The melting pot theory has been used to describe societies that are formed by an assortment of immigrant cultures that eventually produce new hybrid social and cultural forms.
What is melting point?
Melting point. Written By: Melting point, temperature at which the solid and liquid forms of a pure substance can exist in equilibrium. As heat is applied to a solid, its temperature will increase until the melting point is reached.
What happens to the melting point of a solid when heated?
Melting point. More heat then will convert the solid into a liquid with no temperature change. When all the solid has melted, additional heat will raise the temperature of the liquid. The melting temperature of crystalline solids is a characteristic figure and is used to identify pure compounds and elements.
What is the relationship between melting point and free energy?
The melting point is the temperature where the solid and liquid phases are in equilibrium with each other, and the change in free energy ( Δ G o) for the process (solid ⇌ liquid) is zero.
What is the significance of the melting temperature of crystalline solids?
The melting temperature of a crystalline solid is thus an indicator for the stability of its lattice. At the melting point not only the aggregate state changes; quite a lot of other physical characteristics also change significantly.

What is the melting point of lanthanide?
The melting point s of the lanthanide metals rapidly increase with increasing atomic number from 798 °C (1,468 °F) for cerium to 1,663 °C (3,025 °F) for lutetium (a doubling of the melting point temperatures), while the melting point s of scandium and yttrium are…
What happens when a solid melts?
When all the solid has melted, additional heat will raise the temperature of the liquid. The melting temperature of crystalline solids is a characteristic figure and is used to identify pure compounds and elements. Most mixtures and amorphous solids melt over a range of temperatures.
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
Is the melting temperature of a solid the same as the freezing point of a liquid?
The melting temperature of a solid is generally considered to be the same as the freezing point of the corresponding liquid; because a liquid may freeze in different crystal systems and because impurities lower the freezing point, however, the actual freezing point may not be the same as the melting point. Thus, for characterizing ...
Does alloying lower melting point?
Alloying can also be done to lower the melting point of a metal. For example, adding lead to tin lowers the melting point of the tin-rich... The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica This article was most recently revised and updated by Adam Augustyn, Managing Editor, Reference Content.
What is the temperature at which a liquid changes to a solid?
The temperature at which a liquid changes to a solid (the reverse of melting) is the freezing point or crystallization point. The freezing point and the melting point do not necessarily occur at the same temperature.
What is the melting point of a substance?
The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which a solid and liquid phase may coexist in equilibrium and the temperature at which matter changes from solid to liquid form. The term applies to pure liquids and solutions. Melting point depends on pressure, so it should be specified.
Why does water freeze at a lower temperature than it melts?
This is because some substances (e .g., water) experience supercooling, so they may freeze at a temperature much lower than they melt. So, while melting point is a characteristic property of a substance, the freezing point is not.
Can water and ice exist at the melting point?
At the melting point of water, both water and ice can exist. Pixabay
What is Melting Point?
The temperature at which a solid substance melts and transforms into a liquid at atmospheric pressure is termed the melting point of a substance.
What is the melting point of a substance?
At the melting point, the solid and liquid states of matter coexist together. The melting point of a substance is its characteristic property influenced by the applied pressure.
What happens when you raise the temperature of ice?
On raising the temperature, ice changes into water. Also, liquid changes to the vapour state. Ice → Water → Vapour
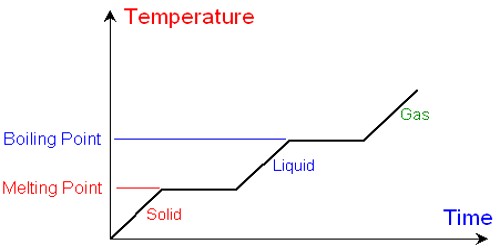
What does the heating curve show?
The heating curve denotes the temperature on the y-axis and the heat that has been supplied on the x-axis respectively. Let us assume a constant rate of heating, owing to which the x-axis can be shown as the amount of time which is shown as the substance is being heated. The curve majorly shows two main points:
What is the process of melting a noncrystalline solid?
The non-crystalline solids, such as glass or pitch undergo melting by slowly decreasing viscosity with the simultaneous increase in the temperature. However, there is no sharp transformation from solid to liquid state.
How does snow skating work?
The application can be observed during the process of snow skating. The weight of the skater gets concentrated on a thin line, there is considerable pressure applied on the ice slab. This results in the melting of ice beneath the shoe of the skater. This melting ice lubricates the undersides of his skating shoes. This makes it possible to skate on the ice.
