These are:
- st degree – The tonic
- nd degree – The supertonic
- rd degree – The mediant
- th degree – The subdominant
- th degree – The dominant
- th degree – The submediant
- th degree – The leading note (or leading tone)
Where is the mediant on the scale?
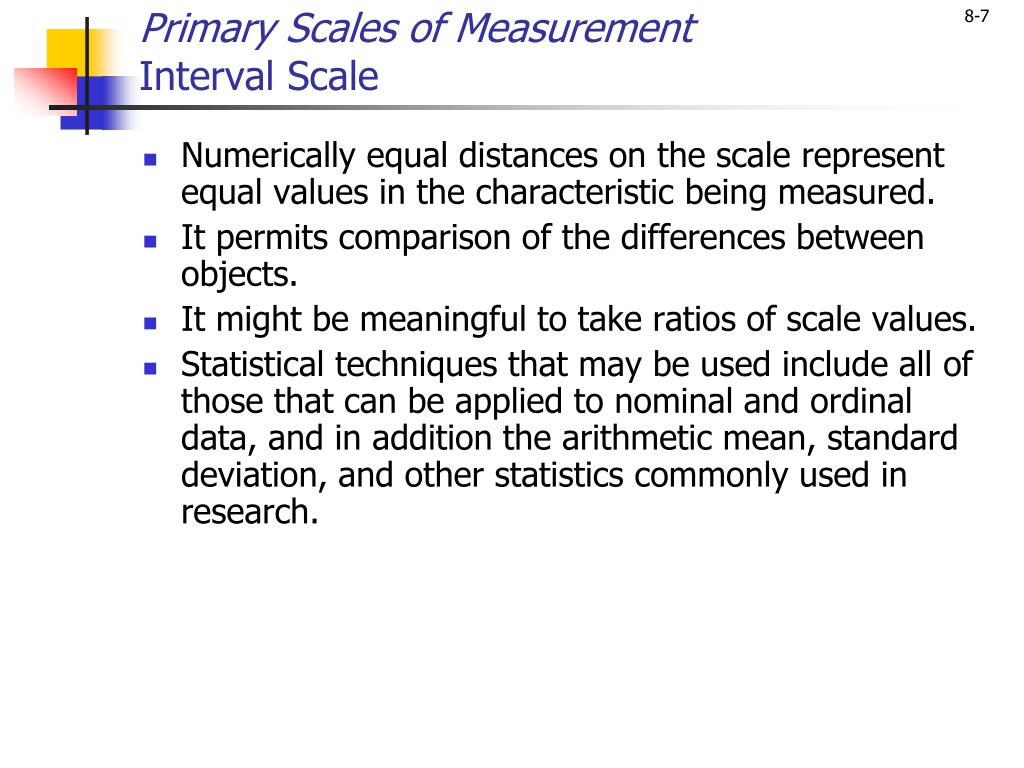
In music, the mediant (Latin: to be in the middle) is the third scale degree ( ) of a diatonic scale, being the note halfway between the tonic and the dominant. In the movable do solfège system, the mediant note is sung as mi.
What is a mediant in music?
The term mediant refers to the third scale-step above and below your point of reference. If we started on the tonic, then scale steps three and six (that's three scale steps down from the tonic) become your mediants. Usually, a major triad has two …
What is the Roman numeral for mediant?
