An underground pipe that passes from clay to gravel will have a high oxygen concentration in the gravel region and almost no oxygen in the impermeable clay. The part of the pipe in contact with the clay becomes anodic and suffers damage.
What is the corroding area of a battery?from corrosion-doctors.org
That part of a metal component which becomes the corroding area is called the "anode"; that which acts as the other plate of the battery is called the "cathode" and does not corrode, but is an essential part of the system. In the corrosion systems commonly involved in buildings there may often be only a single metal involved, with water containing some salts in solution as the electrolyte. Corrosion may even take place with pure water, provided that oxygen is present. In such cases oxygen combines with the hydrogen generated at the cathode, removing it and permitting the reaction to go on.
Passivation
Some metals exhibit a passivity to corrosion. Passivity is the characteristic of a metal exhibited when that metal does not become active in the corrosion reaction.
Forms of Corrosion
The areas where the anodic and cathodic reactions occur can vary greatly during metal corrosion. Corrosion can come in different forms and grow at different rates. This results in various forms of corrosion, such as a uniform attack, pitting, and crevice corrosion.
Protection from Corrosion
As was written, the problem of metallic corrosion is significant. In economic terms, it has been estimated that approximately 5% of an industrialized nation’s income is spent on corrosion prevention and the maintenance or replacement of products lost or contaminated due to corrosion reactions.
Corrosion-resistant Alloys
Corrosion-resistant alloys, as their name indicates, are alloys with enhanced corrosion resistance. Some ferrous and many non-ferrous metals and alloys are widely used in corrosive environments. In all cases, it strongly depends on certain environments and other conditions.
CRUDs in Power Plants
In nuclear engineering, “ CRUD ” is a technical term for corrosion and wear products (rust particles, etc.) in the coolant that becomes radioactive when exposed to radiation. The term is an acronym for Chalk River Unidentified Deposits, originally found on the cladding, or outer coating, of fuel rods in the Canadian reactor for which it was named.
How does corrosion control work in batteries?
Corrosion control processes stop the flow of electrons or disrupt the chemical reaction at the cathode or anode. Rust Requirements.
What is the function of corrosion prevention agents?
Without protection, the iron (Fe) in the steel interacts with oxygen (O) in the atmosphere, causing the steel to corrode. Whether the corrosion takes the form of red rust (ferric oxide, Fe 2 O 3) or black stain (ferrous oxide, Fe 3 O 4 ), the process is similar: Oxidation ...
What causes rust on metalworking fluid?
Figure 1: Rust is caused by corrosion cells. Every corrosion cell has an anode and a cathode (positive and negative pole).
How to investigate rust?
When you first investigate a rust issue, it is important to learn the metal surface’s exposure history; you need to trace back through all of the processes to determine where the corrosion began. The investigation should involve every process and fluid that contacts the parts. Only by tracing the entire process do you have a chance at determining the application that has the greatest impact on the corrosion problem. In addition, the fluids involved in the process should be evaluated for fitness for use relative to fresh fluid.
Why is corrosion prevention important?
Either way, corrosion prevention agents provide a necessary function. Without protection, the iron (Fe) in the steel interacts with oxygen (O) in the atmosphere, causing the steel to corrode.
What is the oxidation of iron metal from Fe to Fe +2?
Ferrous metal corrosion is the oxidation of iron metal from Fe to Fe +2, further to Fe +3 , caused by electrons flowing from an anode (a point of positive polarity) to a cathode (a point of negative polarity). A common battery uses a similar process to carry electrical current from one terminal to the other. Corrosion control processes stop the flow of electrons or disrupt the chemical reaction at the cathode or anode.
What are the characteristics of a corrosion preventive?
Seven tests measure the fluid’s inherent characteristics—acidity, moisture, dirt, percent solids, calcium, viscosity, and specific gravity. An eighth evaluation, the copper corrosion test, is a subjective measure of how the fluid stains copper.
What is Galvanic Corrosion?
When two dissimilar metals are in direct contact in a conducting liquid, experience shows that one of the two may corrode. This is called galvanic corrosion.
What are the conditions for galvanic corrosion?
There must be three conditions for galvanic corrosion to occur: electrochemically dissimilar metals must be present. They must be in electrical contact with these metals, and. It is necessary to expose the metals to an electrolyte.
What is the process of a metal being dissolved into an electrolyte called?
This leads to an electrochemical reaction as a result of which, the anode is dissolved into the electrolyte. This electrochemical process is called galvanic corrosion of metals. Galvanic corrosion can only occur when there exists an electric conducting path connecting the metals and when an electrolyte which can offer a channel for the migration ...
Why is galvanic corrosion important?
Galvanic Corrosion can be used beneficially to protect a cathodic metal from corrosion. A good example of this would be the usage of zinc in batteries to promote the corrosion of zinc to create a potential difference.
What is the cause of the rusting of the statue of liberty?
The Statue of Liberty in New York, USA was subject to galvanic corrosion. The corrosion had occurred between the support structure made up of wrought iron and the copper exterior of the statue. This led to the rusting of the iron support structure. Another example of galvanic corrosion occurred in the combat ship ‘USS Independence’.
How to protect aluminum from galvanic corrosion?
How do you protect aluminum from galvanic corrosion? For aluminium, galvanic corrosion can be easily prevented with a single coat of chrome phosphate pretreatment supplemented by primer and high-performance coating. A single field-applied coat of heavy-bodied bituminous paint may instead be used.
When two dissimilar metals are dissolved in a conductive solution and electrically connected, what happens?