What is the process of a solid turning into a liquid called?
The process of a solid turning into a liquid state is called melting. It is also known as fusion. The reverse process of a liquid becoming a solid, is in turn called solidification .
What is the importance of knowing the melting point of organic compounds?
The melting point is an important physical property of a compound. The melting point can be used to identify a substance and as an indication of its purity. The melting point of solid is defined as the temperature at which the solid exists in equilibrium with its liquid under an external pressure of one atmosphere.
Why is the melting point of butyric acid higher than that of butyric acid?
The melting point of sodium butanoate is higher than that of butyric acid because the attractive force in sodium butanoate is strong ionic interation.
What is the only force of attraction between butane molecules?
The only force of attraction between butane molecules is weak Van der Waals force of attraction , so it has very low melting point. But in the case of methyl propionate, because of the presence of polar C – O group, the molecules are held together by dipole-dipole interaction.
What is the melting point of a solid?
The melting point of solid is defined as the temperature at which the solid exists in equilibrium with its liquid under an external pressure of one atmosphere. A pure crystalline compound usually possesses a sharp melting point and it melts completely over a narrow range of temperature of not more that 0.5-1 o C.
What does it mean when a molecule has a different melting point?
Melting point is also used for the identification and characterisation of a compound. If the melting point of two pure samples shows a clear difference in melting points, it indicates that the two compounds must have different structural arrangements. or they must have different arrangements of atoms or configurations.
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Ionic compounds usually have high melting points because the electrostatic forces holding the ions (ion-ion interaction) are much stronger. In organic compounds the presence of polarity, or especially hydrogen bonding, generally leads to higher melting point. Consider the following examples.
Which isomers have the same molecular formula?
Consider the isomers n-butanol and t-butanol. Both have the same molecular formula (C 4 H 10 O), but differ in their structure.
What is the melting pot theory?
The melting pot theory has been used to describe societies that are formed by an assortment of immigrant cultures that eventually produce new hybrid social and cultural forms. The melting pot theory holds that, like metals melted together at great heat, the melting together of several cultures will produce a new compound, ...
Which country has the melting pot theory?
While the melting pot theory can be applied to any country that has integrated new cultures into its own, such as Brazil, Bangladesh, or even France, the theory is most commonly used to describe the United States as a new world with a distinct new breed of people amalgamated from many various groups of immigrants.
What is a supercooled liquid?
An example of a supercooled liquid can be made by heating solid sodium acetate trihydrate (NaCH 3 CO 2 3 H 2 O). When this solid melts, the sodium acetate dissolves in the water that was trapped in the crystal to form a solution. When the solution cools to room temperature, it should solidify. But it often doesn't. If a small crystal of sodium acetate trihydrate is added to the liquid, however, the contents of the flask solidify within seconds.
What pressure does a pressure cooker use?
Pressure cookers are equipped with a valve that lets gas escape when the pressure inside the pot exceeds some fixed value. This valve is often set at 15 psi, which means that the water vapor inside the pot must reach a pressure of 2 atm before it can escape. Because water doesn't reach a vapor pressure of 2 atm until the temperature is 120 o C, it boils in this container at 120 o C.
How hot does water boil in a pressure cooker?
In a typical pressure cooker, water can remain a liquid at temperatures as high as 120 o C, and food cooks in as little as one-third the normal time. To explain why water boils at 90 o C in the mountains and 120 o C in a pressure cooker, even though the normal boiling point of water is 100 o C, we have to understand why a liquid boils.
What happens when a liquid is heated?
When a liquid is heated, it eventually reaches a temperature at which the vapor pressure is large enough that bubbles form inside the body of the liquid. This temperature is called the boiling point. Once the liquid starts to boil, the temperature remains constant until all of the liquid has been converted to a gas.
Why does it take longer to cook an egg in boiling water?
But if you try to cook an egg in boiling water while camping in the Rocky Mountains at an elevation of 10,000 feet, you will find that it takes longer for the egg to cook because water boils at only 90 o C at this elevation. In theory, you shouldn't be able to heat a liquid to temperatures above its normal boiling point.
Why are melting points used to identify compounds?
Because it is difficult to heat solids to temperatures above their melting points, and because pure solids tend to melt over a very small temperature range, melting points are often used to help identify compounds. We can distinguish between the three sugars known as glucose ( MP = 150 o C), fructose ( MP = 103-105 o C), ...
Why do liquids become supercooled?