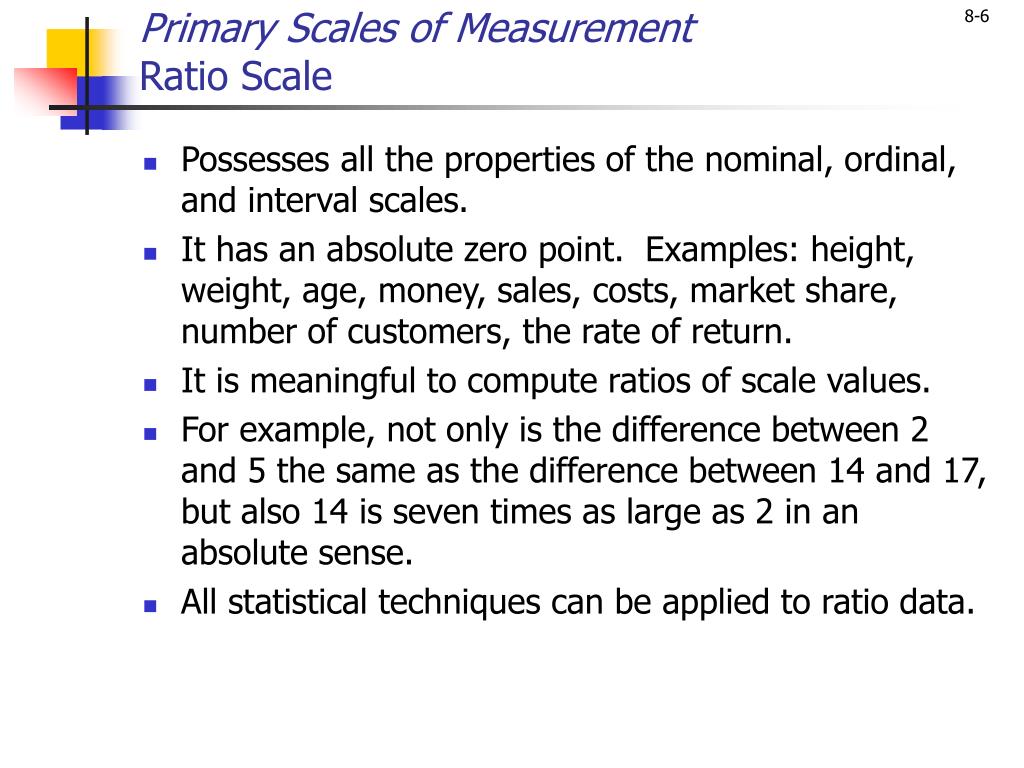
May 02, 2022 · When building a triad chord we use three notes: the 1st, 3rd and 5th degrees of a scale. The 3rd (the mediant) is in the middle of the 1st and 5th notes which is why it’s called the mediant. Just remember the mediant is in the middle of a triad (between the tonic – 1st degree, and the dominant – 5th degree). 4th – The subdominant
What is the difference between a mediant and a submediant?
8 rows · 6. A major scale degrees. This step shows the A major scale degrees - tonic, supertonic, ...
What is the scale number of mediant?
| Scale Degree | Note Number in Scale | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Mediant | 3 | Half way between tonic and dominant |
| Subdominant | 4 | Fifth below tonic |
| Dominant | 5 | Second most important note after tonic |
| Submediant | 6 | Half way between tonic and subdominant |
What is a mediant key?
What major scale is mediant?
| Note no. | Degree name |
|---|---|
| 1 | A is the tonic of the A major scale |
| 2 | B is the supertonic of the A major scale |
| 3 | C# is the mediant of the A major scale |
| 4 | D is the subdominant of the A major scale |
What scale degree is submediant?
What is the meaning of mediant?
(mathematics) A rational number whose numerator is the sum of the numerators of two other given rational numbers and whose denominator is the sum of the denominators of those same two other rational numbers.
What is a mediant in math?
What is the mediant in C minor?
...
1. C natural minor scale.
| Note no. | Degree name |
|---|---|
| 3 | Eb is the mediant of the C natural minor scale |
| 4 | F is the subdominant of the C natural minor scale |
Is the mediant major or minor?
Which is a mediant chord?
What is tonic supertonic mediant?
What is the mediant scale degree of B flat major?
C is the supertonic of the B-flat major scale. D is the mediant of the scale.
What scale degree is supertonic?
What is a mediant?
Mediants are an excellent tool to enhance diatonic chord progressions, which are based on triads. As we are going to find out in this article, mediants can enforce tonal centers but also connect flawlessly to the Circle of Fifths. In other words, they can even help you move away from your current tonal center.
What is mediant in music?
Let's find out why mediants are such a powerful tool for composition and music creation and how you, the composer, can benefit from that knowledge! The term mediant refers to the third scale-step above and below your point of reference. If we started on the tonic, then scale steps three and six (that's three scale steps down from the tonic) ...
What chords can you create by changing scale tones?
To keep things simple for the moment, we want to limit the mediant structures to plain major or minor triads. That means that we want to avoid augmented or diminished triads for the moment. So, if we started in C minor, the most apparent chords that we can create by changing the exact scale tones that we did in major are Ab major and Eb major.
What does it mean when a triad is a perfect diatonic fifth apart?
Obviously, those triads are connected to the tonal center of C major, but they are a perfect Diatonic fifth apart from each other, which means that they replicate themselves back to the Circle of Fifths!
How many minor triads are there in a major triad?
If we started on the tonic, then scale steps three and six (that's three scale steps down from the tonic) become your mediants. Usually, a major triad has two minor triads as mediants and the other way around. Mediants are easy-to-use yet powerful building blocks in composition as they can reinforce a tonal center or even modulate to new ones.
How to do a major triad?
1) Let's start with a major triad, which is a 4+3. 2) The next step is to extend the formula in both directions by alternating between the two building blocks. 3) Locate the two neighboring triads to your root tone; those are your mediants. And yes, it works the same way if we started on a minor triad instead.