When two dissimilar metals are dissolved in a conductive solution and electrically connected, galvanic corrosion happens. One metal is covered (the cathode), while the other (the anode) is corroded. Compared with the rate when the metal is uncoupled, the attack rate on the anode is accelerated.
How can electrochemical corrosion be stopped?
Electrochemical corrosion can be stopped by eliminating any one of the 4 components
What is the deterioration of a substance or its properties as a result of an undesirable reaction with the?
Corrosion is the deterioration of a substance or its properties as a result of an undesirable reaction with the environment.
What is electrochemically altering?
Electrochemically alter the surface condition of the metal to move the anodic reactions elsewhere. Coatings (exterior) and Linings (interior)
Is corrosion control a project or a process?
For both, Corrosion Control is a Process, not a Project.
Does wastewater construction need cathodic protection?
But Wastewater construction does not typically account for the eventual need for cathodic protection
Can cathodic protection be used with out coating?
Cathodic protection can be applied with out coatings. Coatings should not be used with out cathodic protection. Cathodic protection effectively protects defects in the coating.
What are the elements that cause corrosion?
Corrosion is an electrochemical process leads to surface wastage of metals. In order for corrosion to occur, four basic elements are required: 1. Anode – site where corrosion occurs and from which current (electrons) flows. 2. Cathode – site where no corrosion occurs and to which current flows. 3.
How is ferrous chloride formed?
Ferrous chloride is formed. It is a soluble complex which dissolves in the surrounding solution releasing chloride ions to causing more decomposition. After breakdown of passivity, a pit is formed and iron dissolutes in the pore solution releasing electrons (anodic reaction).
Which ions are absorbed by oxygen and water?
The positively charged ferrous ions Fe 2+ at the anode pass into solution while the negatively charged free electrons 2e – pass through the pore solution to the cathode (passive areas), where they are absorbed by oxygen and water to form hydroxyl ions (cathodic reaction).
Does Fe2O3 cause corrosion?
This layer is dense and impermeable ferric oxide (Fe2O3) film and, if fully established and maintained, it prevents further corrosion of the steel. However, chlorides can cause corrosion of steel even if high alkalinity is maintained >12.
What type of corrosion begins at the surface of the metal but can spread downwards?
This leads to a type of galvanic corrosion which begins at the surface of the metal but can spread downwards and eventually lead to the structural failure of the metal.
What happens to the metal in pitting corrosion?
In the mechanism of pitting corrosion, the oxidation of the metal occurs, resulting in an acidity which is localized. The generous separation of the cathodic half-reaction and the anodic half-reaction helps maintain this localized acidity.
What is Pitting Corrosion?
Pitting corrosion is a type of corrosion that attacks a local area of the metal and eventually leads to the formation of holes in the metal. Pitting corrosion can lead to stress corrosion cracking, an example for which is the collapse of the Silver Bridge in West Virginia, the USA in 1967.
What can lead to pits on metal?
Pitting corrosion can lead to the formation of pits on the metal. The shape of these pits can vary from shallow and wide to deep and narrow. An illustration depicting the different shapes that a cavity formed on the metal due to pitting corrosion can take.
What happens when metal cations are produced in a pit?
The local production of metal cations in the pit creates an excessive positive charge that in turn attracts the chlorine anions of the electrolyte. The resulting metal chloride molecules now react with the water in the environment to give the metal hydroxide and hydrochloric acid which further speeds up the rate of corrosion.
Which chemical species causes pitting corrosion?
Ans: The chemical species which causes pitting corrosion is chloride.
How does acidity affect the formation of a potential gradient?
The acidity leads to the electromigration of anions towards the pit which is formed. A potential gradient is also formed by localized acidity. The pits that are formed on the surface of the metal are often filled with the side products formed in the corrosion process.

Defining Corrosion
Caveats For Corrosion Protection
- Water-soluble machining and grinding fluids provide temporary corrosion protection. However, fabricators can’t rely on these to prevent corrosion because the duration of protection needed varies from fabricator to fabricator; some need just a few hours of protection until parts go to the next process, while others store the parts for weeks. The storage and coolant conditions are crit…
Measuring A Corrosion Preventive’S Effectiveness
- A number of short-term and long-term tests can measure corrosion protection. All of these tests are designed to mimic real-life applications under accelerated conditions. Be aware that the interpretation of the test results can be just as important as setting up and controlling the conditions of the tests. Metal Removal Fluids. The chip test is used to assess the interaction of t…
Troubleshooting
- When you first investigate a rust issue, it is important to learn the metal surface’s exposure history; you need to trace back through all of the processes to determine where the corrosion began. The investigation should involve every process and fluid that contacts the parts. Only by tracing the entire process do you have a chance at determining the application that has the grea…
Fluid Analysis
- Analyzing the fluid provides an indication of the corrosion preventive’s effectiveness. Seven tests measure the fluid’s inherent characteristics—acidity, moisture, dirt, percent solids, calcium, viscosity, and specific gravity. An eighth evaluation, the copper corrosion test, is a subjective measure of how the fluid stains copper. 1. Acidity. Excessive acid content, which may be cause…
Corrosion — at What Cost?
- According to the “Corrosion Costs and Preventive Strategies in the United States,” a 2002 study commissioned by the Federal Highway Administration, undertaken by CC Technologies Laboratories Inc. and sponsored by NACE International, the direct costs of metal corrosion in the U.S. total $276 billion annually. To put this into perspective, it amounted to more than 3 percent …