
What are the three main functions of the nose?
Your nose anatomy includes:
- Bone: The hard bridge at the top of your nose is made of bone.
- Hair and cilia: Hair and cilia (tiny, hairlike structures) inside your nose trap dirt and particles. ...
- Lateral walls (outer walls): The outer walls of your nose are made of cartilage and covered in skin. ...
What diseases affect the nose?
They include:
- Deviated septum - a shifting of the wall that divides the nasal cavity into halves
- Nasal polyps - soft growths that develop on the lining of your nose or sinuses
- Nosebleeds
- Rhinitis - inflammation of the nose and sinuses sometimes caused by allergies. The main symptom is a runny nose.
- Nasal fractures, also known as a broken nose
What are the disorders of the nose?
We treat the full scope of nasal and sinus disorders, including:
- Allergic rhinitis – an inflammation of the membranes lining the nose
- Cerebral spinal fluid leaks
- Chronic sinusitis with polyps – an inflammation of the sinuses that lasts more than 12 weeks and is associated with nasal polyps
- Chronic sinusitis without polyps
- Difficult infections
- Deviated septums
What is 'Collie nose' and can you heal it?
- Coconut Oil In recent years, mainstream media has taken note of coconut oil’s superpowers. ...
- Ginger A newer power-root to the health scene, ginger has also been found to have excellent uses. ...
- Sunscreen The sun's harsh rays can make a Collie Nose sufferer’s condition much worse. ...
- Aloe Vera This desert plant is full of healing goodness. ...
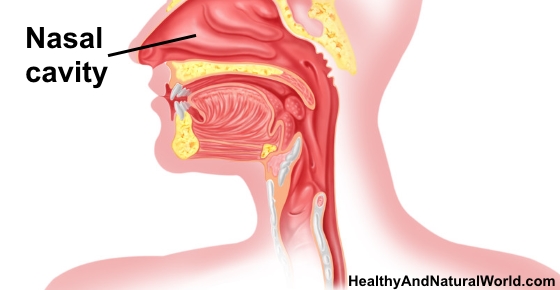
What is the second common medical issue of the nose?
Nosebleeds , known medically as epistaxis, are a second common medical issue of the nose. As many as 60 percent of people report nosebleed experiences, with the highest rates found in children under 10 and adults over 50.
What is a rhinoplasty?
Rhinoplasty is a plastic surgery procedure for problems, both medical and aesthetic, with the nose.
Why does my nose bleed?
The most common medical condition related to the nose is nasal congestion. This can be caused by colds or flu, allergies, or environmental factors, resulting in inflammation of the nasal passages. The body’s response to congestion is to convulsively expel air through the nose by a sneeze. Nosebleeds, known medically as epistaxis, ...
What is the primary organ of the respiratory system?
Nose. Medically reviewed by the Healthline Medical Network — Written by the Healthline Editorial Team on January 21, 2018. The nose is the body’s primary organ of smell and also functions as part of the body’s respiratory system. Air comes into the body through the nose.
What is the nose covered with?
The interior of the nose is lined with mucous membrane, and most of the membrane is covered with minute hairlike projections called cilia. Moving in waves these cilia sweep out from the nasal passages the nasal mucus, which may contain pollen, dust, and bacteria from the air. The mucous membrane also acts to warm and moisten the inhaled air.
What is the function of the nose?
One of the functions of the nose is to drain fluids discharged from the sinuses. The nasal cavities also have a connection with the ears by the eustachian tubes, and with the region of the eyes by the nasolacrimal ducts. The interior of the nose is lined with mucous membrane, and most of the membrane is covered with minute hairlike projections ...
Why does my nose bleed?
Nasal polyps may obstruct the nasal passages. Epistaxis, or nosebleed, may be caused by an injury to the nose or may be a symptom of other diseases.
What to use to clean nose during convalescence?
During convalescence the patient should avoid blowing his nose and picking at crusts. A lubricant may be used to soften the crusts, but no swabs or other objects should be used to clean the nose. A humidifier in the room may help reduce drying and irritation of the mucous membranes during healing.
What are the two cavities that separate the nose?
The nostrils, which form the external entrance of the nose, lead into the two nasal cavities, which are separated from each other by the nasal septum, a partition formed of cartilage and bone . Three bony ridges project from the outer wall of each nasal cavity and partially divide the cavity into three air passages. At the back of the nose these passages lead into the pharynx. The passages also are connected by openings with the paranasal sinuses. One of the functions of the nose is to drain fluids discharged from the sinuses. The nasal cavities also have a connection with the ears by the eustachian tubes, and with the region of the eyes by the nasolacrimal ducts.
What are the three bony ridges in the nose?
Three bony ridges project from the outer wall of each nasal cavity and partially divide the cavity into three air passages. At the back of the nose these passages lead into the pharynx. The passages also are connected by openings with the paranasal sinuses. One of the functions of the nose is to drain fluids discharged from the sinuses.
What is it called when the nasal septum grows?
The nasal septum may grow irregularly or be deflected to one side by injury; this condition is called deviated septum. Surgery of the Nose. Nasal surgery is indicated in disorders of the nasal septum, polyps and other growths, and traumatic injury to the structures that interfere with normal nasal breathing.
What is the purpose of the nose?
Nose: The external midline projection from the face. The purpose of the nose is to warm, clean, and humidify the air that a person breathes. In addition, it helps a person to smell and taste. The nose is divided into two passageways by a partition called the septum. Opening to these passageways are the nostrils.
What is the name of the partition that divides the nose into two passageways?
The nose is divided into two passageways by a partition called the septum. Opening to these passageways are the nostrils. Bony projections, called turbinates, protrude into each breathing passage; they help to increase the surface area of the inside of the nose.
What is the medical term for a nosebleed?
by Nick Musica January 29, 2021. The medical term for a nosebleed is “epistaxis”, which comes from the Ancient Greek word έπίσταξις (or “ Επίσταξη ” in modern Greek) and roughly translates as “to drip from the nose”. It is usually described as either “anterior” or “posterior”, with the majority of cases occurring in the anterior part of the nose.
What is the anterior part of the nose called?
“Anterior” comes from the Latin word meaning “before” and refers to the front part of the nose and specifically the “wall” that separates the two nostrils, known as the “septum”.
What is posterior epistaxis?
Posterior Epistaxis. “Posterior” comes from the Latin word for “post” or “after” and refers to a nosebleed that occurs at the back of your nose. They tend to be heavier than anterior nosebleeds and are also more dangerous, as a lot of the blood may flow down the back of the throat, causing breathing difficulties.
What is septal perforation?
Septal Perforation = A condition in which the septum becomes damaged. Septal Deviation = A displacement of the septum. Foreign Bodies = External objects that have entered the body. Where the nose is concerned, it refers to items that have been lodged up the nose. Back to Articles.
What is the saddle of the nose?
A saddle-shaped area that includes the nasal root and the lateral aspects of the nose. It lies between the glabella and the inferior boundary of the nasal bone, and extends laterally to the inner canthi.
What is the tissue that links the nasal tip to the nasal base and separates the nares?
The tissue that links the nasal tip to the nasal base, and separates the nares. It is the inferior margin of the nasal septum.
Do anatomical landmarks deserve specific mention?
Some anatomical landmarks deserve specific mention as these are not always used with standard meaning.
Does nose growth end at puberty?
A short description of how to measure each dimension is provided as the various terms are defined. Growth of the nose does not end at puberty: the nose continues to increase in size with age. There are no normal standards for nasal size in adulthood.