Where are the mediants located?
Mediants are located a Diatonic third above and below your starting triad. Major triads are surrounded by two minor triadal mediants and minor ones are surrounded by two major triadal mediants. Mediants can reinforce the current tonal center or even modulate elegantly to a new one.
What is the mediant in a minor scale?
In natural minor scales, the mediant is a major triad and is symbolized with the Roman numeral III. In harmonic minor scales and ascending melodic minor scales, the seventh scale degree is raised by a half step from the subtonic ( ♭) to the leading tone ( ♮ ), creating an augmented triad that is symbolized with the Roman numeral ( ♭ )III + .
What is the mediant note in music?
In music, the mediant ( Latin: to be in the middle) is the third scale degree () of a diatonic scale, being the note halfway between the tonic and the dominant. In the movable do solfège system, the mediant note is sung as mi.
What is the dominant parallel of the tonic scale?
On the other hand, in German theory derived from Hugo Riemann the mediant in major is considered the dominant parallel, Dp, and in minor the tonic parallel, tP.
Is the mediant note a minor third?
While the fifth scale degree is almost always a perfect fifth, the mediant can be a major or minor third . Schenkerian analysts consider this scale degree as expansion of the tonic since they have two common tones. On the other hand, in German theory derived from Hugo Riemann ...
Where is the 3rd mediant?
The 3rd (the mediant) is in the middle of the 1st and 5th notes which is why it’s called the mediant.
What is the degree of a scale?
As we covered in our beginner’s guide to musical scales post here, a scale is a group of notes arranged in ascending or descending order of pitch. Each note in a scale is called the degree of the scale depending on how many pitches away it is from the first note of the scale.
Why is the middle note called the middle note?
You might wonder why it’s called the middle note as it’s not even close to being the middle of a scale but it get its name from when we form a triad chord. When building a triad chord we use three notes: the 1st, 3rd and 5th degrees of a scale.
What is the 7th degree of the natural minor scale?
The natural minor scale is ever so slightly different though as the 7th degree of the scale is an interval of a tone (whole step) below the tonic instead of a semitone (half step) like the leading note.
What is the most important note in a scale?
The most important note in a scale is the 1st degree and it’s called the tonic.
What degree is the dominant note?
We’re going to jump a few notes ahead now to the next most important note in a scale which is the 5th degree called the dominant.
What is the 6th degree of the scale called?
The 6th degree of the scale is called the submediant.
What is the mediant of a C major chord?
In this case, because we are in the C major tonality, the mediant of the C major chord would be an E minor and its submediant would be the A minor chord.
What is the G# in chromatic mediant chords?
But if you change the chord quality of any of these chords, for instance, if you would have an E major instead of E minor, you would be introducing a chromatic tone to the C major tonality. In this case, it would be the G#. That is basically the reason why it is called a chromatic mediant chord relationship (see picture below).
What chords hint at Lydian mode?
I also used this device to return to Am, at the end of this section. The Db maj7 #11 chord that hints to the lydian mode, comes from the Ab major tonality and is a major third apart from the C major tonality to which I return to.
How many beats does a bar measure?
Here the bar is subdivided in 5 beats and then goes to 7 beats per measure:
How many beats per measure in 4/4 time signature?
All I did was basically use a 4/4 time signature but instead of having the regular four beats per measure, I would have 5-6 or even 7 beats per measure in a 4/4 time signature to imply a change in the tempo.
Do we have chromatic mediant relationships in the last four bars?
In the last four bars of this section, we still have chromatic mediant relationships but not always, like in the case of E to A major or in the end when we go from F# major to E major.
Can you use chromatic mediant in chord progressions?
You are not limited to the usage of chromatic mediant relationships only between chords or for chord progressions. You can also use it as a way of establishing relationships between tonalities.
What are the major scale degrees?
A major scale degrees. This step shows the A major scale degrees - tonic, supertonic, mediant, subdominant, dominant, submediant, leading note / tone, and octave. In music theory, each note in this scale has what is called a scale degree name, which describes the relationship of that note to the tonic (1st) note.
What is the scale degree chart for all 8 notes?
1. A major scale . This step shows the ascending A major scale on the piano, treble clef and bass clef. It also shows the scale degree chart for all 8 notes. The A major scale has 3 sharps. This major scale key is on the Circle of 5ths - A major on circle of 5ths, which means that it is a commonly used major scale key.
What is note 1 on piano?
Note 1 is the tonic note - the starting note - A, and note 13 is the same note name but one octave higher. 3. A major scale note interval positions. This step applies the major scale note interval pattern starting from A, so that the correct piano keys and note pitches can be identified.