A liquid can become supercooled because the particles in a solid are packed in a regular structure that is characteristic of that particular substance. Some of these solids form very easily; others do not. Some need a particle of dust, or a seed crystal, to act as a site on which the crystal can grow.
What is the importance of knowing the melting point of organic compounds?
The melting point is an important physical property of a compound. The melting point can be used to identify a substance and as an indication of its purity. The melting point of solid is defined as the temperature at which the solid exists in equilibrium with its liquid under an external pressure of one atmosphere.
Why is the melting point of butyric acid higher than that of butyric acid?
The melting point of sodium butanoate is higher than that of butyric acid because the attractive force in sodium butanoate is strong ionic interation.
What is the only force of attraction between butane molecules?
The only force of attraction between butane molecules is weak Van der Waals force of attraction , so it has very low melting point. But in the case of methyl propionate, because of the presence of polar C – O group, the molecules are held together by dipole-dipole interaction.
What temperature does a compound melt?
A pure crystalline compound usually possesses a sharp melting point and it melts completely over a narrow range of temperature of not more that 0.5-1 o C. The presence of even small amount of impurities usually produces a depression in the freezing points and shows a marked increase in the width of the melting point range.
What does it mean when a molecule has a different melting point?
Melting point is also used for the identification and characterisation of a compound. If the melting point of two pure samples shows a clear difference in melting points, it indicates that the two compounds must have different structural arrangements. or they must have different arrangements of atoms or configurations.
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Ionic compounds usually have high melting points because the electrostatic forces holding the ions (ion-ion interaction) are much stronger. In organic compounds the presence of polarity, or especially hydrogen bonding, generally leads to higher melting point. Consider the following examples.
Which isomers have the same molecular formula?
Consider the isomers n-butanol and t-butanol. Both have the same molecular formula (C 4 H 10 O), but differ in their structure.
How many capillaries can be measured at the same time?
With the Melting Point Excellence instruments by METTLER TOLEDO up to 6 capillaries can be measured at the same time. Learn more about the benefits of digital melting point instruments.
Why is the melting point temperature higher?
The reason is that the melting point temperature is not measured directly within the substance, but outside the capillary at the heating block , due to technical reasons. Therefore, the temperature of the sample lags behind the furnace temperature. The higher the heating rate, the more rapid the rise in oven temperature, increasing the difference between the melting point measured and the true melting temperature.
Why is melting point temperature not measured directly within the substance?
Results depend strongly on the heating rate - the higher the heating rate the higher the observed melting point temperature. The reason is that the melting point temperature is not measured directly within the substance, but outside the capillary at the heating block, due to technical reasons.
How to determine melting point?
Powdered crystalline materials are opaque in the crystalline state and transparent in the liquid state. This distinct difference in optical properties can be measured in order to determine the melting point by recording the percentage of light intensity shining through the substance in the capillary, the transmittance, in relation to the measured furnace temperature.
What are the physical properties of melting point?
Amongst these are the thermodynamic values, specific heat capacity, enthalpy, and rheological properties such as volume or viscosity . Last but not least, the optical properties birefringence reflection and light transmission change. Compared to other physical values the change in light transmission can easily be determined and can therefore be used for melting point detection.
What is melting point?
Melting point is a characteristic property of solid crystalline substances. It is the temperature at which the solid phase changes to the liquid phase. Melting point determination is the thermal analysis most frequently used to characterize solid crystalline materials. It is used in research and development as well as in quality control in various ...
What happens to the crystalline structure of a solid?
The crystalline structure is destroyed and the solid material melts. The stronger the forces of attraction between the particles, the more energy is needed to overcome them. The more energy is needed, the higher the melting point.
What is the melting pot?
The melting pot concept is most commonly used to describe the assimilation of immigrants to the United States, though it can be used in any context where a new culture comes to coexist with another. In recent times, refugees from the Middle East have created melting pots throughout Europe and the Americas.
What is melting pot in sociology?
Updated February 16, 2021. In sociology, the "melting pot" is a concept referring to a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous with the different elements “melting together” into a harmonious whole with a common culture.
What is the metaphor for a salad bowl?
An alternative metaphor, therefore, is salad bowl or mosaic, describing how different cultures mix, but still remain distinct.
When was the idea of opportunity first introduced?
is defended in its highest courts. The term first originated in the U.S. around 1788 to describe the cultures of many European, Asian, and African nationalities merging together in the newfound culture of the new United States.
/phasediagram-5a05ab68beba3300371f67c3.png)