What note is the middle C on the piano?
Middle C (midi note 60) is shown with an orange line under the 2nd note on the piano diagram.
What is the starting point of a tonic note?
The tonic note (shown as *) is the starting point and is always the 1st note in the major scale.
Is the note name of the scale tonic or supertonic?
Scale degree names 1,2,3,4,5,6, and 8 below are always the same for all major and minor scales (ie. 1st note is always tonic, 2nd is supertonic etc.) , but obviously the note names will be different for each scale / key combination.
What is a mediant relationship?
A mediant or submediant relationship refers to the relative distance of a third interval, ascending or descending, to a reference pitch or tonic.
How many mediants does C major have?
As a result, it can be said that C major has four chromatic mediants – E, A, Eb and Ab major; and the other two diatonic mediants – E and A minor; and C minor also has four chromatic mediants – E, A, Eb and Ab minor, with Eb and Ab major as diatonic mediants.
What is the relationship between chromatic mediants and tonics?
C major and C minor; because of the way that the chord voices resolve and are transformed following the voice-leading principle – similar to dominant seventh chords, chromatic mediants also have two chord tones that resolve chromatically; and the shared common tones between chromatic mediants.
What are the diatonic and submediant chords in C major?
Extending the previous example, in C major, its diatonic mediant and submediant are Em and Am while its chromatic mediants would be E and A major, their respective parallel chords. At the same time, the chromatically altered mediant and submediant chords would be Eb and Ab, from the parallel tonality of C minor.
What is chromatic mediant?
A chromatic mediant is basically a chromatic alteration to the root of a diatonic mediant and submediant that refers to the parallel tonality of the reference pitch or chord ; or a chromatic alteration to the third of the available diatonic mediant and submediant chords in that tonality, causing a change in the chord quality.
What is expanding tonality?
expanding tonality by neglecting the tonicization of the departure or arrival tonality, maintaining a relationship with those but without confirming them
Can dominant chords be preceded?
Nevertheless, dominant chords can be preceded and/or followed by another chromatic mediant dominant chord and each of these have a relation to a tonic, as well as with each other:
What is the fourth degree of the scale called?
The fourth degree of the scale is called a subdominant. The fifth degree of scale is called dominant, so that’s dominant. That’s subdominant. That’s submediant, submediant. That’s leading tone, and then you come back to tonic.
What scale degrees are used in music?
This is Duane and today I’d like to cover a little music theory, that is of scale degrees such as Tonic, Super-Tonic, Mediant, Sub-Dominant, Dominant, Sub-Mediant Chords. Scale degrees are very important to understand because all of music is made out of those scale degrees. In other words, this is a raw material. If you’re playing in the key of C, that’s the raw material of all the songs you’ll ever play in the key of C.
What is the chord bill on the first degree of scale called?
The chord bill on the first degree of scale is a called a tonic chord. Tonic means home base. It’s the main thing.
How many scale degrees are there in guitar?
There’s eight scale degrees, actually seven different ones, and then the tonic is repeated of course. Among those various chords that I just played, three are more prominent than any others. They’re called primary chords. Those are the 1 chord, the 4 chord, and the 5 chord. That’s true in any key.
What chords do you use the most?
They’re the home base chords. They’re the chords you use more than any others because they’re the only major chords in that particular key. So 1, 4, and 5 are the chords you want to learn first but then once you learn the primary chords, 1, 4, and 5, then you want to learn the secondary chords. 2, the supertonic; 3, the mediant, submediant is the 6th, and the leading tone is used the least.
What is the difference between a subdominant and a submediant?
In practice, it is what comes before the dominant. Submediant: is halfway between the subdominant and the upper tonic. Leading-tone: It is the degree that brings the lead to resolve in the tonic.
What does the C note represent in a scale?
That is, taking the C major scale as an example, the C note would represent the tonic function , the F note would represent the subdominant function and the B note would represent the dominant function.

What Is A Mediant?
In music, the mediant (Latin: to be in the middle ) is the third scale degree () of a diatonic scale, being the note halfway between the tonic and the dominant. In the movable do solfège system, the mediant note is sung as mi. While the fifth scale degree is almost always a perfect fifth, the mediant can be a major or minor third.
Schenkerian analysts consider this scale degree as expansion of the tonic since they have two co…
Chromatic Mediants
Chromatic Mediants in Practice
Metric Modulation
- But if you change the chord quality of any of these chords, for instance, if you would have an E major instead of E minor, you would be introducing a chromatic tone to the C major tonality. In this case, it would be the G#. That is basically the reason why it is called a chromatic mediant chord relationship (see picture below). You could also go from C to Eb major. You would still be i…